Met behulp van de aannamen uit fase 3 levert de beslissingsanalyse de volgende uitkomsten. De uitkomsten betreffen het verlies aan QALy’s. In onderstaande tabellen zijn de operatieleeftijden waarbij het verlies aan QALy’s minimaal is vetgedrukt. Voor elke serie tabellen wordt een korte samenvatting van de resultaten gegeven.
6.2.5 Fase 4: uitkomsten van de beslissingsanalyse
JGZ-richtlijn Niet scrotale testis
JGZ-richtlijn Niet scrotale testis
Let op: deze richtlijn is momenteel in herziening.
Dit betekent niet dat de inhoud van deze richtlijn incorrect is. Tot de herziening blijft de richtlijn leidend voor de praktijk. Wel bestaat er een kans dat een deel van de informatie verouderd is.
Heb je feedback over deze JGZ-richtlijn? Stuur jouw feedback naar onze servicedesk. Zoek het tekstgedeelte waarbij je suggesties voor verbetering hebt. Via de knop ‘Geef jouw feedback’ kun je voor deze JGZ-richtlijn en het specifieke hoofdstuk jouw suggesties doorgeven.
Richtlijn inhoudsopgave
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrond informatie
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
4 Samenwerking Ga naar pagina over 4 Samenwerking
5 Totstandkoming Ga naar pagina over 5 Totstandkoming
6 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 6 Verantwoording
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrond informatie
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
4 Samenwerking Ga naar pagina over 4 Samenwerking
5 Totstandkoming Ga naar pagina over 5 Totstandkoming
6 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 6 Verantwoording
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackBeslissingsanalyse richtlijn Niet-scrotale testis
PP-presentatie voor de scholing Niet-scrotale testis
Factsheet richtlijn Niet-scrotale testis
Randvoorwaardelijke implicaties richtlijn Niet-scrotale testis
BDS-registratieprotocol richtlijn Niet-scrotale testis
[1] van Gelderen HH, Vermeer-de Bondt PE. [Prevalence of undescended testis in the first 4 years of life; a longitudinal study]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1986;130(35):1567-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2876394[2] de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM. [Consensus on management of the undescended testis]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1987;131(41):1817-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2890111[3] Venlet-Melchior CJ, Hirasing RA. [Significance of the registration of testis localization in child health services for the avoidance of unnecessary orchiopexies]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1989;133(42):2084-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2572979[4] Horstink-uit de Weerd BR, Filedt Kok-Weimar TL, Leerdam F. Protocollering binnen de JGZ: testesonderzoek. 2004
[5] Ghirri P, Ciulli C, Vuerich M, Cuttano A, Faraoni M, Guerrini L, Spinelli C, Tognetti S, Boldrini A. Incidence at birth and natural history of cryptorchidism: a study of 10,730 consecutive male infants. Journal of endocrinological investigation 2002;25(8):709-15
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12240903[6] SCORER CG. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS. Archives of disease in childhood 1964;39(208):605-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14230757[7] Berkowitz GS, Lapinski RH, Dolgin SE, Gazella JG, Bodian CA, Holzman IR. Prevalence and natural history of cryptorchidism. Pediatrics 1993;92(1):44-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8100060[8] Cryptorchidism: a prospective study of 7500 consecutive male births, 1984-8. John Radcliffe Hospital Cryptorchidism Study Group. Archives of disease in childhood 1992;67(7):892-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1355643[9] Acerini CL, Miles HL, Dunger DB, Ong KK, Hughes IA. The descriptive epidemiology of congenital and acquired cryptorchidism in a UK infant cohort. Archives of disease in childhood 2009;94(11):868-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.2008.150219 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19542061[10] Boisen KA, Kaleva M, Main KM, Virtanen HE, Haavisto A-M, Schmidt IM, Chellakooty M, Damgaard IN, Mau C, Reunanen M, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J. Difference in prevalence of congenital cryptorchidism in infants between two Nordic countries. Lancet (London, England) 2004;363(9417):1264-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15094270[11] Preiksa RT, Zilaitiene B, Matulevicius V, Skakkebaek NE, Petersen JH, Jørgensen N, Toppari J. Higher than expected prevalence of congenital cryptorchidism in Lithuania: a study of 1204 boys at birth and 1 year follow-up. Human reproduction (Oxford, England) 2005;20(7):1928-32
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15860495[12] Sijstermans K, Hack WWM, van der Voort-Doedens LM, Meijer RW, Haasnoot K. Puberty stage and spontaneous descent of acquired undescended testis: implications for therapy? International journal of andrology 2006;29(6):597-602
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16817910[13] Eijsbouts SW, de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SMPF, Hazebroek FWJ. Further evidence for spontaneous descent of acquired undescended testes. The Journal of urology 2007;178(4 Pt 2):1726-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17707013[14] Lee PA. Fertility after cryptorchidism: epidemiology and other outcome studies. Urology 2005;66(2):427-31
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16098371[15] Lee PA. Fertility in cryptorchidism. Does treatment make a difference? Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America 1993;22(3):479-90
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7902276[16] Lee PA, Coughlin MT. The single testis: paternity after presentation as unilateral cryptorchidism. The Journal of urology 2002;168(4 Pt 2):1680-2; discussion 1682-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12352333[17] Dieckmann K-P, Pichlmeier U. Clinical epidemiology of testicular germ cell tumors. World journal of urology 2004;22(1):2-14
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15034740[18] Pettersson A, Richiardi L, Nordenskjold A, Kaijser M, Akre O. Age at surgery for undescended testis and risk of testicular cancer. The New England journal of medicine 2007;356(18):1835-41
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17476009[19] Baker LA, Docimo SG, Surer I, Peters C, Cisek L, Diamond DA, Caldamone A, Koyle M, Strand W, Moore R, Mevorach R, Brady J, Jordan G, Erhard M, Franco I. A multi-institutional analysis of laparoscopic orchidopexy. BJU international 2001;87(6):484-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11298039[20] Chang B, Palmer LS, Franco I. Laparoscopic orchidopexy: a review of a large clinical series. BJU international 2001;87(6):490-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11298040[21] Elder JS. Two-stage Fowler-Stephens orchiopexy in the management of intra-abdominal testes. The Journal of urology 1992;148(4):1239-41
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1357193[22] Horasanli K, Miroglu C, Tanriverdi O, Kendirci M, Boylu U, Gumus E. Single stage Fowler-Stephens orchidopexy: a preferred alternative in the treatment of nonpalpable testes. Pediatric surgery international 2006;22(9):759-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16896813[23] Russinko PJ, Siddiq FM, Tackett LD, Caldamone AA. Prescrotal orchiopexy: an alternative surgical approach for the palpable undescended testis. The Journal of urology 2003;170(6 Pt 1):2436-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14634447[24] Ritzén EM, Bergh A, Bjerknes R, Christiansen P, Cortes D, Haugen SE, Jörgensen N, Kollin C, Lindahl S, Läckgren G, Main KM, Nordenskjöld A, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Söder O, Taskinen S, Thorsson A, Thorup J, Toppari J, Virtanen H. Nordic consensus on treatment of undescended testes. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):638-43
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17326760[25] Ritzén EM. Undescended testes: a consensus on management. European journal of endocrinology 2008;159 Suppl 1():S87-90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/EJE-08-0181 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18728121[26] Dayanc M, Kibar Y, Irkilata HC, Demir E, Tahmaz L, Peker AF. Long-term outcome of scrotal incision orchiopexy for undescended testis. Urology 2007;70(4):786-8; discussion 788-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17991558[27] Al-Saied G. Balloon inflation-created subdartos pouch during orchiopexy: a new simplified technique. Pediatric surgery international 2008;24(10):1187-90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00383-008-2243-4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18751986[28] Thorup J, Haugen S, Kollin C, Lindahl S, Läckgren G, Nordenskjold A, Taskinen S. Surgical treatment of undescended testes. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):631-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17381472[29] Merguerian PA, Mevorach RA, Shortliffe LD, Cendron M. Laparoscopy for the evaluation and management of the nonpalpable testicle. Urology 1998;51(5A Suppl):3-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9610548[30] Esposito C, Garipoli V. The value of 2-step laparoscopic Fowler-Stephens orchiopexy for intra-abdominal testes. The Journal of urology 1997;158(5):1952-4; discussion 1954-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9334647[31] Toppari J, Kaleva M. Maldescendus testis. Hormone research 1999;51(6):261-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10640886[32] Arbous MS, Grobbee DE, van Kleef JW, de Lange JJ, Spoormans HH, Touw P, Werner FM, Meursing AE. Mortality associated with anaesthesia: a qualitative analysis to identify risk factors. Anaesthesia 2001;56(12):1141-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11736769[33] Tan SS, Bouwmans C, Hakkaart- van Roijen L. Handleiding Voor Kostenonderzoek Methoden En Standaard Kostprijzen Voor Economische Evaluaties in de Gezondheidszorg Tijdschrift voor gezondheidswetenschappen 2012/09/01;90():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12508-012-0128-3[34] Oostenbrink JB, Bouwmans CAM, Koopmanschap MA, Rutten FFH. Handleiding Voor Kostenonderzoek Methoden En Standaard Kostprijzen Voor Economische Evaluaties in de Gezondheidszorg College voor zorgverzekeringen 2004
[35] Hsieh MH, Roth DR, Meng MV. Economic analysis of infant vs postpubertal orchiopexy to prevent testicular cancer. Urology 2009;73(4):776-81
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2008.10.059 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19193413[36] Miller KD, Coughlin MT, Lee PA. Fertility after unilateral cryptorchidism. Paternity, time to conception, pretreatment testicular location and size, hormone and sperm parameters. Hormone research 2001;55(5):249-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11740148[37] Virtanen HE, Cortes D, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Ritzén EM, Nordenskjöld A, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J. Development and descent of the testis in relation to cryptorchidism. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):622-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17462055[38] Virtanen HE, Bjerknes R, Cortes D, Jørgensen N, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Thorsson AV, Thorup J, Main KM. Cryptorchidism: classification, prevalence and long-term consequences. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):611-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17462053[39] Bergh A, Söder O. Studies of cryptorchidism in experimental animal models. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):617-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17462054[40] Kollin C, Hesser U, Ritzén EM, Karpe B. Testicular growth from birth to two years of age, and the effect of orchidopexy at age nine months: a randomized, controlled study. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2006;95(3):318-24
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/164976431 Inleiding
Deze ‘Multidisciplinaire richtlijn Signalering van en verwijzing bij niet-scrotale testis (NST)’ is de praktische uitwerking van het project: ‘Gebruik van beslissingsanalyse en patiënten voorkeuren bij ontwikkeling en toepassing van richtlijnen geïllustreerd aan de hand van de richtlijn niet-scrotale testis’. Bij de vertaling van de uitkomsten uit dat project naar de praktijk zijn enkele uitkomsten op basis van consensus aangepast.
De resultaten van het project inclusief de consensus staan samengevat weergegeven in de Sectie Definities en achtergrond informatie: zie Samenvatting resultaten – beslissingsanalyse en expertisebijeenkomst.
In de Sectie Verantwoording zijn de resultaten van het project uitgebreid verwerkt voor nadere uitleg, toelichting en bijbehorende referenties, Zie Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing.
1.1 Doelstelling
Een richtlijn is een document met aanbevelingen ter ondersteuning van zorgprofessionals en zorggebruikers, gericht op het verbeteren van de kwaliteit van zorg, berustend op wetenschappelijk onderzoek aangevuld met expertise en ervaringen van zorgprofessionals* en zorggebruikers** (Brummen, 2010).
Het uiteindelijke doel hiervan is betere, uniforme advisering, correcte verwijzing en hulp aan ouders en kinderen.
* Onder zorgprofessionals worden alle BiG-geregistreerde zorgverleners verstaan, onder wie artsen, verpleegkundigen, apothekers, fysiotherapeuten, gezondheidszorg- psychologen, psychotherapeuten, tandartsen, verloskundigen en verpleegkundig specialisten.
** Onder zorggebruikers worden patiënten, cliënten, familie van patiënten en cliënten, en mantelzorgers verstaan.
1.2 Afbakening onderwerp en doelgroep
Deze multidisciplinaire richtlijn is gericht op de correcte signalering van en verwijzing bij NST. Dit zijn taken die in elk geval op standaardmomenten worden uitgevoerd door de JGZ (door de jeugdarts en verpleegkundig specialist), maar tevens op indicatie of vraag door de huisarts en de kinderarts. Kinderen worden vervolgens verwezen naar de specialist: (kinder)uroloog, (kinder)chirurg* of kinderarts. Deze artsen zijn derhalve ook de doelgroep van deze richtlijn.
*Hieronder wordt in dit verband verstaan: een uroloog/chirurg werkzaam in een kinderchirurgisch centrum, alsook een uroloog/chirurg die ervaring heeft met de behandeling van NST bij kinderen.
1.3 Aanleiding
Uit een serie publicaties in de jaren 80 bleek dat het aantal chirurgische ingrepen voor NST grofweg twee tot vier maal hoger was dan verwacht op basis van de incidentie van NST bij de geboorte [1][2][3]. Verschillende oorzaken van deze discrepantie werden onderkend, zoals het ontbreken van een eenduidige definitie, onduidelijkheid ten aanzien van de prognose voor toekomstige testisfunctie, het ontstaan van NST ná de geboorte en verschillende opvattingen over hoe en wanneer jongens met NST zouden moeten worden behandeld.
Tegen die achtergrond is in oktober 1986 door het toenmalige Centraal Begeleidings- Orgaan voor de intercollegiale toetsing (CBO; tegenwoordig het Kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg) een consensusbijeenkomst georganiseerd, met als doel om op basis van de (beperkte) beschikbare evidentie tot een multidisciplinaire richtlijn te komen voor het beleid bij NST [2]. Onderdeel van de consensus was de landelijke invoering van de testis-registratiekaart (ook wel het ‘ballenkaartje’ genoemd). Na de CBO-consensus is de registratie van de testispositie bij pasgeborenen opgenomen in het integraal dossier jeugdgezondheidszorg (JGZ) en het groeiboekje.
De consensus is echter nooit formeel uitgewerkt in een richtlijn. Het belangrijkste doel van de consensus, namelijk het niet uitvoeren van orchidopexie als de testis op een eerder moment in het leven normaal scrotaal was gelegen volgens onder andere de gegevens van de JGZ, is niet bereikt.
In 2004 is een scriptie verschenen [4] waarin de destijds bestaande protocollen binnen de JGZ werden geëvalueerd. Het beleid van verwijzen bij NST blijkt in deze protocollen sterk te variëren. Leeftijdsgrenzen voor verwijzing worden in dergelijke protocollen bijvoorbeeld niet altijd aangegeven. In 2008 is mede daarom gestart met de ontwikkeling van een richtlijn voor de JGZ door middel van literatuuronderzoek en bespreking daarvan in expertmeetings. Dit leidde in 2009 tot een concept-eindversie van de richtlijn. Deze werd echter, door controverse in het veld, door de Richtlijn Advies Commissie (RAC) van het toenmalige RiVM/Centrum Jeugdgezondheid (tegenwoordig het NCJ, Nederlands Centrum Jeugdgezondheid) aangehouden.
Vanwege de controverse startte in datzelfde jaar het project: ‘Gebruik van beslissingsanalyse en patiënten voor- keuren bij ontwikkeling en toepassing van richtlijnen geïllustreerd aan de hand van de richtlijn niet-scrotale testis’. in combinatie met een expertbijeenkomst voor de vertaling naar de praktijk heeft dit geleid tot deze onderhavige richtlijn.
Voor een korte samenvatting van het project en de expertbijeenkomst, zie Samenvatting resultaten – beslissingsanalyse en expertisebijeenkomst..
In de Sectie Verantwoording zijn de resultaten van het project uitgebreid verwerkt voor nadere uitleg, toelichting en bijbehorende referenties, Zie Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing.
2 Definities en achtergrond informatie
2.1 Definitie Niet-scrotale testis (NST) algemeen
Niet-scrotale testis (NST) is gedefinieerd als een testis die niet in een stabiele ligging onder in het scrotum (balzak) is te krijgen tijdens het lichamelijk onderzoek. Andere gehanteerde benamingen voor NST zijn: cryptorchisme, niet-ingedaalde testis en maldescensus testis.
Cryptorchisme betekent strikt gezien een verborgen (dat wil zeggen niet-voelbare) testis (crypto = verborgen, orchid = testis) maar wordt in de Angelsaksische literatuur ook gebruikt om de wel palpabele NST aan te duiden. in deze richtlijn wordt gesproken van niet-scrotale testis, omdat dit binnen Nederland de meest gebruikelijke benaming is en de voorkeur van de bij deze richtlijn betrokken experts geniet. In het geval van hoogscrotale testis zou verwarring kunnen ontstaan: alhoewel deze in het scrotum gebracht kan worden, wordt een hoogscrotale testis als NST geclassificeerd omdat de testis, conform de definitie, niet stabiel onder in het scrotum is te brengen.
2.2 Scrotale en niet-scrotale testis: indeling en definities
Niet-scrotale testis (NST) kan op verschillende manieren worden ingedeeld. Doorgaans wordt de indeling gedaan op basis van de ligging van de testis in rust en na palpatie, het palpabel zijn van de testis, de mogelijkheid NST naar een stabiele scrotale positie te manipuleren en/of het moment van ontstaan (aangeboren dan wel verworven).
Hierbij wordt uitgegaan van de volgende acties:
- Tijdens het lichamelijk onderzoek: het herkennen van NST (visuele inspectie en palpatie van de ligging).
- Manipulatie (pogen om de testis scrotaal te krijgen).
- Navraag bij ouders over de recente ligging.
- Verificatie van de voorgeschiedenis van de ligging van de testis middels dossier- onderzoek (bij bijvoorbeeld verloskundige, JGZ, huisarts, kinderarts) naar eerdere ligging van de testis:
- In geval van een niet-scrotale testis wordt de classificatie op basis van de medische voorgeschiedenis gedaan. Als de voorgeschiedenis niet beschikbaar is, wordt deze actief nagevraagd bij de voorgaande ketenpartners (verloskundige, kinderarts, huisarts).
- Als minimaal twee onafhankelijke beoordelaars geconcludeerd hebben dat de testis na de geboorte scrotaal was, is geen sprake van een aangeboren NST.
Dit leidt na manipulatie tot de volgende indeling:
- Scrotaal (spontaan, dan wel na manipulatie (retractiel)).
- Niet-scrotaal:
- Palpabel (waaronder ook de ‘hoog-scrotale testis’ die vóór manipulatie doorgaans in het liesgebied gelegen is).
- Niet-palpabel.
2.2.1 Definitie: Scrotaal
Van een normaal scrotale testis wordt gesproken indien de testis stabiel onder in het scrotum is gelegen of daar door manipulatie is te brengen, zoals in het geval van de retractiele testis.
De retractiele testis (RT) is een volledig ingedaalde en normaal ontwikkelde testis die vanuit zijn positie in het scrotum door contractie van de cremasterspier uit de normale scrotale positie getild kan worden en zo hoog in het scrotum of in het liesgebied kan komen te liggen.
De RT kan meestal door voorzichtige manuele manipulatie naar een normale stabiele lage positie in het scrotum worden gebracht, zonder dat de trekkracht (tractie) die tijdens manipulatie op de funiculus spermaticus wordt uitgeoefend pijnlijk is. Het is mogelijk dat de testis niet palpabel is of niet scrotaal is (te krijgen) tijdens het onderzoek. Men kan op dat moment de diagnose RT niet stellen. Om die reden kan navraag doen bij ouders of zij weten wat de recente positie is aanvullend van belang zijn. De ouders kan worden gevraagd om thuis na te gaan of de testis een scrotale ligging krijgt bijvoorbeeld nadat het jongetje 15 minuten in een warm bad zit. Als de ouders/het kind de testis thuis wel kunnen/kan voelen (alleen het zien van de testis is niet voldoende) in het scrotum is mogelijk sprake van een RT. Die observatie is een zwaarwegend argument voor de arts om het onderzoek te herhalen, desnoods meerdere malen.
De diagnose RT kan echter niet worden gesteld op basis van informatie van de ouder/het kind en kan pas zeker gesteld worden wanneer bij het onderzoek door de arts de testis in een stabiele positie in het scrotum kan worden gebracht. Onder ‘stabiel’ wordt verstaan dat de testis na loslating niet ogenblikkelijk terugveert naar de verhoogde positie. Tractie aan het ophangapparaat is over het algemeen niet pijnlijk.
De RT wordt als fysiologisch normaal beschouwd en is daarmee geen NST.
2.2.2 Definitie: Niet-scrotaal
Een niet-scrotale testis (NST) is een testis die niet in een normale stabiele positie in het scrotum is te brengen. Het betreft zowel de niet-palpabele testis als de palpabele testis die echter niet stabiel scrotaal kan worden gebracht. Tractie (rek) aan de funiculus kan bij NST (zeer) pijnlijk zijn.
Van de aangeboren (congenitale) vorm is sprake wanneer de testis vanaf de geboorte niet volledig is ingedaald.
Als de testis bij de geboorte wél normaal ingedaald was, maar op een later moment niet meer volledig stabiel onder in het scrotum is te brengen, wordt gesproken van een verworven NST.
Als de testis ten tijde van het onderzoek niet scrotaal is te krijgen, maar de ouder/het kind desondanks aangeeft dat zij de testis zelf wél recent scrotaal hebben gevoeld, is dit een argument om het onderzoek te herhalen (verificatie) omdat sprake zou kunnen zijn van een RT (zie Definitie: Scrotaal).
2.3 Samenvatting resultaten – beslissingsanalyse en expertisebijeenkomst
In een beslissingsanalyse wordt het te analyseren probleem (in dit geval de behandeling bij NST) in deelproblemen opgedeeld en vervolgens met behulp van beschikbare kennis geanalyseerd. in het besliskundige model werden de gevolgen op het gebied van vrucht- baarheid, maligniteit, cosmetisch resultaat en complicaties van de operatie meegenomen. Daar waar geen wetenschappelijk bewijs voorhanden was, werden data aangevuld met behulp van expert-opinie. Tevens werden de waarderingen van de algemene bevolking in het model betrokken door middel van vragenlijstonderzoek. Ook de kosten werden in het model opgenomen.
Conclusies
De volgende conclusies werden getrokken:
- Bij aangeboren unilaterale NST (palpabel en niet-palpabel) levert opereren minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALY-verlies) op dan niet opereren. Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met een afwijkend aspect scrotum (veroorzaakt door een leeg scrotum).
- Bij aangeboren bilaterale NST (palpabel en niet-palpabel) levert opereren minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALY-verlies) op dan niet opereren. Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met geen vaderschap bij niet opereren ten opzichte van bij wel opereren en het hogere percentage afwijkend aspect scrotum.
- Bij verworven unilaterale NST (palpabel en niet-palpabel) levert opereren bij diagnose minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALY-verlies) op dan later of niet opereren. Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum bij later of niet opereren ten opzichte van bij diagnose opereren.
- Bij verworven bilaterale NST (palpabel en niet-palpabel) levert opereren bij diagnose minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALY-verlies) op dan later of niet opereren. Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum bij later of niet opereren ten opzichte van bij diagnose opereren. Daarentegen is er bij later opereren een lager percentage complicaties en een lagere kans op heroperaties, omdat in een deel van de gevallen inmiddels indaling heeft plaatsgevonden. Daarnaast geldt voor opereren een hogere kans op vaderschap.
Op basis hiervan kan geconcludeerd worden dat opereren van unilaterale NST, zowel aangeboren als verworven, op een cosmetisch effect na, geen extra voordelen heeft boven niet opereren. Daarom zou het advies bij unilaterale NST gebaseerd op de analyse zijn: voorlichten van ouders/patiënt en gezamenlijk beleid bepalen (opereren, afwachten of geen operatie).
Voor bilaterale NST geeft de beslissingsanalyse aan dat er een hogere kans op vaderschap is bij wel opereren. Voor verworven bilaterale NST is het moment van operatie afhankelijk van de voorkeuren van ouders/patiënt. Direct opereren bij diagnose heeft als voordeel dat er geen QALY-verlies is ten gevolge van een afwijkend aspect scrotum. Bij opereren op een later moment is dit er wel, maar is er de mogelijkheid dat een operatie niet meer nodig is vanwege indaling.
Aanbevelingen
Op grond van de expertbijeenkomst (februari 2012) is gekomen tot een vertaling naar de praktijk, waarbij de volgende aanbevelingen afwijken van bovenstaande uitkomsten.
Bij aangeboren unilaterale NST en verworven unilaterale NST zijn de belangrijkste argumenten om wel te opereren:
- Het testikel is een reserveorgaan en heeft mogelijk herstelpotentie.
- De niet-ingedaalde testikel kan klachten geven in het liesgebied (pijn en risico op draaiing van de testis (torsio testis).
Bij de aangeboren unilaterale NST vindt de operatie in principe plaats tussen de 6 en 12 maanden. Voor de verworven unilaterale NST geldt dat de behandelopties, het moment van opereren (direct opereren of gecontroleerd afwachten tot de puberteit), besproken moeten worden.
Voor een uitvoerige toelichting en referenties: zie Verantwoording.
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
Indeling (zie Definities) is gebaseerd op de volgende acties:
- Tijdens het lichamelijk onderzoek: het herkennen van NST (visuele inspectie en palpatie van de ligging).
- Manipulatie (pogen om de testis scrotaal te krijgen).
- Navraag bij ouders over de recente ligging.
- Verificatie van de voorgeschiedenis van de ligging van de testis middels dossier- onderzoek (bij bijvoorbeeld verloskundige, JGZ, huisarts, kinderarts) naar eerdere ligging van de testis:
- In geval van een niet-scrotale testis wordt de classificatie op basis van de medische voorgeschiedenis gedaan. Als de voorgeschiedenis niet beschikbaar is, wordt deze actief nagevraagd bij de voorgaande ketenpartners (verloskundige, kinderarts, huisarts).
- Als minimaal twee onafhankelijke beoordelaars geconcludeerd hebben dat de testis na de geboorte scrotaal was, is geen sprake van een aangeboren NST.
Zie Verwijscriteria voor extra aandachtspunten bij lichamelijk onderzoek.
3.1 Uitvoering
Omgeving
Het lichamelijk onderzoek wordt verricht in een warme kamer, op een warm oppervlak, waarbij de onderzoeker warme handen heeft. Het onderzoek wordt uitgevoerd met de jongen in de houding die de arts het meest handig acht. Als de testis dan echter niet palpabel is of niet scrotaal is te krijgen, dan zal het onderzoek alsnog in kleermakerszit of hurkzit uitgevoerd moeten worden (of liggend, afhankelijk van de leeftijd).
Visuele inspectie
Voordat het genitaal wordt aangeraakt (omdat de cremasterreflex daarmee geïnduceerd kan worden): beoordeling van grootte en symmetrie van het scrotum en aanwezigheid van de testis.
Manueel onderzoek
Beginnend op de onderbuik, vanaf de bovenste bekkenrand, worden de vingertoppen van de voorkeurshand naar het scrotum bewogen. Als in de lies een testis wordt gevoeld, wordt deze voorzichtig naar ‘beneden’ gemobiliseerd en de laagste ligging bepaalt de classificatie van NST. Als de manipulatie naar caudaal pijnlijk is, moet deze niet worden voortgezet. is de manipulatie pijnloos, dan kan mogelijk een normale scrotale testispositie worden bereikt. Bij twijfel over de aanwezigheid van een testikel of de te bereiken positie kunnen de hand en het te onderzoeken gebied glad worden gemaakt met gel of zeep. Dit vergemakkelijkt palpatie.
Als het onderzoek slecht uitvoerbaar of interpreteerbaar is, wordt het bij een volgende gelegenheid herhaald.
3.2 Registratie
De testispositie (zowel normaal als afwijkend) wordt genoteerd in het Digitaal Dossier JGZ .
Ook dient deze deze, indien aanwezig, in het groeiboekje (dat op veel plaatsen in Nederland gebruikt wordt door de JGZ en aan ouders wordt meegegeven) genoteerd te worden.
In het groeiboekje is hiervoor een specifieke pagina waarop de testispositie gedrukt staat aanwezig.
3.3 Verwijscriteria
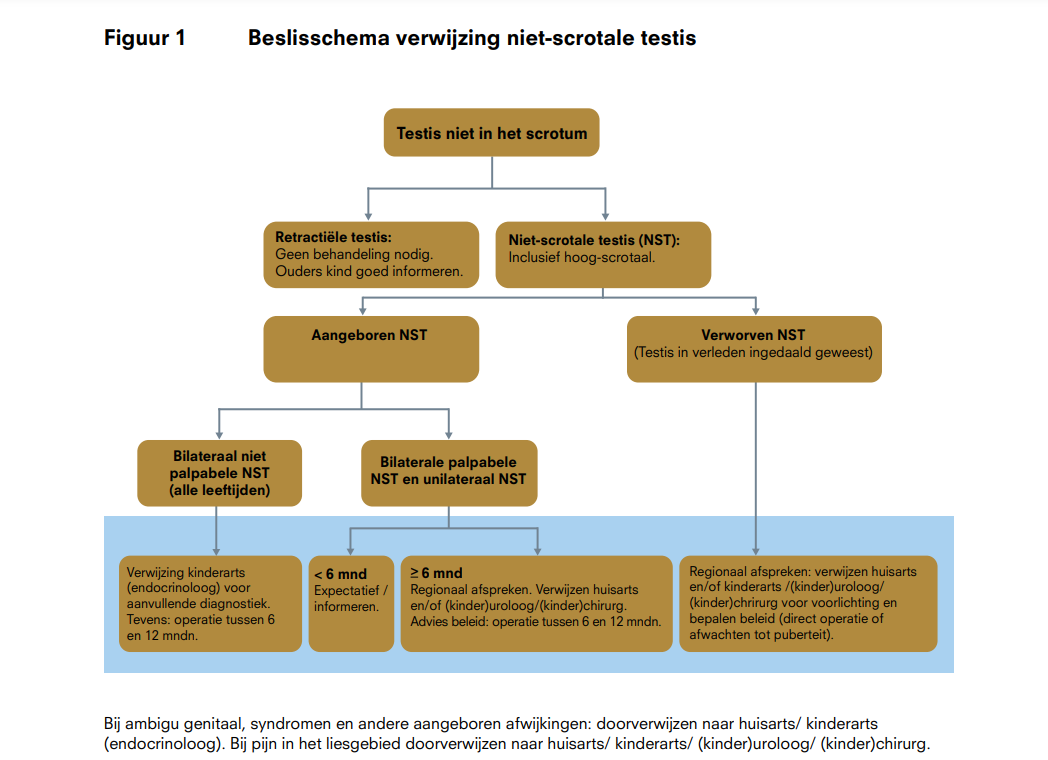
Zie ook Figuur 1 Beslisschema verwijzing Niet-scrotale testis
Altijd verwijzen bij:
- Aangeboren bilaterale niet-palpabele NST en/of ambigu genitaal zo spoedig mogelijk na de geboorte naar kinderarts voor verdere diagnostiek. Bij voorkeur verwijzing naar kinderarts met specifieke belangstelling voor kinderendocrinologie of naar kinder- endocrinoloog. Diagnostiek en behandeling van kinderen met ambigu genitaal altijd in kinderendocrinologisch centrum.
- Aangeboren unilateraal palpabel/niet-palpabel en aangeboren bilateraal palpabel NST vanaf de leeftijd van 6 maanden verwijzen naar huisarts of indien mogelijk rechtstreeks naar de (kinder)uroloog of (kinder)chirurg. Geadviseerd wordt tussen 6 en 12 maanden te opereren.
- Verworven unilateraal en bilateraal NST bij diagnose en na verificatie (zie Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen) verwijzen naar huisarts en/of kinderarts/(kinder)uroloog/(kinder)chirurg om de behandelopties (direct opereren of gecontroleerd afwachten tot de puberteit) te bespreken. Wie deze taak op zich neemt, dient regionaal te worden afgesproken.
Als besloten wordt niet direct te opereren, wordt een vervolgafspraak gemaakt en wordt bij niet spontaan indalen in de puberteit alsnog geopereerd, bij voorkeur voor de 13e verjaardag. - Pijn in liesgebied/scrotum bij verworven NST: doorverwijzen naar huisarts/kinderarts/ (kinder)uroloog/(kinder)chirurg.
- Bij twijfel over retractiliteit verwijzen naar kinderarts, (kinder)uroloog of (kinder)chirurg voor beoordeling.
- Bij ingedaalde testis of NST met een andere aangeboren afwijking aan het genitaal (penisafwijking, hypospadie) en/of syndromale kenmerken verwijzen naar huisarts/ kinderarts(endocrinoloog) voor nader onderzoek en zo nodig behandeling door (kinder)uroloog of (kinder)chirurg.
Niet verwijzen/geen operatie bij jongens met de diagnose: retractiele testis (RT, zie Definitie: Scrotaal).
4 Samenwerking
Regionale afspraken
Bij Verworven unilateraal en bilateraal NST (bij diagnose en na verificatie, zie Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen) verwijzen naar huisarts en/of kinderarts/(kinder)uroloog/(kinder)chirurg om de behandelopties (direct opereren of gecontroleerd afwachten tot de puberteit) te bespreken.
Wie deze taak op zich neemt, dient regionaal te worden afgesproken.
Als besloten wordt niet direct te opereren, wordt een vervolgafspraak gemaakt en wordt bij niet spontaan indalen in de puberteit alsnog geopereerd, bij voorkeur voor de 13e verjaardag.
5 Totstandkoming
5.1 Werkgroepleden
Auteurs
Dr. Mascha Kamphuis, jeugdarts KNMG, onderzoeker, TNO Child Health (Leiden)/ Stichting JGZ Zuid-Holland West
Dr. Frank H. Pierik, gezondheidswetenschapper, TNO Urban Environment and Safety
Drs. Helma B.M. van Gameren-Oosterom, arts, onderzoeker, TNO Child Health (Leiden)
Dr. M. Elske van den Akker-van Marle, afdeling medische besliskunde, LUMC (Leiden)
Expertgroep
dr. Joery Goede, arts-onderzoeker kindergeneeskunde (MCA, Alkmaar, tegenwoordig LUMC)
dr. Frans Hazebroek, emeritus hoogleraar kinderchirurgie (Erasmus MC-Sophia, Rotterdam),
drs. Erik van der Horst, kinderuroloog (VUmc, Amsterdam);
dr. Sabine de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, kinderartsendocrinoloog (Erasmus MC-Sophia, Rotterdam)
Prof. Dr. J Kievit (LUMC Medische Besliskunde)
drs. Stefaan Tytgat, kinderchirurg (UMC, Utrecht)
dr. Tjerk Wiersma, huisarts (NHG, Utrecht)
dr. Pauline Verloove-Vanhorick, emeritus hoogleraar kindergeneeskunde, kinderarts, voorzitter (TNO).
Autorisatie
De richtlijn is geautoriseerd door:
JGZ: Inhoudelijk door de AJN, V&VN fractie jeugd en NVDA. Randvoorwaardelijk door ActiZ en GGD Nederland.
Andere medische beroepsverenigingen: NVK (Nederlandse Vereniging Kindergeneeskunde), NVU (Nederlandse Vereniging Urologie), NVvH (Nederlandse Vereniging voor Heelkunde), NVKC (Nederlandse Vereniging Kinderchirurgie)
5.2 Werkwijze beslissingsanalyse
In een beslissingsanalyse wordt het te analyseren probleem in deelproblemen opgedeeld en vervolgens met behulp van beschikbare kennis geanalyseerd. In een beslissingsanalyse zijn vier fasen te onderscheiden.
Fase 1. specificatie van het beslisprobleem
In deze fase wordt bepaald wat het klinische probleem is, om welke patiënten het gaat, tussen welke alternatieve behandelopties moet worden gekozen en wat de voor- en nadelen van elke behandeling zijn.
Fase 2. het structureren van het probleem
De in fase 1 beschreven probleemstelling wordt in een beslisboom gepresenteerd: een logisch en chronologisch correcte grafische representatie van alle relevante gebeurtenissen die, gegeven het probleem, kunnen optreden.
Fase 3. Kwantitatieve gegevens
In fase 3 worden getalsmatige gegevens (kansen en uitkomstwaarderingen) geïnventariseerd die noodzakelijk zijn om de in fase 2 geconstrueerde beslisboom te kwantificeren.
Fase 4. uitkomsten van de beslissingsanalyse
In deze fase wordt voor de verschillende behandelopties van de beslisboom de verwachte waarde uitgerekend.
Voor de uitwerking: zie Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing.
5.3 Herziening
In principe heeft de richtlijn een geldigheidsduur van vijf jaar. Uiterlijk in 2017 wordt bepaald of actualisering noodzakelijk is. De geldigheid van deze richtlijn verloopt eerder indien resultaten uit wetenschappelijk onderzoek of nieuwe ontwikkelingen een eerdere aanpassing vereisen.
5.4 Belangenverstrengeling
De leden van de expertgroep hebben verklaard in de laatste vijf jaar (tot December 2012) geen inhoudelijke relatie of bemoeienis te hebben gehad met bedrijven of organisaties die op enigerlei wijze zijn verbonden aan het onderwerp van de onderhavige ‘Multidisciplinaire Richtlijn signalering van en verwijzing bij een niet-scrotale testis’, waardoor een belangen- conflict zou kunnen ontstaan met de werkzaamheden in de expertgroep.
6 Verantwoording
6.1 Juridische betekenis van richtlijnen
Richtlijnen zijn geen wettelijke voorschriften, maar op ‘evidence’ gebaseerde inzichten
en aanbevelingen waaraan zorgverleners moeten voldoen om kwalitatief goede zorg te verlenen. Aangezien deze aanbevelingen hoofdzakelijk gebaseerd zijn op de ‘gemiddelde cliënt/patiënt’, kunnen zorgverleners op basis van hun professionele autonomie zo nodig afwijken van de richtlijn. Het afwijken van richtlijnen kan in bepaalde situaties zelfs nood- zakelijk zijn. Wanneer van de richtlijn wordt afgeweken, dient dit beargumenteerd en gedocumenteerd te worden.
6.2 Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing: ‘Beslissingsanalyse niet-scrotale testis’
Deze sectie ‘Beslissingsanalyse niet-scrotale testis’ bevat de gedetailleerde informatie over het project: ‘Gebruik van beslissingsanalyse en patiënten voorkeuren bij ontwikkeling en toepassing van richtlijnen geïllustreerd aan de hand van de richtlijn niet-scrotale testis’.
Bij de vertaling van de uitkomsten uit dat project naar de praktijk zijn enkele uitkomsten op basis van consensus aangepast. Zie de Subsectie Conclusies.
De uiteindelijke aanbevelingen voor de signalering van en de verwijzing bij een niet-scrotale testis worden beschreven in de ‘Multidisciplinaire Richtlijn signalering van en verwijzing bij niet-scrotale testis’ (Kamphuis et al. 2012): zie de Sectie Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen.
In de Sectie Verantwoording worden de kennishiaten naar aanleiding van het project kort weergegeven.
6.2.1 Uitgangsvragen
In dit onderzoeksproject zijn met behulp van een beslissingsanalyse twee vragen met betrekking tot de behandeling van niet-scrotale testis (NST) bestudeerd. Hierbij is onderscheid gemaakt in unilateraal (enkelzijdig) en bilateraal (tweezijdig) NST, en inguïnale (testis in het liesgebied) en abdominale (testis in de buikholte) vormen van NST.
De vragen zijn:
- Wat is de optimale leeftijd voor operatie van aangeboren NST?
- Unilaterale aangeboren inguïnale NST
- Bilaterale aangeboren inguïnale NST
- Unilaterale aangeboren abdominale NST
- Bilaterale aangeboren abdominale NST
- Wat is de optimale leeftijd om verworven vormen van NST te opereren?
- Unilaterale verworven inguïnale NST
- Bilaterale verworven inguïnale NST
- Unilaterale verworven abdominale NST
- Bilaterale verworven abdominale NST
6.2.2 Fase 1: specificatie van het probleem
Zoals aangegeven bij de Subsectie Uitgangsvragen is het klinische probleem een patiënt met een vorm
van NST (unilateraal aangeboren, bilateraal aangeboren, unilateraal verworven, bilateraal verworven, waarbij de ligging inguïnaal of abdominaal kan zijn).
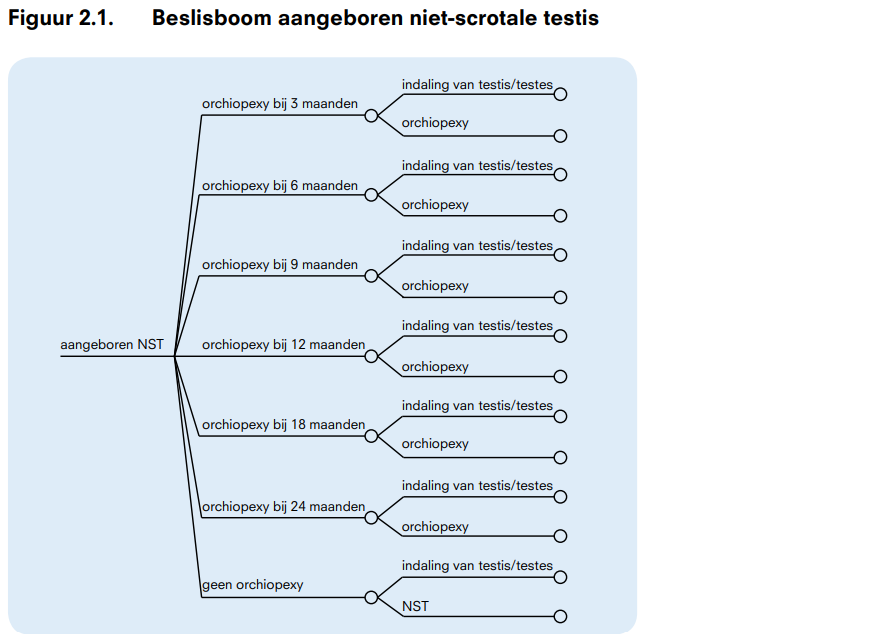
Voor patiënten met een aangeboren vorm van NST zijn als mogelijke behandelopties gekozen operatie op de leeftijd van 3 maanden, operatie op de leeftijd van 6 maanden, operatie op de leeftijd van 9 maanden, operatie op de leeftijd van 12 maanden, operatie op de leeftijd van 18 maanden, operatie op de leeftijd van 24 maanden en niet opereren.
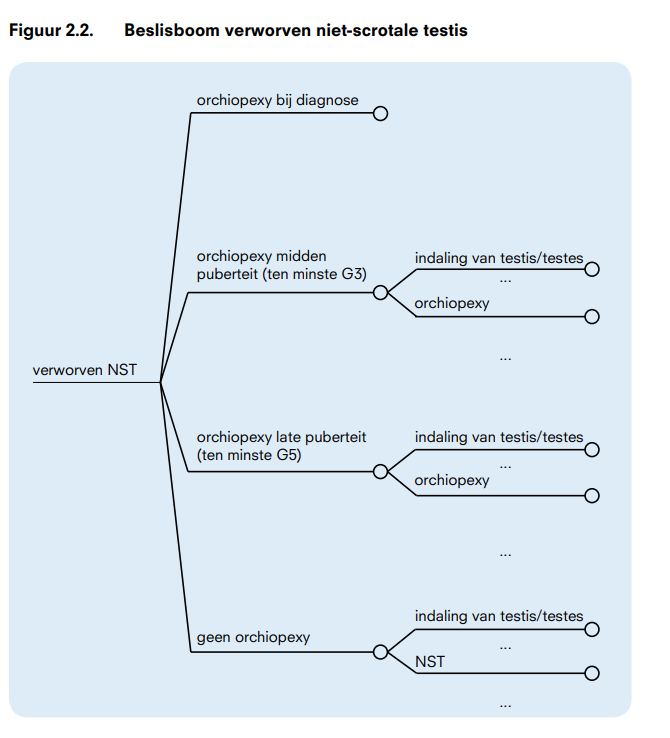
Voor patiënten met een verworven vorm van NST is op basis van de beschikbare Nederlandse literatuur besloten om niet de leeftijd als criterium te nemen voor het moment van operatie, maar het stadium van de puberteit. De mogelijke operatiemomenten zijn dan opereren bij diagnose, opereren in het midden van de puberteit en opereren in de late puberteit en ook hier is de mogelijkheid van niet opereren opgenomen.
Vóór het tijdstip van de operatie zou een deel van de NST ingedaald kunnen zijn (en is operatie dus niet nodig).
Welk deel van de NST ingedaald is, is afhankelijk van het operatiemoment.
Bij bilaterale NST kan indaling leiden tot unilaterale NST als maar één van de testes is ingedaald of geen NST als beide testes zijn ingedaald. In het model wordt verondersteld dat zolang er een unilaterale of bilaterale NST aanwezig is er sowieso een operatie plaatsvindt (behalve bij de behandeloptie ‘niet opereren’).
De behandelopties hebben gevolgen voor de verschillende uitkomstmaten. In het model worden de gevolgen op het gebied van vruchtbaarheid, maligniteit, cosmetisch resultaat en complicaties van OK meegenomen. We hebben op deze uitkomstmaten onderscheid gemaakt in de volgende levels.
Vruchtbaarheid
- Vaderschap.
- Geen vaderschap.
Maligniteit
- Geen testistumor.
- Testistumor zonder overlijden.
- Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt.
Cosmetisch resultaat
- Normaal aspect scrotum.
- Afwijkend aspect scrotum.*
Resultaat OK
- Geen OK.
- Succesvolle OK met litteken, geen gevolgen van anesthesie en OK.
- Succesvolle OK met litteken, enkele** gevolgen van anesthesie en OK.
- Niet- succesvolle OK vanwege atrofie, litteken, geen gevolgen van anesthesie en OK.
- Niet-succesvolle OK vanwege atrofie, litteken, enkele gevolgen van anesthesie en OK.
- Niet-succesvolle OK met litteken, geen gevolgen van anesthesie en OK, re-OK nodig.
- Niet-succesvolle OK met litteken, enkele2 gevolgen van anesthesie en OK, re-OK nodig.
- Overlijden ten gevolge van OK.
Voor elke patiënt zal de uitkomst een combinatie van een van de levels per uitkomstmaat zijn. De uitkomst voor een patiënt kan dus bijvoorbeeld zijn: vaderschap, testistumor waarbij genezing plaatsvindt, normaal aspect scrotum, succesvolle OK met litteken, enkele gevolgen van anesthesie en OK.
* Het afwijkend scrotum is gedefinieerd als één scrotaal en één niet scrotaal gelegen testis (asymmetrie) of twee niet scrotaal gelegen testes.
** Met enkele gevolgen van anesthesie en OK worden bedoeld: pijn, zwelling, hematoom, bloeding, (wondontsteking, misselijkheid, keelpijn na intubatie, allergische reactie op medicatie, gevoelloosheid rond litteken.
6.2.3 Fase 2: het structureren van het probleem
Het beslisprobleem uit fase 1 is voor de 4 afzonderlijke deelvragen gerepresenteerd in een beslisboom. De resulterende beslisbomen voor aangeboren en verworven NST zijn weergegeven in respectievelijk figuur 2.1 en 2.2. In een beslisboom zijn gebeurtenissen geordend van links naar rechts. Gebeurtenissen worden weergeven met behulp van ‘nodes’.
Een beslissingsnode (vierkant) geeft aan dat de beslisser een keuze heeft. De takken die uit deze node voortkomen, geven de keuzemogelijkheden aan. In onze boom betreft dit de mogelijke behandelopties.
Een kansnode (rondje) geeft aan dat een gebeurtenis meerdere mogelijke uitkomsten heeft die niet onder de controle van de beslisser vallen. Dit zijn elkaar uitsluitende uitkomsten. In ons geval is dit het al dan niet indalen van de testis voor het operatiemoment.
Ook de uitkomsten zijn takken van een kansnode. In het beslismodel staan deze voor het behoud van het overzicht niet allemaal weergegeven; in figuur 2.3 is het begin van de vertakkingen behorend bij de laatste (meest rechtse) nodes van de beslisbomen uit figuur 2.1. en 2.2. weergegeven. Deze takken eindigen in een terminal node (driehoek). Hieraan zal de waardering van deze uitkomst worden toegekend. De waardering van de verschillende uitkomsten zal via een vragenlijstonderzoek worden bepaald vanuit maatschappelijk perspectief (algemene bevolking) en patiënten perspectief (ouders en patiënten met NST).

6.2.4 Fase 3: kwantitatieve gegevens
De kansen die nodig zijn om de beslisboom te kwantificeren zijn door middel van literatuurstudie bepaald (zie Tabel 3.1 voor overzicht kansen). In de modellen is onderscheid gemaakt tussen unilaterale en bilaterale vormen van NST, aangeboren en verworven vormen van NST en inguïnale en abdominale vormen van NST. In de hieronder beschreven literatuur wordt dit onderscheid doorgaans niet gemaakt. De beschreven studies bevatten vaak een mix van bovenstaande vormen. Als er geen onderscheid gemaakt wordt, nemen we aan dat de resultaten voor alle vormen gelijk zijn. Als er wel onderscheid gemaakt wordt, wordt dit expliciet in onderstaande tekst vermeld.
In Tabel 3.1 staan de waarden van de parameters vermeld voor de primaire analyse. Daarnaast zal in dit onderzoek met behulp van sensitiviteitsanalyses onderzocht worden wat de gevolgen zijn van alternatieve modelaannamen. De waarden van de parameters die in de sensitiviteitsanalyse worden gebruikt, staan in tabel 3.1 tussen ( ) vermeld.
De gevolgen van de onzekerheid in de parameters op de uitkomsten van het model zijn onderzocht in een probabilistische sensitiviteitsanalyse (PSA). In de probabilistische sensitiviteitsanalyse wordt de onzekerheid in de parameters gekarakteriseerd door kans- verdelingen rond de parameters. In de PSA wordt vervolgens niet de basiswaarde (Tabel 3.1) voor de parameters gebruikt, maar er worden waarden getrokken uit de gedefinieerde kansverdelingen (Tabel 3.2) en vervolgens wordt voor deze waarden de uitkomst bepaald. Dit wordt 10.000 keer herhaald.
Kans op spontane indaling testis
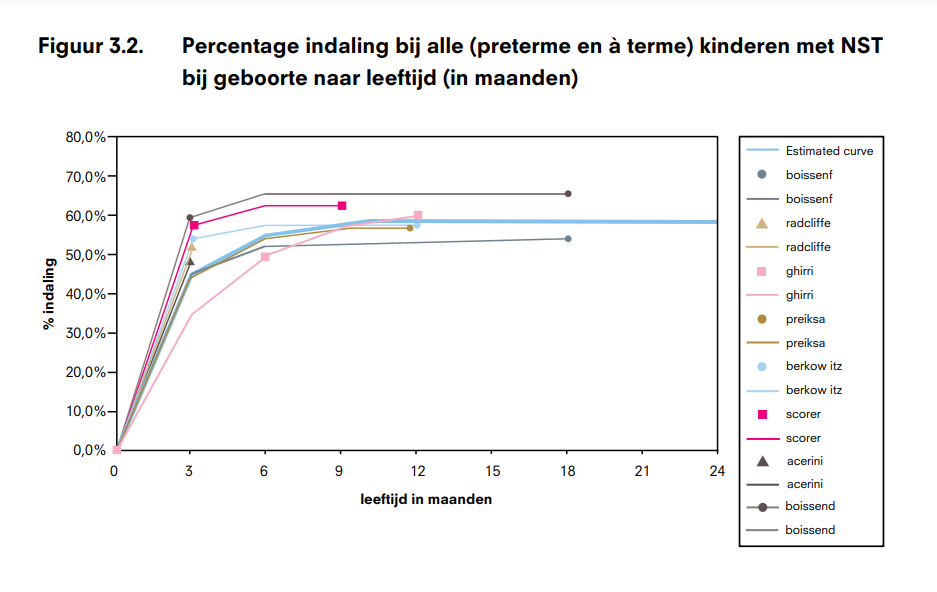
Voor aangeboren vormen van NST is deze kans bepaald op basis van de gegevens die verkregen zijn door middel van prospectieve studies [5][6][7][8][9][10][11]. Op basis van de gegevens uit de artikelen is een gemiddelde curve geschat (zie Figuur 3.1). Deze curve is gebaseerd op gegevens van jongens met een geboortegewicht ≥ 2500 gram, als proxy voor à terme geboorte. Deze proxy is gebruikt omdat er nauwelijks gegevens in de literatuur beschikbaar zijn voor NST op basis van zwangerschapsduur. In de literatuur zijn geen prevalentie- gegevens na de leeftijd van 12 maanden bekend. Daarom is voor de oudere leeftijden (> 12 maanden) de curve geëxtrapoleerd.
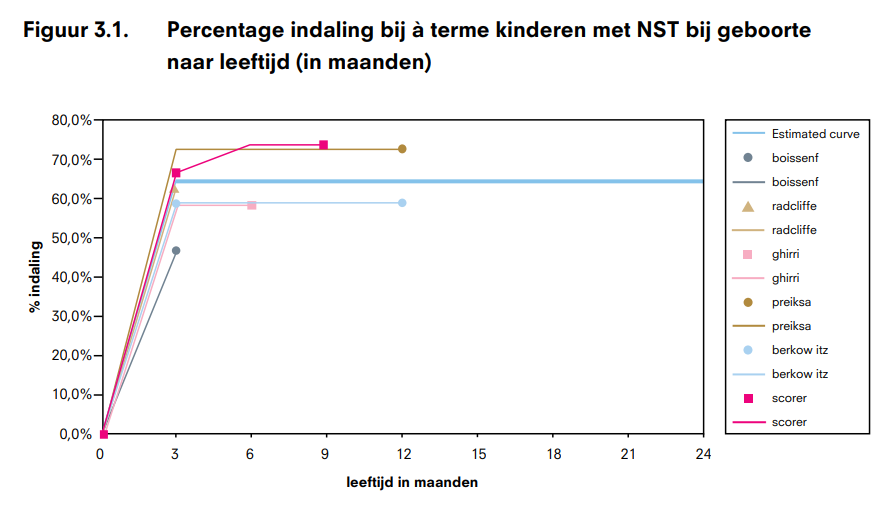
In de sensitiviteitsanalyse gaan we uit van de curve die gevonden wordt indien we de kinderen met een geboortegewicht ≤ 2500 gram niet excluderen (zie figuur 3.2). Op basis van deze gegevens is het percentage NST dat indaalt hoger dan in de primaire analyse. Door deze sensitiviteitsanalyse kunnen we ook de gevolgen bestuderen van de veronderstelling dat in de geraadpleegde literatuur het aantal NST bij geboorte te laag wordt ingeschat en later in het eerste levensjaar te hoog, wat impliceert dat het percentage NST dat indaalt hoger is dan wij in de primaire analyse aannemen.
Voor verworven vormen van NST is de kans op indaling bepaald op basis van 2 Nederlandse cohortstudies [12][13]. De resultaten van beide studies zijn gemiddeld. In de PSA worden de resultaten van de afzonderlijke studies gebruikt.
Kans op vaderschap
De kans op vaderschap na operatie is gebaseerd op Lee [14]. De bilaterale vorm van NST resulteert in een kans van 65,0%, 95% betrouwbaarheidsinterval [52,0% tot 78,6%] op vaderschap na operatie. Voor de unilaterale vorm van NST werd een kans op vaderschap na operatie van 89,7%, 95% betrouwbaarheidsinterval [86,5% tot 92,8%] gevonden. De kans op vaderschap in de normale populatie is 93,2%, 95% betrouwbaarheidsinterval [90,9% tot 95,6%].
In de sensitiviteitsanalyse wordt onderscheid gemaakt tussen aangeboren en verworven vormen van NST met betrekking tot de kans op vaderschap. Hierbij wordt aangesloten bij de discussie dat verworven vormen van NST mogelijk een andere oorzaak hebben en wellicht minder gevolgen hebben voor de testisfunctie [15]. In de sensitiviteitsanalyse wordt daarom uitgegaan van een kans op vaderschap na operatie voor verworven unilaterale NST van 93,2% (verworven vorm van NST heeft dan geen gevolgen voor de testisfunctie). Voor aangeboren unilaterale NST wordt een lagere kans op vaderschap aangenomen, deze kans is op 85% gesteld. Voor de bilaterale NST worden in de sensitiviteitsanalyse de kansen voor de aangeboren en verworven vorm van respectievelijk 55% en 75% aangenomen. Deze aannamen zijn gebaseerd op de onder- en bovengrenzen van de genoemde betrouwbaarheidsintervallen (‘afgerond’ op een rond getal).
Zonder operatie is er een kans op vaderschap bij bilaterale NST geschat op 5% door de expertgroep. Over de kans op vaderschap bij unilaterale NST zonder operatie zijn geen data beschikbaar. Er zijn echter wel indirecte aanwijzingen dat operatie van de unilaterale testis geen effect heeft op de kans op vaderschap. Namelijk, in de onderzoekspopulatie van Lee verliep bij 20 mannen de operatie dusdanig ongeslaagd, dat uiteindelijk de testikel werd verwijderd. Zelfs na het verwijderen van deze enkelzijdig niet-ingedaalde testis was de kans op vaderschap niet anders dan bij geslaagde operaties [16]. Er is daarom aan- genomen dat ook zonder operatie de kans op vaderschap bij unilaterale NST 89,7% is, 95% betrouwbaarheidsinterval [86,5% tot 92,8%]. In de sensitiviteitsanalyse wordt uit- gegaan van een kans op vaderschap zonder operatie bij unilaterale aangeboren NST van 85% en voor de verworven vorm van NST van een kans van 93,2% (zie uitleg hierboven).
Kans op testistumor
Voor patiënten met spontane indaling van aangeboren en verworven NST wordt de kans op een testistumor gelijk verondersteld aan de kans van de algemene populatie. In 2007 was de incidentie van testistumoren 7,5 per 100.000 mannen en de sterfte 0,3 per 100.000 mannen (www.ikc-net.nl). Met behulp van leeftijdsspecifieke incidentie- en sterftecijfers (www.ikc-net.nl) en de overlevingstabel voor mannen (statline.cbs.nl) is het lifetime risico op een testistumor van 0,54% berekend en het lifetime risico op overlijden ten gevolge van een testistumor 0,03% (www.ikc-net.nl, statline.cbs.nl). Dit levert de kans op een testistumor zonder overlijden van 0,52% en een kans op een testistumor waaraan de patiënt overlijdt van 0,03%.
De kans op een testistumor bij patiënten met NST is op basis van een review-artikel van Dieckmann & Pichlmeier [17] 4,8 (95% betrouwbaarheidsinterval [4,0 tot 5,7]) keer hoger verondersteld dan in de algemene populatie. In de primaire analyse gaan we ervan uit dat ook de NST die niet spontaan indaalt een verhoogd risico geeft, ongeacht of er chirurgisch ingegrepen wordt of niet. Dit levert de kansen van respectievelijk 2,49% en 0,12% op een testistumor zonder overlijden en een testistumor waaraan de patiënt overlijdt.
In een studie van Pettersson et al. [18] wordt een (plotselinge) sterke toename in kans op een testistumor gevonden bij operatie na de leeftijd van 13 jaar. Bij kinderen die voor de leeftijd van 13 jaar geopereerd zijn, werd een 2,23 (95% betrouwbaarheidsinterval [1,6 tot 3,1]) keer verhoogd risico op een testistumor gevonden en er werd een 5,40 (95% betrouwbaarheidsinterval [3,2 tot 8,5]) keer verhoogd risico gevonden voor patiënten die na deze leeftijd geopereerd zijn in vergelijking met de algemene populatie.
In de sensitiviteitsanalyse wordt daarom aangenomen dat kinderen die worden geopereerd aan de aangeboren vormen van NST en de kinderen met een verworven vorm van NST die voor de leeftijd van 13 jaar (d.w.z. voor de puberteit) worden geopereerd een 2,23 keer verhoogd risico hebben op een testistumor (i.e. 1,16% voor een testistumor zonder overlijden en 0,06% voor een testistumor waaraan de patiënt overlijdt), en kinderen die in de puberteit, na de leeftijd van 13 jaar, worden geopereerd of niet worden geopereerd een 5,40 keer verhoogd risico hebben van respectievelijk 2,80% en 0,14%.
Kans op succesvolle operatie
De kans op een succesvolle operatie voor inguïnale vormen van NST is op basis van verschillende studies [19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28] op 94% gesteld. In de PSA zullen, naar aanleiding van de gevonden resultaten in de studies, ook slagingspercentages tussen de 88% en 100% worden verondersteld.
De kans op een succesvolle laparoscopie voor abdominale vormen van NST is gebaseerd op een review [29] en is op 87% gesteld. In de PSA zullen, naar aanleiding van de gevonden resultaten in de studies, ook slagingspercentages tussen de 85% en 90% worden verondersteld.
Voor de niet-succesvolle operaties is door de experts na discussie aangenomen dat in de helft van de gevallen een heroperatie mogelijk is en in de overige gevallen niet vanwege testisatrofie.
Kans op complicaties na OK
De kans op een of meerdere (lichte) gevolgen van anesthesie is gebaseerd op verschil- lende studies [2][23][30][31] en bedraagt 3,6%. In de PSA zullen ook percentages tussen de 3,0 en 4,2% worden verondersteld.
In een prospectieve studie onder volwassenen vonden Arbous et al. [32] dat anesthesie in 1,4 per 10.000 anesthesieën bijdragend was aan de sterfte. Het aantal sterfgevallen dat door anesthesie wordt veroorzaakt zal naar verwachting 10-100 keer kleiner zijn. Voor kinderen zal dit getal nog lager liggen. In deze studie wordt uitgegaan van een OK-mortaliteit van 1,4 per 1.000.000.
Tabel 3.1. Parameters beslismodel, parameterwaarden primaire analyse (parameterwaarden sensitiviteitsanalyse)
3.1 a. Inguïnale NST
|
Parameter |
Unilateraal aangeboren |
Bilateraal aangeboren |
Unilateraal verworven |
Bilateraal verworven |
||||
|
Kans |
Bron |
Kans |
Bron |
Kans |
Bron |
Kans |
Bron |
|
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 3 maanden |
65% (59%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (59%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 6 maanden |
65% (73%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (73%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 9 maanden |
65% (76%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (76%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 12 maanden |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 18 maanden |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 24 maanden |
65% (77%) |
Extrapol. |
65% (77%) |
Extrapol. |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling verworven NST voor bereiken van midden puberteit (G3) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
43% |
[12][13] |
43% |
[12][13] |
|
Indaling verworven NST voor bereiken late puberteit (G5) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
66% |
[12][13] |
66% |
[12][13] |
|
Indaling verworven NST |
– |
– |
– |
– |
66% |
[12][13] |
66% |
[12][13] |
|
Vaderschap na indaling |
93,2% |
[14] |
93,2% |
[14] |
93,2% |
[14] |
93,2% |
[14] |
|
Vaderschap zonder indaling zonder operatie |
89,7% (85%) |
[14] |
5% |
Experts* |
89,7% (93,2%) |
[14] |
5% |
Experts* |
|
Vaderschap onder indaling met operatie |
89,7% (85%) |
[14] |
65% (55%) |
[14] |
89,7% (93,2%) |
[14] |
65% (75%) |
[14] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden bij onbehandelde NST |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt bij onbehandelde NST |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden na NST-operatie in pubertijd |
– |
– |
– |
– |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt na NST-operatie in pubertijd |
– |
– |
– |
– |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden na vroege* NST-operatie |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt na vroege* NST- operatie |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden bij spontane indaling |
0,52% |
[16] |
0,52% |
[16] |
0,52% |
[16] |
0,52% |
[16] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt na spontane indaling |
0,03% |
[16] |
0,03% |
[16] |
0,03% |
[16] |
0,03% |
[16] |
|
Succesvolle OK |
94% |
[19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28] |
94% |
[19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28] |
94% |
[19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28] |
94% |
[19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28] |
|
Niet succesvolle OK, atrofie |
3% |
Experts* |
3% |
Experts* |
3% |
Experts* |
3% |
Experts* |
|
Niet succesvolle OK, re-OK nodig |
3% |
Experts* |
3% |
Experts* |
3% |
Experts* |
3% |
Experts* |
|
Een of meerdere gevolgen van anesthesie OK |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
|
Overlijden na operatie |
0,00014% |
[32], Experts* |
0,00014% |
[32], Experts* |
0,00014% |
[32], Experts* |
0,00014% |
[32], Experts* |
*Op basis van discussie
3.1 b. Abdominale NST
|
Parameter |
Unilateraal aangeboren |
Bilateraal aangeboren |
Unilateraal verworven |
Bilateraal verworven |
||||
|
Kans |
Bron |
Kans |
Bron |
Kans |
Bron |
Kans |
Bron |
|
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 3 maanden |
65% (59%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (59%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 6 maanden |
65% (73%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (73%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 9 maanden |
65% (76%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (76%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 12 maanden |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 18 maanden |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
65% (77%) |
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling aangeboren NST < 24 maanden |
65% (77%) |
Extrapol. |
65% (77%) |
Extrapol. |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Indaling verworven NST voor bereiken midden puberteit (G3) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
43% |
[12][13] |
43% |
[12][13] |
|
Indaling verworven NST voor bereiken late puberteit (G5) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
66% |
[12][13] |
66% |
[12][13] |
|
Indaling verworven NST |
– |
– |
– |
– |
66% |
[12][13] |
66% |
[12][13] |
|
Vaderschap na indaling |
93,2% |
[14] |
93,2% |
[14] |
93,2% |
[14] |
93,2% |
[14] |
|
Vaderschap zonder indaling zonder operatie |
89,7% (85%) |
[14] |
5% |
Experts* |
89,7% (85%) |
[14] |
5% |
Experts* |
|
Vaderschap zonder indaling met operatie |
89,7% (85%) |
[14] |
65% (55%) |
[14] |
89,7% (93,2%) |
[14] |
65% (75%) |
[14] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden bij onbehandelde NST |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt bij onbehandelde NST |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden na NST-operatie in pubertijd |
– |
– |
– |
– |
2,49% (2,80%) |
|
2,49% (2,80%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt na NST-operatie in pubertijd |
– |
– |
– |
– |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,14%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden na vroege* NST-operatie |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
2,49% (1,16%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt na vroege* NST-operatie |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
0,12% (0,06%) |
[16][17][18] |
|
Testistumor zonder overlijden bij spontane indaling |
0,52% |
[16] |
0,52% |
[16] |
0,52% |
[16] |
0,52% |
[16] |
|
Testistumor waaraan patiënt overlijdt bij spontane indaling |
0,03% |
[16] |
0,03% |
[16] |
0,03% |
[16] |
0,03% |
[16] |
|
Succesvolle OK |
87% |
[29] |
87% |
[29] |
87% |
[29] |
87% |
[29] |
|
Niet succesvolle OK, atrofie |
6,5% |
Experts* |
6,5% |
Experts* |
6,5% |
Experts* |
6,5% |
Experts* |
|
Niet succesvolle OK, re-OK nodig |
6,5% |
Experts* |
6,5% |
Experts* |
6,5% |
Experts* |
6,5% |
Experts* |
|
Een of meerdere gevolgen van anesthesie OK |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
3,6% |
[2][30][23][31] |
|
Overlijden na operatie |
0,00014% |
[32] |
0,00014% |
[32] |
0,00014% |
[32] |
0,00014% |
[32] |
Tabel 3.2. modelparameters opgenomen in probabilistische sensitiviteitsanalyse en hun verdelingsfunctie
| Modelparameter | Verdelingsfunctie* |
| Indaling aangeboren NST | Bèta-verdeling, gemiddelde = 0,65 |
|
Indaling verworven NST
|
|
| Vaderschap na indaling | Binomiale verdeling, p = 0,932, n = 443‡ |
|
Vaderschap zonder indaling en zonder operatie
|
|
|
Vaderschap zonder indaling en met operatie
|
|
| Succesvolle operatie | Bèta-verdeling, gemiddelde = 0,94 |
| Enige complicaties | Bèta-verdeling, gemiddelde = 0,036 |
| Overlijden ten gevolge van anesthesie/OK | Uniforme verdeling (0,00007%, 0,00014%) |
| Duur behandeling testistumor | Driehoeksverdeling, min. = 5 jaar, max. = 10 jaar, gemiddelde = 7,5 jaar |
|
Duur afwijkend aspect scrotum
|
|
| Utiliteit van gezondheidsuitkomsten NST | Bèta-verdeling, gemiddelde en standaard- deviatie als in tabel 3.4 |
*De uniforme verdeling is gebruikt als er gegevens waren over de uiterste waarden, maar niet over hoe de verdeling was tussen de uiterste waarden; we hebben de verdeling dan constant gehouden. Voor de duur van de testistumorbehandeling hadden we informatie dat een follow-up van 5 jaar het meest gebruikelijk is, daarom is hier de driehoeksverdeling gebruikt. De binomiale verdeling is gebruikt voor kansparameters waarvoor we één bron
tot onze beschikking hadden en dus de benodigde gegevens uit deze ene bron konden halen. Voor de overige parameters is de bèta-verdeling gebruikt, de gebruikelijke keuze voor parameters die alleen waarden op het 0-1-interval kunnen aannemen (kansen, utiliteiten).
† Gebaseerd op Sijstermans et al.(2006) en Eijsbouts et al. (2007).
‡ Gebaseerd op Lee (2005).
Naast de kansen zijn ook de uitkomstwaarderingen van de gezondheidstoestanden die een relatie hebben met niet-scrotale testis bepaald. Deze waarderingen bestaan uit een duur en een utiliteit. De duur is bepaald op basis van expert-opinions.
Tabel 3.3. Duur van verschillende gezondheidstoestanden niet-ingedaalde testis op basis van expert-opinions (sensitiviteitsanalyse)
| Toestand | Duur | Argumentatie |
| Geen vaderschap |
10 jaar 34,1 jaar |
78,3* – 34,2** = 44,1 jaar, gedurende de rest van het leven verminderde kwaliteit van leven, hierbij wel aangenomen dat na 10 jaar de mate waarin de kwaliteit van leven vermindert gehalveerd wordt. |
| Testistumor (operatie en vervolgbehandeling) | 7,4 jaar (5-10 jaar) | Duur van behandeling en nacontroles 10 jaar na chemotherapie en/of lymfklierdissectie, anders 5 jaar. 48,3% van de mannen met testistumor krijgt chemothe- rapie of lymfklierdissectie (Brydoy, JNCI 2009); dit levert een gemiddelde duur van behandeling en follow-up van 7,4 jaar (0,483 * 10 + (1 – 0,483) * 5) = 7,4). |
| Overlijden door testistumor | 31,9 jaar | 78,3 – 46,4***= 31,9 jaar, door overlijden aan testistu- mor een verlies van 31,9 levensjaren |
|
Afwijkend aspect scrotum
|
|
|
| Succesvolle OK | 2 weken | Duur van spanning vooraf, operatie zelf en bijkomen van operatie en eventuele lichte complicaties, inge- schat op 2 weken. |
| Niet succesvolle OK vanwege testisatrofie | 2 weken | Idem. |
| Niet succesvolle OK, re-OK nodig | 2 weken | Idem. |
| Enige complicaties OK | 2 weken | Idem. |
| Littekens operatie | 1 jaar | Na 1 jaar operatielittekens vervaagd. |
| Overlijden bij OK | 78,3* jaar – leeftijd bij OK | Is dus afhankelijk van de leeftijd bij operatie. |
* 78,3 jaar is de levensverwachting van mannen.
** 34,2 jaar is de gemiddelde leeftijd waarop een man een kind krijgt.
*** 46,4 jaar is de gemiddelde leeftijd van overlijden aan testistumor.
Via een vragenlijstonderzoek zijn de waarderingen van de verschillende gezondheids- toestanden met betrekking tot de niet-scrotale testis verkregen vanuit de algemene bevolking, ouders van patiënten die voor de keuze van al dan niet een operatie staan
en oud-patiënten die voor deze keuze hebben gestaan. Aan hen is gevraagd om de verschillende gezondheidstoestanden te waarderen op een VAS-schaal variërend tussen ‘0’ (dood) en ‘100’ (perfect gezond).
In totaal zijn 111 vragenlijsten verkregen (64 vragenlijsten algemene populatie, 34 vragen- lijsten ouders, 13 vragenlijsten patiënten). Vragenlijsten die voldeden aan ten minste een van de volgende 3 criteria zijn geëxcludeerd, omdat deze respondenten de vragenlijst echt niet goed hebben begrepen:
- Succesvolle OK zonder complicaties lager gewaardeerd dan succesvolle OK met complicaties of niet-succesvolle OK.
- Testistumor als perfect gezond gewaardeerd.
- Uit opmerkingen aan eind van vragenlijst valt op te maken dat de respondent de vragenlijst niet begrepen heeft.
Op basis van de resterende vragenlijsten (n = 72) zijn de volgende waarderingen verkregen. De op de VAS-schaal aangegeven waarderingen zijn met behulp van de transformatie 1−(1−visueel analoge schaal/100)1,61 (Stiggelbout et al. 1996) getransformeerd tot utiliteiten.
Tabel 3.4. waardering van verschillende gezondheidstoestanden met betrekking tot niet-scrotale testis
| Toestand | Alg. bevolking (n=41) | Ouder (n=24) | Patiënt (n=7) | |||
| Gemiddelde | SD1 | Gemiddelde | SD | 8,0% | SD | |
| Geen vaderschap | 0,660 | 0,263 | 0,410 | 0,198 | 0,593 | 0,268 |
| Testistumor (operatie en vervolgbehandeling) | 0,598 | 0,228 | 0,422 | 0,276 | 0,388 | 0,190 |
| Enkelzijdig lege balzak | 0,895 | 0,116 | 0,852 | 0,186 | 0,822 | 0,183 |
| Beiderzijds lege balzak | 0,757 | 0,204 | 0,649 | 0,301 | 0,694 | 0,287 |
| Succesvolle OK, geen complicaties | 0,963 | 0,57 | 0,942 | 0,100 | 0,974 | 0,034 |
| Succesvolle OK, enige complicaties | 0,852 | 0,118 | 0,743 | 0,225 | 0,752 | 0,201 |
| Niet-succesvolle OK vanwege testisatrofie | 0,780 | 0,207 | 0,634 | 0,270 | 0,600 | 0,283 |
| Niet-succesvolle OK, re-OK nodig, geen complicaties | 0,810 | 0,156 | 0,710 | 0,241 | 0,651 | 0,277 |
| Niet succesvolle OK vanwege testisatrofie, enige complicaties | 0,680 | 0,223 | 0,562 | 0,241 | 0,517 | 0,282 |
| Niet succesvolle OK, re-OK nodig, enige complicaties | 0,718 | 0,208 | 0,579 | 0,275 | 0,623 | 0,185 |
| Littekens operatie | 0,919 | 0,116 | 0,839 | 0,190 | 0,935 | 0,119 |
1 SD = standaarddeviatie
De bovenstaande toestanden hebben alle een waardering die lager is dan 1,0 (‘volledig gezond’). Het verlies in utiliteit (=1,0- gemiddelde utiliteitsscore uit tabel 3.4) voor de verschillende gezondheidsstadia is vermenigvuldigd met de duur van het betreffende stadium (zie tabel 3.3) om het verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy’s) voor de verschillende gezondheidsstadia te berekenen (zie tabel 3.5).
Tabel 3.5. QAly-verlies ten gevolge van verschillende gezondheidstoestanden met betrekking tot niet-scrotale testis
| Toestand | Alg. bevolking (n=41) | Ouder (n=24) | Patiënt (n=7) |
| Geen vaderschap | 9,2* | 16,0 | 11,0 |
| Testistumor (operatie en vervolgbehandeling) | 3,0 | 4,3 | 4,5 |
| Testistumor met overlijden | 34,9 | 36,2 | 36,4 |
|
Afwijkend aspect scrotum
|
|
|
|
| Succesvolle OK, geen complicaties | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| Succesvolle OK, enige complicaties | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
|
Niet-succesvolle OK vanwege testisatrofie, geen complicaties*
|
|
|
|
| Niet-succesvolle OK, re-OK nodig, geen complicaties | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
|
Niet succesvolle OK vanwege testisatrofie, enige complicaties**
|
|
|
|
| Niet succesvolle OK, re-OK nodig, enige complicaties | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| Littekens operatie | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,1 |
* Voorbeeld QALy-berekening: 10 jaar * (1 – 0,66) + 31,4 jaar * (1 – 0,83) = 3,4 + 5,8 = 9,2 QALy (0,83 is gemiddelde tussen 0,66 en 1,00, omdat we aangenomen hebben dat na 10 jaar de mate waarin de kwaliteit van leven vermindert gehalveerd wordt).
** Inclusief afwijkend aspect scrotum.
Kosten
Naast de effectiviteit zijn ook globale schattingen meegenomen van de kosten van behandeling en gevolgen van NST. Voor conservatief beleid bij NST is uitgegaan van 2 extra poliklinische consulten. De kosten hiervan zijn € 148. De kosten van de operatie bedragen € 821 (31, prijspeil 2011) en € 1728 [34][33] als aansluitend een ziekenhuisop- name nodig is vanwege de gevolgen van anesthesie/OK. De kosten van de behandeling van een testistumor zijn gebaseerd op Hsleh et al. [35] en bedragen € 14.000. De kosten van een onvruchtbaarheidsbehandeling bedragen€ 2000 [34].
6.2.5 Fase 4: uitkomsten van de beslissingsanalyse
Met behulp van de aannamen uit fase 3 levert de beslissingsanalyse de volgende uitkomsten. De uitkomsten betreffen het verlies aan QALy’s. In onderstaande tabellen zijn de operatieleeftijden waarbij het verlies aan QALy’s minimaal is vetgedrukt. Voor elke serie tabellen wordt een korte samenvatting van de resultaten gegeven.
6.2.6 Fase 4a Aangeboren unilaterale NST
Samenvatting 4.1: aangeboren unilaterale NST (tabellen 4.1a tot en met e):
- Bij aangeboren unilaterale NST (inguïnaal en abdominaal) levert opereren minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan niet opereren (4.1a en 4.1d). Als de onzekerheid van de parameters wordt meegenomen, levert opereren met 94,7% kans een lager QALy-verlies op.
- Dit wordt vooral verklaard (4.1c) door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum bij niet opereren (35%) ten opzichte van wel opereren (1,1%).
- Operatie op de verschillende leeftijden (3, 6, 9, 12, 18 en 24 maanden) levert in de basisanalyse geen verschil in QALy-verlies op. De sensitiviteitsanalyse (4.1b) toont alleen een verschil in QALy-verlies voor de parameter kans op spontane indaling. Voor deze parameter wordt het minste QALy-verlies gezien als geopereerd wordt bij 12, 18 en 24 maanden (0,781). Echter het kleine verschil in QALy-verlies met opereren bij 6 en 9 maanden is beperkt relevant; in tegenstelling tot het grotere verschil in QALy-verlies met opereren bij 3 maanden. Dit leidt tot de conclusie dat op basis van de kans op spontane indaling operatie na de leeftijd van 6 maanden optimaal is. Geen verschil werd gezien in de sensitiviteitsanalyse voor de parameters kans op vaderschap, kans op testistumor, kans op succesvolle operatie, kans op complicaties na operatie, kans op overlijden t.g.v. operatie, duur van afwijkend aspect van het scrotum en duur van behandeling bij testistumor.
- De kosteneffectiviteitsanalyse (4.1e) toont dat bij opereren (ongeacht de leeftijd waarop) de kosteneffectiviteitsratio 582 €/QALy is t.o.v. niet opereren. Conclusie van de kosten- effectiviteitsanalyse is dat kosten in de beslissingsanalyse geen rol spelen, omdat de verschillen acceptabel zijn (binnen de grenzen die in het algemeen geaccepteerd worden).
Tabel 4.1a. Verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren unilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 1,534 |
| Waardering ouders | 1,444 | 1,444 | 1,444 | 1,444 | 1,444 | 1,444 | 2,390 |
| Waardering patiënten | 1,022 | 1,022 | 1,022 | 1,022 | 1,022 | 1,022 | 2,209 |
Tabel 4.1b. Verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren unilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment met waardering algemene populatie (sensitiviteitsanalyse)
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 1,534 |
| Indaling – leeftijdsafhankelijk |
0,808 | 0,787 | 0,782 | 0,781 | 0,781 | 0,781 | 1,232 |
| Vaderschap – laag |
1,000 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 1,685 |
| Testistumor – afhankelijk van OK-leeftijd |
0,827 | 0,827 | 0,827 | 0,827 | 0,827 | 0,827 | 1,540 |
Tabel 4.1c. percentage patiënten met gezondheidstoestand afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse
| Gezondheidstoestand | 3 mnd | 6 mnd | 9 mnd | 12 mnd | 18 mnd | 18 mnd | 24 mnd | Geen OK |
| Geen vaderschap | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% |
| Testistumor zonder overlijden | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% |
| Testistumor met overlijden | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% |
| Afwijkend aspect scrotum | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 35,0% |
| Complicaties OK | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 0,0% |
| Re-OK | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 0,0% |
| Overlijden bij OK | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% |
* Voorbeeld van een berekening: 65% van de aangeboren NST dalen binnen 3 maanden in, patiënten met aangeboren NST waarbij indaling plaatsvindt hebben een kans op vaderschap van 93,2%. De overige 35% hebben een kans van 89,7% op vaderschap. 0,65 * 93,2 + 0,35 * 89,7 = 92,0% vaderschap, hieruit volgt dat percentage geen vaderschap 8,0% is.
Tabel 4.1d. verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren unilaterale nst (abdominaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 1,534 |
| Waardering ouders | 1,484 | 1,484 | 1,484 | 1,484 | 1,484 | 1,484 | 2,390 |
| Waardering patiënten | 1,070 | 1,070 | 1,070 | 1,070 | 1,070 | 1,070 | 2,209 |
Wanneer in de PSA de onzekerheid van de parameters uit de basisanalyse wordt meegenomen zoals aangegeven in tabel 3.2, leidt dit tot de volgende resultaten:
QALy-verlies operatie (ongeacht welke leeftijd): 0,86, 95% bti [0,12; 2,05].
QALy-verlies geen OK: 1,43, 95% bti [0,27; 3,13].
Met 94,7% kans levert opereren een lager QALy-verlies op.
Tabel 4.1e. verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren unilaterale nst (abdominaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en kosten per kind met NST
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| QALY-verlies | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 0,848 | 1,534 |
| Kosten (€) | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 647 | 390 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALy) | 375 | 375 | 375 | 375 | 375 | 375 |
| Discontering 3%* | 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK |
| QALY-verlies | 0,22 | 0,22 | 0,22 | 0,22 | 0,22 | 0,22 | 0,66 |
| Kosten (€) | 421 | 421 | 421 | 421 | 421 | 421 | 165 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALy) | 582 | 582 | 582 | 582 | 582 | 582 |
* In deze tabel is rekening gehouden met 3% verdiscontering, wat betekent dat kosten en effecten in de toekomst lager gewaardeerd worden.
6.2.7 Fase 4b Aangeboren bilaterale NST
Samenvatting 4.2: aangeboren bilaterale NST (tabellen 4.2a tot en met e):
- Bij aangeboren bilaterale NST (inguïnaal en abdominaal) levert opereren minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan niet opereren (4.2a en 4.2d). Als de onzekerheid van de parameters wordt meegenomen, levert met 100% kans opereren een lager QALy-verlies op.
- Dit wordt vooral verklaard (4.2c) door het hogere percentage patiënten met geen vaderschap bij niet opereren (37,7%) ten opzichte van bij wel opereren (16,7%) en het hogere percentage afwijkend aspect scrotum (35% versus 1,1%). Dit alles pleit dus voor opereren.
- Operatie op de verschillende leeftijden (3, 6, 9, 12, 18 en 24 maanden) levert in de basisanalyse geen verschil in QALy-verlies op. De sensitiviteitsanalyse (4.2b) toont alleen een verschil in QALy-verlies voor de parameter kans op spontane indaling. Voor deze parameter wordt het minste QALy-verlies gezien als geopereerd wordt bij 12, 18 en 24 maanden (1,323). Echter het kleine verschil in QALy-verlies met opereren bij 6 en 9 maanden is beperkt relevant; in tegenstelling tot het grotere verschil in QALy-verlies met opereren bij 3 maanden. Dit leidt tot de conclusie dat op basis van de kans op spontane indaling operatie na de leeftijd van 6 maanden optimaal is. Geen verschil werd gezien in de sensitiviteitsanalyse voor de parameters kans op vaderschap, kans op testistumor, kans op succesvolle operatie, kans op complicaties na operatie, kans op overlijden t.g.v. operatie, duur van afwijkend aspect van het scrotum en duur van behandeling bij testistumor.
- De kosteneffectiviteitsanalyse (4.2e) toont dat bij opereren (ongeacht de leeftijd waarop) de kosteneffectiviteitsratio 69 €/QALy is t.o.v. niet opereren. Conclusie van de kosteneffectiviteitsanalyse is, dat kosten in de beslissingsanalyse geen rol spelen, omdat de extra kosten per QALy zeer acceptabel zijn in het licht van de grenzen die in het algemeen geaccepteerd worden (€ 20.000 – € 40.000 per QALy).
tabel 4.2a. Verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren bilaterale nst afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 5,227 |
| Waardering ouders | 2,867 | 2,867 | 2,867 | 2,867 | 2,867 | 2,867 | 8,536 |
| Waardering patiënten | 2,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 6,359 |
Tabel 4.2b. Verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren bilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment met waardering algemene populatie (sensitiviteitsanalyse)
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 5,227 |
| Indaling – leeftijdsafhankelijk |
1,365 | 1,333 | 1,327 | 1,323 | 1,323 | 1,323 | 3,658 |
| Vaderschap – laag |
1,996 | 1,996 | 1,996 | 1,996 | 1,996 | 1,996 | 5,227 |
| Testistumor – afhankelijk van OK-leeftijd |
1,653 | 1,653 | 1,653 | 1,653 | 1,653 | 1,653 | 5,232 |
Tabel 4.2c. percentage patiënten met gezondheidstoestand afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse
| Gezondheidstoestand | 3 mnd | 6 mnd | 9 mnd | 12 mnd | 18 mnd | 18 mnd | 24 mnd | Geen OK |
| Geen vaderschap | 16,7% | 16,7% | 16,7% | 16,7% | 16,7% | 16,7% | 16,7% | 37,7% |
| Testistumor zonder overlijden | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% |
| Testistumor met overlijden | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% | 0,1% |
| Afwijkend aspect scrotum | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 1,1% | 35,0% |
| Complicaties OK | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 1,3% | 0,0% |
| Re-OK | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 2,1% | 0,0% |
| Overlijden bij OK | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% |
* Voorbeeld van een berekening: 65% van de aangeboren NST dalen binnen 3 maanden in, patiënten met aangeboren NST waarbij indaling plaatsvindt hebben een kans op vaderschap van 93,2%. De overige 35% hebben een kans van 89,7% op vaderschap. 0,65 * 93,2 + 0,35 * 89,7 = 92,0% vaderschap, hieruit volgt dat percentage geen vaderschap 8,0% is.
Tabel 4.2d. verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren bilaterale nst (abdominaal) af- hankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering alge- mene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 1,740 | 1,740 | 1,740 | 1,740 | 1,740 | 1,740 | 5,227 |
| Waardering ouders | 2,962 | 2,962 | 2,962 | 2,962 | 2,962 | 2,962 | 8,536 |
| Waardering patiënten | 2,083 | 2,083 | 2,083 | 2,083 | 2,083 | 2,083 | 6,359 |
Wanneer in de PSA de onzekerheid van de parameters uit de basisanalyse wordt meegenomen zoals aangegeven in tabel 3.2, leidt dit tot de volgende resultaten:
QALy-verlies operatie (ongeacht welke leeftijd): 1,71, 95% bti [0,20; 4,20].
QALy-verlies geen OK: 5,11, 95% bti [0,96; 11,76].
Met 100% kans levert opereren een lager QALy-verlies op.
Tabel 4.2e. verlies in QAly’s voor aangeboren unilaterale nst (abdominaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en kosten per kind met NST
| 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK | |
| QALY-verlies | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 1,674 | 5,227 |
| Kosten (€) | 819 | 819 | 819 | 819 | 819 | 819 | 983 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALy) | gedomineerd |
| Discontering 3%* | 3 mndn | 6 mndn | 9 mndn | 12 mndn | 18 mndn | 24 mndn | Geen OK |
| QALY-verlies | 0,41 | 0,41 | 0,41 | 0,41 | 0,41 | 0,41 | 1,90 |
| Kosten (€) | 485 | 485 | 485 | 485 | 485 | 485 | 382 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALy) | 69 | 69 | 69 | 69 | 69 | 69 |
6.2.8 Fase 4c Verworven unilaterale NST
Samenvatting 4.3: verworven unilaterale nst (tabellen 4.3a tot en met f):
- Bij verworven unilaterale NST (inguïnaal en abdominaal) levert opereren bij diagnose minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan later of niet opereren (tabel 4.3a en 4.3d en figuur 4.3g).
- Ook in de sensitiviteitsanalyse (4.3b) levert opereren bij diagnose het minste QALy-verlies op.
- Dit wordt vooral verklaard (4.3c) door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum bij later opereren (100%) ten opzichte van bij diagnose opereren (3,1%). Voor afwijkend aspect scrotum is in deze studie een aanzienlijke impact op
de kwaliteit van leven aangenomen op basis van de waarderingen uit het vragenlijst- onderzoek onder de algemene bevolking, ouders en patiënten (tabel 3.4). Daarentegen is er bij operatie later dan direct bij diagnose een lager percentage complicaties (2,1% versus 3,7%) en lagere kans op heroperaties (3,4% versus 6,0%). - Conclusie van de kosteneffectiviteitsanalyse is dat kosten in de beslissingsanalyse geen rol spelen, omdat de extra kosten per QALy (tabel 4.3e.) zeer acceptabel zijn in het licht van de grenzen die in het algemeen geaccepteerd worden (€ 20.000 – € 40.000 per QALy).
Tabel 4.3a. Verlies in QAly’s voor verworven unilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering al- gemene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 0,926 | 1,168 | 1,310 | 1,591 |
| Waardering ouders | 1,584 | 1,902 | 2,091 | 2,469 |
| Waardering patiënten | 1,109 | 1,548 | 1,806 | 2,305 |
Tabel 4.3b. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven unilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment met waardering algemene populatie (sensitiviteitsanalyse)
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 0,926 | 1,168 | 1,310 | 1,591 |
| Vaderschap – hoog |
0,817 | 1,058 | 1,201 | 1,482 |
| Testistumor – afhankelijk van de OK- leeftijd |
0,906 | 1,173 | 1,316 | 1,597 |
tabel 4.3c. percentage patiënten met gezondheidstoestand afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse
| Gezondheidstoestand | Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK |
| Geen vaderschap | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% | 8,0% |
| Testistumor zonder overlijden | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% |
| Testistumor met overlijden | 0,07% | 0,07% | 0,06% | 0,06% |
| Afwijkend aspect scrotum* | 3,1% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Complicaties OK | 3,7% | 2,1% | 1,3% | 0,0% |
| Re-OK | 6,0% | 3,4% | 2,0% | 0,0% |
| Overlijden bij OK | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% |
* Combinatie van patiënten die enige tijd een afwijkend aspect scrotum hebben gehad (vanaf diagnose tot operatie in puberteit of indaling) en patiënten die langdurig een afwijkend aspect scrotum hebben (indien geen operatie of mislukte operatie).
tabel 4.3d. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven unilaterale nst (abdominaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 0,991 | 1,196 | 1,323 | 1,591 |
| Waardering ouders | 1,674 | 1,942 | 2,109 | 2,469 |
| Waardering patiënten | 1,218 | 1,596 | 1,827 | 2,305 |
tabel 4.3e. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven unilaterale nst (abdominaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en kosten per kind met nst
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 0,991 | 1,196 | 1,323 | 1,591 |
| Kosten (€) | 1216 | 835 | 634 | 317 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALy) | 1498 | 1311 | 1183 | |
| Incrementele KE-ratio* (€/QALy) | 1859 | 1583 | 1183 |
* Incrementele KI-ratio is ten opzichte van ‘next best’ alternatief.
| 3% discontering | Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK |
| Basis | 0,35 | 0,60 | 0,64 | 0,84 |
| Kosten (€) | 1027 | 647 | 446 | 164 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALy) | 1761 | 2013 | 1410 | |
| Incrementele KE-ratio* (€/QALy) | 1520 | 5025 | 1410 |
tabel 4.3f. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven unilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment, uitkomsten PSA
| Operatiemoment | Gemiddelde | 95% bti |
| Diagnose | 0,955 | [0,174, 2,085] |
| Midden puberteit | 1,195 | [0,255, 2,467] |
| Eind puberteit | 1,341 | [0,274, 2,777] |
| Geen OK | 1,526 | [0,276, 3,355] |
Figuur 4.3g. Kans dat behandeloptie optimaal is (laagste verlies aan QAly’s) voor unilaterale verworven NST op basis van PSA
6.2.9 Fase 4d Verworven bilaterale NST
Samenvatting 4.4: verworven bilaterale nst (tabellen 4.4a tot en met f):
- Bij verworven bilaterale NST (inguïnaal en abdominaal) levert opereren bij diagnose minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan later of niet opereren (4.4a en 4.4d en figuur 4.4f).
- Ook in de sensitiviteitsanalyse (4.4b) levert opereren bij diagnose het minste QALy-verlies op.
- Dit wordt vooral verklaard door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum bij later opereren (100%) ten opzichte van bij diagnose opereren (3,1%). Daarentegen is er bij later opereren dan direct bij diagnose een lager percentage complicaties (2,1% versus 3,7%) en een lagere kans op heroperaties (3,4% versus 6,0%). Daarnaast geldt voor niet opereren een hogere kans op geen vaderschap (36,8% versus 16,4% bij wel opereren).
- Conclusie van de kosteneffectiviteitsanalyse is dat kosten in de beslissingsanalyse geen rol spelen, omdat de extra kosten per QALy (tabel 4.4e) zeer acceptabel zijn in het licht van de grenzen die in het algemeen geaccepteerd worden (€ 20.000 – € 40.000 per QALy).
Tabel 4.4a. Verlies in QAly’s voor verworven bilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 1,766 | 2,370 | 2,724 | 5,286 |
| Waardering ouders | 3,022 | 3,874 | 4,373 | 8,599 |
| Waardering patiënten | 2,095 | 2,871 | 3,322 | 6,438 |
Tabel 4.4b. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven bilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment met waardering algemene populatie (sensitiviteitsanalyse)
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 1,766 | 2,370 | 2,724 | 5,286 |
| Vaderschap – hoog |
1,453 | 2,119 | 2,411 | 5,286 |
| Testistumor – afhankelijk van OK-leeftijd |
1,746 | 2,375 | 2,729 | 5,291 |
Tabel 4.4c. percentage patiënten met gezondheidstoestand afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse
| Gezondheidstoestand | Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK |
| Geen vaderschap | 16,4% | 16,4% | 16,4% | 36,8% |
| Testistumor zonder overlijden | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% | 1,2% |
| Testistumor met overlijden | 0,06% | 0,06% | 0,06% | 0,06% |
| Afwijkend aspect scrootum | 3,1% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Complicaties OK | 3,7% | 2,1% | 1,3% | 0,0% |
| Re-OK | 6,0% | 3,4% | 2,0% | 0,0% |
| Overlijden bij OK | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% | 0,0% |
* Combinatie van patiënten die enige tijd een afwijkend aspect scrotum hebben gehad (vanaf diagnose tot operatie in puberteit of indaling) en patiënten die langdurig een afwijkend aspect scrotum hebben (indien geen operatie of mislukte operatie).
Tabel 4.4d. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven bilaterale nst (abdominaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en voor waarderingen van ouders en patiënten
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| Basis | 1,914 | 2,434 | 2,752 | 5,286 |
| Waardering ouders | 3,235 | 3,967 | 4,414 | 8,599 |
| Waardering patiënten | 2,281 | 2,952 | 3,358 | 6,438 |
Tabel 4.4e. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven bilaterale nst (abdominaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment voor basisanalyse (waardering algemene populatie) en kosten per kind met nst
| Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK | |
| QALY-verlies | 1,766 | 2,370 | 2,724 | 5,286 |
| Kosten (€) | 1376 | 1001 | 800 | 961 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALY) | 118 | 14 | domineert | |
| Incrementele KE-ratio (€/QALY) | 621 | 568 | domineert |
* Incrementele KE-ratio is ten opzichte van ‘next best’ alternatief.
| 3% discontinering | Diagnose | Midden puberteit | Eind puberteit | Geen OK |
| QALY-verlies | 0,534 | 1,150 | 1,286 | 2,192 |
| Kosten (€) | 1100 | 725 | 524 | 472 |
| KE-ratio t.o.v. geen OK (€/QALY) | 379 | 243 | 57 | |
| Incrementele KE-ratio (€/QALY) | 609 | 1478 | 57 |
Tabel 4.4f. verlies in QAly’s voor verworven bilaterale nst (inguïnaal) afhankelijk van operatiemoment, uitkomsten probabilistische sensitiviteitsanalyse
| Operatiemoment | Gemiddelde | 95% bti |
| Diagnose | 1,719 | [0,246, 4,363] |
| Midden puberteit | 2,345 | [0,402, 5,298] |
| Eind puberteit | 2,722 | [0,448, 0,764] |
| Geen OK | 4,958 | [0,764, 11,286] |
Figuur 4.4g. Kans dat behandeloptie optimaal is (laagste verlies aan QALY’s) voor bilaterale verworven voor bilaterale verworven nst op basis van psA
6.2.10 Conclusies
Op basis van de uitkomsten van de besliskundige analyse kunnen de volgende conclusies getrokken worden:
- Bij aangeboren unilaterale NST levert opereren minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan niet opereren. Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum.
- Bij aangeboren bilaterale NST levert opereren minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan niet opereren. Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met geen vaderschap bij niet opereren ten opzichte van wel opereren en het hogere percentage afwijkend aspect scrotum.
- Bij verworven unilaterale NST levert opereren bij diagnose minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan later of niet opereren. Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum bij later of niet opereren ten opzichte van bij diagnose opereren.
- Bij verworven bilaterale NST levert opereren bij diagnose minder verlies in voor kwaliteit gecorrigeerde levensjaren (QALy-verlies) op dan later of niet opereren.
Dit wordt veroorzaakt door het hogere percentage patiënten met afwijkend aspect scrotum bij later of niet opereren ten opzichte van bij diagnose opereren. Daarentegen is er bij later opereren een lager percentage complicaties en een lagere kans op heroperaties, omdat in een deel van de gevallen inmiddels indaling heeft plaatsgevonden. Daarnaast geldt voor opereren een hogere kans op vaderschap.
Op basis hiervan kan geconcludeerd worden dat opereren van zowel aangeboren als verworven unilaterale NST, op een cosmetisch effect na, geen extra voordelen heeft boven niet opereren en zou het advies bij unilaterale NST gebaseerd op de analyse zijn: het voorlichten van ouders/patiënt en het gezamenlijk bepalen van beleid (opereren, afwachten of geen operatie).
Voor bilaterale NST geeft de beslissingsanalyse aan dat er een hogere kans op vaderschap is bij wel opereren. Voor verworven bilaterale NST is het moment van operatie afhankelijk van de voorkeuren van ouders/patiënt. Direct opereren bij diagnose heeft als voordeel dat er geen QALy-verlies is ten gevolge van een afwijkend aspect scrotum. Bij opereren op een later moment is dit er wel, maar is er de mogelijkheid dat een operatie niet meer nodig is vanwege indaling.
Vertaling uitkomsten beslissingsanalyse naar richtlijn
Naar aanleiding van de uitkomsten van de beslissingsanalyse is een expertmeeting* gehouden (februari 2012). Aan het begin van de beslissingsanalyse is een aantal uitkomst- maten gekozen, zoals fertiliteit, testistumor, gevolgen van operatie en asymmetrisch scrotum. Wat deze maten betreft is er feitelijk geen reden om iedereen te opereren.
Unaniem werd echter door de expertgroep tijdens die bijeenkomst aangegeven dat men niet in kan stemmen met de optie ‘niet opereren’ voor zowel de aangeboren als de verworven unilaterale vormen van NST. De volgende beweegredenen (ten dele consensus based) werden daarbij genoemd:
- De testikel wordt atrofisch als deze niet scrotaal ligt. Hoewel dit niet uitmaakt voor de fertiliteit [14][36], is het ‘natuurlijk’ dat een jongen twee testes heeft.
- Het tweede testikel is een reserveorgaan. Krijg je in de andere testikel een trauma of torsio testis, dan heb je een tweede die voor fertiliteit kan zorgen.
- We weten niet wat het gevolg van opereren is voor de kwaliteit van de testikel bij de mens, maar het lijkt logisch dat opereren positief is voor de kwaliteit. Er is wel bewijs, ten dele in dierexperimenteel onderzoek, voor het achterblijven in groei van de testikel bij operatie na het 2e jaar [37][38][39], maar bewijs voor een verband met kwaliteit is niet gepubliceerd. Wel wordt volume als afgeleide van kwaliteit beschouwd [40]. Echter, ook bij vroeg opereren blijft het volume wel achter.
- Een testikel in het liesgebied geeft risico op torsio testis en mogelijk klachten (onbehaaglijk gevoel/pijn). De ervaring is dat dit kan gebeuren. In het Alkmaarse cohort is niet naar klachten gevraagd.
- Hoewel de evidence (beslissingsanalyse) toont dat er nauwelijks QALY-verlies is door een tumor bij niet opereren, blijft het gevoel aanwezig dat het wel degelijk uitmaakt of je kanker krijgt of niet. In de beslissingsanalyse vervalt de impact van de kanker omdat niet iedereen het krijgt en de kansen op overlijden vervolgens klein zijn. Voor een individu echter kan een zeer kleine kans op een tumor wel reden zijn om te opereren, terwijl dat voor de grote groep niet geldt.
- Reden om te opereren voor de puberteit is altijd geweest: vroegtijdig detecteren van testistumor, en hoewel dit niet wetenschappelijk bewezen is, blijft dit gevoelsmatig belangrijk.
- Een aantal deelnemers herkende wel dat ‘geanticipeerde spijt’ (achteraf niet het gevoel hebben dat niet het maximale voor de patiënt is gedaan) een rol zou kunnen spelen.
- Apart hiervan staat nog de invloed van opereren op het cosmetische aspect van het scrotum. Het is aan de patiënt/ouders om hiervan de relevantie te bepalen.
- Psychosociaal: een jongen moet zelf een afweging maken over iets wat levenslang gevolgen kan hebben.
- Er is op veel punten gebrek aan bewijs: we weten de positieve en negatieve effecten op de langere termijn niet.
Bij aangeboren unilaterale nst en verworven unilaterale nst zijn de belangrijkste argumenten om wel te opereren:
- Het testikel is een reserveorgaan en heeft mogelijk herstelpotentie.
- De niet-ingedaalde testikel kan klachten geven in het liesgebied (pijn en risico op draaiing van de testis (torsio testis)).
Bij de aangeboren unilaterale NST vindt de operatie in principe plaats tussen de 6 en 12 maanden. Voor de verworven unilaterale nst geldt dat de behandelopties, het moment van opereren (direct opereren of gecontroleerd afwachten tot de puberteit), besproken moeten worden.
Op grond van bovenstaande argumenten is gekomen tot de aanbevelingen voor doorverwijzing van alle vormen van NST zoals beschreven in de richtlijn.
* Aanwezig waren:
Elske van den Akker-van Marle, gezondheidseconoom, besliskundige, LUMC Helma van Gameren-Oosterom, arts-onderzoeker, TNO, notulist
Joery Goede, arts-onderzoeker, MCA
Frans Hazebroek, emeritus hoogleraar kinderchirurgie, SKZ
Erik van der Horst, kinderuroloog, VUMC
Mascha Kamphuis, jeugdarts KNMG, TNO, voorzitter
Sabine de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, kinderarts-endocrinoloog, SKZ
6.3 Kennishiaten
Kennishiaten naar aanleiding van de wetenschappelijke onderbouwing (besliskundige analyse en overige overwegingen (expertisebijeenkomst)) binnen het project ‘Gebruik van beslissingsanalyse en patiënten voorkeuren bij ontwikkeling en toepassing van richtlijnen geïllustreerd aan de hand van de richtlijn niet-scrotale testis’.
- Specifiek voor het model zijn data gemist waarin onderscheid gemaakt wordt tussen unilateraal en bilateraal, aangeboren en verworven, en inguïnaal en abdominaal. Verder is de onzekerheid over een verhoogde tumorkans afhankelijk van de leeftijd bij operatie nog groot.
- Naar aanleiding van de expertmeeting is gebleken dat de volgende informatie tevens ontbreekt: impact pijn/ongemak ten gevolge van niet-scrotaal gelegen testis, de consequenties van opereren voor de kwaliteit van de testis.
Referenties
[1] van Gelderen HH, Vermeer-de Bondt PE. [Prevalence of undescended testis in the first 4 years of life; a longitudinal study]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1986;130(35):1567-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2876394[2] de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM. [Consensus on management of the undescended testis]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1987;131(41):1817-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2890111[3] Venlet-Melchior CJ, Hirasing RA. [Significance of the registration of testis localization in child health services for the avoidance of unnecessary orchiopexies]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1989;133(42):2084-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2572979[4] Horstink-uit de Weerd BR, Filedt Kok-Weimar TL, Leerdam F. Protocollering binnen de JGZ: testesonderzoek. 2004
[5] Ghirri P, Ciulli C, Vuerich M, Cuttano A, Faraoni M, Guerrini L, Spinelli C, Tognetti S, Boldrini A. Incidence at birth and natural history of cryptorchidism: a study of 10,730 consecutive male infants. Journal of endocrinological investigation 2002;25(8):709-15
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12240903[6] SCORER CG. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS. Archives of disease in childhood 1964;39(208):605-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14230757[7] Berkowitz GS, Lapinski RH, Dolgin SE, Gazella JG, Bodian CA, Holzman IR. Prevalence and natural history of cryptorchidism. Pediatrics 1993;92(1):44-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8100060[8] Cryptorchidism: a prospective study of 7500 consecutive male births, 1984-8. John Radcliffe Hospital Cryptorchidism Study Group. Archives of disease in childhood 1992;67(7):892-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1355643[9] Acerini CL, Miles HL, Dunger DB, Ong KK, Hughes IA. The descriptive epidemiology of congenital and acquired cryptorchidism in a UK infant cohort. Archives of disease in childhood 2009;94(11):868-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.2008.150219 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19542061[10] Boisen KA, Kaleva M, Main KM, Virtanen HE, Haavisto A-M, Schmidt IM, Chellakooty M, Damgaard IN, Mau C, Reunanen M, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J. Difference in prevalence of congenital cryptorchidism in infants between two Nordic countries. Lancet (London, England) 2004;363(9417):1264-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15094270[11] Preiksa RT, Zilaitiene B, Matulevicius V, Skakkebaek NE, Petersen JH, Jørgensen N, Toppari J. Higher than expected prevalence of congenital cryptorchidism in Lithuania: a study of 1204 boys at birth and 1 year follow-up. Human reproduction (Oxford, England) 2005;20(7):1928-32
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15860495[12] Sijstermans K, Hack WWM, van der Voort-Doedens LM, Meijer RW, Haasnoot K. Puberty stage and spontaneous descent of acquired undescended testis: implications for therapy? International journal of andrology 2006;29(6):597-602
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16817910[13] Eijsbouts SW, de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SMPF, Hazebroek FWJ. Further evidence for spontaneous descent of acquired undescended testes. The Journal of urology 2007;178(4 Pt 2):1726-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17707013[14] Lee PA. Fertility after cryptorchidism: epidemiology and other outcome studies. Urology 2005;66(2):427-31
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16098371[15] Lee PA. Fertility in cryptorchidism. Does treatment make a difference? Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America 1993;22(3):479-90
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7902276[16] Lee PA, Coughlin MT. The single testis: paternity after presentation as unilateral cryptorchidism. The Journal of urology 2002;168(4 Pt 2):1680-2; discussion 1682-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12352333[17] Dieckmann K-P, Pichlmeier U. Clinical epidemiology of testicular germ cell tumors. World journal of urology 2004;22(1):2-14
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15034740[18] Pettersson A, Richiardi L, Nordenskjold A, Kaijser M, Akre O. Age at surgery for undescended testis and risk of testicular cancer. The New England journal of medicine 2007;356(18):1835-41
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17476009[19] Baker LA, Docimo SG, Surer I, Peters C, Cisek L, Diamond DA, Caldamone A, Koyle M, Strand W, Moore R, Mevorach R, Brady J, Jordan G, Erhard M, Franco I. A multi-institutional analysis of laparoscopic orchidopexy. BJU international 2001;87(6):484-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11298039[20] Chang B, Palmer LS, Franco I. Laparoscopic orchidopexy: a review of a large clinical series. BJU international 2001;87(6):490-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11298040[21] Elder JS. Two-stage Fowler-Stephens orchiopexy in the management of intra-abdominal testes. The Journal of urology 1992;148(4):1239-41
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1357193[22] Horasanli K, Miroglu C, Tanriverdi O, Kendirci M, Boylu U, Gumus E. Single stage Fowler-Stephens orchidopexy: a preferred alternative in the treatment of nonpalpable testes. Pediatric surgery international 2006;22(9):759-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16896813[23] Russinko PJ, Siddiq FM, Tackett LD, Caldamone AA. Prescrotal orchiopexy: an alternative surgical approach for the palpable undescended testis. The Journal of urology 2003;170(6 Pt 1):2436-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14634447[24] Ritzén EM, Bergh A, Bjerknes R, Christiansen P, Cortes D, Haugen SE, Jörgensen N, Kollin C, Lindahl S, Läckgren G, Main KM, Nordenskjöld A, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Söder O, Taskinen S, Thorsson A, Thorup J, Toppari J, Virtanen H. Nordic consensus on treatment of undescended testes. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):638-43
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17326760[25] Ritzén EM. Undescended testes: a consensus on management. European journal of endocrinology 2008;159 Suppl 1():S87-90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/EJE-08-0181 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18728121[26] Dayanc M, Kibar Y, Irkilata HC, Demir E, Tahmaz L, Peker AF. Long-term outcome of scrotal incision orchiopexy for undescended testis. Urology 2007;70(4):786-8; discussion 788-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17991558[27] Al-Saied G. Balloon inflation-created subdartos pouch during orchiopexy: a new simplified technique. Pediatric surgery international 2008;24(10):1187-90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00383-008-2243-4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18751986[28] Thorup J, Haugen S, Kollin C, Lindahl S, Läckgren G, Nordenskjold A, Taskinen S. Surgical treatment of undescended testes. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):631-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17381472[29] Merguerian PA, Mevorach RA, Shortliffe LD, Cendron M. Laparoscopy for the evaluation and management of the nonpalpable testicle. Urology 1998;51(5A Suppl):3-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9610548[30] Esposito C, Garipoli V. The value of 2-step laparoscopic Fowler-Stephens orchiopexy for intra-abdominal testes. The Journal of urology 1997;158(5):1952-4; discussion 1954-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9334647[31] Toppari J, Kaleva M. Maldescendus testis. Hormone research 1999;51(6):261-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10640886[32] Arbous MS, Grobbee DE, van Kleef JW, de Lange JJ, Spoormans HH, Touw P, Werner FM, Meursing AE. Mortality associated with anaesthesia: a qualitative analysis to identify risk factors. Anaesthesia 2001;56(12):1141-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11736769[33] Tan SS, Bouwmans C, Hakkaart- van Roijen L. Handleiding Voor Kostenonderzoek Methoden En Standaard Kostprijzen Voor Economische Evaluaties in de Gezondheidszorg Tijdschrift voor gezondheidswetenschappen 2012/09/01;90():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12508-012-0128-3[34] Oostenbrink JB, Bouwmans CAM, Koopmanschap MA, Rutten FFH. Handleiding Voor Kostenonderzoek Methoden En Standaard Kostprijzen Voor Economische Evaluaties in de Gezondheidszorg College voor zorgverzekeringen 2004
[35] Hsieh MH, Roth DR, Meng MV. Economic analysis of infant vs postpubertal orchiopexy to prevent testicular cancer. Urology 2009;73(4):776-81
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2008.10.059 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19193413[36] Miller KD, Coughlin MT, Lee PA. Fertility after unilateral cryptorchidism. Paternity, time to conception, pretreatment testicular location and size, hormone and sperm parameters. Hormone research 2001;55(5):249-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11740148[37] Virtanen HE, Cortes D, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Ritzén EM, Nordenskjöld A, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J. Development and descent of the testis in relation to cryptorchidism. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):622-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17462055[38] Virtanen HE, Bjerknes R, Cortes D, Jørgensen N, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Thorsson AV, Thorup J, Main KM. Cryptorchidism: classification, prevalence and long-term consequences. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):611-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17462053[39] Bergh A, Söder O. Studies of cryptorchidism in experimental animal models. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(5):617-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17462054[40] Kollin C, Hesser U, Ritzén EM, Karpe B. Testicular growth from birth to two years of age, and the effect of orchidopexy at age nine months: a randomized, controlled study. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2006;95(3):318-24
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16497643Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackLET OP: print de JGZ-richtlijn in liggende afdrukstand!
Grote tabellen zijn niet volledig zichtbaar als de JGZ-richtlijn in staande afdrukstand geprint wordt. Om kleuren in de printversie goed door te laten komen, moet bij de printerinstellingen Achtergrondillustraties aangezet worden.
Disclaimer printversie JGZ-richtlijnen
De printversie van de JGZ-richtlijn bevat de algemene tekst inclusief de aanbevelingen. De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing is terug te vinden op de website, bij de aanbevelingen onder de link “Evidence”.
