Wordt een motorische ontwikkelingsstoornis veroorzaakt door NAH of beweegarmoede, dan kan de JGZ met het afnemen van een goede (hetero-)anamnese bijdragen aan tijdige signalering. Tijdige herkenning en behandeling lijken de kansen van het kind op een optimale ontwikkeling te vergrotenexpert opinion. Ten aanzien van hersenletsel dat veroorzaakt wordt door ongevallen kan de JGZ enerzijds een rol spelen bij het geven van adviezen teneinde ongevallen te voorkomen (primaire preventie), en anderzijds bij de herkenning van de symptomen van NAH en daarop het verwijsbeleid afstemmen.
2.5.3 Niet-aangeboren Hersenletsel of beweegarmoede
JGZ-richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling
JGZ-richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling
Let op: deze richtlijn is momenteel in herziening.
Dit betekent niet dat de inhoud van deze richtlijn incorrect is. Tot de herziening blijft de richtlijn leidend voor de praktijk. Wel bestaat er een kans dat een deel van de informatie verouderd is.
Heb je feedback over deze JGZ-richtlijn? Stuur jouw feedback naar onze servicedesk. Zoek het tekstgedeelte waarbij je suggesties voor verbetering hebt. Via de knop ‘Geef jouw feedback’ kun je voor deze JGZ-richtlijn en het specifieke hoofdstuk jouw suggesties doorgeven.
Richtlijn inhoudsopgave
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie
3 Signaleren en diagnostiek Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren en diagnostiek
4 Preventie Ga naar pagina over 4 Preventie
5 Samenwerkingsafspraken: verwijzen en nazorg Ga naar pagina over 5 Samenwerkingsafspraken: verwijzen en nazorg
6 Totstandkoming Ga naar pagina over 6 Totstandkoming
7 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 7 Verantwoording
8 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 8 Bijlagen
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie
3 Signaleren en diagnostiek Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren en diagnostiek
4 Preventie Ga naar pagina over 4 Preventie
5 Samenwerkingsafspraken: verwijzen en nazorg Ga naar pagina over 5 Samenwerkingsafspraken: verwijzen en nazorg
6 Totstandkoming Ga naar pagina over 6 Totstandkoming
7 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 7 Verantwoording
8 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 8 Bijlagen
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
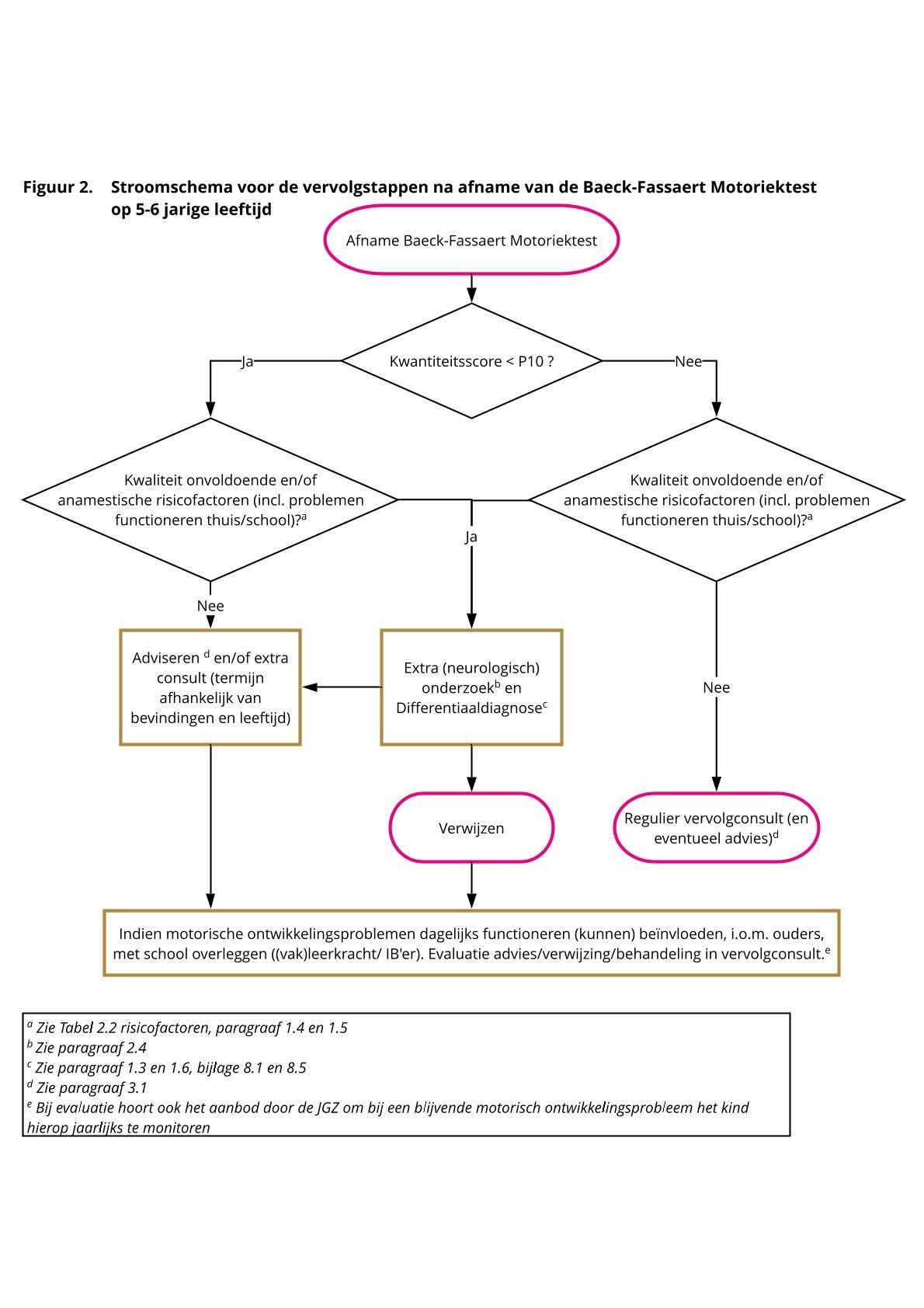
Geef jouw feedbackStroomschema’s motorische ontwikkeling 0-5 jr en 5-6 jaar
PP-presentatie voor de scholing Motorische ontwikkeling
Factsheet richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling
Randvoorwaardelijke implicaties richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling
Rapportage praktijktest richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling
BDS-registratie-protocol richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling
[1] Lubans DR, Morgan PJ, Cliff DP, Barnett LM, Okely AD. Fundamental movement skills in children and adolescents: review of associated health benefits. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) 2010;40(12):1019-35
http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/11536850-000000000-00000 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21058749[2] Smith LB, Thelen E. A Dynamic Systems Approach to the Development of Cognition and Action 1994
http://dx.doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/2524.001.0001 https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/2524.001.0001[3] Chow JY, Davids K, Button C, Renshaw I. Nonlinear Pedagogy in Skill Acquisition: An Introduction 2021
http://dx.doi.org/10.4324/9781003247456[4] Skinner RA, Piek JP. Psychosocial implications of poor motor coordination in children and adolescents. Human movement science 2001;20(1-2):73-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11471399[5] Emck C, Bosscher R, Beek P, Doreleijers T. Gross motor performance and self-perceived motor competence in children with emotional, behavioural, and pervasive developmental disorders: a review. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2009;51(7):501-17
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03337.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19538424[6] Chen H-F, Cohn ES. Social participation for children with developmental coordination disorder: conceptual, evaluation and intervention considerations. Physical & occupational therapy in pediatrics 2003;23(4):61-78
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14750309[7] Piek JP, Barrett NC, Allen LSR, Jones A, Louise M. The relationship between bullying and self-worth in children with movement coordination problems. The British journal of educational psychology 2005;75(Pt 3):453-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16238876[8] Losse A, Henderson SE, Elliman D, Hall D, Knight E, Jongmans M. Clumsiness in children--do they grow out of it? A 10-year follow-up study. Developmental medicine and child neurology 1991;33(1):55-68
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1704864[9] Delgado MR, Albright AL. Movement disorders in children: definitions, classifications, and grading systems. Journal of child neurology 2003;18 Suppl 1():S1-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13677567[10] Touwen B.C.L., Touwen-Eringa A1-2, Frese H.. De neurologische ontwikkeling van de zuigeling : ontwikkelingsgang en samenhang van de onderdelen van het neurologisch onderzoek 1984
[11] Touwen BC. How normal is variable, or how variable is normal? Early human development 1993;34(1-2):1-12
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8275868[12] Hadders-Algra M., Dirks JF.. de Motorische Ontwikkeling Van de Zuigeling: Variëren, Selecteren, Leren Adapteren 2000
https://books.google.be/books?id=AMtt8tOTRrsC[13] Hadders-Algra M, Maathuis KGB, Pangalila RF, Becher JG, de Moor J. Kinderrevalidatie. Assen: Van Gorcum 2015
[14] Hadders-Algra M. Variation and variability: key words in human motor development. Physical therapy 2010;90(12):1823-37
http://dx.doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20100006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20966209[15] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de Jeugdgezondheidszorg. Het Van Wiechenonderzoek. De Baecke-Fassaert Motoriektest. Van Gorcum. 2008
[16] Heineman KR, Bos AF, Hadders-Algra M. The Infant Motor Profile: a standardized and qualitative method to assess motor behaviour in infancy. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2008;50(4):275-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.02035.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18279412[17] Bailey DB, Hebbeler K, Scarborough A, Spiker D, Mallik S. First experiences with early intervention: a national perspective. Pediatrics 2004;113(4):887-96
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15060241[18] Gerber RJ, Wilks T, Erdie-Lalena C. Developmental milestones: motor development. Pediatrics in review 2010;31(7):267-76; quiz 277
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/pir.31-7-267 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20595440[19] Lüchinger AB, Hadders-Algra M, van Kan CM, de Vries JIP. Fetal onset of general movements. Pediatric research 2008;63(2):191-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18091359[20] Prechtl HFR. The importance of fetal movements. In: KJ Connolly & H Forssberg (Eds). Neurophysiology and neuropsychology of motor development. Clinics in Developmental Medicine. London: Mac Keith Press 1997
[21] Hadders-Algra M. Putative neural substrate of normal and abnormal general movements. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews 2007;31(8):1181-90
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17568672[22] Bilo RAC, Voorhoeve HWA. Kind in Ontwikkeling Uitgeversmaatschappij De Tijdstroom bv. 1990
[23] Davis BE, Moon RY, Sachs HC, Ottolini MC. Effects of sleep position on infant motor development. Pediatrics 1998;102(5):1135-40
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9794945[24] Crouchman M. The effects of babywalkers on early locomotor development. Developmental medicine and child neurology 1986;28(6):757-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3817314[25] Thelen E, Corbetta D, Kamm K, Spencer JP, Schneider K, Zernicke RF. The transition to reaching: mapping intention and intrinsic dynamics. Child development 1993;64(4):1058-98
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8404257[26] Largo RH, Molinari L, Weber M, Comenale Pinto L, Duc G. Early development of locomotion: significance of prematurity, cerebral palsy and sex. Developmental medicine and child neurology 1985;27(2):183-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3996775[27] Adolph KE, Vereijken B, Denny MA. Learning to crawl. Child development 1998;69(5):1299-312
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9839417[28] Yang JF, Stephens MJ, Vishram R. Infant stepping: a method to study the sensory control of human walking. The Journal of physiology 1998;507 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):927-37
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9508851[29] Van Dokkum NH, Kerstjens JM, Bos AF, Reijneveld SA, De Kroon MLA. Association between gestational age, attainment age of smiling and walking and development at school entry Abstract NVK-congres 2017
[30] Hempel MS. Neurological development during toddling age in normal children and children at risk of developmental disorders. Early human development 1993;34(1-2):47-57
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8275882[31] van Dokkum NH, de Kroon MLA, Bos AF, Reijneveld SA, Kerstjens JM. Attainment of gross motor milestones by preterm children with normal development upon school entry. Early human development 2018;119():62-67
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2018.03.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29579559[32] Pascal A, Govaert P, Oostra A, Naulaers G, Ortibus E, Van den Broeck C. Neurodevelopmental outcome in very preterm and very-low-birthweight infants born over the past decade: a meta-analytic review. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2018;60(4):342-355
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13675 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29350401[33] Pearsall-Jones JG, Piek JP, Levy F. Developmental Coordination Disorder and cerebral palsy: categories or a continuum? Human movement science 2010;29(5):787-98
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2010.04.006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20594606[34] Williams J, Hyde C, Spittle A. Developmental Coordination Disorder and Cerebral Palsy: Is There a Continuum? Current Developmental Disorders Reports 2014/06/01;1():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40474-014-0009-3[35] Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson BO, Damiano D, . Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2005;47(8):571-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16108461[36] Paneth N. Establishing the diagnosis of cerebral palsy. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology 2008;51(4):742-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/GRF.0b013e318187081a https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18981799[37] Wichers MJ, Odding E, Stam HJ, van Nieuwenhuizen O. Clinical presentation, associated disorders and aetiological moments in Cerebral Palsy: a Dutch population-based study. Disability and rehabilitation 2005;27(10):583-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16019867[38] Richtlijn Spastische cerebrale parese bij kinderen 2015
http://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/spastische_cerebrale_parese_bij_kinderen/diagnostiek_van_cerebr%20ale_parese.html[39] International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Children and Youth Version WHO 2007
[40] Becker H, Blank R, Jenni O, Linder-Lucht M, Polatajko H, Steiner F, Geuze R, Smits-Engelsman B, Wilson P. Aanbevelingen van de EACD. Duits-Zwitserse richtlijn voor de klinische praktijk. Definitie, diagnose, evaluatie en behandeling van Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD). Nederlandse vertaling en aanpassing door landelijke DCD netwerk. 2013
[41] Hafkamp-de Groen E, van den Bos L, Raat H. Motorische Ontwikkeling Programmeringsstudie 2012
[42] Zwicker JG, Missiuna C, Harris SR, Boyd LA. Developmental coordination disorder: a review and update. European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society 2012;16(6):573-81
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2012.05.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22705270[43] Aanbevelingen van de EACD; Definitie, diagnose, evaluatie en behandeling van DCD, versie juli 2011. Nederlandse vertaling en aanpassing door landelijke DCD netwerk European Academy of Childhood Disability (EACD) 2013
[44] Dutch consensus statement DCD. Vertaling van de Leeds Consensus Statement Development Coördination Disorder as a Specific Learning Difficulty ESRC Research Seminar Series, 2004-2005 2011
http://www.motoriek.nl/userfiles/file/Dutch_Consensus_Statement_DCD_2011_.pdf[45] Noordstar JJ, van der Net J, Jak S, Helders PJM, Jongmans MJ. The change in perceived motor competence and motor task values during elementary school: A longitudinal cohort study. The British journal of developmental psychology 2016;34(3):427-46
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bjdp.12142 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26989988[46] Noordstar JJ, Stuive I, Herweijer H, Holty L, Oudenampsen C, Schoemaker MM, Reinders-Messelink HA. Perceived athletic competence and physical activity in children with developmental coordination disorder who are clinically referred, and control children. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(12):3591-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.09.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25244693[47] Edwards J, Berube M, Erlandson K, Haug S, Johnstone H, Meagher M, Sarkodee-Adoo S, Zwicker JG. Developmental coordination disorder in school-aged children born very preterm and/or at very low birth weight: a systematic review. Journal of developmental and behavioral pediatrics : JDBP 2011;32(9):678-87
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0b013e31822a396a https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21900828[48] Zhu JL, Olsen J, Olesen AW. Risk for developmental coordination disorder correlates with gestational age at birth. Paediatric and perinatal epidemiology 2012;26(6):572-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3016.2012.01316.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23061693[49] www.spierziekten.nl geraadpleegd op 14-02-2016
http://www.spierziekten.nl[50] van Empelen R. R van Empelen, R. Nijhuis-van der Sanden & A Hartman (Eds.), Kinderfysiotherapie. 3e druk 2013 Reed Business. 2012
[51] Gijzen R, Zadoks J. Zorgstandaard Traumatisch Hersenletsel, Kinderen & Jongeren. In opdracht van de Hersenstichting 2016
[52] www.dehoogstraat.nl (Traumatologie, hoofdstuk 12). Geraadpleegd op 02-04-2016
http://www.dehoogstraat.nl/revalidatie/kinderen-en-jeugd/aandoening/niet-aangeboren-hersenletsel[53] Jelsma LD, Geuze RH, Klerks MH, Niemeijer AS, Smits-Engelsman BCM. The relationship between joint mobility and motor performance in children with and without the diagnosis of developmental coordination disorder. BMC pediatrics 2013;13():35
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-13-35 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23497034[54] de Boer RM, van Vlimmeren LA, Scheper MC, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MWG, Engelbert RHH. Is Motor Performance in 5.5-Year-Old Children Associated with the Presence of Generalized Joint Hypermobility? The Journal of pediatrics 2015;167(3):694-701.e1
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.06.034 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26190232[55] Engelbert RHH, Juul-Kristensen B, Pacey V, de Wandele I, Smeenk S, Woinarosky N, Sabo S, Scheper MC, Russek L, Simmonds JV. The evidence-based rationale for physical therapy treatment of children, adolescents, and adults diagnosed with joint hypermobility syndrome/hypermobile Ehlers Danlos syndrome. American journal of medical genetics. Part C, Seminars in medical genetics 2017;175(1):158-167
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31545 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28306230[56] Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, Layden J, Carnes BA, Brody J, Hayflick L, Butler RN, Allison DB, Ludwig DS. A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. The New England journal of medicine 2005;352(11):1138-45
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15784668[57] Thompson Coon J, Boddy K, Stein K, Whear R, Barton J, Depledge MH. Does participating in physical activity in outdoor natural environments have a greater effect on physical and mental wellbeing than physical activity indoors? A systematic review. Environmental science & technology 2011;45(5):1761-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/es102947t https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21291246[58] Gillberg C, Kadesjö B. Why bother about clumsiness? The implications of having developmental coordination disorder (DCD). Neural plasticity 2003;10(1-2):59-68
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14640308[59] Fliers E, Rommelse N, Vermeulen SHHM, Altink M, Buschgens CJM, Faraone SV, Sergeant JA, Franke B, Buitelaar JK. Motor coordination problems in children and adolescents with ADHD rated by parents and teachers: effects of age and gender. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 2008;115(2):211-20
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17994185[60] Lingam R, Golding J, Jongmans MJ, Hunt LP, Ellis M, Emond A. The association between developmental coordination disorder and other developmental traits. Pediatrics 2010;126(5):e1109-18
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-2789 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20956425[61] Kaplan B, Wilson B, Dewey D, Crawford S. DCD may not be a discrete disorder Human Movement Science 1998/08/01;17():471
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9457(98)00010-4[62] Dewey D, Kaplan BJ, Crawford SG, Wilson BN. Developmental coordination disorder: associated problems in attention, learning, and psychosocial adjustment. Human movement science 2002;21(5-6):905-18
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12620725[63] Njokiktjien C. Gedragsneurologie van het kind. Handboek voor ontwikkelingsneurologie, neuropsychiatrie en neuropsychologie, Amsterdam 2004
[64] Novak I, McIntyre S, Morgan C, Campbell L, Dark L, Morton N, Stumbles E, Wilson S-A, Goldsmith S. A systematic review of interventions for children with cerebral palsy: state of the evidence. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2013;55(10):885-910
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12246 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23962350[65] Missiuna C, Campbell W. Psychological Aspects of Developmental Coordination Disorder: Can We Establish Causality? Current Developmental Disorders Reports 2014/06/01;1():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40474-014-0012-8[66] Soleimani F, Badv RS, Momayezi A, Biglarian A, Marzban A. General movements as a predictive tool of the neurological outcome in term born infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Early human development 2015;91(8):479-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2015.05.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26070097[67] . Assessment of sex differences and heterogeneity in motor milestone attainment among populations in the WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992). Supplement 2006;450():66-75
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16817680[68] . WHO Motor Development Study: windows of achievement for six gross motor development milestones. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992). Supplement 2006;450():86-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16817682[69] Giagazoglou P, Kabitsis N, Kokaridas D, Zaragas C, Katartzi E, Kabitsis C. The movement assessment battery in Greek preschoolers: the impact of age, gender, birth order, and physical activity on motor outcome. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(6):2577-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.06.020 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21816567[70] Hardy LL, King L, Farrell L, Macniven R, Howlett S. Fundamental movement skills among Australian preschool children. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2010;13(5):503-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2009.05.010 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19850520[71] Kelly Y, Sacker A, Schoon I, Nazroo J. Ethnic differences in achievement of developmental milestones by 9 months of age: The Millennium Cohort Study. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2006;48(10):825-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16978462[72] Angulo-Barroso RM, Schapiro L, Liang W, Rodrigues O, Shafir T, Kaciroti N, Jacobson SW, Lozoff B. Motor development in 9-month-old infants in relation to cultural differences and iron status. Developmental psychobiology 2011;53(2):196-210
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/dev.20512 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21298634[73] Van Hus JW, Potharst ES, Jeukens-Visser M, Kok JH, Van Wassenaer-Leemhuis AG. Motor impairment in very preterm-born children: links with other developmental deficits at 5 years of age. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2014;56(6):587-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24926490[74] Taanila A, Murray GK, Jokelainen J, Isohanni M, Rantakallio P. Infant developmental milestones: a 31-year follow-up. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2005;47(9):581-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16138663[75] Jenni OG, Chaouch A, Caflisch J, Rousson V. Infant motor milestones: poor predictive value for outcome of healthy children. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2013;102(4):e181-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/apa.12129 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23289493[76] Mayson TA, Harris SR, Bachman CL. Gross motor development of Asian and European children on four motor assessments: a literature review. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2007;19(2):148-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17505292[77] Touwen BCL. Psychomotorische ontwikkelingen en stoornissen. In A.J.M. Bonnet-Breusers e.a. (Eds.), Handboek Jeugdgezondheidszorg 1990
http://dx.doi.org/Utrecht:%20Wetenschappelijke%20Uitgeverij%20Bunge[78] Gorga D, Stern FM, Ross G, Nagler W. The neuromotor behavior of preterm and full-term children by three years of age: quality of movement and variability. Journal of developmental and behavioral pediatrics : JDBP 1991;12(2):102-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2045482[79] Bouchard C, Malina RM. Genetics of physiological fitness and motor performance. Exercise and sport sciences reviews 1983;11():306-39
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6350021[80] Francks C, Fisher S, Marlow A, MacPhie I, Taylor K, Richardson A, Stein J, Monaco A. Familial and Genetic Effects on Motor Coordination, Laterality, and Reading-Related Cognition The American journal of psychiatry 2003/12/01;160():1970
http://dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.160.11.1970[81] Stromswold K, Rosenthal M, Patel K, Molnar D. Development of Visual-Motor Integration: The Role of Genetic & Environmental Factors Journal of Vision 2011;11(11):462
http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/11.11.462 https://doi.org/10.1167/11.11.462[82] Williams LR, Gross JB. Heritability of motor skill. Acta geneticae medicae et gemellologiae 1980;29(2):127-36
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7196128[83] Saccani R, Valentini NC. Cross-cultural analysis of the motor development of Brazilian, Greek and Canadian infants assessed with the Alberta Infant Motor Scale. Revista paulista de pediatria : orgao oficial da Sociedade de Pediatria de Sao Paulo 2013;31(3):350-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-05822013000300012 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24142318[84] Hwang A-W, Liao H-F, Granlund M, Simeonsson RJ, Kang L-J, Pan Y-L. Linkage of ICF-CY codes with environmental factors in studies of developmental outcomes of infants and toddlers with or at risk for motor delays. Disability and rehabilitation 2014;36(2):89-104
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2013.777805 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23594061[85] Golding J, Emmett P, Iles-Caven Y, Steer C, Lingam R. A review of environmental contributions to childhood motor skills. Journal of child neurology 2014;29(11):1531-47
http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0883073813507483 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24170258[86] Castetbon K, Andreyeva T. Obesity and motor skills among 4 to 6-year-old children in the United States: nationally-representative surveys. BMC pediatrics 2012;12():28
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-12-28 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22420636[87] Lopes VP, Stodden DF, Bianchi MM, Maia JAR, Rodrigues LP. Correlation between BMI and motor coordination in children. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2012;15(1):38-43
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2011.07.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21831708[88] Mond JM, Stich H, Hay PJ, Kraemer A, Baune BT. Associations between obesity and developmental functioning in pre-school children: a population-based study. International journal of obesity (2005) 2007;31(7):1068-73
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17471298[89] D'Hondt E, Deforche B, Gentier I, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Vaeyens R, Philippaerts R, Lenoir M. A longitudinal analysis of gross motor coordination in overweight and obese children versus normal-weight peers. International journal of obesity (2005) 2013;37(1):61-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.55 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22508339[90] Glascoe FP. Parents' concerns about children's development: prescreening technique or screening test? Pediatrics 1997;99(4):522-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9093291[91] Harris SR, Mickelson ECR, Zwicker JG. Diagnosis and management of developmental coordination disorder. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2015;187(9):659-665
http://dx.doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.140994 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26009588[92] Williams J, Lee KJ, Anderson PJ. Prevalence of motor-skill impairment in preterm children who do not develop cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(3):232-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03544.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20002114[93] Bakker I, Bakker C, van Dijke A, Terpstra L. Balansmodel Nederlands Instituut voor Zorg en Welzijn (NIZQ) O&O in perspectief 1998
[94] Kerstjens JM, de Winter AF, Bocca-Tjeertes IF, ten Vergert EMJ, Reijneveld SA, Bos AF. Developmental delay in moderately preterm-born children at school entry. The Journal of pediatrics 2011;159(1):92-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.12.041 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21324481[95] Rivilis I, Hay J, Cairney J, Klentrou P, Liu J, Faught BE. Physical activity and fitness in children with developmental coordination disorder: a systematic review. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(3):894-910
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.017 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21310588[96] Emery AE. Population frequencies of inherited neuromuscular diseases--a world survey. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD 1991;1(1):19-29
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1822774[97] Buijssen M, Jajou R, van Kessel FGB, Vonk Noordegraaf-Schouten MJM, Zeilmaker MJ, Wijga AH, van Rossum CTM. Health effects of breastfeeding: an update. Systematic literature review RIVM rapport, 043 2015
[98] Wilson JMG, Jungner G. Principles and practice of screening for disease World Health Organization. Public Health Paper 1968
[99] Een jeugdgezondheidszorg richtlijn voor screening van de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen: een haalbaarheidsstudie TNO-rapport 2008
[100] Grevinga M, van Harten L, Hofstetter H, Verkerk P, Detmar S. Het afnemen van de Van Wiechenkenmerken door ouders: een pilotonderzoek Manuscript draft JGZ Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 2018
[101] Schwartze P. Entwicklungsuntersuchung in der SPrechstunde. Arbeitsbuch nach dem revidierten Van-Wiechen-Schema Pädiatrie Grenzgebiete 1991;30():1
[102] Gesell A, Amatruda CS. Developmental diagnosis Hoeber, Harper & Row, New York 1947
[103] Gesell A, Amatruda CS, Knobloch H, Pasamanick B. Gesell and Amatruda's Developmental diagnosis : the evaluation and management of normal and abnormal neuropsychologic development in infancy and early childhood. 1974
[104] Touwen BCL. Ontwikkelingsneurologisch onderzoek. In: Verhulst en Verhey GV (red). Kinder- en jeugdpsychiatrie; onderzoek en diagnostiek Van Gorcum 1992
[105] Touwen BCL. De neurologische ontwikkeling van 0 tot 3 jaar. In: de Boer JE (red): Infantpsychiatrie II. Van Gorcum 1993
[106] Schlesinger-Was EA. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek van zuigelingen en kleuters op het consultatiebureau Proefschrift Rijksuniversiteit Leiden 1981
[107] Verkerk PH, Reerink JD, Herngreen WP. Evaluatie van het Van Wiechenschema - I: De overeenkomst tussen de referentiewaarden en waarnemingen in de praktijk Tijdschrift voor Jeugdgezondheidszorg 1993;25(5):71
[108] Schoemaker M, Ketelaar M, Reinders-Messelink H. Hoofdstuk 6: Meetinstrumenten - Voor de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen. In: Kinderfysiotherapie. Van Empelen R, Nijhuis-van der Sanden & Hartman 1 (Eds). Springer Media B.V. 2013
[109] Baecke JAH, Boersma-Slütter WGM, van Heeswijk ALM. Ontwikkeling van een motoriektest voor kleuters: de betrouwbaarheid Tijdschrift voor de Sociale Gezondheidszorg 1984;62():38
[110] Dijkmans-Scheepstra D, Rietveld E. De constructvaliditeit van de Baecke-Fassaert motoriektest en de Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 Nederlandstalige versie Masterthesis. Transfergroep Rotterdam 2013
[111] De Kroon ML, van Kernebeek WG, Neve BF, ter Veer JM, Reijeveld SA, de Vet HCW, Toussaint HM. Validity and discriminative ability of Dutch motor tests in 5 to 6 year old children 2018
[112] Jacobusse G, Buuren S, Verkerk P. Ontwikkeling van de D-score : een samenvattende maat voor het Van Wiechenonderzoek 2008/01/01
[113] Hafkamp-de Groen E, Dusseldorp E, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Jacobusse GW, Oudesluijs-Murphy AM, Verkerk PH. Relatie tussen het Van Wiechenonderzoek en het intelligentieniveau op 5 jaar Tijdschrift voor Jeugdgezondheidszorg 2009;41():10
[114] Pilotstudie D-screening: screening op ontwikkelingsachterstand bij het jonge kind, uitgevoerd door de jeugdarts TNO-rapport 2011
[115] Dunnink G, Lijs-spek WJG. Activiteiten basistakenpakket jeugdgezondheidszorg 0-19 jaar per contactmoment. Geraadpleegd op 21-03-2016 2008
http://www.rivm.nl/Documenten_en_publicaties/Wetenschappelijk/Rapporten/2008/juli/Activit%20eiten_Basistakenpakket_Jeugdgezondheidszorg_0_19_jaar_per_Contactmoment[116] Baecke JAH, Fassaert YAH, van Rossum JHA, van de Kolk W. Motoriek bij kleuters: samenstelling en normering van een in de Jeugdgezondheidszorg hanteerbare test Tijdschrift voor Sociale Geneeskunde 1989;67():100
[117] Van Waelvelde H, Peersman W, Lenoir M, Smits Engelsman BCM. The reliability of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children for preschool children with mild to moderate motor impairment. Clinical rehabilitation 2007;21(5):465-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17613568[118] Blank R, Smits-Engelsman B, Polatajko H, Wilson P, . European Academy for Childhood Disability (EACD): recommendations on the definition, diagnosis and intervention of developmental coordination disorder (long version). Developmental medicine and child neurology 2012;54(1):54-93
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.04171.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22171930[119] Smits-Engelsman BCM, Niemeijer AS, van Waelvelde H. Is the Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2nd edition a reliable instrument to measure motor performance in 3 year old children? Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(4):1370-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.031 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21349686[120] Spittle AJ, Doyle LW, Boyd RN. A systematic review of the clinimetric properties of neuromotor assessments for preterm infants during the first year of life. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2008;50(4):254-66
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.02025.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18190538[121] Van Gelder W, Stroes H. Leerlingvolgsysteem bewegen en spelen. Over observeren, registreren en extra zorg 2010
[122] Van Kernebeek WG, de Schipper AW, Savelsbergh GJP, Toussaint HM. Inter-rater and test-retest (between-sessions) reliability of the 4-Skills Scan for dutch elementary school children. Measurement in Physical Education and Exercise Science 2018;22(2):129
[123] van Kernebeek WG, de Kroon MLA, Savelsbergh GJP, Toussaint HM. The validity of the 4-Skills Scan A double-validation study. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2018;28(11):2349-2357
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/sms.13231 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29858501[124] Runhaar J, Collard DCM, Singh AS, Kemper HCG, van Mechelen W, Chinapaw M. Motor fitness in Dutch youth: differences over a 26-year period (1980-2006). Journal of science and medicine in sport 2010;13(3):323-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2009.04.006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19592305[125] Schoffelmeer L, Toussaint H. De oogst van beweegarmoede in de jeugd; overgewicht en minder makkelijk bewegen Lichamelijke Opvoeding 2013;11():39
[126] Ellinoudis T, Evaggelinou C, Kourtessis T, Konstantinidou Z, Venetsanou F, Kambas A. Reliability and validity of age band 1 of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children--second edition. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(3):1046-51
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.035 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21333488[127] Schoemaker MM, Niemeijer AS, Flapper BCT, Smits-Engelsman BCM. Validity and reliability of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 Checklist for children with and without motor impairments. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2012;54(4):368-75
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04226.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22320829[128] Holm I, Tveter AT, Aulie VS, Stuge B. High intra- and inter-rater chance variation of the movement assessment battery for children 2, ageband 2. Research in developmental disabilities 2013;34(2):795-800
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2012.11.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23220056[129] Piper M.C., Darrah J.. Motor Assessment of the Developing Infant 1994
https://books.google.be/books?id=kdVsAAAAMAAJ[130] Neonatale Prematuren Follow-up (NPF) Richtlijn: Aanbeveling landelijke neonatale follow-up-NICU follow-up 2015
[131] Pin TW, de Valle K, Eldridge B, Galea MP. Clinimetric properties of the alberta infant motor scale in infants born preterm. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2010;22(3):278-86
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PEP.0b013e3181e94481 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20699776[132] Syrengelas D, Siahanidou T, Kourlaba G, Kleisiouni P, Bakoula C, Chrousos GP. Standardization of the Alberta infant motor scale in full-term Greek infants: Preliminary results. Early human development 2010;86(4):245-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.03.009 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20452736[133] Piper MC, Pinnell LE, Darrah J, Maguire T, Byrne PJ. Construction and validation of the Alberta Infant Motor Scale (AIMS). Canadian journal of public health = Revue canadienne de sante publique 1992;83 Suppl 2():S46-50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1468050[134] Van Baar AL, Steenis LJP, Verhoeven M, Hessen DJ. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development - Third Edition - Nederlandse versie (Bayler-III-NL). Geraadpleegd op 19-03-2016 2015
http://www.pearsonclinical.nl/bayley-3[135] Connolly BH, McClune NO, Gatlin R. Concurrent validity of the Bayley-III and the Peabody Developmental Motor Scale-2. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2012;24(4):345-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PEP.0b013e318267c5cf https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22965209[136] Steenis LJP, Verhoeven M, Hessen DJ, van Baar AL. Performance of Dutch children on the Bayley III: a comparison study of US and Dutch norms. PloS one 2015;10(8):e0132871
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132871 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26267907[137] Kroes M, Feron FJM, Sleijpen FAM, Vles JSH. De Maastrichtse Motoriek Test Tijdschrift van de NVFK 2006;18(51):3
[138] STIMULIZ Leerlingvolgsysteem 0-24 jaar. Geraadpleegd op 10-10-2017
https://stimuliz.com/[139] Hoeboer J, de Vies S. Big data in het bewegingsonderwijs Presentatie VvBN symposium 2015
[140] Jongbloed-Pereboom M, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MWG, Steenbergen B. Norm scores of the box and block test for children ages 3-10 years. The American journal of occupational therapy : official publication of the American Occupational Therapy Association 2013;67(3):312-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.5014/ajot.2013.006643 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23597689[141] Hornman J, Kerstjens JM, de Winter AF, Bos AF, Reijneveld SA. Validity and internal consistency of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire 60-month version and the effect of three scoring methods. Early human development 2013;89(12):1011-5
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2013.08.016 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24041814[142] Kerstjens JM, Bos AF, ten Vergert EMJ, de Meer G, Butcher PR, Reijneveld SA. Support for the global feasibility of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire as developmental screener. Early human development 2009;85(7):443-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2009.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19356866[143] van der Linde BW, van Netten JJ, Otten BE, Postema K, Geuze RH, Schoemaker MM. Psychometric properties of the DCDDaily-Q: a new parental questionnaire on children's performance in activities of daily living. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(7):1711-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.03.008 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24685097[144] Schoemaker MM, Flapper BCT, Reinders-Messelink HA, Kloet AD. Validity of the motor observation questionnaire for teachers as a screening instrument for children at risk for developmental coordination disorder. Human movement science 2008;27(2):190-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2008.02.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18346804[145] Caravale B, Baldi S, Gasparini C, Wilson BN. Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability and predictive validity of the Italian version of Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ). European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society 2014;18(3):267-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2013.11.009 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24332678[146] Caravale B, Baldi S, Capone L, Presaghi F, Balottin U, Zoppello M. Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ-Italian). Research in developmental disabilities 2015;36C():543-550
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.10.035 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25462515[147] Schoemaker MM, Flapper B, Verheij NP, Wilson BN, Reinders-Messelink HA, de Kloet A. Evaluation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire as a screening instrument. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2006;48(8):668-73
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16836779[148] Wilson BN, Crawford SG, Green D, Roberts G, Aylott A, Kaplan BJ. Psychometric properties of the revised Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire. Physical & occupational therapy in pediatrics 2009;29(2):182-202
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01942630902784761 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19401931[149] Martini R, St-Pierre M-F, Wilson BN. French Canadian cross-cultural adaptation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire '07: DCDQ-FC. Canadian journal of occupational therapy. Revue canadienne d'ergotherapie 2011;78(5):318-27
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22338299[150] Kennedy-Behr A, Wilson BN, Rodger S, Mickan S. Cross-cultural adaptation of the developmental coordination disorder questionnaire 2007 for German-speaking countries: DCDQ-G. Neuropediatrics 2013;44(5):245-51
http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1347936 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23716299[151] Parmar A, Kwan M, Rodriguez C, Missiuna C, Cairney J. Psychometric properties of the DCD-Q-07 in children ages to 4-6. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(2):330-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.10.030 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24321562[152] Van Empelen R, Nijhuis-van der Sanden R, Hartman A. Kinderfysiotherapie Springer Media B.V. 2013
[153] Bender-de Haan S, Broer van Dijk-van der Hulst M, Hommes-Hospers HJ, van Wijlen-Hempel MS, Touwen BCL. Een neuromotorische onderzoekmethode voor de peuterleeftijd Tijdschrift Jeugdgezondheidszorg 1998;30():49
[154] Chagas PSC, Cunha RSM, Mancini MC, Magalhaes LC. There is no evidence to support or refute the effect of baby walkers on motor development in typically developing children. Geraadpleegd op 19-04-2016 2007
http://www.otcats.com/topics/CAT%20-%20%20Paula%20Chagas%202007.pdf[155] Abbott AL, Bartlett DJ. Infant motor development and equipment use in the home. Child: care, health and development 2001;27(3):295-306
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11350456[156] Fay D, Hall M, Murray M, Saatdjian A, Vohwinkel E. The Effect of Infant Exercise Equipment on Motor Milestone Achievement Pediatric Physical Therapy 2006/01/01;18():90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00001577-200601810-00039[157] Pin T, Eldridge B, Galea MP. A review of the effects of sleep position, play position, and equipment use on motor development in infants. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):858-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979866[158] Kuo Y-L, Liao H-F, Chen P-C, Hsieh W-S, Hwang A-W. The influence of wakeful prone positioning on motor development during the early life. Journal of developmental and behavioral pediatrics : JDBP 2008;29(5):367-76
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0b013e3181856d54 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18766114[159] Saccani R, Valentini NC, Pereira KR, Müller AB, Gabbard C. Associations of biological factors and affordances in the home with infant motor development. Pediatrics international : official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society 2013;55(2):197-203
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ped.12042 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23279095[160] Tremblay MS, Leblanc AG, Carson V, Choquette L, Connor Gorber S, Dillman C, Duggan M, Gordon MJ, Hicks A, Janssen I, Kho ME, Latimer-Cheung AE, Leblanc C, Murumets K, Okely AD, Reilly JJ, Spence JC, Stearns JA, Timmons BW, . Canadian Physical Activity Guidelines for the Early Years (aged 0-4 years). Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme 2012;37(2):345-69
http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/h2012-018 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22448608[161] Graf C, Koch B, Kretschmann-Kandel E, Falkowski G, Christ H, Coburger S, Lehmacher W, Bjarnason-Wehrens B, Platen P, Tokarski W, Predel HG, Dordel S. Correlation between BMI, leisure habits and motor abilities in childhood (CHILT-project). International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders : journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 2004;28(1):22-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14652619[162] Morgan PJ, Barnett LM, Cliff DP, Okely AD, Scott HA, Cohen KE, Lubans DR. Fundamental movement skill interventions in youth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2013;132(5):e1361-83
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2013-1167 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24167179[163] Kirk MA, Rhodes RE. Motor skill interventions to improve fundamental movement skills of preschoolers with developmental delay. Adapted physical activity quarterly : APAQ 2011;28(3):210-32
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21725115[164] Logan SW, Robinson LE, Wilson AE, Lucas WA. Getting the fundamentals of movement: a meta-analysis of the effectiveness of motor skill interventions in children. Child: care, health and development 2012;38(3):305-15
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2214.2011.01307.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21880055[165] Lai SK, Costigan SA, Morgan PJ, Lubans DR, Stodden DF, Salmon JO, Barnett LM. Do school-based interventions focusing on physical activity, fitness, or fundamental movement skill competency produce a sustained impact in these outcomes in children and adolescents? A systematic review of follow-up studies. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) 2014;44(1):67-79
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24122775[166] Smith GA, Bowman MJ, Luria JW, Shields BJ. Babywalker-related injuries continue despite warning labels and public education. Pediatrics 1997;100(2):E1
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9233972[167] van Wieringen JCM, Beckers MCB. Hoe krijgt de jeugdgezondheidszorg de jeugd in beweging Tijdschrift Jeugdgezondheidszorg 2015
[168] Riethmuller AM, Jones R, Okely AD. Efficacy of interventions to improve motor development in young children: a systematic review. Pediatrics 2009;124(4):e782-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0333 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19736263[169] Boonzajer Flaes SAM, Chinapaw MJM, Koolhaas CM, van Mechelen W, Verhagen EALM. More children more active: Tailored playgrounds positively affect physical activity levels amongst youth. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2016;19(3):250-254
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2015.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25846126[170] Cohen DA, Han B, Isacoff J, Shulaker B, Williamson S, Marsh T, McKenzie TL, Weir M, Bhatia R. Impact of park renovations on park use and park-based physical activity. Journal of physical activity & health 2015;12(2):289-95
http://dx.doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2013-0165 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24956608[171] Janssen M, Twisk JWR, Toussaint HM, van Mechelen W, Verhagen EALM. Effectiveness of the PLAYgrounds programme on PA levels during recess in 6-year-old to 12-year-old children. British journal of sports medicine 2015;49(4):259-64
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2012-091517 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23293007[172] Kriemler S, Meyer U, Martin E, van Sluijs EMF, Andersen LB, Martin BW. Effect of school-based interventions on physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents: a review of reviews and systematic update. British journal of sports medicine 2011;45(11):923-30
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2011-090186 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21836176[173] Wood C, Gladwell V, Barton JO. A repeated measures experiment of school playing environment to increase physical activity and enhance self-esteem in UK school children. PloS one 2014;9(9):e108701
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108701 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25264610[174] De Schipper A, Deerenberg H, Bouthoorn B, Toussaint H. Gymmen kleuters beter met een gymleraar? Sportgericht 2014;3(68):29
[175] Van Gelder W, Goedhart B, Janssen M. Het plein wacht...(1). Lichamelijke Opvoeding magazine 2015;103():26
[176] Van Gelder W, Goedhart B, Janssen M. Het plein wacht...(2). Lichamelijke Opvoeding magazine ;103():23
[177] Van Gelder W, Goedhart B, Janssen M. Het plein wacht...(3). Lichamelijke Opvoeding magazine ;103():19
[178] Jantje Beton - De Jantje Beton aanpak; samen met kinderen werken aan buitenspelen. Geraadpleegd op 22-03-2016 2013
http://www.jantjebeton.nl/gemeenten/de-jantje-betonaanpak/[179] Reddingsbrigade Nederland. 'Reddingsbrigade wil dat schoolzwemmen terugkomt'. Geraadpleegd op 22-03-2016 2015
http://www.nu.nl/werk-en-prive/4113093/reddingsbrigadewil-%20schoolzwemmen-terugkomt.html[180] Standpunt beweegstimulering door de jeugdgezondheidszorg RIVM/Centrum jeugdgezondheidszorg (Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu) 2009
[181] Kenniscentrum Sport. Evaluatie van kansrijke beweegprogramma's om lichaamsbeweging in de bevolking te bevorderen: fase 2. Geraadpleegd op 21-04-2016 2016
http://www.nivel.nl/sites/default/files/bestanden/Rapport-evaluatie-kansrijkebeweegprogrammas-%20fase2.pdf[182] Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, . GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2008;336(7650):924-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18436948[183] Delacy MJ, Reid SM, . Profile of associated impairments at age 5 years in Australia by cerebral palsy subtype and Gross Motor Function Classification System level for birth years 1996 to 2005. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2016;58 Suppl 2():50-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13012 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26777873[184] Goldet G, Howick J. Understanding GRADE: an introduction. Journal of evidence-based medicine 2013;6(1):50-54
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jebm.12018 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23557528[185] Barnett LM, Minto C, Lander N, Hardy LL. Interrater reliability assessment using the Test of Gross Motor Development-2. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2014;17(6):667-70
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2013.09.013 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24211133[186] Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, Dan B, Jacobsson BO. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Developmental medicine and child neurology. Supplement 2007;109():8-14
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17370477[187] Rosenbaum PL, Walter SD, Hanna SE, Palisano RJ, Russell DJ, Raina P, Wood E, Bartlett DJ, Galuppi BE. Prognosis for gross motor function in cerebral palsy: creation of motor development curves. JAMA 2002;288(11):1357-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12234229[188] Bruininks R, Bruininks B. Bruininks-Oseretsky test of motor proficiency (2nd ed.) Minneapolis, MN: NCS Pearson 2005
[189] Campbell SK, Swanlund A, Smith E, Liao P-J, Zawacki L. Validity of the TIMPSI for estimating concurrent performance on the test of infant motor performance. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2008;20(1):3-10
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PEP.0b013e31815f66a6 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18300928[190] De-Andrés-Beltrán B, Rodríguez-Fernández ÁL, Güeita-Rodríguez J, Lambeck J. Evaluation of the psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Denver Developmental Screening Test II. European journal of pediatrics 2015;174(3):325-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2410-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25164064[191] Doralp S, Bartlett D. Infant Movement Motivation Questionnaire: development of a measure evaluating infant characteristics relating to motor development in the first year of life. Infant behavior & development 2014;37(3):326-33
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2014.04.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24861943[192] Fingerhut P, Madill H, Darrah J, Hodge M, Warren S. Classroom-based assessment: validation for the school AMPS. The American journal of occupational therapy : official publication of the American Occupational Therapy Association 2002;56(2):210-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11905306[193] Folio MR, Fewell RR. Peabody Developmental Motor Scales, Second edition (PDMS-2) Occupational and Physical Therapy 2000
[194] Fransen J, D'Hondt E, Bourgois J, Vaeyens R, Philippaerts RM, Lenoir M. Motor competence assessment in children: convergent and discriminant validity between the BOT-2 Short Form and KTK testing batteries. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(6):1375-83
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.03.011 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24713517[195] GUDMUNDSSON EINAR, GRETARSSON SJ. Reliability and validity of mothers' developmental estimates for children between 4 and 41 months Scandinavian Journal of Psychology 1994;35(4):336
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.1994.tb00958.x https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.1994.tb00958.x[196] Gudmundsson E, Gretarsson SJ. Mothers' questionnaire of preschoolers' language and motor skills: a validation study. Child: care, health and development 2013;39(2):246-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2214.2011.01362.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22329598[197] Gudmundsson E. The Toddler Language and Motor Questionnaire: A mother-report measure of language and motor development. Research in developmental disabilities 2015;45-46():21-31
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26209772[198] van Hartingsveldt MJ, Cup EHC, de Groot IJM, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MWG. Writing Readiness Inventory Tool in Context (WRITIC): reliability and convergent validity. Australian occupational therapy journal 2014;61(2):102-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1440-1630.12082 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24689921[199] Heineman KR, La Bastide-Van Gemert S, Fidler V, Middelburg KJ, Bos AF, Hadders-Algra M. Construct validity of the Infant Motor Profile: relation with prenatal, perinatal, and neonatal risk factors. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(9):e209-15
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03667.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20477835[200] Heineman KR, Middelburg KJ, Bos AF, Eidhof L, La Bastide-Van Gemert S, Van Den Heuvel ER, Hadders-Algra M. Reliability and concurrent validity of the Infant Motor Profile. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2013;55(6):539-45
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12100 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23480426[201] Johansen K, Persson K, Sarkadi A, Sonnander K, Magnusson M, Lucas S. Can nurses be key players in assessing early motor development using a structured method in the child health setting? Journal of evaluation in clinical practice 2015;21(4):681-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jep.12366 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25958886[202] Kakebeeke TH, Caflisch J, Chaouch A, Rousson V, Largo RH, Jenni OG. Neuromotor development in children. Part 3: motor performance in 3- to 5-year-olds. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2013;55(3):248-56
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12034 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23278183[203] Kambas A, Venetsanou F. The Democritos Movement Screening Tool for Preschool Children (DEMOST-PRE©): development and factorial validity. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(7):1528-33
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.03.046 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24763377[204] Kambas A, Venetsanou F, Giannakidou D, Fatouros IG, Avloniti A, Chatzinikolaou A, Draganidis D, Zimmer R. The Motor-Proficiency-Test for children between 4 and 6 years of age (MOT 4-6): an investigation of its suitability in Greece. Research in developmental disabilities 2012;33(5):1626-32
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2012.04.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22543059[205] Tabatabainia MM, Ziviani J, Maas F. Construct validity of the Bruininks‐Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency and the Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Australian Occupational Therapy Journal 1995;42(1):3
[206] MacCobb S, Greene S, Nugent K, O'Mahony P. Measurement and prediction of motor proficiency in children using Bayley infant scales and the Bruininks-Oseretsky test. Physical & occupational therapy in pediatrics 2005;25(1-2):59-79
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15760824[207] Venetsanou F, Kambas A, Aggeloussis N, Serbezis V, Taxildaris K. Use of the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency for identifying children with motor impairment. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):846-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979863[208] Venetsanou F, Kambas A, Aggeloussis N, Fatouros I, Taxildaris K. Motor assessment of preschool aged children: A preliminary investigation of the validity of the Bruininks-Oseretsky test of motor proficiency - short form. Human movement science 2009;28(4):543-50
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2009.03.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19443065[209] Saraiva L, Rodrigues LP, Cordovil R, Barreiros J. Motor profile of Portuguese preschool children on the Peabody Developmental Motor Scales-2: a cross-cultural study. Research in developmental disabilities 2013;34(6):1966-73
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.03.010 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23584176[210] Reuben DB, Magasi S, McCreath HE, Bohannon RW, Wang Y-C, Bubela DJ, Rymer WZ, Beaumont J, Rine RM, Lai J-S, Gershon RC. Motor assessment using the NIH Toolbox. Neurology 2013;80(11 Suppl 3):S65-75
http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182872e01 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23479547[211] Pergami P, Seemaladinne N, Billings A. Validation of a computer application as a test of motor function in healthy children and adults. NeuroRehabilitation 2012;31(4):453-61
http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/NRE-2012-00816 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23232170[212] Westcott McCoy S, Bowman A, Smith-Blockley J, Sanders K, Megens AM, Harris SR. Harris Infant Neuromotor Test: comparison of US and Canadian normative data and examination of concurrent validity with the Ages and Stages Questionnaire. Physical therapy 2009;89(2):173-80
http://dx.doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20080189 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19131397[213] Sun S-H, Zhu Y-C, Shih C-L, Lin C-H, Wu SK. Development and initial validation of the Preschooler Gross Motor Quality Scale. Research in developmental disabilities 2010;31(6):1187-96
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2010.08.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20843658[214] Sun S-H, Sun H-L, Zhu Y-C, Huang L-C, Hsieh Y-L. Concurrent validity of Preschooler Gross Motor Quality Scale with Test of Gross Motor Development-2. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(3):1163-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21295441[215] Williams HG, Pfeiffer KA, Dowda M, Jeter C, Jones S, Pate RR. A Field-Based Testing Protocol for Assessing Gross Motor Skills in Preschool Children: The CHAMPS Motor Skills Protocol (CMSP). Measurement in physical education and exercise science 2009;13(3):151-165
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21532999[216] Smith YA, Hong E, Presson C. Normative and validation studies of the Nine-hole Peg Test with children. Perceptual and motor skills 2000;90(3 Pt 1):823-43
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10883762[217] Majewska R, Mrozek-Budzyn D, Kieltyka A, Augustyniak M. Usefulness of maternal assessment of children development based on reported age of achieved milestones. Przeglad epidemiologiczny 2013;67(3):487-90, 585-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24340566[218] Lin C-K, Meng L-F, Yu Y-W, Chen C-K, Li K-H. Factor analysis of the contextual fine motor questionnaire in children. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(2):512-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.11.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24374604[219] Netelenbos JB. Teachers’ ratings of gross motor skills suffer from low concurrent validity Human Movement Science 2005;24(1):116
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2005.02.001 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167945705000059[220] Schoemaker MM. Manual of the motor observation questionnaire for teachers Groningen: internal Publication, Center for Human Movement Sciences, In Dutch 2003
[221] Kerkmeer M, Zijlstra J, Dek J. Bayley-III-NL - Psychometrische eigenschappen Pearson Assesment and Information BV 2015
[222] Burger M, Louw QA. The predictive validity of general movements--a systematic review. European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society 2009;13(5):408-20
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2008.09.004 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19036618[223] Hadders-Algra M, Heineman KR, Bos AF, Middelburg KJ. The assessment of minor neurological dysfunction in infancy using the Touwen Infant Neurological Examination: strengths and limitations. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(1):87-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03305.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19549207[224] Bouwstra H, Dijk-Stigter GR, Grooten HMJ, Janssen-Plas FE, Koopmans AJ, Mulder CD, van Belle A, Hadders-Algra M. Predictive value of definitely abnormal general movements in the general population. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(5):456-61
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03529.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20002118[225] Peters LK, Maathuis KG, Kouw E, Hamming M, Hadders-Algra M. Test-retest, inter-assessor and intra-assessor reliability of the modified Touwen examination Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2008;12(4):328
[226] Trendrapport Bewegen en Gezondheid TNO. Onder redactie van: V.H. Hildebrandt, A.M.J. Chorus, J.H. Stubbe 2008
[227] Visser JD. Kinderorthopedie: Pluis of Niet Pluis. Een leidraad voor eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. 11e druk 2009
[228] Global recommendations on physical activity for health World Health Organization (WHO): Genève 2010
1 Inleiding
Introductie
De richtlijn ‘Motorische Ontwikkeling’ biedt kennis en praktische handvatten voor professionals in de jeugdgezondheidszorg (JGZ). De richtlijn is bestemd voor jeugdartsen1, verpleegkundig-specialisten Preventieve Zorg, jeugdverpleegkundigen en doktersassistenten. Het doel van de JGZ-richtlijn Motorische Ontwikkeling is een landelijk uniforme werkwijze tot stand te brengen die effectief en efficiënt is ten aanzien van monitoring, preventie, signalering, advisering en verwijzing bij motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen. De richtlijn is wetenschappelijk onderbouwd en is praktisch bruikbaar binnen de JGZ.
De richtlijn biedt een handvat hoe JGZ-professionals kunnen samenwerken met aanpalende beroepsgroepen en met scholen. We besteden daarom aandacht aan preventie, signalering, monitoring van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen. Ook gaan we in op de gevolgen van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen, komt het onderzoek van de motoriek aan de orde en gaan we in op de toeleiding naar verdere diagnostiek en behandeling. Tot slot bespreken we de terugkoppeling en nazorg vanuit de JGZ.
Door beantwoorden van de uitgangsvragen worden bovengenoemde aspecten beschreven:
- Wat is een normale motorische ontwikkeling, gerelateerd aan leeftijd? (1.2)
- Wat is een motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem, hoe ontstaat het, hoe vaak komt het voor in de specifieke leeftijdsfasen van het kind? Wat zijn mogelijke consequenties voor het kind in termen van gezondheid, welzijn en kosten? (1.3)
- Welke samenhang bestaat er tussen motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen en problemen op andere ontwikkelingsdomeinen? (1.4)
- Hoe kunnen JGZ-professionals enkelvoudige motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen onderscheiden van complexe ontwikkelingsproblemen? (1.5)
- Wat is het belang van tijdige signalering en behandeling? Wat is de rol van de JGZ; hoe kan de JGZ hieraan op een effectieve en efficiënte wijze bijdragen? (1.6)
- Wat is een normaal, en wat is een afwijkend patroon van het behalen van motorische mijlpalen? In welke mate hangen deze samen met geslacht en etniciteit? (2.1) Wat zijn risicofactoren en beschermende factoren voor een afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling? (2.2)
- Wat zijn, ingedeeld naar leeftijd, valide en betrouwbare meetinstrumenten? Wat zijn effectieve werkwijzen om motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen te signaleren en motorische ontwikkeling in de tijd adequaat te volgen? (2.3)
- Waaruit dient een oriënterend neurologisch JGZ-onderzoek te bestaan? (2.4)
- Wat zijn individuele, preventieve, effectieve adviezen en interventies die de JGZ kan aanbieden om de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen te stimuleren? (3.1)
- Wat zijn bij het vaststellen van risicofactoren of met het oog op preventie vanuit de JGZ collectieve adviezen aan de omgeving van het kind (zoals kinderopvang, peuterspeelzalen, scholen, gemeenten) om de motorische ontwikkeling te stimuleren? (3.2)
- Welke samenwerkingsafspraken moet de JGZ met welke partijen maken over signalering en beoordeling van motorische ontwikkeling? (4.1)
- Welke samenwerkingsafspraken moet de JGZ met welke partijen maken over verwijzing naar effectieve zorgpaden/interventies vanuit de JGZ of in samenwerking met de JGZ? (4.2
- Welke samenwerkingsafspraken moet de JGZ met welke partijen maken over monitoring bij het vaststellen van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen? En met welke partijen? (4.3)
- Welke samenwerkingsafspraken moet de JGZ met welke partijen maken over terugrapportage van de verwijsinstantie (bijvoorbeeld kinderarts, kinderfysiotherapeut) naar de JGZ/school/huisarts en vice versa? (4.4)
Binnen deze richtlijn bestaat, in lijn met de opdracht van ZonMw, specifieke aandacht voor een aantal onderwerpen. Deze zijn geslacht, etniciteit, prematuriteit (omdat prematuur geboren kinderen een relatief grote groep kinderen betreft met een verhoogd risico hebben op motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen) en enkele veel voorkomende problemen zoals Cerebrale Parese (CP, zie 1.3.1) en Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD, zie 1.3.2)
Aan de richtlijn hebben veel experts meegewerkt, als lid van de projectgroep, werkgroep of klankbordgroep, en/of als geraadpleegde expert. De projectgroepleden hebben bijgedragen aan de totstandkoming en meegedacht over de conceptteksten van de richtlijn.
De werkgroepleden zijn verantwoordelijk voor de inhoud van de richtlijn en hebben bij verschillende delen bijgedragen als auteur. Namens alle leden van de project- en werkgroep wens ik u veel leesplezier!
Marlou de Kroon
1: Waar in de richtlijn ‘jeugdarts’ staat, kan ook ‘verpleegkundig specialist Preventieve Zorg’* worden gelezen. De verpleegkundig specialist Preventieve Zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG-geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied. De verpleegkundig specialist Preventieve Zorg werkt op expertniveau en is binnen dit expertisegebied onder andere bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en zo nodig te verwijzen. De verpleegkundig specialist Preventieve Zorg is lid van het JGZ-team en maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
1.1 Aanleiding
Voor de fysieke en psychosociale ontwikkeling van een kind is een normale motorische ontwikkeling van belang. Een normale motorische ontwikkeling draagt bij aan een actieve leefstijl (en vice versa). De kans is dan groter dat kinderen mogen meedoen, op school en daarbuiten[1]. Bepalend voor de motorische ontwikkeling zijn de neurologische ontwikkeling, aandoeningen van het bewegingsapparaat, lichamelijke activiteit (kindfactoren), omgevingsfactoren (ouders, scholen etcetera), en de interactie tussen deze factoren[2][3][4]. De gevolgen van een verminderde motorische ontwikkeling zijn divers. Kinderen met motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen hebben vaak een lager zelfbeeld[4][5] worden vaak gepest[7] en ervaren meer emotionele problemen[5], angststoornissen of depressies4. Hierdoor nemen ze beperkter deel aan sociale activiteiten, wat weer kan leiden tot een inactieve leefstijl, isolatie en angst[4][5][6]. Het resultaat is een negatieve spiraal door verdere afname van motorische vaardigheden met een stijgende kans op overgewicht en verslechtering van lichamelijke en psychosociale gezondheid. De meeste kinderen met motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen hebben deze problemen tien jaar later nog steeds[8]. Als een kind een motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem heeft, kan dit ook invloed hebben op het gezin: door een verhoogde kans op spanningen en stress, kan dit tot gevolg hebben dat het gezin minder sociale activiteiten onderneemt[6].
Samengevat: het is van belang motorische-ontwikkelingsproblemen zo vroeg mogelijk vast te stellen, zodat er ingegrepen kan worden. De effecten van een afwijking hebben namelijk negatieve gevolgen voor zowel het individuele kind, als het gezin.
1.1.1 Centrale rol van de JGZ
Door de toename van mogelijkheden voor diagnostiek en behandeling is de interesse in motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen bij kinderen toegenomen[9]. De JGZ vervult een centrale rol bij het longitudinaal monitoren van de motorische ontwikkeling en bij het signaleren en verwijzen naar adequate behandeling. Ook houdt de JGZ zicht op de opvolging van verwijzingen en effecten van behandelingen. Met name dankzij de longitudinale monitoring heeft de JGZ een centrale rol in de ketenzorg. Naast de JGZ kunnen natuurlijk ook ouders en andere betrokkenen een ontwikkelingsachterstand opmerken. Denk aan medewerkers van een peuterspeelzaal (PSZ) of kinderdagverblijf (KDV), sportverenigingen, scholen of personen vanuit informelere netwerken. Ook dan is het van belang dat de JGZ in samenspraak met de ouders wordt geïnformeerd en geconsulteerd. Hierdoor kan een totaalbeeld van de gezondheid en ontwikkeling van het kind worden gevormd voordat er wordt overgegaan tot behandeling.
Door de huidige flexibilisering van de JGZ (zoals ook wordt beschreven in het Landelijk Professioneel kader (LPK: bit.ly/NJCLPK), verschillen de leeftijden, het aantal en de inhoud van de contactmomenten tussen alle JGZ-organisaties. De longitudinale monitoring van de JGZ verschilt daardoor.
1.1.2 Waarom deze nieuwe richtlijn?
Vanwege de centrale rol van de JGZ is het belangrijk dat de JGZ haar preventieve taken goed uitvoert en goede samenwerkingsafspraken maakt met de scholen, kinderopvang en andere partners in de ketenzorg (zie beslisbomen 4.1.1).
JGZ-professionals hebben adequate kennis nodig om motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen goed te kunnen signaleren. Zo moet bekend zijn wat oorzaken kunnen zijn van een motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem, wat de meest geschikte signaleringsinstrumenten zijn, hoe deze moeten worden toegepast en wat adequate vervolgacties zijn die de JGZ inzet bij het signaleren van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen. De JGZ-richtlijn ‘Motorische Ontwikkeling’ voorziet in deze behoefte, zodat professionals zich ondersteund weten bij hun professioneel handelen.
Het doel van de JGZ-richtlijn Motorische Ontwikkeling is een landelijk uniforme werkwijze te bewerkstelligen die effectief en efficiënt is ten aanzien van monitoring, preventie, signalering, advisering en verwijzing bij motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen. De richtlijn is wetenschappelijk onderbouwd en beoogt in praktische zin goed hanteerbaar te zijn binnen de JGZ.
1.2 Afbakening
1.2.1 Doel en doelgroep
De JGZ-richtlijn Motorische Ontwikkeling geeft richting aan het handelen van JGZ-professionals in hun contacten met kinderen en jongeren tussen 0-18 jaar en hun ouders. De richtlijn geeft zicht op de normale motorische ontwikkeling, de beoordeling van de motorische ontwikkeling en de risicofactoren.
De richtlijn gaat ook in op de preventie, (vroeg)signalering, begeleiding en verwijzing bij motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen. De doelgroep betreft JGZ-professionals: jeugdartsen, verpleegkundig specialisten, jeugdverpleegkundigen, doktersassistenten.
1.2.2 Afbakening
De richtlijn is gebaseerd op de knelpuntenanalyse van het CBO en de Argumentenfabriek (ZonMw). De deelnemers aan deze knelpuntenanalyse hebben de volgende uitgangsvragen opgesteld, die na herformulering in de projectgroep en werkgroep in de eerste vier hoofdstukken worden beantwoord.
1.2.3 Aansluiting bij andere richtlijnen
De JGZ-richtlijn ‘Motorische Ontwikkeling’ sluit aan bij de volgende richtlijnen en documenten:
• JGZ (2013). Te vroeg en/of small for gestational age (SGA) geboren kinderen.
• JGZ (2012). Preventie, signalering en aanpak van voorkeurshouding en schedelvorming.
• JGZ (2012). Overgewicht: Preventie, signalering, interventie en verwijzing.
• JGZ (2015). Richtlijn ADHD: Signalering, begeleiding en toeleiding naar diagnostiek.
• JGZ (2015). Richtlijn ASS: Signalering, begeleiding en toeleiding naar diagnostiek.
• JGZ (2018): Richtlijn Spraak-taalontwikkeling (bit.ly/NJCSpraakTaal).
• Landelijk professioneel kader uitvoering Basispakket JGZ.
• EACD (2013). Definitie, diagnose, evaluatie en behandeling van Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD). Nederlandse vertaling en aanpassing.
• NVK (2015). Aanbeveling Landelijke Neonatale Follow-Up- NICU follow-up.
• RIVM/Centrum Jeugdgezondheid (2009). Standpunt Beweegstimulering door de jeugdgezondheidszorg.
• TNO (2005). Kinderen in prioriteitswijken: lichamelijke (in)activiteit en overgewicht
• TNO (2008). Een jeugdgezondheidszorg richtlijn voor screening van de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen: een haalbaarheidsstudie
• VRA (2015). Richtlijn spastische cerebrale parese bij kinderen
1.3 Leeswijzer
Leeswijzer
De richtlijn is onderverdeeld in vier hoofdstukken. Na de inleiding (hoofdstuk 1) volgen er drie inhoudelijke thema’s: Normale en afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling, vroege opsporing en signalering (hoofdstuk 2), Voorlichting, advisering en begeleiding door de JGZ (hoofdstuk 3) en Samenwerkingsafspraken: verwijzing en nazorg (hoofdstuk 4). In de subparagrafen van de hoofdstukken 2 tot en met 4 zijn de uitgangsvragen beantwoord. Hierbij is iedere paragraaf van hoofdstuk 2 en 3 als volgt opgebouwd:
- Aanbevelingen
- Uitgangsvraag
- Onderbouwing, bestaande uit:
- Evidence-based onderbouwing, waarin conclusies op basis van de literatuursearches verwerkt zijn
- Overige overwegingen, geformuleerd door werkgroep- en projectgroepleden, geraadpleegde experts, of in overige literatuur
In de tekst verwijzen nummers in superscript naar de literatuurreferenties. Soms wordt op deze wijze verwezen naar de mening van de geraadpleegde experts of van project- of werkgroepleden. De subparagrafen van hoofdstuk 4 zijn iets anders opgebouwd.
Tot slot is van belang te melden dat:
- Het gebruik van een puntkomma tussen twee cijfers bij het melden van een leeftijd van x;a jaar betekent dat het om een leeftijd gaat van x jaar en a maanden;
- Er veel links in de tekst zijn opgenomen naar sites of pagina’s in de richtlijn waar nadere informatie staat over het betreffende onderwerp.
2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie
Het doel van dit hoofdstuk is om de JGZ de meest relevante informatie te geven over normale en afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling, en over de vroege opsporing en signalering van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen. De kennis van de JGZ moet daarmee toereikend zijn om motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen te kunnen signaleren. Ook zijn betrouwbaarheid, validiteit en de praktische toepassing van de signaleringsinstrumenten van belang.
Daarom gaan we in dit hoofdstuk in op:
• Het normale en abnormale patroon bij het behalen van mijlpalen (uitgangsvraag 2.1);
• De oorzaken en risicofactoren voor een afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling (uitgangsvraag 2.2);
2.1 Normale motorische ontwikkeling gerelateerd aan leeftijd
Deze paragraaf gaat in op de uitgangsvraag: Wat is een normale motorische ontwikkeling gerelateerd aan leeftijd?
Er bestaan veel verschillen tussen kinderen in de normale motorische ontwikkeling[10][11]: deze verschillen betreffen de uitvoering van motorisch gedrag, de volgorde van de ontwikkelingsmijlpalen en de leeftijd waarop een kind zich een motorische vaardigheid eigen heeft gemaakt[12]. Deze grote verschillen kunnen worden verklaard met behulp van de Neurale Groep Selectie Theorie (NGST), die de ideeën van verschillende theorieën combineert[13]. Met de NGST wordt een doelmatig kader geschetst voor het begrijpen van zowel een normale als een afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling. Een normale motorische ontwikkeling kenmerkt zich door veel variatie, complexiteit en door een toenemend aanpassingsvermogen. Een afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling kenmerkt zich, vooral op jonge leeftijd, door het ontbreken van variatie[13][14]. In bijlage 8.1 staat een nadere toelichting op de NGST.
2.1.1 Beoordeling van de motorische ontwikkeling
Het behalen van mijlpalen
De motorische ontwikkeling kan beoordeeld worden op basis van het bereiken van motorische mijlpalen en op basis van kwaliteit van bewegen. Voorbeelden van mijlpalen zijn rollen, kruipen, zitten, staan en lopen. Met behulp van deze mijlpalen wordt beoordeeld of kinderen een voor een bepaalde leeftijd passende motorische vaardigheid beheersen. De leeftijd waarop gezonde kinderen bepaalde mijlpalen bereiken, kent een grote spreiding[15]. Dit geldt ook voor het verdwijnen van vroegkinderlijke reacties, zoals de Moro- en grijpreflex. De variatie in de ontwikkeling van de vaardigheden neemt verder toe naarmate kinderen ouder worden. Het is daarom goed te beseffen dat er weinig wetenschappelijke bewijsvoering bestaat voor de leeftijden waarop deze zogenoemde mijlpalen moeten zijn bereikt. Wel
worden er alarmsignalen onderscheiden die ook afzonderlijk op een afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling kunnen wijzen. Die zijn dan reden tot bezorgdheid over de motorische ontwikkeling van het kind. Zie paragraaf 2.1 en 8.2.
Een tragere ontwikkeling in één van de functies kan ook duiden op een variant van de normale ontwikkeling. Echter, als het kind verschillende mijlpalen laat bereikt of bij flinke vertraging van één mijlpaal, is er volgens geraadpleegde experts reden tot zorg. Wat als ‘flink’ wordt ervaren, is helaas aan subjectiviteit onderhevig. Tenslotte is het belangrijk om bij het beoordelen van de motorische ontwikkeling ook het aanpassingsvermogen (adaptatie) te beoordelen. In paragraaf 1.2.2 wordt hier verder op ingegaan.
Bij het monitoren van de motorische ontwikkeling is ook de kwaliteit van bewegen van groot belang[14]. Als kinderen mijlpalen tijdig bereiken, kunnen ze tòch motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen hebben als de kwaliteit van bewegen onvoldoende is[16].
Samengevat, het is niet eenvoudig om motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen op te sporen. Dat komt door de variërende leeftijdsrange per mijlpaal, de samenhang met andere ontwikkelingsdomeinen (zoals sociaal-emotionele of cognitieve ontwikkeling), het belang van de kwaliteit van de bewegingen, en deze vervolgens te onderscheiden van een normale motorische ontwikkeling[17]. Dit kan ertoe leiden dat interventies niet tijdig of juist ten onrechte worden aangeboden.
2.1.2 Normale ontwikkelingsfasen
Hoewel veel variatie bestaat, worden vanaf de geboorte tot aan de leeftijd van 18 jaar globaal vier ontwikkelingsperioden onderscheiden[11][18]:
- foetale fase: tot 2-3 maanden na de geboorte;
- babyleeftijd: van 2-3 maanden tot loslopen;
- peuterleeftijd: van loslopen tot 4-jarige leeftijd;
- kleuter- en schoolleeftijd: 4-18 jaar
Foetale fase: tot 2-3 maanden na de geboorte
De eerste bewegingen bestaan uit kleine zijwaartse bewegingen van hoofd en romp[17]. Daarna ontstaan langzame extensiebewegingen van de nek[20]. Hierna ontstaan ‘startles’ (kortdurende contracties van spieren), en de gegeneraliseerde bewegingen ofwel ‘general movements’ (GM’s), waaraan alle onderdelen van het lichaam meedoen. De meeste foetussen hebben na een zwangerschapsduur van 16 weken het gehele foetale bewegingsrepertoire tot hun beschikking. De kwaliteit van de GM’s reflecteert de integriteit van het jonge zenuwstelsel. Zie ook paragraaf 1.3.1 voor een nadere toelichting op GM’s. Na de leeftijd van drie à vier maanden worden GM’s geleidelijk vervangen door doelgerichte motoriek (overgang van primaire naar adaptieve variabiliteit); dit is een belangrijke transitiefase[21]. Op de leeftijd van drie maanden heeft het kind een stabiele hoofdbalans ontwikkeld; de voorkeur voor flexiehouding in de armen is verdwenen. Belangrijke voorwaarden voor de ontwikkeling van doelgerichte motoriek zijn de op gang gekomen houdings- en aandachtsregulatie en de ontwikkeling van de visuele perceptie. De overgang naar doelgerichte motoriek verloopt geleidelijk, waarbij sprake is van een cranio-caudale ontwikkelingstendens[10].
Pasgeborenen beschikken over een aantal vroegkinderlijke reflexen en reacties: ze volgen een bepaald ontwikkelingspatroon en verdwijnen op latere leeftijd. Enkele voorbeelden van vroegkinderlijke reacties[15][22] zijn de volgende:
- De Moro-reactie: dit is een reactie die postnataal tot expressie komt omdat de nekpropriocepsis en het vestibulum postnataal forser worden geprikkeld. De reactie kan worden uitgelokt door bij het kind in rugzweefhouding het hoofd plotseling enkele centimeters omlaag te laten vallen en het direct weer op te vangen. De reactie bestaat uit abductie en extensie van beide armen en het openen van de handen, gevolgd door adductie en flexie van de armen. De Moro-reactie verdwijnt op de leeftijd van 4 tot 10 maanden[10][22].
- De grijpreflex van de handen: dit is een tonische flexie van alle vingers na een tactiele stimulus in de handpalm van het kind, bijvoorbeeld een vinger van de onderzoeker. Een stimulus op de handrug veroorzaakt een extensie van de vingers. De grijpreactie verdwijnt op de leeftijd van vier tot negen maanden[22].
Babyleeftijd: van 2-3 maanden tot loslopen
Ontwikkeling van bewegingspatronen
In deze periode ontwikkelen de bewegingspatronen zich verder: reiken, grijpen en manipuleren (van palmair grijpen rond de vijfde maand naar pincetgreep rond de twaalfde maand), omrollen, hoofd gedurende langere tijd opheffen, zitten, kruipen, staan en lopen. De doelgerichte motoriek van de armen loopt een tot twee maanden voor op die van de benen. Ook in deze fase hebben niet alleen rijping van neurale structuren maar ook omgevingsfactoren invloed op de motorische ontwikkeling. Kinderen die vaker op hun buik slapen of geen loopstoeltje hebben, leren bijvoorbeeld sneller kruipen[23][24]. In buikligging leert het kind namelijk de armen te gebruiken om zichzelf omhoog te duwen van de
onderlaag en actief te steunen op zijn armen. Buikligging kan echter uitsluitend geadviseerd worden onder toezicht, omdat voorkomen moet worden dat het kind op de buik in slaap valt. Slapen op de buik geeft immers een verhoogde kans op wiegendood (bit.ly/NJCPrevWd en bit.ly/NJCGezSlp). Daarom wordt ouders aangeraden om het kind uitsluitend onder toezicht op de buik te leggen en alleen als het wakker is.
Reiken en grijpen
Bij het reiken van de arm is eerst sprake van een pre-reikfase: deze fase duurt tot de leeftijd van 4-5 maanden en bestaat uit spontane, niet-doelgerichte bewegingen als onderdeel van de GM’s. De GM’s worden gekenmerkt door een enorme variatie[25]. Vanaf de leeftijd van 4-5 maanden ontstaat het grijpen[10], samen met het ontwikkelen van het diepte zien. Ook de houdingsregulatie ontwikkelt zich dan. Aanvankelijk gebruiken baby’s beide armen om te grijpen; geleidelijk aan ontstaat een voorkeur voor unilateraal grijpen zonder dat er een handvoorkeur aanwezig is.
Door naar doelgericht kruipen
Tussen de leeftijd van zes en 12 maanden ontwikkelt zich het doelgerichte kruipen. Sommige kinderen komen nooit tot kruipen, en sommige andere kinderen slaan bepaalde fasen over, zoals het tijgeren. Er zijn ook kinderen die een andere methode gebruiken om zich te verplaatsen: de billenschuivers. Deze kinderen lopen vaak op een iets latere leeftijd los[26][27].
Gaandeweg leren zitten
Bij het leren zitten is de ontwikkeling van richtingspecificieke houdingsactiviteit een voorwaarde: vanaf de leeftijd van 7-8 maanden neemt de houdingsactiviteit van de spieren toe zodat het kind het evenwicht steeds beter kan bewaren. De selectie van het meest efficiënte houdingsspieractivatiepatroon is rond de leeftijd van 9-10 maanden voltooid. Tussen 12-15 maanden ontwikkelen kinderen ook nog een anticipatoire houdingsactiviteit: het aannemen van een houding die voorafgaat aan een willekeurige beweging, wat een belangrijke rol speelt bij het leren lopen.
Naar doelgericht lopen
Loopbewegingen zijn al vroeg in de ontwikkeling aanwezig. Het duurt ongeveer een jaar voordat doelgericht lopen ontstaat. Neonatale loopbewegingen verdwijnen meestal rond de leeftijd van drie tot vier maanden, tenzij deze dagelijks worden geoefend[28]. Rond de leeftijd van een jaar leert een kind lopen met hulp. Hierop volgen twee belangrijke motorische mijlpalen: het los staan en het lopen zonder hulp. Beide doen een belangrijk beroep op het houdingsregulatiemechanisme van het kind: Het staan en lopen bieden het kind veel informatie die door zenuwcellen naar het centrale zenuwstelsel wordt geleid (afferente informatie) en op basis waarvan het zenuwstelsel zich steeds verder ontwikkelt[12].
Peuterleeftijd: van loslopen tot 4-jarige leeftijd
Loslopen
Op peuterleeftijd leert het kind loslopen en ontwikkelt het vaardigheden die niet in de genetische aanleg/blauwdruk opgenomen zijn, zoals rennen, springen, klimmen/klauteren en voorwerpen hanteren. Het loslopen wordt als een belangrijke vaardigheid beschouwd. Daarom is het vaststellen van deze mijlpaal rond de leeftijd van 18 maanden van belang. Zo is bij prematuren aangetoond dat dit moment sterk voorspellend is voor motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen op vierjarige leeftijd[29].
Hindernissen nemen
Tussen het tweede en derde levensjaar breidt het bewegingsrepertoire zich uit en is het kind voortdurend bezig nieuwe combinaties uit te proberen[14]. Het kind leert in deze periode steeds beter doelgericht strategieën te selecteren. Het kind kan zich zo beter aanpassen aan de omgeving, bijvoorbeeld door het looppatroon aan te passen om over een drempel te stappen en het grijpen aan te passen aan de vorm van het materiaal. In de loop van deze ontwikkelingsfase worden functies verder geïntegreerd en geautomatiseerd. Een verminderde kwaliteit in de motoriek in deze leeftijdsfase kan een aanwijzing zijn om te denken aan (minor) neurologisch disfunctioneren[30].
Kleuter- en schoolleeftijd (4 – 18 jaar)
Op basis van neurologische rijping, ervaring en uitdaging leert het kind zijn motoriek steeds beter af te stemmen. Deze fase wordt ook gekenmerkt door de ontwikkeling van complexe motorische vaardigheden waarvoor speciale oefening nodig is. Voorbeelden zijn schrijven, veters strikken, hinkelen, fietsen en schrijven, maar ook nog meer complexe vaardigheden zoals piano spelen. Deze ontwikkeling loopt door tot in en gedurende de volwassenheid.
2.1.3 Motorische mijlpalen en kwaliteit van de motoriek
Aanbevelingen
2.1.4 Beoordeling van de motorische ontwikkeling door de JGZ
Het afnemen van het Van Wiechenonderzoek (VWO) en de Baacke Fassaert Motoriek Test (BFMT), de twee meest toegepaste testen binnen de JGZ, geeft een indruk van de grove en fijne motoriek. Enkele deeltesten van het VWO en de BFMT en anamnestische gegevens geven ook een indruk van adaptatie (ofwel aanpassingsvermogen).
De JGZ is verantwoordelijk voor het in kaart brengen van de gevolgen van een problematische motorische ontwikkeling voor het dagelijks functioneren, voor de mogelijkheden van het kind om zich aan te passen aan de omstandigheden in relatie tot zijn (eventueel) beperkte mogelijkheden (adaptatie). Het afnemen van deze tests en anamnestische gegevens ondersteunen de JGZ-professionals bij het adviseren van ouders en school over de begeleiding van het kind.
2.2 Motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem: ontstaan, prevalentie en consequenties
Deze paragraaf gaat in op de uitgangsvraag: Wat is een motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem? Hoe ontstaat het? Hoe vaak komen ontwikkelingsproblemen voor in de specifieke leeftijdsfasen van het kind? Wat zijn mogelijke consequenties voor het kind in termen van gezondheid, welzijn en kosten?
Wat is een motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem?
Van een motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem is sprake als een kind zich qua motoriek trager of afwijkend ontwikkelt en hierdoor belemmerd wordt in zijn activiteiten en participatie. Meestal is er dan sprake van beperkingen in zowel variatie (beperkt bewegingsrepertoire) als adaptibiliteit (beperkt vermogen om een handelingsstrategie te selecteren in verschillende omstandigheden)[13]. De oorzaken van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen kunnen gelijktijdig voorkomen en elkaar versterken. Te denken valt hierbij aan een specifieke diagnose die leidt tot beweegarmoede die vervolgens het motorisch leren belemmert. De oorzaken en redenen van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen kunnen worden verdeeld in aangeboren en overige. De meest voorkomende in de algemene populatie worden hieronder beschreven. Het gaat om de volgende:
Aangeboren oorzaken:
• Cerebrale Parese (CP) (zie 1.3.1)
• Developmental Coordination Disorder, (DCD) (zie 1.3.2)
• Neuromusculaire aandoeningen (zie 1.3.3)
Overige oorzaken/redenen:
• Niet-aangeboren hersenletsel (NAH, zie 1.3.4)
• Beweegarmoede (zie 1.3.5)
• Vertraagde en/of atypische ontwikkeling zonder duidelijke of bekende oorzaak (zie 1.3.6).
Prematuriteit is eveneens een belangrijke oorzaak van een motorische ontwikkelingsachterstand[31][32]; dit kan met name leiden tot CP of DCD, en komt daarom bij betreffende subparagrafen (1.3.1 en 1.3.2) aan de orde.
Prevalentiecijfers
Er zijn nagenoeg geen prevalentiecijfers bekend van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen per ontwikkelingsfase. Wel bestaan er prevalentiecijfers van afzonderlijk onderscheiden diagnoses. Het is wel lastig om betrouwbare uitspraken te doen over deze prevalentiecijfers omdat de onderzoeken naar de prevalentie niet goed vergelijkbaar zijn: de criteria om een diagnose te stellen zijn vaak onduidelijk of verschillen. Bovendien bestaan er discussies over de onderscheiden diagnoses CP en DCD. Het is niet duidelijk of het werkelijk om verschillende entiteiten gaat. Volgens inzichten van sommige wetenschappers hebben deze twee belangrijke diagnoses ten dele gemeenschappelijke oorzaken en zijn
ze onderdeel van een continuüm[33]. Andere wetenschappers bestrijden deze visie en geven aan dat de oorsprong van beide diagnoses anders is. Volgens hen zijn bij CP vooral de motorische banen aangedaan en bij DCD het cerebellum en/of de pariëtale cortex[34]. Zolang de discussies hierover nog niet zijn afgerond, wordt in de richtlijn uitgegaan van aparte ziekte-entiteiten. Ze zijn namelijk in de praktijk goed hanteerbaar.
2.2.1 Cerebrale parese
Definitie, prevalentie en diagnosestelling van CP
CP is een blijvende aandoening van de hersenen met blijvende effecten voor de ontwikkeling van houding en beweging, ontstaan voor de eerste verjaardag, die leidt tot beperkingen in dagelijkse activiteiten”[35]. Lees voor meer informatie over de diagnose CP in bijlage 8.3.1. CP is een frequente oorzaak van bewegingsproblemen bij kinderen en komt voor bij ongeveer 2-2,5 van de 1.000 levendgeborenen[36][37][38]. CP komt vaker voor bij kinderen met een zeer laag geboortegewicht, bij prematuren en bij kinderen met zuurstoftekort rond de bevalling. De manier van bevallen (natuurlijke bevalling of sectio) heeft nauwelijks invloed op het ontstaan van CP. Het verloop kan hierop wel van invloed zijn (strakke omstrengeling, foetale nood)[38].
De rol van leeftijd voor de prevalentie van CP
De prevalentie hangt ook samen met de leeftijd waarop de diagnose wordt gesteld. Enerzijds komt het voor dat de bewegingsstoornissen verdwijnen en de diagnose komt te vervallen. Anderzijds wordt de diagnose CP vaak ten onrechte uitgesteld, vooral als er geen belaste medische voorgeschiedenis is. Dit heeft ertoe geleid dat de Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe tot de leeftijd van vijf jaar spreekt van de waarschijnlijkheidsdiagnose CP en vanaf vijf jaar van een definitieve diagnose CP. Uit recent onderzoek blijkt echter dat afwijkende GM’s voor de leeftijd van 3 maanden (zie 2.4) voorspellend zijn voor CP. GM’s zijn bewegingen waarbij alle delen van het lichaam meedoen met gevarieerde bewegingstrajecten, gevarieerde snelheid en gevarieerde amplitude; de bewegingen zijn continue zichtbaar bij een wakker kind, behalve als het kind zich heel druk maakt of huilt66. Kijk voor verdere informatie over CP op www.richtlijnendatabase.nl, www.bosk.nl, www.canchild.ca. Voor een beeld van normale en afwijkende GM’s zie youtube.com/watch?v=N00oXgxrKEo.
Behandeling en begeleiding bij CP
De primaire verantwoordelijkheid voor de behandeling van CP ligt bij kinderfysiotherapeuten en revalidatieartsen[13]. De behandeling van de motorische problemen gerelateerd aan CP is gericht op het stimuleren van de motorische ontwikkeling en het voorkomen van complicaties, zoals contracturen. De behandeling is niet alleen gericht op de kinderen zelf, maar ook op hun ouders. Ze worden begeleid bij de stimulering en verzorging van hun kind. De revalidatie richt zich op activiteiten en participatie volgens het International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health for Children and Youth (ICF-CY) model dat ook wordt ingezet bij andere diagnoses als DCD en neuromusculaire aandoeningen[13][39]. Zie bijlage 8.4 voor een verdere toelichting op de ICF-CY.
Volgens geraadpleegde experts kan men bij ernstige CP hulpmiddelen overwegen zoals een rolstoel, spalk of na het eerste levensjaar botuline-toxine-injecties. Voor zowel een kind met CP als de ouders heeft deze handicap belangrijke consequenties. Het kind heeft vaak extra zorg en hulp nodig om naar school te gaan. Het kind is meer dan andere kinderen afhankelijk van (de hulp en ondersteuning van) andere kinderen, wat een negatieve invloed kan hebben op het gevoel van onafhankelijkheid en welzijn. Het kost ouders soms veel moeite om extra zorg te realiseren. Daarnaast maken ouders vaak extra kosten voor de benodigde zorg, zelfs als het gezin een goede ziektekostenverzekering heeft. Dit is mede het gevolg van het feit dat een groot deel van de financiering van aanpassingen en hulpmiddelen ook afhankelijk is van regelgeving bij gemeenten en scholen. Zie ook paragraaf 1.6 en www.canchild.ca, waarin het belang van tijdige signalering en behandeling van CP wordt toegelicht.
2.2.2 Developmental Coordination Disorder
Definitie en prevalentie van DCD
De belangrijkste criteria voor de diagnose DCD zijn dat de totaalscore of subscore op de Movement ABC-2 onvoldoende is, en dat de aandoening de schoolse prestaties of de algemene dagelijkse activiteiten voortdurend en in belangrijke mate beïnvloedt. Voor een precieze (uitgebreidere) definitie van DCD[40] en nadere informatie over DCD, zie bijlage 8.3.2. De prevalentie van Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) bij schoolgaande kinderen ligt tussen de 1,7 en 19,0%, met een hogere prevalentie bij jongens dan bij meisjes[33][41][42], zie 2.2. Deze variatie is afhankelijk van de definities die men in de literatuur gebruikt (zie bijlage 8.3 Definities van CP en DCD). Het meest gerapporteerd wordt een prevalentiecijfer van 5-6%[42]. Dit betekent dat in Nederland in elke klas van de basisschool tenminste één kind met DCD zit.
Verschijnselen en diagnose
De eerste verschijnselen van DCD kunnen zich al op zeer jonge leeftijd openbaren, maar dit is lang niet altijd het geval. De diagnose wordt doorgaans niet gesteld voor het vijfde levensjaar. Bij een kind van drie tot vijf jaar oud kan de diagnose DCD bij uitzondering worden gesteld als het duidelijk motorische beperkingen laat zien ondanks voldoende leermogelijkheden. Andere oorzaken voor de motorische achterstand moeten dan zijn uitgesloten, zoals deprivatie, genetische syndromen of neurodegeneratieve aandoeningen. Om tussen de leeftijd van drie en vijf jaar oud de diagnose DCD te stellen moeten er ten minste twee onderzoeken worden uitgevoerd met daartussen een interval van minimaal drie maanden. De diagnose kan in dit leeftijdsinterval alleen worden gesteld als op beide momenten aan de criteria voor DCD is voldaan[43][44].
Typische kenmerken van kinderen met DCD
Kinderen met DCD hebben problemen met de fijne motoriek, de grove motoriek of met beide[42]. Fijnmotorische ontwikkelingsproblemen en balansproblemen komen vaak samen voor, maar het komt ook zeer frequent voor dat kinderen alleen fijnmotorische problemen hebben en geen balansproblemen of grofmotorische problemen[46]. Meestal is de motorische uitvoering langzamer, minder accuraat en meer variabel dan van leeftijdgenoten. Dit geeft het algemene beeld dat deze kinderen erg onhandig zijn. Hierdoor ervaren ze vaak problemen met hun leeftijdgenoten, wat kan leiden tot een laag zelfbeeld en/of faalangst[42][45][46]. Hoewel DCD geen gevolg is van een medische conditie, komt DCD vaak voor in combinatie met andere ontwikkelings- en/of gedragsstoornissen, zoals attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autisme spectrumstoornissen (ASS), taalontwikkelingsstoornis (TOS) en leerproblemen (zoals dyslexie). Indien dit het geval is, worden verschillende diagnoses gesteld. De Europese (en Nederlandse) aanbevelingen stellen dat de diagnose en behandeling van comorbiditeit volgens de desbetreffende richtlijnen moeten gebeuren. Zie ook paragraaf 1.4.
Risicofactoren voor DCD
Risicofactoren voor DCD zijn prematuriteit, small-for-gestational-age (SGA; dat wil zeggen: laag geboortegewicht ten opzichte van de zwangerschapsduur), lage APGAR-score, perinatale hypoxie en hypotonie. Bij ernstig prematuren (geboren na een zwangerschapsduur <29 weken) en kinderen die klein zijn bij geboorte (<1.500 gram) is de kans op DCD 40-48%, ook als hun motorische ontwikkeling in de eerste vijf jaar niet noemenswaardig afwijkend is verlopen[47]. Van matig prematuren is eveneens bekend dat ze een verhoogd risico hebben op DCD: elke week dat de zwangerschapsduur korter duurt verhoogt het risico op DCD met 19%[48].
Consequenties van DCD
Een belangrijk gevolg van DCD is dat kinderen minder actief zijn, ook in hun dagelijkse leven (tijdens schoolpauzes, gymlessen en in hun vrije tijd). Experts veronderstellen dat dit het risico verhoogt op overgewicht, minder uithoudingsvermogen en verminderde spierkracht. Ook voor ouders heeft DCD bij hun kind consequenties, vooral op sociaal-emotioneel vlak. De consequenties zijn ernstiger als de diagnose DCD pas laat wordt gesteld. Vaak wordt late diagnose veroorzaakt doordat zorgen van ouders niet serieus zijn genomen. Voor meer informatie zie ook www.balansdigitaal.nl. De primaire verantwoordelijkheid in de begeleiding van DCD is niet eenduidig en afhankelijk van de ernst van de ervaren (complexiteit van de) problematiek. De revalidatiegeneeskunde speelt een belangrijke rol ten aanzien van diagnostiek en (perifere) begeleiding. Zie ook paragraaf 1.6 voor het belang van tijdige signalering en behandeling van DCD. Ouders hebben vaak te maken met extra zorgkosten, al worden deze meestal vergoed door zorgverzekeraars.
2.2.3 Neuromusculaire aandoeningen
Neuromusculaire aandoeningen (NMA) ofwel spierziekten zijn zeldzaam en bijna altijd erfelijk. Ze tasten het functioneren van de spieren aan. Soms is bij de geboorte al duidelijk dat een kind een spierziekte heeft. Een NMA kan echter op elke leeftijd tot uiting komen. De meest voorkomende spierziekten zijn spierdystrofie van Duchenne, Becker spierdystrofie en spinale musculaire atrofie (SMA). Deze ziekten zijn ongeneeslijk.
NMA uiten zich in een vertraagde (psycho)motorische ontwikkeling die gepaard gaat met spierzwakte, hypotonie, hypermobiliteit, verminderde inspanningstolerantie, pijn en/of tintelingen in de spieren[49][50]. NMA zijn meestal sterk invaliderend en vaak levensverkortend. Door een verminderde zelfredzaamheid kan het kind een verminderd welzijn ervaren. In een gezin hebben vaak meer kinderen een NMA. Het gezin ondervindt daarmee doorgaans zowel sociaal-emotionele als financieel-economische consequenties. Het is voor ouders van deze kinderen soms ook moeilijk realiseerbaar om allebei betaald werk te verrichten als ze de zorg hebben voor een kind met een dergelijke aandoening. De primaire verantwoordelijkheid ten aanzien van de behandeling bij NMA ligt bij de NMA-teams van de academische centra, in nauwe samenwerking met de revalidatiegeneeskunde van perifere centra.
2.2.4 Niet-aangeboren hersenletsel
Prevalentie en oorzaken van NAH
Niet-aangeboren hersenletsel (NAH) wordt onderscheiden in traumatisch en niet-traumatisch hersenletsel. De gevolgen van NAH zijn blijvend. Ze kunnen lange tijd een verborgen karakter hebben omdat op jonge leeftijd nog weinig beroep wordt gedaan op hogere cognitieve functies die beschadigd kunnen zijn. Er zijn in Nederland geen prevalentiecijfers bekend voor de leeftijdscategorie die bij de JGZ in zorg is (0-18 jaar). Wel worden jaarlijks 19.000 personen tussen de 0-24 jaar gediagnostiseerd met hersenletsel, van wie 10% matig tot ernstig hersenletsel heeft.
Bij traumatisch hersenletsel is het letsel ontstaan door een oorzaak buiten het lichaam, zoals een val van een trap, een harde klap op het hoofd, het shaken baby-syndroom of binnendringende botgedeeltes als gevolg van schedelbreuk. Zie voor meer informatie over traumatisch hersenletsel ‘Zorgstandaard traumatisch hersenletsel kinderen & jongeren’ die in opdracht van de Hersenstichting is opgesteld[51]. Niet-traumatisch hersenletsel ontstaat door een proces in het lichaam, zoals een infectie van de hersenvliezen (meningitis), tumor, intoxicatie door drugs of alcohol, zuurstofgebrek (hypoxie/anoxie door rookvergiftiging), en epilepsie.
Gevolgen van een NAH
NAH is een belangrijke oorzaak van bewegingsstoornissen die zich soms pas maanden tot jaren na het trauma kunnen openbaren[50][52]. Naast zichtbare consequenties, kunnen kinderen met NAH kampen met minder zichtbare consequenties, zoals concentratieproblemen, overgevoeligheid voor prikkels, geheugenstoornissen, chronische vermoeidheid, een taalontwikkelingsstoornis (TOS), gedragsproblemen of emotionele problemen zoals depressie en gebrek aan zelfvertrouwen. Voor de ouders brengt deze aandoening vaak extra zorgen, stress, inspanningen en kosten met zich mee. Zie https://www.hersenstichting.nl/ALLES-OVER-HERSENEN/HERSENAANDOENINGEN/NIET-AANGEBORENHERSENLETSEL bit.ly/SignNAH. Zie ook paragraaf 1.6 voor het belang van tijdige signalering en behandeling van NAH.
De primaire verantwoordelijkheid voor diagnostiek, behandeling en begeleiding is minder eenduidig dan bij CP en NMA en is afhankelijk van de fase (acuut/chronisch) en ernst van het letsel. Een nauwe samenwerking tussen kinderneuroloog en revalidatieteam is hierbij van belang.
2.2.5 Vertraagde en/of atypische motorische ontwikkeling
Wat is een vertraagde en/of atypische motorische ontwikkeling?
Een vertraagde of atypische motorische ontwikkeling wordt gekenmerkt door een later behalen van mijlpalen en/of een beperkte motorische variatie[15]. Een vertraagde of atypische motorische ontwikkeling is niet gerelateerd aan andere pathologie of ontwikkelingsproblemen. Het is geen afwijkende ontwikkeling maar een extreme presentatie binnen het spectrum van de normale ontwikkeling. Een vertraging (zonder dat sprake is van pathologie of ontwikkelingsproblemen) kan ook het gevolg kan zijn van hypermobiliteit, hetgeen bij ongeveer van 6% van alle kinderen voorkomt[53]. Indien hierbij geen sprake is van klachten wordt het beschouwd als een variatie van het normale[54]. Indien er wel klachten bestaan (zoals pijn, problemen met schrijven en vermoeidheid), kan worden gedacht aan het Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (het hypermobiele type), hetgeen echter niet vaak voorkomt (ongeveer 1 per 10.000 mensen)[55].
Diagnosestelling en gevolgen
Vaak kan pas achteraf worden geconstateerd of er alleen sprake was van een vertraging in de motorische ontwikkeling, dat wil zeggen dat er geen duidelijke oorzaak gevonden is. Als een vertraging invloed heeft op het dagelijks functioneren, zijn kinderen vaak gebaat bij een therapeutische interventie door een gespecialiseerde professional, zoals kinderfysiotherapeut, ergotherapeut of kinderoefentherapeut (zie hoofdstuk over Samenwerking, stroomschema’s figuur 1 en 2 en Bijlage 8.5). Niet alleen een vertraagde ontwikkeling, ook motorisch stereotiep gedrag vraagt om een differentiaaldiagnose. Tenengang bijvoorbeeld kan gerelateerd zijn aan een CP, een orthopedisch probleem (te korte achillespezen) of een stoornis binnen het autismespectrum. Bij hypotonie kan men ook denken aan DCD of CP. Billenschuiven is soms gerelateerd aan hypermobiliteit van de gewrichten. Bij dysmorfieën kan men denken aan genetische of een chromosomale afwijking[50]. De consequenties van een vertraagde of atypische motorische ontwikkeling voor kinderen en hun ouders liggen volgens geraadpleegde experts vooral op het sociaal-emotionele vlak. Vaak is sprake van gedragsmatige aspecten en/of comorbiditeit die om een multidisciplinaire aanpak vragen. Ook geven geraadpleegde experts aan dat ouders soms extra zorgkosten maken.
2.2.6 Ontwikkelingsprobleem als gevolg van onvoldoende beweging
De rol van (on)voldoende bewegen
Motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen kunnen ook ontstaan door onvoldoende beweging. De Beweegrichtlijn definieert een minimaal niveau van bewegen dat nodig is om gezondheidswinst te behalen Zie www.gezondheidsraad.nl voor de aanbevelingen die in de Beweegrichtlijn staan opgenomen.
Onvoldoende beweging kan het gevolg zijn van:
- Omgevingsfactoren zoals een ongunstige fysieke omgeving, gebrekkig beleid van kinderopvang die kinderen onvoldoende in de gelegenheid stelt of ruimte biedt om te bewegen;
- Ouderfactoren: onderstimulatie;
- Onvoldoende financiële middelen van ouders;
- Kindfactoren zoals ziekten, handicaps, psychische of motorische problemen.
Prevalentie van onvoldoende bewegen
Onvoldoende beweging komt steeds meer voor en gaat vaak gepaard met overgewicht. Ook de ernst ervan neemt toe[56]. De prevalentie is hoger in achterstandswijken, waar de mogelijkheden voor kinderen om te bewegen beperkt zijn. In deze wijken voldoet meer dan 95% van zowel de jongens als de meisjes niet aan de Beweegrichtlijn. Geleidelijk aan zien we dit probleem in alle lagen van de bevolking toenemen als gevolg van veel ‘gamen’, computeren en weinig fysiek spelexpert-opinion.
Behalve gunstige effecten voor de gezondheid (zoals de preventie van overgewicht) bestaan er ook aanwijzingen dat meer bewegen bij kinderen leidt tot een hoger gevoel van welzijn. Buiten bewegen in een natuurlijke omgeving draagt daar volgens sommige studies ook meer aan bij dan binnen bewegen[57]. Mogelijke kosten ten gevolge van motorische problemen door onderstimulatie hangen samen met de mogelijke comorbiditeit en de extra benodigde inzet en investeringen van ouders om het kind alsnog te laten bewegen.
2.3 Samenhang tussen motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen en andere ontwikkelingsproblemen
Deze paragraaf gaat in op de uitgangsvraag: Welke samenhang bestaat er tussen motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen en problemen in andere ontwikkelingsdomeinen?
Achterstanden in verschillende ontwikkelingsdomeinen
De motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen loopt parallel met de spraak-taal-ontwikkeling en de sensorische, psychosociale en cognitieve ontwikkeling. Ook bestaat interactie tussen deze ontwikkelingen[15][41]. Een achterstand valt regelmatig eerst op in een enkel ontwikkelingsdomein, vaak in de grove motoriek. Daarna wordt een achterstand vaak pas zichtbaar in andere ontwikkelingsdomeinen (zoals de cognitieve ontwikkeling) of wordt een achterstand in een ontwikkelingsdomein beïnvloed door een achterstand in een ander ontwikkelingsdomein[41].
Het samengaan met andere diagnoses
Vooral bij DCD is vaak sprake van comorbiditeit. DCD komt zeer frequent voor bij kinderen met AD(H)D, ASS/PDD-NOS, leerproblemen (dyslexie en dyscalculie), taalontwikkelingsproblemen, een dysfatische ontwikkeling en/of (faal-)angst. Daarnaast kan DCD gepaard gaan met psychosociale problemen. Voor nadere informatie over betreffende onderwerpen verwijzen we naar de JGZ-richtlijnen
Er is geen sprake van DCD als er problemen zijn in de cognitieve ontwikkeling en als de motorische uitvoering past bij het cognitieve niveau[58][59]. Zie ook paragraaf 2.1.2 en bijlage 3.
Niet alleen wordt bij veel kinderen met ADHD ook de diagnose DCD gesteld (namelijk bij een derde deel)[59], kinderen met verdenking op DCD hebben ook vaker aandachtsproblemen/hyperactiviteit, problemen met lezen en spellen en problemen met non-verbale en sociale communicatievaardigheden[60][61][62]. Ook bij CP gaan motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen vaak gepaard met andere ontwikkelingsproblemen, zoals stoornissen in sensoriek, cognitie, communicatie, perceptie, gedrag, visus en gehoor. Verder worden motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen vaak gezien bij chromosomale en genetische afwijkingen (zoals het syndroom van Down), en bij stofwisselingsaandoeningen. Zie voor een uitgebreid overzicht het handboek van Njokiktjien[63]. Meer informatie over CP is te vinden in bijlage 3.
Beschreven sterke samenhang is voor de JGZ reden om bij het vermoeden of bestaan van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen, alert te zijn op comorbiditeit of andere diagnoses. Dit kan immers grote consequenties hebben voor begeleiding, verwijzing en behandeling.
2.4 Enkelvoudige motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen versus complexe ontwikkelingsproblemen
Deze paragraaf gaat in op de uitgangsvraag: Hoe kunnen JGZ-professionals enkelvoudige motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen onderscheiden van complexe ontwikkelingsproblemen?
Bij enkelvoudige problematiek bestaan er uitsluitend problemen in de motoriek zelf. Bij meervoudige problematiek daarentegen zijn er verschillende ontwikkelingsdomeinen betrokken. Dit onderscheid kan men alleen maken wanneer naast de motoriek ook de overige ontwikkelingsdomeinen worden onderzocht.
Ontwikkelingsonderzoek bij 0-4 jarigen
Bij kinderen van nul tot vier jaar biedt het Van Wiechenonderzoek (VWO) een handvat aan JGZprofessionals om enkelvoudige en meervoudige ontwikkelingsproblemen te onderscheiden. Het VWO omvat immers verschillende ontwikkelingsdomeinen: fijne motoriek/adaptatie/persoonlijkheid/sociaalgedrag, communicatie en grove motoriek, al biedt het VWO volgens experts een vrij grove indeling van de verschillende ontwikkelingsdomeinen. Naast het VWO kan men door middel van onderzoek, observatie of anamnese een indruk krijgen van onder andere, de sociaalemotionele ontwikkeling.
Ontwikkelingsonderzoek bij 5-6;6 jarigen
Om bij kinderen van vijf tot zesenhalf jaar enkelvoudige motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen te kunnen onderscheiden van complexe ontwikkelingsproblemen, kunnen, naast de Baacke Fassaert Motoriek Test (BFMT), aanvullende onderzoeken (inclusief observatie) worden uitgevoerd en/of vragenlijsten worden afgenomen. Ook kunnen (hetero)anamnestisch gegevens worden verkregen. Er ontstaat een indruk van de psychosociale ontwikkeling aan de hand van, bijvoorbeeld, de afname van de Strenghts and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ), door observatie van de interactie van het kind met ouder(s) en/of JGZprofessional of door anamnese bij zowel ouder(s) als kind. Van de cognitieve ontwikkeling, van de spraak-taalontwikkeling maar ook van andere ontwikkelingsdomeinen kan een beeld verkregen worden door na te vragen hoe het op school gaat. Op deze leeftijd wordt doorgaans ook een visus- en gehoortest afgenomen. Deze testen geven niet alleen een indruk van de visus en het gehoor maar ook van het gedrag van het kind tijdens het afnemen van deze testen. Bij het vermoeden van meervoudige problematiek, kan besloten worden tot een contactmoment op indicatie, multidisciplinair overleg en/of verwijzing naar een therapeut of specialist.
2.5 Belang van tijdige signalering en behandeling
Deze paragraaf gaat in op de uitgangsvraag: Wat is het belang van tijdige signalering en behandeling?
Hoe kan de JGZ hieraan op een effectieve en efficiënte wijze bijdragen?
Belang van timing en kwaliteit van diagnosestelling
Voor kinderen met een motorische ontwikkelingsachterstand is het belangrijk dat hun problemen op tijd worden gesignaleerd. De verschillende diagnoses vragen elk om een andere behandeling. Tijdige en adequate behandeling en begeleiding verhogen niet alleen de kans op een betere motorische ontwikkeling, maar ook de kans op participatie op school. Wel moet men ervoor waken een diagnose te vroeg te stellen omdat dit vaker zal leiden tot een fout-positieve diagnose.
De rol van JGZ in signalering en behandeling
De JGZ kan op een effectieve wijze bijdragen aan tijdige signalering door enerzijds goede kennis te hebben van de mogelijke oorzaken van een motorische ontwikkelingsachterstand, de signalen die hierop kunnen wijzen en de mogelijke gevolgen, en anderzijds bestaande onderzoeksmethoden vakkundig te gebruiken. Tevens is van belang dat de JGZ adequaat handelt naar aanleiding van de bevindingen, dus de juiste adviezen geeft, adequaat verwijst en het vervolg bewaakt. Naast goede scholing is ervaring voor goed medisch besliskundig handelen bij het beoordelen van de motorische ontwikkeling eveneens van belangexpert-opinion. Ook is gewenst dat de JGZ-professionals de sociale kaart goed kennen en benutten, zodat overleg met andere professionals en/of verwijzing effectief en efficiënt is, zie hoofdstuk 4. Hierna wordt kort ingegaan op het belang van tijdige diagnostiek en behandeling bij de verschillende diagnoses.
2.5.1 Cerebrale parese
Hoewel er weinig onderzoek is verricht naar de behandeling van CP, bestaat er wel evidentie voor de effectiviteit van vroeg aangeboden interventies. Dit wijst erop dat vroege opsporing en vroegtijdige behandeling de effectiviteit van de behandeling kunnen verbeteren[64]. Daarnaast is aannemelijk dat juist een behandeling op jonge leeftijd zinvol is, omdat in de jongere jaren de plasticiteit van de hersenen het grootst is. Er worden dan zeer veel nieuwe verbindingen aangelegd. De JGZ kan bijdragen aan vroegtijdige behandeling door het (op indicatie) (laten) verrichten van neurologisch onderzoek, vooral in het eerste levensjaar (zie paragraaf 3.2)
2.5.2 Developmental Coordination Disorder
De diagnose DCD moet niet te vroeg gesteld worden vanwege mogelijke overdiagnostiek (zie paragraaf 2.1.2). Tegelijkertijd is vroege herkenning wel belangrijk om op tijd therapie te kunnen inzetten, zeker omdat DCD leidt tot veel andere problemen, zoals leer- en schrijfproblemen en psychologische stress[65]. De JGZ kan een prominente rol spelen bij de diagnostiek van DCD door zowel grofmotorische als fijnmotorische signalen goed te monitoren. Grofmotorische signalen voor DCD bij het voorschoolse kind zijn vertraagde motorische mijlpalen (zitten, staan, lopen), en vergeleken met leeftijdsgenoten vaak vallen, uit evenwicht zijn, moeite met optillen van één voet zonder uit balans te raken, een hekel aan klimmen hebben (angstig), moeite hebben met springen of op een driewieler rijden, en sneller vermoeid zijn. Fijnmotorische signalen voor DCD vanaf de schoolse leeftijd zijn weinig interesse voor constructiespeelgoed (LEGO, blokken), moeite met vasthouden van potloden en krijtjes, moeite met tweehandige activiteiten, zoals knippen en knopen dichtdoen, en moeite met het generaliseren van het geleerde.
2.5.3 Niet-aangeboren Hersenletsel of beweegarmoede
Wordt een motorische ontwikkelingsstoornis veroorzaakt door NAH of beweegarmoede, dan kan de JGZ met het afnemen van een goede (hetero-)anamnese bijdragen aan tijdige signalering. Tijdige herkenning en behandeling lijken de kansen van het kind op een optimale ontwikkeling te vergrotenexpert opinion. Ten aanzien van hersenletsel dat veroorzaakt wordt door ongevallen kan de JGZ enerzijds een rol spelen bij het geven van adviezen teneinde ongevallen te voorkomen (primaire preventie), en anderzijds bij de herkenning van de symptomen van NAH en daarop het verwijsbeleid afstemmen.
2.6 Risicofactoren en beschermende factoren
Wat zijn risicofactoren en beschermende factoren voor een afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling?
Zie voor wetenschappelijke onderbouwing Evidence 2.6.1
Tabel 2.2 Relatiesa tussen risicofactoren/beschermende factoren en motorische ontwikkeling volgens
reviews van Golding[85] en Hwang[84], en het balansmodel van Bakker[96].
| Niveau | Risicofactoren | Beschermende factoren | |
| Microsysteem | Ouder factoren | Meer dan 4 glazen alcohol per dag tijdens de zwangerschap | Consumptie van vis of visolie tijdens de zwangerschap |
| Roken tijdens de zwangerschap | Borstvoeding | ||
| Cannabis en drug gebruik (ecstasy, cocaïne) | Positief zelfbeeld bij de moeder | ||
| Ziekte bij de moeder (epilepsie, diabetes) | Positieve attitude van de moeder ten opzichte van het kind | ||
| Acute prenatale infecties bij de moeder (influenza, HIV) | Hoger IQ bij de moeder | ||
| Complicaties tijdens zwangerschap en geboorte | Hogere leeftijd van de moeder (grove motoriek) | ||
| Aspirine gebruik tijdens de zwangerschap | Meerdere kinderen in het gezin | ||
| Hogere leeftijd van de moeder (fijne motoriek) | Etnische achtergrond (Afrikaanse of Indiase oorsprong) | ||
| Deficiënties van essentiële sporenelementen (ijzer, jodium en schildklierhormoon) | |||
| Blootstelling aan polychloorbifenylen (PCB), broomhoudende vlamvertragers, pesticiden of zware metalen (lood, kwik, arseen, mangaan) tijdens zwangerschap en borstvoeding |
|||
| Ongewenste zwangerschap | |||
| Kind factoren | Prematuriteit (< 37 weken) | ||
| Laag geboortegewicht (< 2500g) | |||
| Asfyxie en lage APGAR score (<3) bij geboorte | |||
| Neonatale problemen (hyperbilirubinemie, respiratory distress-syndroom, meningitis) | |||
| Ondervoeding en achterblijvende groei | |||
| Medicatie (steroïden, morfine, dexamethason) en medische behandeling | |||
| Gezin factoren | Weinig spel en leermaterialen in huis | Voldonde spel en leermaterialen in huis | |
| Hoge inname van eiwit en calorieën | Goede gehechtheid | ||
| Autoritaire opvoedingsstijl | |||
| Slechte gehechtheid | |||
| Mesosysteem | Sociale (buurt-) factoren | Slechte huisvesting | Goede huisvesting |
| Macrosysteem | Laag opleidingsniveau | Goed gezinsinkomen |
(a De sterkte van de relaties varieert, evenals de bewijskracht van de in de reviews aangehaalde literatuur. Ook geldt dat als er geen nadere informatie is vermeld, zoals bijvoorbeeld aantallen, zoals bij de risicofactor roken (vanaf welk aantal sigaretten) of hogere leeftijd van de moeder (vanaf welke leeftijd), deze ook niet zijn beschreven in de reviews van Golding en Hwang[84][85].)
Aanbevelingen
2.7 Lijst met gebruikte afkortingen
ADHD = Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
ADL = Algemene Dagelijkse Levensverrichtingen
AIMS = Alberta Infant Motor Scale
APGAR = Appearance (kleur), Pulse (hartslag), Grimace (reactie op prikkels), Activity (spiertonus) en Respiration (ademhaling)
ASQ = Ages and Stages Questionnaire
ASS = Autisme Spectrum Stoornis
ATNR = Asymmetrische tonische nekreflex
Bayley-III-NL = Bayley Scale of Infant and Toddler Development – Third edition (Dutch version)
BFMT = Baecke-Fassaert Motoriektest
BOTMP = Bruininks-Oseretsky-Test of Motor Proficiency
CMSP = Children’s Activity and Movement in Preschool Study Motor Skills Protocol
CP = Cerebrale Parese
CVO = Coordinatie Vragenlijst voor Ouders (nederlandse vertaling van de DCDQ)
DCD = Developmental Coordination Disorder
DCDQ = Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire
DSM = Diagnostic Statistical Manual
EACD = European Academy of Childhood Disability
EB = Evidence- based
FSHD = Facioscapulohumerale spierdystrofie
GA = Gestational Age
GM(‘s) = General Movement(s)
GMO = Groninger Motoriek Observatie Schaal
GMRS = Gross Motor Rating Scale
HINT = Harris Infant Neuromotor Test
HMSN = Hereditaire Motorische en sSensorische nNeuropathie
IB’er = Interne Begeleider
IMMQ = Infant Motor Motivation Questionnaire
IMP = Infant Motor Profile
JGZ = Jeugdgezondheidszorg
KFT = Kinderfysiotherapeut
KNMG = Koninklijke Nederlandse Maatschappij tot bevordering der Geneeskunst
LEFF = Lifestyle, Energy, Fun & Friends
LGD = Limb-girdle spierdystrofie
LPK = Landelijk Professioneel Kader
M-ABC = Movement Assessment Battery for Children
MET = Metabolic Equivalent of Taks
MGRS = Multicentre Growth Reference Study
MMT = Maastrichtse Motoriek Test
MOQ-T = Motor Observation Questionnaire for Teachers (Engelse versie van de GMO)
MRT = Motor Remedial Teacher
NAH = Niet-aangeboren hersenletsel
NGST = Neurale Groep Selectie Theorie
NICU = Neonatale Intensive Care Unit
NMA = Neuromusculaire aandoening
NNGB = Nederlandse Norm Gezond Bewegen
NPV = Negative Predictive Value
NVK = Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde
PB = Practice-based
PCB = Polychloorbifenylen
PCDI = Preschool Child Development Inventory
PDMS-2 = Peabody Developmental Motor Scales-2
PGMQ = Preschooler Gross Motor Quality Scale
PPV = Positive Predictive Value
RCT = Randomized Control Trial
School AMPS = School version of the Assessment of Motor and Process skills
SDQ = Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire
SGA = Small for Gestational Age
SMA = Spinale Musculaire Atrofie
TIMPSI = Test of Infant Motor Performance Screening Items
TINE = Touwen Infant Neurological Examination
TNO = Nederlandse Organisatie voor Toegepast Natuurwetenschappelijk Onderzoek
ToP programma = Transmurale Ontwikkelingsondersteuning voor Prematuur geboren kinderen en
hun ouders
VRA = Nederlandse Vereniging voor Revalidatieartsen
VWO = Van Wiechenonderzoek
VWS = Van Wiechenschema
WHO = World Health Organisation
WRITIC = Writing Readiness Inventory Tool in Context
ZNA = Zurich Neuromotor Assessment
3 Signaleren en diagnostiek
In dit hoofdstuk worden de volgende uitgangsvragen beantwoord:
• Meetinstrumenten om deze ontwikkeling te meten en over de tijd te volgen (uitgangsvraag 3.1);
• De vraag waaruit een oriënterend neurologisch JGZ-onderzoek dient te bestaan (uitgangsvraag 3.2).
Zie voor de wetenschappelijke onderbouwing de Evidence 3.1.1 en 3.1.2.
3.1 Meetinstrumenten en werkwijzen om motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen te signaleren en te volgen binnen de JGZ
Aanbevelingen
3.2 Oriënterend neurologisch onderzoek in de JGZ
Aanbevelingen
4 Preventie
Voorlichting, advisering en begeleiding door de JGZ
Het doel van dit hoofdstuk is om te beschrijven welke adviezen gegeven kunnen worden door de JGZ aan ouders (uitgangsvraag 3.1), aan scholen, kinderdagverblijven, voor- en naschoolse opvang en gemeenten (uitgangsvraag 3.2) om de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen te stimuleren en te verbeteren.
4.1 Individuele preventieve adviezen en interventies aan ouders om de motorische ontwikkeling te stimuleren
De aanbevelingen zijn gesplitst in leeftijdscategorieën, daar waar nodig. De aanbevelingen zijn bestemd voor de JGZ-professionals zelf (en dus niet bestemd voor uitvoering op organisatieniveau).
Aanbevelingen
4.2 Collectieve adviezen aan de omgeving van het kind ten behoeve van het stimuleren van de motorische ontwikkeling (universele preventie)
Uitgangsvraag
Wat zijn bij het vaststellen van risicofactoren of met het oog op preventie vanuit de JGZ, collectieve adviezen aan de omgeving van het kind (zoals kinderopvang, peuterspeelzalen, scholen, gemeenten) om de motorische ontwikkeling te stimuleren?
Zie wetenschappelijke onderbouwing in Evidence 4.2.1.
Aanbevelingen
5 Samenwerkingsafspraken: verwijzen en nazorg
Optimale zorg voor kinderen met motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen vraagt om een goede samenwerking tussen de JGZ, ketenpartners en andere zorgverleners. Experts geven aan dat er grote verschillen bestaan in zorgaanbod (van specialisten) tussen de verschillende regio’s. De heterogeniteit van de sociale kaart maakt het moeilijk om landelijke afspraken te realiseren. Daarom is het van belang dat de JGZ vooral regionale afspraken maakt en niet zo zeer landelijke afspraken nastreeft. In deze richtlijn staat een blauwdruk voor lokale samenwerkingsafspraken, weergegeven in stroomschema’s (Figuur 1 en 2).
Leeswijzer
De subparagrafen van sectie 5 zijn iets anders opgebouwd dan van secties 2 en 3. Er bleek veel overlap te bestaan tussen de antwoorden op de uitgangsvragen die geformuleerd staan in de paragrafen 5. Daarom zijn de aanbevelingen die voortkomen uit deze uitgangsvragen samengevoegd in paragraaf 4.0. Om dezelfde reden zijn ook de stroomschema’s (Figuur 1 en 2) die samenhangen met de beantwoording van deze uitgangsvragen, in sectie 5.0 opgenomen. In deze stroomschema’s staat een overzicht van de vervolgstappen die kunnen plaatsvinden na het afnemen van respectievelijk het Van Wiechenonderzoek (VWO) en de Baecke-Fassaert Motoriektest (BFMT). Deze beslisbomen zijn ook van toepassing voor prematuur geboren kinderen, maar voor deze speciale doelgroep zijn ook extra zorgpaden beschikbaar. Deze staan benoemd in de aanbevelingen. Volledigheidshalve wordt gemeld dat de JGZ (extra) controles, overleggen met externen (zoals (voor-)scholen, huisartsen, specialisten), en verwijzingen altijd in overleg doet met en na toestemming van de ouders of wettelijk vertegenwoordigers en/of jeugdigen zelf (conform Wet Geneeskundige Behandel Overeenkomst, WGBO). Dit wordt daarom niet apart vermeld in de aanbevelingen.
Figuur 1 en 2: Stroomschema’s voor de vervolgstappen na afname van het Van Wiechenonderzoek (VWO) bij elk consult tussen de leeftijd van 0 en 4;6 jaar (Figuur 1) en na afname van de Baecke- Fassaert Motoriektest (BFMT) op 5-6;6-jarige leeftijd (Figuur 2)
Toelichting: Elke ruit omvat een vraag waarop ‘ja’ of ‘nee’ kan worden geantwoord. Daaropvolgend volgt hetzij een nieuwe vraag (ruit), hetzij een actie (rechthoek), hetzij een conclusie (rond). Soms zijn meerdere vervolgacties mogelijk, afhankelijk van de ernst van de situatie en/of de DD.
DD = differentiaaldiagnose en is een lijst met mogelijke diagnoses, die door nadere diagnostiek kunnen worden uitgesloten (Zie voor een globaal overzicht van de verschillende diagnoses hoofdstuk 1).
KFT = kinderfysiotherapeut; afhankelijk van de problematiek en de lokale samenwerkingsafspraken kan ook verwezen worden naar ergotherapeut of kinderoefentherapeut
MRT = motorisch remedial teacher
IB’er = intern begeleider
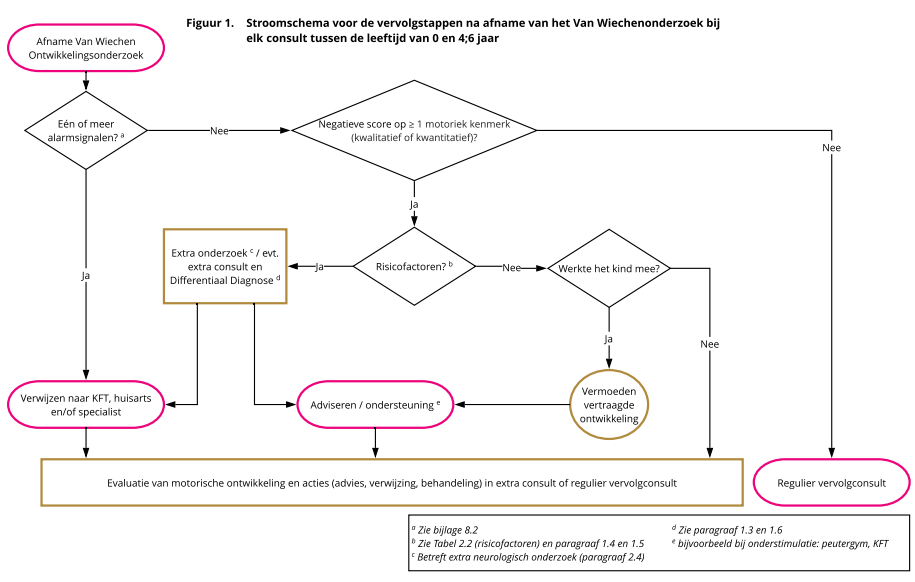
Aanbevelingen
6 Totstandkoming
Werkwijze
De teksten voor de conceptrichtlijn zijn geschreven door een kernteam (Marlou de Kroon, MD PhD projectleider, Sanne te Wierike, MSc, Judith de Best, MSc, Caren Lanting, MD PhD). Voor de start van het project zijn een projectgroep en een werkgroep samengesteld. De projectgroep en de werkgroep zijn samengesteld uit experts op het gebied van motorische ontwikkeling. In elke fase van het project zijn met de leden afspraken gemaakt en vastgelegd over taken en rollen. Tijdens de eerste projectgroep- en werkgroep vergadering zijn de uitgangsvragen besproken en nader gespecificeerd. Hierna is er een systematische literatuurreview verricht door ErasmusMC gebaseerd op de uitgangsvragen. De leden van het kernteam hebben de literatuur bestudeerd en samengevat. De teksten werden inzichtelijk gepresenteerd aan de deelnemers van de projectgroep en werkgroep. Deze teksten zijn tijdens vier projectgroepvergaderingen en vier werkgroepvergaderingen doorgenomen en aangepast; ook zijn er aanbevelingen opgesteld. Tot slot heeft een gemeenschappelijke vergadering plaats gevonden van werken projectgroep om de aanpassingen op basis van de landelijke commentaarronde en de praktijktest te toetsen.
De afspraken die tijdens de projectgroepvergaderingen werden gemaakt, kwamen steeds ter toetsing terug in de werkgroep. De definitieve beslissingen werden genomen in de werkgroepvergaderingen. Veel leden van de projectgroep en werkgroep zijn ook afzonderlijk per e-mail of telefonisch geraadpleegd. Zowel binnen als buiten de projectgroep en werkgroep zijn met experts semigestructureerde diepteinterviews afgenomen. Alle activiteiten hebben geresulteerd in een conceptrichtlijn (april 2016). Op basis van de inhoud van de conceptrichtlijn en indicatoren is een registratieprotocol opgesteld.
Tot slot is een klankbordgroep geraadpleegd bestaande uit een (landelijke) vertegenwoordiging van ouders (Balans) en uit experts op het gebied van de JGZ, kinderfysiotherapie, kinderrevalidatie, kinderoefentherapie, ergotherapie, kindergeneeskunde, kinderneurologie, en vertegenwoordigers van kinderopvang en scholen.
Concepten van de richtlijn, het registratieprotocol en de indicatoren zijn op 6 juni 2016, 20 september 2016 en 23 januari 2017 beoordeeld door de Richtlijn Advies Commissie (RAC).
Hierna is gestart met een praktijktest van vier maanden in de tweede helft van 2017, onder JGZprofessionals van verschillende JGZ-organisaties: CJG Rijnmond, en GGD West-Brabant en GGD Zeeland. Deze JGZ-professionals hebben middels een vragenlijst hun feedback gegeven. De conceptrichtlijn is in juni 2016 ook voorgelegd aan de leden van de klankbordgroep. Tijdens de praktijktest, is ook de landelijke commentaarronde uitgevoerd.
Na het verwerken van de feedback van de resultaten van de praktijktest en de feedback van de landelijke commentaarronde, is de richtlijn op 22 juni 2018 bijgesteld en opnieuw beoordeeld door de RAC. Vanwege vele landelijke discussies en de moeite tot algemene consensus te komen is de richtlijn via de RAC voorgelegd aan vertegenwoordigers van de AJN, V&VN, VVDA en aan ACTIZ en GGD GHOR, waarna de laatste wijzigingen aan de richtlijn zijn verwerkt in november 2018. Op …..2019 is de richtlijn definitief goedgekeurd en geautoriseerd door de RAC.
Cliëntenparticipatie
In de klankbordgroep nam Balans deel als vertegenwoordiger van ouders met kinderen met motorische problematiek. Ouderparticipatie heeft tevens plaatsgevonden door middel van een schriftelijke vragenlijst, die door de JGZ-professional bij het contactmoment aan ouders werd gegeven. Ouders hebben hierbij toestemming geven voor het geanonimiseerd gebruik van de gegevens.
7 Verantwoording
Wetenschappelijke bewijsvoering
De eerste stap bij de ontwikkeling van de richtlijn bestond uit een systematisch literatuuronderzoek in de database Embase voor de verschillende uitgangsvragen. Hierbij is gebruik gemaakt van de expertise van de informatiespecialist van het Erasmus MC, Wichor Bramer. De gevonden artikelen werden door twee leden van het kernteam (StW en JdB) beoordeeld op relevantie op basis van titel en abstract. Bij verschil van mening tussen de twee beoordelaars werd in onderling overleg en zo nodig met de projectleider (MdK) consensus bereikt. Relevante artikelen werden gewaardeerd aan de hand van drie aspecten: methodologische kwaliteit, toepasbaarheid in de praktijk en toepasbaarheid binnen de Nederlandse gezondheidszorg. De kwaliteit van bewijs, ook wel aangeduid als de mate van zekerheid van de effectgrootte, werd beoordeeld met behulp van GRADE185. GRADE is een methode die per uitkomstmaat van een interventie een gradering toekent aan de kwaliteit van bewijs op basis van de mate van vertrouwen in de schatting van de effectgrootte (zie tabel 6.1.1). Een belangrijk verschil tussen GRADE en andere beoordelingssystemen, zoals het niveau I-IV systeem of A1-D systeem, is dat GRADE niet alleen kijkt naar het studie design maar ook andere factoren overweegt die de kwaliteit van bewijs bepalen (zie tabel 6.1.1).
Na selectie van de meest relevante literatuur werden de artikelen over interventies (hoofdstuk 3) beoordeeld op kwaliteit van het onderzoek en gegradeerd naar mate van bewijs. Bij studies naar mijlpalen en risicofactoren met betrekking tot de motorische ontwikkeling (hoofdstuk 2) werd afgezien van een gradering van de kwaliteit van bewijs. Dat geldt ook voor studies naar de validiteit, betrouwbaarheid en normering van screenings- en diagnostische instrumenten. De studies zijn wel volgens de GRADE-systematiek beoordeeld.
Daarnaast is de Nederlandstalige literatuur die betrekking heeft op de Nederlandse situatie intensief bestudeerd. Het ging hierbij vooral om literatuur over het Van Wiechenonderzoek (VWO) en de Baecke-Fassaert Motoriektest (BFMT). Deze tests worden beiden toegepast binnen de Nederlandse JGZ.
Tabel 6.1.1 Indeling van de kwaliteit van bewijs of mate van zekerheid ten aanzien van de effectgrootte voor een uitkomstmaat volgens GRADE.
| Mate ven zekerheid over effectgrootte | Omschrijving |
| Groot | Het werkelijke effect ligt dicht in de buurt van de schatting van het effect. |
| Matig | Het werkelijke effect ligt waarschijnlijk dicht bij de schatting van het effect, maar er is een mogelijkheid dat het hier substantieel van afwijkt. |
| Gering | Het werkelijke effect kan substantieel verschillend zijn van de schatting van het effect. |
| Zeer gering | Het werkelijke effect wijkt waarschijnlijk substantieel af van de schatting van het effect. |
Tabel 6.1.2 Criteria op basis waarvan de kwaliteit van bewijs of mate van zekerheid ten aanzien van de effectgrootte wordt bepaald.
| Type bewijs | RCT start in de categorie ‘hoog’. Observationele studie start in de categorie ‘laag’. Alle overige studietypen starten in de categorie ‘zeer laag’. |
|
| Afwaarderen | ‘Risk of bias’ | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
| Inconsistentie | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
|
| Indirect bewijs | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
|
| Onnauwkeurigheid | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
|
| Publicatiebias | − 1 Waarschijnlijk − 2 Zeer waarschijnlijk |
|
| Opwaarderen | Groot effect | + 1 Groot + 2 Zeer groot |
| Dosis response relatie | + 1 Bewijs voor gradiënt | |
| Alle plausibele confounding | + 1 zou een effect kunnen reduceren + 1 zou een tegengesteld effect kunnen suggereren terwijl de resultaten geen effect laten zien |
|
Aanbevelingen in deze richtlijn zijn, waar mogelijk, gebaseerd op wetenschappelijk bewijs. Ze zijn verder aangevuld met kennis, ervaring en meningen van de leden van de projectgroep en werkgroep. Voor het formuleren van aanbevelingen moet men ook rekening houden met voorkeuren van kinderen/jongeren en hun ouders, kosten, beschikbaarheid, randvoorwaarden of organisatorische aspecten. De uiteindelijk geformuleerde aanbeveling is het resultaat van het beschikbare bewijs in combinatie met voorgaande genoemde aspecten.In alle fasen van de richtlijnontwikkeling is geprobeerd rekening te houden met de implementatie van de richtlijn en de daadwerkelijke uitvoerbaarheid van de aanbevelingen. Daarbij is expliciet gelet op factoren die de invoering van de richtlijn in de praktijk kunnen bevorderen of belemmeren.
Zoekstrategie
Artikelen werden gezocht door het verrichten van systematische zoekacties in Embase. Bij elke uitgangsvraag hoort een aparte zoekstrategie (bijlage 8.6). Naast de literatuur uit de search zijn er bij een aantal vragen ook publicaties meegenomen uit de archieven van de leden van de projectgroep en werkgroep, mits zij voldeden aan de inclusiecriteria.
Overige overwegingen
De richtlijntekst is zoveel mogelijk gebaseerd op bewijs uit de literatuur. Het bleek niet altijd mogelijk bewijs te vinden omdat er geen literatuur voorhanden was, of de kwaliteit van de gevonden literatuur onvoldoende of onbekend was. Als het niet mogelijk was uit te gaan van eigen, door het kernteam uitgevoerd, systematisch literatuuronderzoek werd gebruik gemaakt van, of verwezen naar richtlijnen, protocollen en verslagen van nationale en internationale gezondheidsorganisaties, beroepsorganisaties en wetenschappelijke verenigingen. Ook zijn meerdere experts geraadpleegd in diepte-interviews. Leverde ook dit geen resultaat op, dan werd gezocht naar consensus binnen de werkgroep.
Belangenverstrengeling
Alle deelnemers aan de projectgroep en werkgroep hebben een onafhankelijkheidsverklaring ingevuld.
Er hebben zich geen leden gemeld met een mogelijke belangenverstrengeling.
7.1 Verantwoording literatuursearches en searchstrategieën (was bijlage 6)
Literatuursearches
Uitgangsvraag 2.1
In Embase is in de periode januari-juni 2016 gezocht naar literatuur waarin voor gezonde kinderen (0-19 jaar) de gemiddelde leeftijd wordt gegeven waarop motorische mijlpalen werden bereikt. Er is gezocht naar artikelen die betrekking hebben op zowel grove motoriek als fijne motoriek. De gebruikte zoekstrategie staat in bijlage 8.3.2.
Artikelen werden geëxcludeerd op basis van het bestuderen van titel en abstract indien:
(1) zij betrekking hadden op specifieke doelgroepen, zoals dove kinderen of kinderen met een syndroom
(2) zij betrekking hadden op motorische ontwikkeling in relatie tot risicofactoren en/of interventies. Na exclusie werden 131 artikelen geïncludeerd.
Het doel van de uitgangsvraag was om gegevens over mijlpalen in relatie tot leeftijd, geslacht en etniciteit in relatie tot motorische ontwikkeling te destilleren uit bestaande wetenschappelijke onderzoeken. Omdat het niet de bedoeling was verschillende zorgprocessen te vergelijken, zijn geen GRADE-tabellen opgesteld (zie Uitleg over GRADE in 6.1. De studies zijn wel volgens de GRADE-systematiek beoordeeld188.
De kwaliteit van het bewijs voor deze uitgangsvraag is zeer laag omdat studies over dit onderwerp vaak een dwarsdoorsnede onderzoeksopzet hanteren. Daardoor kon niet worden uitgesloten dat gevonden relaties door andere dan de bestudeerde factoren veroorzaakt worden. Er is één studie gevonden, de WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study (MGRS)67, waarin mijlpalen voor de grove motoriek gedurende het eerste levensjaar wetenschappelijk worden onderbouwd.
Uitgangsvraag 2.2
Voor het antwoord op deze uitgangsvraag is gezocht naar reviews en primaire studies die betrekking hadden op oorzaken, risicofactoren en beschermende factoren voor de motorische ontwikkeling. De gebruikte database en de bijbehorende termen staan in bijlage 8.3.2. Daarnaast werd nog specifiek gezocht naar primaire studies die de relatie tussen afwijkende motorische ontwikkeling en prematuriteit, laag geboortegewicht en overgewicht bestudeerden. Omdat het voor de praktijk van de JGZ van belang is inzicht te hebben in de relatie tussen motorische ontwikkeling en andere ontwikkelings- en/of gedragsproblematiek en/of zorgen van ouders werden ook deze onderwerpen meegenomen in het literatuuronderzoek.
Het doel van de uitgangsvraag was om risicofactoren voor motorische ontwikkeling te inventariseren in bestaande wetenschappelijke studies, niet om verschillende interventies of zorgprocessen te vergelijken. Om deze reden zijn geen GRADE-tabellen opgesteld. De studies zijn wel volgens de GRADE-systematiek beoordeeld.
Uitgangsvraag 2.3.1
Voor het beantwoorden van deze uitgangsvraag is een beroep gedaan op de expertise van de leden van de project- en werkgroep en zijn enkele experts geïnterviewd. Daarnaast zijn diverse handboeken met betrekking tot de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen geraadpleegd waaronder ‘Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de Jeugdgezondheidszorg, het Van Wiechenonderzoek en de Baecke-Fassaert Motoriektest’15 en ‘Kinderfysiotherapie’50.
Uitgangsvraag 2.3.2
Voor het beantwoorden van uitgangsvraag 2.3.2 is een systematische literatuursearch verricht. Daarbij is de database Embase gebruikt. De zoekstrategie is te vinden in bijlage 8.3.2. In totaal zijn er 1457 artikelen gevonden. Deze artikelen zijn gescreend op relevantie op basis van titel en abstract. Artikelen werden geïncludeerd als deze Engelstalig of Nederlandstalig waren en de validiteit en betrouwbaarheid van minimaal één motoriektest beschreven,
- waarmee de totale motorische ontwikkeling (alle domeinen) gescreend kon worden of de grofmotorische ontwikkeling of (relevante) fijnmotorische ontwikkeling (met name writing readiness),
- die met een andere test (‘gouden standaard’) vergeleken werd,
- waarmee de motorische ontwikkeling in een algemene, niet-geselecteerde Westerse populatie van kinderen in de leeftijd van 0-18 jaar gemeten of gemonitord kan worden.
Artikelen werden geëxcludeerd wanneer ze gericht waren op een specifieke deelpopulatie, zoals kinderen met het syndroom van Down, en wanneer ze gericht waren op kinderen bij wie al een motoriekprobleem was geconstateerd. Uitzonderingen hierop waren artikelen over selecte groepen kinderen met wie de JGZ regelmatig te maken heeft tijdens de reguliere contactmomenten, zoals prematuur geboren kinderen of kinderen van andere etnische groepen.
Op basis van bovengenoemde in- en exclusiecriteria zijn 148 artikelen geselecteerd. Deze artikelen zijn vervolgens gescand op basis van titel en abstract door een tweede auteur, wat resulteerde in een totaal van 52 geïncludeerde artikelen. Naast deze systematische literatuursearch zijn er artikelen toegevoegd door het zogenaamde sneeuwbaleffect en uit de grijze literatuur, bijvoorbeeld op aanraden van de experts uit de project- en werkgroep.
Het doel van de uitgangsvraag was om de testeigenschappen te bestuderen van de diverse screeningstesten. Omdat het niet de bedoeling was verschillende testen te vergelijken op effectiviteit van de hieraan gerelateerde zorg zijn er geen GRADE-tabellen opgesteld. De studies zijn wel volgens de GRADE-systematiek beoordeeld.
Tot slot werd beoordeeld of deze tests binnen de JGZ toepasbaar waren. De criteria hiertoe waren:
- Het meetinstrument is valide, betrouwbaar en sensitief.
- Er zijn Nederlandse normwaarden beschikbaar.
- De test dient om praktische redenen binnen korte tijd (binnen maximaal 10 minuten) afgenomen te kunnen worden.
- De test kan uitgevoerd worden door verschillende disciplines: jeugdarts, jeugdverpleegkundige of doktersassistente.
- De afname, interpretatie en notatie zijn eenvoudig.
Uitgangsvraag 2.4
Voor een antwoord op deze uitgangsvraag is een systematische literatuursearch uitgevoerd in de database Medline met behulp van de zoektermen in bijlage 8.3.2. De literatuursearch leverde 634 artikelen op die in eerste instantie gescand zijn op relevantie op basis van titel en abstract. Hierbij zijn artikelen geëxcludeerd die gericht waren op kenmerken van meetinstrumenten (bijvoorbeeld betrouwbaarheid of validiteit) en/of specifieke doelgroepen (bijvoorbeeld kinderen met autisme of het syndroom van Down) of die niet gericht waren op neurologisch onderzoek.
Uiteindelijk zijn er geen relevante artikelen gevonden die de uitgangsvraag konden beantwoorden. Er is daarom gebruikgemaakt van de expertise van de leden van de projectgroep en die van de werkgroep, en van de door hen aangeleverde literatuur. Ook zijn er diepte-interviews afgenomen bij onder andere kinderneurologen en kinderfysiotherapeuten.
Uitgangsvraag 3.1 en 3.2
Ook voor uitgangsvraag 3.1 en 3.2 is een systematische literatuursearch uitgevoerd in de database Embase (zoektermen in bijlage 8.3.2). We hebben 3.353 artikelen gevonden die gescand zijn op relevantie op basis van titel en abstract. Dit heeft geleid tot 83 artikelen die potentieel gebruikt konden worden voor uitgangsvraag 3.1, 76 artikelen voor uitgangsvraag 3.2, en 22 artikelen voor beide uitgangsvragen. De meest relevante artikelen en de artikelen met de hoogste bewijswaarde zijn gebruikt als wetenschappelijke ondersteuning voor het beantwoorden van de onderzoeksvragen.
Artikelen zijn geïncludeerd wanneer ze
- betrekking hadden op het stimuleren van motorische vaardigheden en/of fysieke activiteit bij kinderen en adolescenten,
- wanneer ze in het Nederlands of Engels gepubliceerd waren.
Artikelen zijn geëxcludeerd wanneer er
- geen duidelijke conclusies konden worden getrokken omdat het onderzoek van te lage kwaliteit was,
- ze gericht waren op een specifieke doelgroep (bijvoorbeeld kinderen met syndroom van Down of talentvolle atleten), tenzij de doelgroep kinderen met obesitas betrof,
- wanneer het artikel gericht was op een uitsluitend Niet-Westerse populatie.
Er zijn geen artikelen die verschillende adviezen of interventies met elkaar vergeleken. Om deze reden zijn geen GRADE-bewijstabellen opgesteld. De studies die bij 3.1 en 3.2 zijn geïncludeerd, zijn wel volgens de GRADE-systematiek beoordeeld.
Uitgangsvraag 4.1
Het vinden van evidence voor het beantwoorden van deze uitgangsvraag was niet mogelijk, omdat deze ontbreekt. Daarom zijn hiertoe leden van de project- en werkgroep en ook geïnterviewde experts geraadpleegd.
Search strategieën
Uitgangsvraag 2.1
Embase 2508
(‘sex difference’/exp OR gender/de OR ‘ethnic or racial aspects’/exp OR ‘age distribution’/exp OR (((sex* OR gender* OR racial OR race OR ethnic* OR age) NEAR/10 (difference* OR variat* OR impact OR specific* OR relation* OR distribution* OR influenc*)) OR ((Differenc* OR compar* OR earl* OR late*) NEAR/3 boy* NEAR/3 girl*) OR ((age OR sex) NEXT/1 relat*)):ab,ti) AND (‘motor development’/exp OR ‘motor performance’/exp OR ‘psychomotor development’/exp OR ‘motor coordination’/exp OR ‘psychomotor disorder’/de OR ‘motor dysfunction’/de OR ‘motor retardation’/de OR (‘onset age’/exp AND (walking/de OR standing/de OR sitting/de OR jumping/de OR running/exp)) OR (((motor* OR psychomotor*) NEAR/3 (develop* OR abilit* OR skill* OR function* OR retard* OR disorder* OR coordination* OR outcome* OR defecit* OR dysfunction* OR impair* OR proficien* OR capacit*)) OR (development* NEAR/3 coordination* NEAR/3 disorder*) OR (development* NEAR/3 milestone*) OR ((onset OR early OR earlier OR late OR later) NEAR/3 (walk* OR stand OR standing OR crawl* OR midline OR sit OR sitting OR roll OR rolling OR jump OR jumping OR hop OR hopping OR balancing OR running OR run)) OR ((ball OR catch*) NEAR/3 skill*) OR (bilateral* NEAR/3 (coordinat* OR hand))):ab,ti) AND (‘cohort analysis’/exp OR ‘longitudinal study’/exp OR ‘follow up’/exp OR ‘prospective study’/exp OR ‘retrospective study’/exp OR ‘cross-sectional study’/exp OR epidemiology/de OR ‘human experiment’/exp OR ‘analysis of variance’/exp OR ‘case control study’/de OR ‘population based case control study’/de OR ‘population research’/exp OR (cohort* OR longitudinal* OR (follow* NEXT/1 up*) OR followup* OR prospectiv* OR retrospectiv* OR (cross NEXT/1 section*) OR epidemiolog* OR (human NEAR/3 experiment*) OR (analy* NEAR/3 variance*) OR (case NEXT/1 control*) OR (population NEAR/3 (research OR based))):ab,ti) AND (child/exp OR newborn/exp OR adolescent/exp OR adolescence/exp OR ‘child behavior’/de OR pediatrics/exp OR childhood/exp OR ‘child development’/de OR ‘child growth’/de OR ‘child health’/de OR ‘child health care’/exp OR ‘child care’/exp OR ‘childhood disease’/exp OR (adolescen* OR infan* OR newborn* OR (new NEXT/1 born*) OR baby OR babies OR neonat* OR child* OR kid OR kids OR toddler* OR teen* OR boy* OR girl* OR minors OR underag* OR (under NEXT/1 (age* OR aging)) OR juvenil* OR youth* OR kindergar* OR puber* OR pubescen* OR prepubescen* OR prepubert* OR pediatric* OR paediatric* OR school* OR preschool* OR highschool*):ab,ti) NOT ([animals]/lim NOT [humans]/lim)
Uitgangsvraag 2.2
Embase 2508
(‘motor dysfunction’/de OR ‘coordination disorder’/de OR ‘developmental coordination disorder’/de OR ‘gait disorder’/exp OR ‘motor retardation’/de OR ‘walking difficulty’/de OR ‘psychomotor disorder’/de OR (((motor* OR gait OR walking OR psychomotor* OR mobiltit* OR Movement*) NEAR/3 (disorder* OR dysfunct* OR retard* OR difficult* OR delay* OR problem* OR impair* OR deficit* OR limitation*)) OR (coordination NEXT/1 disorder*)):ab,ti) AND (risk/de OR ‘risk factor’/de OR ‘genetic risk’/de OR genetics/de OR ‘genetic predisposition’/exp OR ‘human genetics’/de OR ‘developmental genetics’/de OR ‘social aspects and related phenomena’/exp OR ‘home environment’/de OR Neighborhood/de OR ‘psychosocial environment’/de OR ‘social status’/exp OR etiology/de OR probability/de OR prematurity/exp OR ‘low birth weight’/exp OR ‘small for date infant’/exp OR ‘premature labor’/de OR ‘intrauterine growth retardation’/exp OR ‘prenatal drug exposure’/exp OR ‘prenatal exposure’/de OR (risk OR causalit* OR cause OR causes OR etiolog* OR aetiolog* OR probab* OR reason* OR genetic* OR ((social OR psychosocial* OR sociolog* OR Residen* OR socioeconom*) NEAR/3 (environment* OR class* OR background* OR status* OR condition* OR aspect* OR Characteristic* OR factor*)) OR Neighborhood* OR ((preterm* OR prematur* OR dysmatur*) NEAR/3 (birth* OR born OR infant*)) OR (low* NEAR/3 (‘birth weight’ OR birthweight)) OR lbw OR vlbw OR elbw OR sga OR (small NEXT/2 (date OR gestational)) OR iugr OR ((intrauterine OR uterine OR fetal OR fetus OR foetal OR foetus OR utero) NEAR/3 growth NEAR/3 (retard*)) OR ((prenatal OR intrauterine OR uterine OR fetal OR fetus OR foetal OR foetus OR utero) NEAR/3 expos*) OR predisposit* OR susceptib*):ab,ti) AND (child/exp OR newborn/exp OR adolescent/exp OR adolescence/exp OR ‘child behavior’/de OR ‘child parent relation’/de OR pediatrics/exp OR childhood/exp OR ‘child nutrition’/de OR ‘infant nutrition’/exp OR ‘child welfare’/de OR ‘child abuse’/de OR ‘child advocacy’/de OR ‘child growth’/de OR ‘child health’/de OR ‘child health care’/exp OR ‘child care’/exp OR ‘child death’/de OR ‘child development’/de OR ‘child psychiatry’/de OR ‘child psychology’/de OR ‘pediatric ward’/de OR ‘pediatric hospital’/de OR ‘pediatric nursing’/exp OR ‘pediatric anesthesia’/exp OR ‘pediatric surgery’/exp OR (adolescen* OR infan* OR newborn* OR (new NEXT/1 born*) OR baby OR babies OR neonat* OR child* OR kid OR kids OR toddler* OR teen* OR boy* OR girl* OR minors OR underag* OR (under NEXT/1 (age* OR aging)) OR juvenil* OR youth* OR kindergar* OR puber* OR pubescen* OR prepubescen* OR prepubert* OR pediatric* OR paediatric* OR school* OR preschool* OR highschool* OR picu OR nicu OR picus OR nicus):ab,ti) NOT ([animals]/lim NOT [humans]/lim) NOT ([Conference Abstract]/lim OR [Letter]/lim OR [Note]/lim OR [Editorial]/lim) AND (review/de OR ‘systematic review’/de OR ‘meta analysis’/de OR (review OR (meta NEXT/1 analy*) OR metaanaly*):ti)
Uitgangsvraag 2.3.2
Embase 1457
(‘motor development’/exp OR ‘motor performance’/exp OR ‘psychomotor development’/exp OR ‘motor coordination’/exp OR ‘psychomotor disorder’/de OR ‘motor dysfunction’/de OR ‘motor retardation’/de OR (‘onset age’/exp AND (walking/de OR standing/de OR sitting/de OR jumping/de OR running/exp)) OR (((motor* OR psychomotor*) NEAR/3 (develop* OR abilit* OR skill* OR function* OR retard* OR disorder* OR coordination* OR outcome* OR defecit* OR dysfunction* OR impair* OR proficien* OR capacit* OR milestone* OR achiev* OR perform*)) OR (development* NEAR/3 coordination* NEAR/3 disorder*) OR (development* NEAR/3 milestone*) OR ((onset OR early OR earlier OR late OR later) NEAR/3 (walk* OR stand OR standing OR crawl* OR midline OR sit OR sitting OR roll OR rolling OR jump OR jumping OR hop OR hopping OR balancing OR running OR run)) OR ((ball OR catch*) NEAR/3 skill*) OR (bilateral* NEAR/3 (coordinat* OR hand))):ab,ti) AND (reliability/exp OR validity/exp OR ‘validation process’/exp OR ‘validation study’/exp OR ‘observer variation’/exp OR ‘diagnostic error’/exp OR error/exp OR ‘diagnostic accuracy’/exp OR ‘measurement precision’/exp OR ‘measurement repeatability’/exp OR ‘measurement accuracy’/exp OR ‘correlation coefficient’/exp OR ‘intermethod comparison’/exp OR (reliab* OR valid* OR ((interrater* OR interobserv* OR intraobserv* OR observer*) NEAR/3 (variati* OR variabil*)) OR ((diagnos* OR measure* OR procedur*) NEAR/3 (error* OR mis* OR fail* OR accura* OR agree*)) OR (false NEAR/3 (positiv* OR negativ*)) OR precision OR reproduc* OR ((internal*) NEAR/3 consisten*) OR repeatab* OR (test* NEAR/3 retest*) OR ((correlat* OR variation*) NEAR/3 (coefficient* OR intraclass)) OR ((intermethod* OR method* OR test* OR intertest*) NEAR/6 compar*)):ab,ti) AND (child/exp OR newborn/exp OR adolescent/exp OR adolescence/exp OR ‘child behavior’/de OR ‘child parent relation’/de OR pediatrics/exp OR childhood/exp OR ‘child nutrition’/de OR ‘infant nutrition’/exp OR ‘child welfare’/de OR ‘child abuse’/de OR ‘child advocacy’/de OR ‘child development’/de OR ‘child growth’/de OR ‘child health’/de OR ‘child health care’/exp OR ‘child care’/exp OR ‘childhood disease’/exp OR ‘child death’/de OR ‘child psychiatry’/de OR ‘child psychology’/de OR ‘pediatric ward’/de OR ‘pediatric hospital’/de OR ‘pediatric nursing’/exp OR ‘pediatric anesthesia’/exp OR ‘pediatric surgery’/exp OR (adolescen* OR infan* OR newborn* OR (new NEXT/1 born*) OR baby OR babies OR neonat* OR child* OR kid OR kids OR toddler* OR teen* OR boy* OR girl* OR minors OR underag* OR (under NEXT/1 (age* OR aging)) OR juvenil* OR youth* OR kindergar* OR puber* OR pubescen* OR prepubescen* OR prepubert* OR pediatric* OR paediatric* OR school* OR preschool* OR highschool* OR picu OR nicu OR picus OR nicus):ab,ti) NOT ([animals]/lim NOT [humans]/lim) NOT (‘neurologic disease’/exp OR ‘mental disease’/exp OR ‘prenatal exposure’/exp OR ‘prenatal drug exposure’/exp OR disability/exp OR ‘newborn disease’/exp OR ‘musculoskeletal disease’/exp OR ‘environmental exposure’/exp OR ’toxicity and intoxication’/exp OR (disab* OR ((neurolog* OR mental* OR musculoskelet*) NEAR/3 (disease* OR disorder*)) OR ((prenatal* OR uter* OR environment*) NEAR/3 expos*) OR congenital* OR toxic* OR intoxicat*):ab,ti)
Uitgangsvraag 2.4
Embase 634
(‘neurologic examination’/exp OR ‘developmental screening’/de OR ((‘motor dysfunction’/exp OR ‘nervous system development’/de OR ‘motor activity’/de OR ‘brain maturation’/de OR ‘motor performance’/de) AND (screening/de OR ‘screening test’/de OR ‘scoring system’/exp OR ‘functional assessment’/de OR ‘assessment of humans’/de)) OR ((neurologic* OR neuropediatric* OR motor OR development*) NEAR/3 (examination* OR assess* OR sign OR signs OR evaluat* OR condition* OR finding* OR recogni* OR profile* OR test OR tests OR testing OR screen* OR maturat* OR deficit* OR impression* OR orientat* OR detect*)):ab,ti) AND (pediatrician/exp OR ‘pediatric hospital’/exp OR (pediatrician* OR paediatrician* OR ((pediatric OR paediatric OR children*) NEXT/1 (hospital* OR practice*))):ab,ti) AND (methodology/de OR ‘practice guideline’/exp OR (methodolog* OR design OR requirement* OR guideline* OR protocol* OR consensus* OR ((method* OR tool* OR system* OR standard) NEAR/3 develop*) OR norm OR norms):ab,ti)
Uitgangsvragen 3.1 en 3.2
Embase 3353
(‘motor development’/exp OR ‘motor performance’/exp OR ‘psychomotor development’/exp OR ‘motor coordination’/exp OR ‘psychomotor disorder’/de OR ‘psychomotor performance’/de OR ‘motor dysfunction’/de OR ‘motor retardation’/de OR (‘onset age’/exp AND (walking/de OR standing/de OR sitting/de OR jumping/de OR running/exp)) OR (((motor* OR psychomotor*) NEAR/3 (develop* OR abilit* OR skill* OR function* OR retard* OR disorder* OR coordination* OR outcome* OR defecit* OR dysfunction* OR impair* OR proficien* OR capacit* OR milestone* OR achiev* OR perform*)) OR (development* NEAR/3 coordination* NEAR/3 disorder*) OR (development* NEAR/3 milestone*) OR ((onset OR early OR earlier OR late OR later) NEAR/3 (walk* OR stand OR standing OR crawl* OR midline OR sit OR sitting OR roll OR rolling OR jump OR jumping OR hop OR hopping OR balancing OR running OR run)) OR ((ball OR catch*) NEAR/3 skill*) OR (bilateral* NEAR/3 (coordinat* OR hand))):ab,ti) AND (child/exp OR newborn/exp OR adolescent/exp OR adolescence/exp OR ‘child behavior’/de OR ‘child parent relation’/de OR pediatrics/exp OR childhood/exp OR ‘child nutrition’/de OR ‘infant nutrition’/exp OR ‘child welfare’/de OR ‘child abuse’/de OR ‘child advocacy’/de OR ‘child development’/de OR ‘child growth’/de OR ‘child health’/de OR ‘child health care’/exp OR ‘child care’/exp OR ‘childhood disease’/exp OR ‘child death’/de OR ‘child psychiatry’/de OR ‘child psychology’/de OR ‘pediatric ward’/de OR ‘pediatric hospital’/de OR ‘pediatric nursing’/exp OR ‘pediatric anesthesia’/exp OR ‘pediatric surgery’/exp OR (adolescen* OR infan* OR newborn* OR (new NEXT/1 born*) OR baby OR babies OR neonat* OR child* OR kid OR kids OR toddler* OR teen* OR boy* OR girl* OR minors OR underag* OR (under NEXT/1 (age* OR aging)) OR juvenil* OR youth* OR kindergar* OR puber* OR pubescen* OR prepubescen* OR prepubert* OR pediatric* OR paediatric* OR school* OR preschool* OR highschool* OR picu OR nicu OR picus OR nicus):ab,ti) NOT (‘neurologic disease’/exp OR ‘mental disease’/exp OR ‘prenatal exposure’/exp OR ‘prenatal drug exposure’/exp OR disability/exp OR ‘newborn disease’/exp OR ‘musculoskeletal disease’/exp OR ‘environmental exposure’/exp OR ’toxicity and intoxication’/exp OR (disab* OR ((neurolog* OR mental* OR musculoskelet*) NEAR/3 (disease* OR disorder*)) OR ((prenatal* OR uter* OR environment*) NEAR/3 expos*) OR congenital* OR toxic* OR intoxicat*):ab,ti) NOT ([animals]/lim NOT [humans]/lim) AND (prevention/exp OR prevention:lnk OR ‘physical education’/de OR ‘parenting education’/de OR stimulation/de OR ‘early childhood intervention’/de OR ‘manipulative medicine’/exp OR ‘movement therapy’/de OR ‘social environment’/de OR ‘social status’/exp OR ‘child parent relation’/exp OR recreation/exp OR play/de OR ‘educational status’/exp OR ‘employment status’/exp OR (prevent* OR ((facilitat* OR obstacle*) NEAR/3 (factor*)) OR ((environment* OR educat* OR teach* OR parent* OR mother* OR father* OR famil* OR school OR daycare OR day-care OR government* OR municipal* OR communit* OR motivation*) NEAR/3 (restrict* OR placement* OR variabl* OR factor* OR influen* OR facilitat* OR intervention* OR obstacle* OR condition* OR method* OR challeng* OR poor OR rich OR unstab* OR approach*)) OR (physical* NEAR/3 educat*) OR ((school OR early OR communit*) NEAR/3 (intervention* OR program*)) OR (intervention* NEAR/3 program*) OR parenting OR stimulat* OR (manipulat* NEAR/3 medicine) OR massage* OR (movement NEAR/3 therap*) OR cesar OR mensendieck* OR (baby NEXT/1 walker*) OR maxicosi OR maxi-cosi OR bouncer* OR (social* NEAR/3 environment*) OR neighborhood* OR neighbourhood* OR (child NEAR/3 (parent* OR father* OR mother* ) NEAR/6 (interact* OR relation*)) OR (parent* NEAR/3 educat*) OR recreation* OR play OR playing OR ((educational* OR employment* OR socioeconomic* OR socio-economic OR social OR sociocultural*) NEAR/3 (status OR class* OR aspect*)) OR poverty OR unemploy* ):ab,ti)
Met dank aan Wichor Bramer, biomedisch informatiespecialist, ErasmusMC voor het uitvoeren van en ondersteunen bij alle zoekstrategieën.
7.2 Kennislacunes
Tijdens het opstellen van de richtlijn bleken er kennislacunes te bestaan.
Zo geldt bij het VWO voor zowel à terme als prematuur geboren kinderen het volgende:
• De betrouwbaarheid en validiteit van het VWO zijn onbekend, ook als het gaat om het opsporen van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen.
• Er zijn kanttekeningen bij de P90-waarden zoals deze momenteel gehanteerd worden. Ze wijken bijvoorbeeld vaak af van de P90-waarden van de onlangs herziene Bayley-III-NL.
• Het is onbekend welke kenmerken van het VWO op welke leeftijd het belangrijkst zijn bij het herkennen van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen. Ook is onduidelijk welke kenmerken eventueel overbodig zijn en welke kenmerken eventueel toegevoegd zouden moeten worden.
• Het is onbekend of de wijze waarop gescoord wordt in het VWS, adequaat weerspiegelt hoe het kind zich motorisch ontwikkelt. Bij het VWO wordt negatief gescoord bij hetzij het niet kunnen uitvoeren (volgens JGZ-professional of ouder) van een bepaalde motorische vaardigheid, hetzij bij onvoldoende kwaliteit ervan. Onduidelijk is of dit iedere keer adequaat (dat wil zeggen conform instructies) wordt geregistreerd in het digitaal dossier. Ten aanzien van prematuren zijn deze problemen met scoren nog groter, al geeft de JGZ-richtlijn ‘Te vroeg en/of small for gestational age’ hier wel aanbevelingen voor.
• Tot slot is onduidelijk of en tot welke leeftijd de VWO kenmerken gecorrigeerd moet worden voor de zwangerschapsduur bij prematuur geboren kinderen.
Gezien bovenstaande kennishiaten, verdient onderzoek naar het VWO (en het hieraan gekoppelde VWS), hoge prioriteit. Omdat gebleken is dat bij een enkele JGZ-organisatie de ASQ op bepaalde momenten wordt uitgevoerd in plaats van het VWO, is het nuttig dat de validiteit van het VWO, de ASQ, en mogelijk ook andere testen met elkaar worden vergeleken.
Wat de BFMT geldt zowel voor à terme als prematuur geboren kinderen het volgende.
• De betrouwbaarheid en validiteit zijn onvoldoende onderzocht. Ook is onduidelijk of de huidige gebruikte afkappunten voldoen.
• Onbekend is welke elementen noodzakelijk zijn voor een voldoende sensitiviteit, specificiteit, positief voorspellende waarde (positive predictive value = PPV) en negatief voorspellende waarde (negative predictive value = NPV). Onbekend is ook of deze elementen verschillen voor relatief jongere en relatief oudere kinderen (in de range van 5 tot 6;6 jaar).
• Onbekend is of bepaalde onderdelen van de BFMT verouderd zijn doordat bepaalde activiteiten door kleuters nog nauwelijks worden geoefend (zoals veters strikken).
• Onbekend is of de testeigenschappen (van met name de BFMT) kunnen worden verbeterd door het uitvoeren van een extra test, zoals bijv. de 4-vaardighedenscan, met het oog op stapsgewijze screening/diagnostiek.
Wat betreft de JGZ-praktijk geldt dat:
• Het niet bekend is, ondanks de inhoud van de opleiding tot jeugdarts en bestaande scholingen en trainingen (bit.ly/VWTraining) in hoeverre JGZ-professionals het VWO en de BFMT adequaat afnemen, het neurologisch onderzoek op indicatie adequaat uitvoeren, en of zij hun vaardigheden en kennis voldoende onderhouden;
• Het niet bekend is welke competenties vereist zijn voor het adequaat uitvoeren van motorische testen, de interpretatie en de hierop ingezette vervolgacties;
• Onbekend is hoe de uitvoering van het monitoren en beoordelen van de motorische ontwikkeling door JGZ-professionals, al dan niet in samenwerking met scholen, is geïmplementeerd;
• Niet duidelijk is of testen die door vakleerkrachten op school kunnen worden uitgevoerd betere of minder goede testeigenschappen (dat wil zeggen betrouwbaarheid, validiteit, discriminerend vermogen) hebben dan de BFMT;
• Niet precies bekend is van alle JGZ-organisaties welke keuzes zij en gemeenten in het kader van flexibilisering en bezuinigingen hebben gemaakt ten aanzien van de uit te voeren contactmomenten en de daarbij behorende uitvoering van de motoriektesten, en welke keuze het meest kosteneffectief is. Daarom is ook niet duidelijk of het aantal contactmomenten en/of de tijdstippen waarop deze worden uitgevoerd, nog wel toereikend zijn om het VWO en de BFMT af te nemen op de wijze zoals deze bedoeld zijn, namelijk voor de monitoring van de (motorische) ontwikkeling.
Bij de huidige ontwikkelingen in de flexibilisering binnen de JGZ, is de evidence ten aanzien van de uitvoering van (kenmerken van) het VWO en de BFMT niet in ogenschouw genomen. Gezien het feit dat beide testen al vele jaren dagelijks vele keren worden toegepast, is het noodzakelijk hiernaar en naar eventuele alternatieven zo spoedig mogelijk goed onderzoek te verrichten. Als er dan keuzes moeten worden gemaakt, berusten deze op inhoudelijk verantwoorde gronden. Verder weten we onvoldoende in welke mate het ontbreken van zorgen bij ouders over de motorische ontwikkeling van hun kind voorspellend is voor een normale motorische ontwikkeling. Ook is onbekend welke testen en vragenlijsten kunnen worden gecombineerd om met hoge voorspellende waarde te kunnen inschatten of een kind een motorisch ontwikkelingsprobleem heeft.
De relatie van SES, etniciteit en culturele traditie met zowel grof- als fijnmotorische ontwikkeling in Nederland is onvoldoende onderzocht.
Er worden in de praktijk verschillende methoden gebruikt om motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen bij schoolkinderen te signaleren. Bovendien is de setting waarin dit plaatsvindt verschillend, bijvoorbeeld JGZ versus school. Onbekend is op welke wijze het signaleren van motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen het meest (kosten-)effectief is. Hiernaar is onderzoek is nodig.
Wat betreft de behandeling is voor de JGZ-praktijk en scholen van belang dat een effectevaluatie van motor remedial teaching (MRT) ontbreekt. Ook van veel andere behandelingen gericht op de motorische ontwikkeling ontbreekt een effectevaluatie, maar dat gaat buiten het bestek van een richtlijn binnen de JGZ. Onbekend is verder tot welke leeftijd het zinvol is de motorische ontwikkeling te volgen met het oog op het aanbieden van een effectieve interventie.
8 Bijlagen
- Bijlagen
- 1. Neurale Groep Selectie Theorie
- 2. Alarmsignalen Van Wiechenonderzoek
- 3. CP en DCD
- 4. De ICF-CY
- 5. Casuïstiek
- 6. Literatuursearch en zoekstrategie (zie sectie verantwoording)
- 7. P90 waarden bij motoriek
- 8. Criteria Wilson en Jungner
- 9. Kenmerken motorische testen
- 10. Kenmerken vragenlijsten motoriek
- 11. Kenmerken observatie instrumenten motoriek
- 12. Gouden standaard validiteit motoriektesten
- 13. Overzichtsformulier 4-vaardigheden scan
- 14. Groninger Motoriek Observatieschaal (GMO)
- 15. Coördinatie Vragenlijst voor Ouders
- 16. Neurologisch onderzoek
- 17. Beweegrichtlijn
- 18. Interventies Veilig Groot worden en Armoede en Gezondheid
8.1 Bijlage 1 De Neurale Groep Selectie Theorie
De Neurale Groep Selectie Theorie (NGST) stelt dat ontwikkeling het resultaat is van een complexe interactie tussen genetische informatie en omgevingsfactoren. De ontwikkeling begint al vroeg-foetaal (eerste trimester van de zwangerschap) met een groep cellen en verbindingen, de zogenaamde primaire neurale repertoires. Deze repertoires zijn evolutionair en epigenetisch bepaald. De cellen en verbindingen kennen veel variatie door een continue wisselwerking tussen de genetische eigenschappen en de omgevingsfactoren van het kind. Motorisch gedrag in deze periode kent hierdoor veel variaties. In deze periode zijn bewegingen niet precies aangepast aan de omstandigheden, maar zijn een uiting van een fundamenteel ontwikkelingsfenomeen, ook wel de fase van de primaire variabiliteit genoemd.
Vervolgens worden op basis van ervaringsgeleide selecties, op functiespecifieke momenten in het leven, de repertoires gekozen die functioneel het beste resultaat opleveren. Dit leidt tot secundaire, adaptieve neurale repertoires. Het tijdstip van deze selecties hangt af van de benodigde functie. Zo vindt de selectie van een efficiënt zuigpatroon al plaats in het laatste trimester van de zwangerschap, terwijl de selectie van een energetisch gunstige hiel-teengang plaatsvindt tussen 12 en 18 maanden. De fase van het aanpassingsvermogen is een fase van secundaire of adaptieve variabiliteit[14][105]. Deze laatste fase duurt tot in de adolescentie.
De secundaire neurale repertoires worden gekenmerkt door veel parallelschakelingen. Hierdoor zijn er voor eenzelfde motorische taak verschillende oplossingen beschikbaar. Van het tweede tot derde levensjaar maakt de secundaire variabiliteit een groeispurt door[12].
8.2 Bijlage 2 Alarmsignalen Van Wiechenonderzoek (VWO)
Hieronder staan alarmsignalen die tijdens het eerste levensjaar240 beoordeeld worden met het Van Wiechen Ontwikkelingsonderzoek (VWO)[15].
| Armoede aan bewegingen Gebrek aan initiatief Niet aankijken |
| Eén- of dubbelzijdig stereotiepe1 houding: vuistjes, holle rug, hoofd achterover, arm- of beenhouding opvallend Verwaarlozen van een hand, arm, been Asymmetrische hoeveelheid bewegingen Asymmetrische bewegingspatronen |
| Tussen de handen doorglijden indien onder de oksels vastgehouden Slap afhangend hoofd bij (optrekken tot) zit |
| Tremor bij spontane motoriek bij niet huilend kind |
| Strekken en onbeweeglijk houden van heupen, knieën en enkels bij verticale zweefhouding en heen-en-weer zwaaien |
| Stereotiep1 aanwezige asymmetrische tonische nekreflex2 of opisthotonus3 |
| Zittend op ondereind van de gebogen rug, indien benen gestrekt op de onderlaag worden gehouden |
| Geen of onvoldoende reactie op geluid |
| Geen of onvoldoende volgen van ogen (en hoofd) |
| Constant strabisme (afwijkende oogstand) |
| Constant ondergaande-zon-fenomeen4 Wijkende schedelnaden Gespannen fontanel Abnormale groei van de schedelomvang (vaak spugen, gespannen gelaatsuitdrukking) |
| Niet optreden van onderscheid tussen bekend en vreemd (‘eenkennigheid’) |
| Geen imitatiespelletjes Geen kiekeboe spelletjes |
Alarmsignalen gerelateerd aan neuromotorische ontwikkeling zijn vet gedrukt:
1 Stereotiep: als een houding langer dan circa 10 minuten duurt en het kind deze niet zelf overwint.
2 Asymmetrische tonische nekreflex: bij opzij draaien van het hoofd wordt de arm en/of been aan de kant waarheen het gezicht is gericht gestrekt, en de andere arm en/of het andere been gebogen.
3 Opisthotonus: achteroverkrommen van hoofd en rug, vaak met achteruitgetrokken schouders.
4Ondergaande-zon-fenomeen: de helft van de cornea verdwijnt onder het onderooglid, in uitgesproken gevallen is de witte sclera boven het hoornvlies zichtbaar door retractie van het bovenooglid.
Hieronder staan alarmsignalen die na het eerste levensjaar beoordeeld kunnen worden met het VWO15.
| Alarmsignalen na het eerste levensjaar240, te beoordelen volgens het VWS |
| Onvermogen tot (gaan) zitten, kruipen, rollen, staan, lopen ( de beide laatste vanaf 18-20 maanden) |
| Bolle rug bij zitten met gestrekte benen |
| Geen evenwicht bij zitten met aaneengesloten benen |
| Stereotiepe asymmetrische houding of bewegingspatronen bij zitten, staan of lopen |
| Langs de benen ‘omhoogklimmen’ bij gaan staan (teken van Gower’s) |
| Constant op de tenen staan of lopen |
| Brede basis bij staan en lopen (na 24 maanden) |
| Staan en/of lopen met stereotiep naar binnen gedraaide benen en voeten en beperkte heupstrekking (‘scharen’) |
| Voortdurende buiging van de tenen (‘klauwen’) bij staan en/of lopen |
| Onvermogen tot gedifferentieerd bewegen van de schouders ten opzichte van het bekken bij staan en lopen (vanaf 3 jaar) |
| Onvermogen voorwerp vanuit stand van de vloer op te rapen (vanaf 2 jaar) |
| Blokachtige rompbewegingen bij kruipen (na 2,5 jaar)1 |
| Trillerige handmotoriek |
| Storende hoeveelheid meebewegingen in de contralaterale hand/arm bij eenzijdig hand/arm-gebruik, zoals bijvoorbeeld prikken, knippen, plakken |
| Voortdurend kwijlen |
| Onvermogen hoeveelheid (kleine) bewegingen aan te passen aan de bezigheden (armbeweeglijkheid, rusteloosheid) |
| Onvoldoende interesse voor de omgeving |
| Stoornissen in de oogbewegingen of de oogstand |
| Onvoldoende horizontale en verticale geluidsbronlokalisatie2 |
Alarmsignalen gerelateerd aan neuromotorische ontwikkeling zijn vet gedrukt.
1 Schouders en heupen worden niet of nauwelijks ten opzichte van elkaar bewogen: de romp beweegt ‘als uit één stuk’
2 Een hoge en een lage tonen producerend belletje achter, opzij, boven het hoofd of laag achter de rug.
8.3 Bijlage 3 Definities van CP en DCD
3.1 Cerebrale Parese
De internationaal aanvaarde definitie van CP is: “Cerebrale Parese omvat een groep van blijvende aandoeningen van de hersenen met blijvende effecten voor de ontwikkeling van houding en beweging, ontstaan voor de eerste verjaardag, die leiden tot beperkingen in dagelijkse activiteiten”[35]. De stoornissen worden toegeschreven aan een niet-progressief pathologisch proces dat de hersenen tijdens hun vroege ontwikkeling heeft beschadigd”. Zie de Richtlijn Spastische Cerebrale Parese (2015). De houdings- of bewegingsstoornis bij CP gaat vaak gepaard met stoornissen in het sensorische systeem, perceptie, cognitie, communicatie en gedrag, met epilepsie en met secundaire stoornissen van het spierskeletstelsel. Veel kinderen met CP hebben spraakstoornissen (60%), gehoorproblemen (12%) of visusproblemen (36%)[183]. Ongeveer 30% van de kinderen met CP kan niet lopen, en bijna 20% kan uitsluitend met hulpmiddelen lopen190.
Bij CP is sprake van een beschadiging van de witte en/of de grijze stof van de hersenen. Als er sprake is van een zich voortzettende actieve ziekte van het centraal zenuwstelsel, is er geen sprake van CP. Bij vermoedens van CP dient altijd naar de specialist verwezen te worden. Doordat er allerlei vormen bestaan van neurologische beschadigingen die leiden tot CP, zijn er ook veel uitingsvormen van CP mogelijk. Daarom ook is het soms moeilijk om onderscheid te maken tussen kinderen met een milde vorm van CP en motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen bij andere neurologische ontwikkelingsproblemen.
Er worden verschillende classificaties van CP gebruikt. Een veel gebruikte is de Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS)[187]. Met deze score kan vanaf ongeveer de leeftijd van twee jaar worden voorspeld wat het niveau van grof-motorisch functioneren kan zijn op 12-jarige leeftijd bij kinderen met CP. Er bestaat ook een indeling naar kwaliteit van bewegen: spastische-, dyskinetische- en atactische bewegingsstoornis.
3.2 Developmental Coordination Disorder
DCD is een veel voorkomende vorm van een motorische ontwikkelingsachterstand. In Nederland wordt de DSM-5 classificatie gebruikt, waarin deze term wordt gebruikt voor kinderen met motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen[43]. De hierin vermelde classificatiecriteria (DSM-5, 315.4) zijn:
- Het verwerven en uitvoeren van gecoördineerde motorische vaardigheden verloopt aanzienlijk onder het niveau dat verwacht mag worden gezien de kalenderleeftijd van de betrokkene en de mogelijkheden om de vaardigheden te leren en te gebruiken. De moeilijkheden komen tot uiting in onhandigheid (zoals dingen laten vallen of ergens tegenaan botsen), en een trage en onnauwkeurige uitvoering van motorische vaardigheden (zoals iets vangen, gebruik van een schaar of bestek, schrijven, fietsen of sporten).
- De deficiëntie in motorische vaardigheid van criterium A vormt een significante en persisterende belemmering bij algemene dagelijkse levensverrichtingen (ADL) passend bij de kalenderleeftijd (zoals zelfverzorging en voorziening in levensonderhoud), en hebben invloed op de schoolprestaties, voorbereidende beroepsactiviteiten, beroepsactiviteiten, vrijetijdsbesteding en spel.
- De symptomen beginnen in de vroege ontwikkelingsperiode.
- De deficiënties in de motorische vaardigheden worden niet beter verklaard door een verstandelijke beperking (verstandelijke-ontwikkelingsstoornis) of visusstoornis, en kunnen niet worden toegeschreven aan een neurologische aandoening die invloed heeft op beweging (zoals CP, spierdystrofie, een degeneratieve stoornis).
De Nederlandse operationalisatie van de DSM-5 criteria voor DCD[40] luidt:
- De totaalscore op de Movement ABC-2 ligt op of beneden standaardscore 7 (16de percentiel) of de score op één van de drie componenten van de Movement ABC-2 ligt op of beneden standaardscore 5 (5de percentiel) (voor verdere uitleg over de Movement ABC zie bijlage 8.10).
- Uit de hulpvraag moet blijken dat de aandoening de schoolse prestaties of de algemene dagelijkse activiteiten voortdurend en in belangrijke mate beïnvloedt. Dit is ter beoordeling aan de medisch specialist of profielarts die hiertoe geschoold en competent is (kinderrevalidatiearts, kinderarts, jeugdarts, kinderneuroloog, kinderpsychiater). Met alleen de aanmelding bij een interprofessioneel team is nog niet voldaan aan dit criterium. De motorische vragenlijsten: Coördinatie Vragenlijst voor Ouders (CVO, is de Nederlandse vertaling van DCD-Q) en Groninger Motoriek Observatieschaal (GMO) worden standaard gebruikt voor aanvullende informatie over functionele problemen thuis en op school.
- Het criterium “De symptomen beginnen zich tijdens de vroege ontwikkeling te manifesteren” is in de Nederlandse definitie (nog) niet geoperationaliseerd.
- De aandoening is niet het gevolg van een medische conditie volgens de resultaten van een medisch-neurologisch onderzoek. De diagnose kan alleen gesteld worden door een medisch specialist of profielarts die hiertoe geschoold en competent is zoals een kinderrevalidatiearts, kinderarts, jeugdarts, kinderneuroloog en kinderpsychiater. Voorafgaand aan de diagnose moet onderzoek plaatsvinden naar: algemene lichamelijk conditie (motoriek, neurologie, visus), communicatieve vaardigheden, gedrag (Child Behavior Checklist/Teacher Report Form) en sociale omstandigheden. Indien twijfel bestaat over de cognitie dient ook een IQ-test te worden afgenomen. De diagnose DCD kan niet gesteld worden als het IQ op of beneden de 70 valt op een individueel afgenomen, gestandaardiseerde intelligentietest. Verondersteld mag worden dat het IQ boven de 70 valt, wanneer een kind in het regulier onderwijs zit, niet gedoubleerd heeft en er geen andere twijfel bestaat over het intelligentieniveau (bijvoorbeeld via leerlingvolgsysteem).
8.4 Bijlage 4 De ICF-CY
De International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health for Children and Youth, ICF-CY, is een classificatiesysteem van de Wereldgezondheidsorganisatie, dat het bio-psychosociaal model van het menselijk functioneren concretiseert. Het systeem biedt een begrippenkader vanuit drie onderling verbonden perspectieven:
- Het perspectief van het menselijke organisme (functies, anatomische eigenschappen),
- Dat van het menselijke handelen (activiteiten)
- Dat van deelname aan het maatschappelijke leven (participatie).
Bovendien biedt de ICF-FY de mogelijkheid om persoonlijke en externe factoren die het functioneren van een persoon mee beïnvloeden, in de beschrijving op te nemen. De ICF-CY is een classificatie in neutrale termen. Elke component kan zowel in positieve als in negatieve zin worden gebruikt[13],[39],.
8.5 Bijlage 5 Casuistiek
In onderstaande casussen wordt voor een aantal veel voorkomende problemen in de JGZ, het onderzoek en de mogelijke vervolgstappen voor (neurologisch) onderzoek beschreven. Voor alle casussen zijn visus, gehoor, asymmetrie (in kracht, tonus en reflexen), regressie in de ontwikkeling, dysmorfieën en de kwaliteit van bewegen relevante aandachtspunten. Van belang is te weten dat dit overzicht niet volledig is, en dat het op de eerste plaats aan de professional zelf is hoe hij/zij omgaat met de gepresenteerde problemen in de praktijk.
Casus 1 ‘Mijn kind ontwikkelt zich in het bewegen anders dan mijn andere kinderen’
Differentiaaldiagnose
Normale spreiding van ontwikkeling, motorische ontwikkelingsachterstand als gevolg van een visuele stoornis, neuromusculaire aandoening, CP, DCD, NAH, orthopedische problematiek, interne problematiek, onderstimulering, sociaal-emotionele problematiek.
Onderzoek jeugdarts
Anamnese
0-4 jaar: Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis).
Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren (zoals vermoeidheid), wat heeft de ouder al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect.
Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
Participatie-problemen.
4-18 jaar: Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis).
Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren (zoals vermoeidheid), wat heeft de ouder al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect.
Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
Vragen naar motorische redzaamheid (ADL, kleutervaardigheden, schrijven, participatie: deelname aan sport en spel) en motorisch leren.
Observatie
0-4 jaar: Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan (op de tenen vanaf 2 jaar), lopen, met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen vanaf 3 jaar, op de hakken vanaf 3 jaar), staan op 1 been (vanaf 4 jaar), springen (vanaf 2 jaar), hinkelen (vanaf 4 jaar), rennen.
Fijne motoriek: manipuleren met voorwerpen, stapelen van voorwerpen.
4-18 jaar: Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan, lopen met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen, op de hakken), springen, hinkelen, huppelen, rennen.
Automatisering van bewegingen door aanbieden van dubbele taken (praten en handelen tijdens lopen).
Anticiperen: variëren in snelheid en richting van bewegen. Kijken naar kwaliteit en symmetrie van bewegingen in relatie tot leeftijd, looppatroon (breedte van loopbasis, afwikkeling, ondersteuning van de armen, romprotatie). Invloed van verhogen van de taakeis op kwaliteit van bewegen, vermoeidheid, stressreactie (frustratie, taakeis willen veranderen, clownesk gedrag, niet meer willen werken).
Lichamelijk onderzoek Visus
Kracht (volhouden van), herhaaldelijk laten opstaan met zoeken naar Gower’s sign. Hierbij heeft een kind dat op de grond ligt en moet gaan staan, te weinig spierkracht in de benen om dit zo te kunnen doen. Zij gaan daarom eerst op handen en voeten staan en gebruiken vervolgens hun handen om met steun op de knieën en bovenbenen, overeind tot staand te komen. Zie definitie www.mijnkinderarts.nl, tonus (actieve en passieve tonus), reflexen, proef van Romberg, test onwillekeurige bewegingen (0-4 jaar door observatie, 4-18 jaar test), diadochokinese (0-4 jaar door observatie tijdens spel, 4-18 jaar met test), vinger-neus test (vanaf 4 jaar), vinger-oppositie test (vanaf 5 jaar).
Mobiliteit: range-of-motion, dat wil zeggen de mate waarin het gewricht kan bewegen (in graden), passief en actief
Executief: aandacht, motivatie, begrip van opdrachten, lichaamsbesef
Asymmetrie qua vorm en functies (CP, NAH: niet frequent maar toch mogelijk)
Coördinatie- en automatiseringsproblemen bij vijf jaar, dan denken aan DCD
Beoordelen pes planus
Beleid
| Signaal | Verwijzing |
| Asymmetrie in kracht, onwillekeurige bewegingen | Naar neuroloog |
| Naast motorische ontwikkeling ook andere domeinen betrokken | Naar kinderarts (en/of kinderrevalidatiearts) |
| Duidelijke motorische achterstand en geen ontwikkelingsproblemen bij andere domeinen | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut kinderergotherapeut/ motorisch remedial teacher |
| Regressie in motorische ontwikkeling | Naar kinderarts |
| Orthopedische problemen, zoals stugge pes planus valgus, beenlengteverschil > 2 cm, scoliose |
Naar orthopeed (conform het boek van Dr. Visser Pluis/Niet Pluis231 Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/kinderoefentherapeut bij niet structurele scoliose (check ervaring met diagnostiek en behandeling) |
| Bij twijfel | Overweeg een extra controle/verwijzing naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ kinderergotherapeut/ motorisch remedial teacher voor eenmalig onderzoek |
Algemeen: verwijzing naar de kinderarts bij dysmorfieën, als meerdere ontwikkelingsdomeinen afwijkend zijn of bij een vermoeden van systeemziekte.
Casus 2 ‘Mijn kind valt vaak’
Differentiaaldiagnose
Visusstoornis, neuromusculaire aandoening (NMA), DCD, NAH, voornamelijk in groeiperioden voorkomende orthopedische problemen, (gegeneraliseerde) hypermobiliteit, extreme pes planus, endorotatie van heupen, endorotatie van de tibia en pes adductus), CP, sensorische problemen.
Onderzoek door de jeugdarts
Anamnese
0-4 jaar Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis).
Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren (zoals vermoeidheid), wat heeft de ouder al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect.
Vragen naar motorische redzaamheid (ADL, kleutervaardigheden, Participatieproblemen: deelname aan sport en spel en motorisch leren.
Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
4-18 jaar Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis). Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren (zoals vermoeidheid, toename van eisen vanuit de omgeving), wat heeft de ouder al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect.
Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
Vragen naar motorische redzaamheid (ADL, kleutervaardigheden, schrijven, participatie: deelname aan sport en spel) en motorisch leren.
Observatie
0-4 jaar Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan (op de tenen vanaf 2 jaar), lopen, met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen vanaf 3 jaar, op de hakken vanaf 3 jaar), staan op 1 been (vanaf 4 jaar), springen (vanaf 2 jaar), hinkelen (vanaf 4 jaar), rennen.
Fijne motoriek: manipuleren met voorwerpen, stapelen van voorwerpen.
4-18 jaar Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan, lopen met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen, op de hakken), springen, hinkelen, huppelen, rennen.
Automatisering van bewegingen door aanbieden dubbele taken (praten en handelen tijdens lopen).
Anticiperen: variëren in snelheid en richting van bewegen (uitwijken voor speelgoed dat op de grond ligt). Kijken naar kwaliteit en symmetrie van bewegingen in relatie tot leeftijd, looppatroon (breedte van loopbasis, afwikkeling, ondersteuning van de armen, romprotatie). Invloed van verhogen van de taakeis op kwaliteit van bewegen, vermoeidheid, stressreactie (frustratie, taakeis willen veranderen, niet meer willen werken).
Lichamelijk onderzoek Visus
Kracht (volhouden van), herhaaldelijk laten opstaan (zoeken naar Gower’s sign), tonus (actieve en passieve tonus), reflexen, proef van Romberg, test onwillekeurige bewegingen (0-4 jaar door observatie, 4-18 jaar test), diadochokinese (0-4 jaar door observatie tijdens spel, 4-18 jaar met test), vinger-neus test (vanaf 4 jaar), vinger-oppositie test (vanaf 5 jaar).
Onderzoek houdings-en bewegingsgevoel/lichaamsschema
Mobiliteit: range-of-motion (passief en actief)
Executief: aandacht, motivatie, begrip van opdrachten, lichaamsbesef
Asymmetrie qua vorm en functies (CP, NAH: niet frequent maar toch mogelijk)
Coördinatie-en automatiseringsproblemen bij vijf jaar, dan denken aan DCD
Beleid
| Signaal | Verwijzing |
| Asymmetrie in kracht, onwillekeurige bewegingen | Naar neuroloog |
| Naast motorische ontwikkeling ook andere domeinen betrokken | Naar kinderarts (en/of kinderrevalidatiearts) |
| Duidelijke motorische achterstand en geen ontwikkelingsproblemen bij andere domeinen | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderergotherapeut/ ergotherapeut |
| Regressie in motorische ontwikkeling | Naar kinderarts |
| Orthopedische problemen, zoals Stugge pes planus valgus, beenlengteverschil > 2 cm, scoliose |
Naar orthopeed Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut bij niet structurele scoliose (check ervaring met diagnostiek en behandeling) |
| Bij twijfel | Overweeg een extra controle/verwijzing naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ kinderergotherapeut/ motorisch remedial teacher voor eenmalig onderzoek |
Algemeen: verwijzing naar de kinderarts bij dysmorfieën, als meerdere ontwikkelingsdomeinen afwijkend zijn of bij een vermoeden van systeemziekte.
Casus 3 ‘Mijn kind is sneller moe dan andere kinderen’
Differentiaaldiagnose
Conditie (beweegarmoede, overgewicht, NMA, algemene interne problematiek: stofwisselingsziekte, cardiale problematiek, pulmonale problematiek), hypermobiliteit, DCD, gedrag.
Onderzoek door de jeugdarts
Anamnese
0-18 jaar Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis).
Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren, wat heeft de ouder al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect. Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
Participatieproblemen.
Vragen naar motorische redzaamheid in ADL, participatie: deelname aan sport en spel, frequentie en intensiteit, en motorisch leren. Vragen naar specifieke signalen van interne problematiek. Ontwikkeling groei (BMI), voedingspatroon.
Observatie
0-4 jaar Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan (op de tenen vanaf 2 jaar), lopen, met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen vanaf 3 jaar, op de hakken vanaf 3 jaar), staan op 1 been (vanaf 4 jaar), springen (vanaf 2 jaar), hinkelen (vanaf 4 jaar), rennen, traplopen.
4-18 jaar Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan, lopen met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen, op de hakken), springen, hinkelen, huppelen, rennen, traplopen (indien mogelijk).
Automatisering van bewegingen door aanbieden van dubbele taken (praten en handelen tijdens lopen).
Anticiperen: variëren in snelheid en richting van bewegen. Kijken naar kwaliteit en symmetrie van bewegingen in relatie tot leeftijd, looppatroon (breedte van loopbasis, afwikkeling, ondersteuning van de armen, romprotatie). Invloed van verhogen van de taakeis op kwaliteit van bewegen, vermoeidheid, stressreactie (frustratie, taakeis willen veranderen, niet meer willen werken, vegetatieve reacties), pijnklachten, benauwdheid, hersteltijd.
Lichamelijk onderzoek
Kracht, BMI, mobiliteit gewrichten, hart- en longonderzoek
Beleid
| Signaal | Verwijzing |
| Bij vermoeden van interne problematiek of NMA | Naar kinderarts (en/of kinderrevalidatiearts) |
| Bij vermoeden van anemie | Naar huisarts |
| Bij ongezonde leefstijl | Gezonde leefstijl bevorderen (sport, gymgroepen)/Verwijzen naar diëtist/verwijzen naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut voor beweegprogramma |
| Bij motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen, zonder interne problematiek/tekenen van NMA |
Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ motorisch remedial teacher voor testen conditie en motorische vaardigheden |
Casus 4 ‘Mijn kind loopt op de tenen’
Differentiaaldiagnose
Normale variant, familiair, tactiele afweer, NMA, autisme-spectrum stoornis (ASS), orthopedisch probleem (bijvoorbeeld verkorte achillespezen), CP
Onderzoek door de jeugdarts
Anamnese
0-18 jaar: Beloop van de klacht, verschil tussen blote voeten en met schoenen, familiaire voorgeschiedenis, uitingen van tactiele afweer. Voorbeelden zijn haren wassen, nagels knippen, bepaalde structuur van voedsel, labels van kleding.
Motorische ontwikkeling.
Positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren. Voorbeelden zijn stress, onzekerheid. Sociaal emotionele ontwikkeling, gedrag: stereotypieën, rigiditeit.
Observatie
0-4 jaar Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan (op de tenen vanaf 2 jaar), lopen, met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen vanaf 3 jaar, op de hakken vanaf 3 jaar), staan op 1 been (vanaf 4 jaar), springen (vanaf 2 jaar), hinkelen (vanaf 4 jaar), rennen, traplopen
4-18 jaar Contactname, spelgedrag, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond, opstaan vanaf de grond, gaan zitten vanuit stand, staan, lopen met en zonder schoenen (op een lijn vanaf 4 jaar, op de tenen, op de hakken), springen, hinkelen, huppelen, rennen, traplopen (indien mogelijk).
Automatisering van bewegingen door aanbieden dubbele taken (praten en handelen tijdens lopen).
Anticiperen: variëren in snelheid en richting van bewegen.
Kijken naar kwaliteit en symmetrie van bewegingen in relatie tot leeftijd, looppatroon (breedte van loopbasis, afwikkeling, ondersteuning van de armen, romprotatie). Invloed van verhogen van de taakeis op kwaliteit van bewegen, vermoeidheid, stressreactie (frustratie, taakeis willen veranderen, niet meer willen werken, vegetatieve reacties), pijnklachten.
Lichamelijk onderzoek
0-18 jaar Inspectie totale statiek, mobiliteit (specifiek onderste extremiteiten), tonus kuitspieren
Beleid
| Signaal | Verwijzing |
| Vermoeden van tactiele afweer | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ ergotherapeut/ kinderrevalidatiearts/ motorisch remedial teacher |
| Vermoeden NMA/CP | Naar kinderarts |
| Tekenen van ASS | Naar kinderarts |
| Structurele beperking mobiliteit | Naar orthopeed |
Casus 5 ‘Mijn kind schuift op de billen’
Differentiaaldiagnose
Normale variant, NMA, CP, evenwichtsproblemen, hypermobiliteit
Onderzoek door de jeugdarts
Anamnese
0-18 maanden Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis).
Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren. Wat heeft de ouder al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect.
Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
Verloop motorische ontwikkeling.
Participatie
Observatie
Contactname, spelgedrag, transfers ruglig naar buiklig, gaan zitten, zitten en verplaatsen op de grond.
Lichamelijk onderzoek
Houdings- en evenwichtsreacties, mobiliteit, symmetrie van bewegen, spontane bewegingen onderste ledematen
Beleid
| Signalen | Verwijzing |
| Vermoeden van NMA | Naar kinderarts / kinderrevalidatiearts |
| Hypermobiliteit, zonder andere signalen van pathologie | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ ergotherapeut |
| Evenwichtsproblemen, zonder verdere signalen | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ ergotherapeut |
Casus 6 ‘Het kind heeft moeite met leren schrijven (groep 3)’
Differentiaaldiagnose
Lage cognitieve capaciteiten, DCD, onvoldoende ervaring/oefening, motivatieproblemen, subtiele NAH, taalstoornis, leerproblemen, visuele stoornis
Onderzoek door de jeugdarts
Anamnese
4-6/7 jaar Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis)
Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren. Wat heeft de ouder/schoolleerkracht al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect?
Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
Verloop motorische ontwikkeling (m.n. fijne motoriek).
Participatie. Evaluatie overige ontwikkelingsdomeinen. Cognitief functioneren, ADL-vaardigheden.
Risicofactoren voor NAH: trauma capitis, ernstige infecties/ ziektes, zie 1.3.4.
Observatie
4-6/7 jaar Contact name, spraak-taalontwikkeling (zelf laten vertellen, antwoorden), tekenen, kleuren, maken schrijfpatronen, manipuleren met voorwerpen. Letten op: pengreep, vingerbewegingen, dosering, inzicht.
Lichamelijk onderzoek
Onwillekeurige bewegingen, diadochokinese, vinger-neus test (vanaf 4 jaar), vinger-oppositie test (vanaf 5 jaar).
Mobiliteit: range-of-motion (passief en actief), kracht van de armen.
Tonus armspieren.
Visus.
Executief: aandacht, motivatie, begrip van opdrachten, lichaamsbesef.
Beleid
| Signaal | Verwijzing |
| Schrijfproblemen, zonder tekenen van pathologie | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ kinderergotherapeut/ motorisch remedial teacher |
| Tekenen van NAH | Naar kinderarts / kinderrevalidatiearts |
| Visus problemen | Naar oogarts/opticien afhankelijk van de leeftijd en conform richtlijn visus |
| Problemen met de fijne motoriek | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut/ kinderoefentherapeut/ kinderergotherapeut/ motorisch remedial teacher |
| Schrijfproblemen en leerproblemen | Orthopedagoog/psycholoog voor orthodidactisch onderzoek/IQ-test |
Casus 7 ‘Het kind heeft schrijfproblemen bij verhoging van tempo (groep 5)’
Differentiaaldiagnose
DCD, aandachtsproblemen, cognitieve factoren, visuele stoornis
Onderzoek door de jeugdarts
Anamnese
Risicofactoren (perinatale complicaties, familiaire voorgeschiedenis)
Beloop van de klacht, positief en negatief beïnvloedende factoren. Wat heeft de ouder/schoolleerkracht al zelf gedaan en wat was daarvan het effect. Ontwikkeling van andere ontwikkelingsgebieden.
Verloop motorische ontwikkeling (met name fijne motoriek)
Participatie.
Evaluatie overige domeinen van ontwikkeling. Cognitief functioneren, ADL-vaardigheden.
Observatie
Contactname, globaal kijken naar het schrijven (houding, pengreep, druk op pen en papier, verfijning van bewegingen). Kijken naar het handschrift (vloeiendheid, vormgeving van letters, pauzes, spaties tussen woorden), ruimtelijke aspecten (gebruik van het vel, regelloop), natekenen van figuren, manipulatie met materiaal, verschil naschrijven en uit het hoofd schrijven, indruk cognitie.
Beleid
| Signaal | Verwijzing |
| Schrijfproblemen zonder andere ontwikkelingsproblemen | Naar kinderfysiotherapeut / kinderoefentherapeut / kinderergotherapeut/ motorisch remedial teacher |
| Visusproblemen | Naar oogarts/opticien afhankelijk van de leeftijd en conform richtlijn visus |
8.6 Bijlage 7 P90-waarden van motoriekkenmerken in het Van Wiechenonderzoek en in de Bayley-III-NL
P90-waarden van motoriekkenmerken die zowel in het Van Wiechenonderzoek als in de Bayley-III_NL worden weergegeven[15],[134].
| Van Wiechen-kenmerk | P90 volgens VWO | P90 volgens Bayley-III |
| 1. Ogen fixeren | 4 weken | 6 weken |
| 2. Volgt met ogen en hoofd (300 <- 00 -> 300) | 8 weken | 6 weken |
| 3. Handen af en toe open | 13 weken | 20 weken |
| 4. Speelt met handen middenvoor | 26 weken | 17 weken |
| 5. Pakt in rugligging voorwerp binnen bereik | 26 weken | 24 weken |
| 6. Pakt blokje over | 39 weken | 44 weken |
| 7. Speelt met beide voeten (M) | 39 weken | 46 weken |
| 8. Pakt propje met duim en wijsvinger | 52 weken | 48 weken |
| 52. Heft kin even van onderlaag | 4 weken | 5 weken |
| 53. Heft in buikligging hoofd tot 450 | 13 weken | 17 weken |
| 54. Kijkt rond met 900 geheven hoofd | 26 weken | 26 weken |
| 55. Rolt zich om van rug naar buik en omgekeerd (M) | 39 weken | 42 weken |
| 56. Kan hoofd goed ophouden in zit | 39 weken | 34 weken |
| 57. Zit stabiel los | 52 weken | 44 weken |
| 58. Kruipt vooruit, buik op de grond (M) | 12 maanden | 13 maanden |
| 59. Trekt zich op tot staan (M) | 12 maanden | 14 maanden |
| 60. Kruipt vooruit, buik vrij van de grond (M) | 15 maanden | 14 maanden |
| 61. Loopt langs (M) | 15 maanden | 15/16 maanden |
| 11. Stapelt 2 blokjes | 18 maanden | 21 maanden |
| 12. Stapelt 6 blokjes | 24 maanden | 31 maanden |
| 13. Bouwt vrachtauto na | 36 maanden | > 42 maanden |
| 14. Tekent verticale lijn na | 36 maanden | 36 maanden |
| 15. Tekent cirkel na | 48 maanden | 38 maanden |
| 16. Houdt potlood met vingers vast | 48 maanden | 36 maanden |
| 17. Tekent kruis na | 52 maanden | > 42 maanden |
| 66. Kruipt vooruit, buik vrij van de grond (M) | 15 maanden | 14 maanden |
| 67. Loopt langs (M) | 15 maanden | 15/16 maanden |
| 68. Loopt los / loopt goed los / loopt soepel | 18 / 24 /36 maanden | 20 / 21 maanden |
| 69. Gooit bal zonder om te vallen | 18 maanden | 19 maanden |
| 70. Raapt vanuit hurkzit iets op | 24 maanden | 22 maanden |
| 71. Schopt bal weg | 30 maanden (P93) | 28 maanden |
| 72. Kan minstens 5 seconden op één been staan | 54 maanden | > 42 maanden |
* Instructies tussen Bayley III en VWO zijn enigszins verschillend[15],[134].
8.7 Bijlage 8 Criteria van Wilson en Jungner
De 10 criteria hebben betrekking op de ziekte en op de screeningsprocedure[98]:
1. Voorwaarden ten aanzien van ziekte
- De ziekte in kwestie vormt een belangrijk gezondheidsprobleem;
- Het natuurlijk beloop van de ziekte is bekend;
- Er bestaat een algemeen aanvaarde behandelwijze;
- Er is sprake van een herkenbare presymptomatische fase, die zich effectiever laat beïnvloeden dan de symptomatische fase van de ziekte;
- Voorzieningen voor het stellen van de diagnose en voor de behandeling zijn aanwezig.
2. Voorwaarden ten aanzien van de screeningsprocedure
- De voor de screening gebruikte methode is effectief;
- De procedure is acceptabel voor de te screenen populatie;
- Het is duidelijk wie behandeld moet worden;
- De procedure is efficiënt gezien de te maken kosten;
- De aangeboden voorziening is structureel.
8.8 Bijlage 9 Kenmerken van motorische testen voor de beoordeling van de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen van 0-18 jaar
Motorische testen voor de algemene (niet-geselecteerde) populatie, zonder Nederlandse normwaarden.
| Meetinstrument | Leeftijd doelgroep | Wie neemt de test af? | Inhoud | Afname-duur | Valide? | Betrouwbaar? | Nederlandse normwaarden? |
| Totale motoriek | |||||||
|
Bruininks-Oseretsky-Test of Motor Proficiency (BOTMP)[108],[188], [205][206][207]
|
4-21 jaar en 11 maanden |
Lange versie: professionals
Korte versie: Professionals |
Lange versie: 53 items onderverdeeld in 4 motorische domeinen: (1) fijne manuele controle, (2) manuele coördinatie, (3) lichaamscoördinatie en (4) kracht en behendigheid.
Korte versie: 14 items |
Lange versie: 40-60 min.
Korte versie: 15-20 min. |
Lange versie: Nee
Korte versie: Nee Venetsanou et al212 geven suggesties voor aanpassingen; volgens Kambas129 is de test wel valide bij Griekse kleuters en basisschoolkinderen |
Lange versie: onbekend
Korte versie: onbekend |
Lange versie: Nee
Korte versie: Nee
|
|
Denver Developmental Screening Test-II[190]
|
0-6 jaar | Kinder- fysiotherapeut | 125 items onderverdeeld in 4 aspecten (sociaal, fijne motoriek, grove motoriek en taal) | 20-30 min. | Ja | Ja | Nee |
|
Peabody Developmental Motor Scales-2 (PDMS-2)[135],[193], [209]
|
0 – 71 maanden | Fysiotherapeut | 6 motorische subtesten: reflexen, stilstaan, bewegingen, object manipulatie, grijpen en visuele-motorische integratie. Deze 6 subtesten worden onderverdeeld in 3 uitkomstmaten: fijne motoriek quotiënt, grove motoriek quotiënt en totale motoriek quotiënt. | 45-60 min. | Ja | Ja | Nee |
|
NIH Toolbox Motor Domain Battery[210]
|
3-85 jaar | Niet omschreven | 5 subdomeinen: behendigheid, kracht, balans, loopsnelheid en uithoudingsvermogen | Onbekend |
Ja
|
Onbekend | Onbekend |
|
Computer-based test[211]
|
8-55 jaar | Niet omschreven | Personen moeten een joystick bedienen om virtuele doelen van verschillende groottes te raken die op een scherm verschijnen. Er zijn 3 verschillende groottes van het doel (klein, gemiddeld en groot) | 20 min. |
Ja (onderzocht met Purdue Pegboard en 9-hole Pegboard test) |
Ja | Onbekend |
|
Motor Proficiency Test for Children[203]
|
4-6 jaar | Getrainde fysiotherapeut | 18 items (voorwaarts springen, vooruitlopen, stippen maken op een vel papier, tissue grijpen met tenen, zijwaarts springen, vangen van een gevallen stok, ballen verplaatsen, achteruitlopen, bal naar een doel gooien, verzamelen matches, door een hoepel gaan, springen in een hoepel op een voet, een ring vangen, jumping jacks, springen over een koord, rollen over de lengteas van je lichaam, opstaan met een bal op je hoofd, springen en draaien in een hoepel. | 15-20 min. | Ja | Ja | Onbekend |
|
Harris Infant Neuromotor Test (HINT)[212]
|
2,5-12,5 maanden | Zorgverleners, zoals fysiotherapeut, jeugdverpleegkundige | De test bestaat uit 4 onderdelen: (1) achtergrondinformatie, (2) vragen waarbij de mate van bezorgdheid van verzorgers over de bewegingen en spel van het kind wordt vastgesteld, (3) een observationele of test sectie (21 items) om de bewegingen van het kind vast te stellen, en (4) de algehele impressie van de clinicus over de ontwikkeling van het kind | 15-30 min. |
Ja (onderzocht met ASQ) |
Ja (onderzocht in andere artikelen) |
Onbekend |
|
Zurich Neuromotor Assessment (ZNA)[202]
|
3-5 jaar | – | De test meet de snelheid en kwaliteit van bepaalde motorische taken. | Onbekend | Onbekend | Ja | Onbekend |
|
Test of Infant Motor Performance Screening Items (TIMPSI) (verkorte versie van de TIMP)[189]
|
34 weken pma-17 weken post-term | Niet omschreven | 11 items van de TIMP | 22 min. | Ja (onderzocht met de TIMP) | Onbekend | Onbekend |
| Grove motoriek | |||||||
|
Democritos Movement Screening Tool[203]
|
4-6 jaar | Niet omschreven | 9 items onderverdeeld in 2 aspecten (grofmotorische vaardigheden en visuele motorische vaardigheden) | Onbekend | Ja (voorlopig; verder onderzoek is nodig) | Onbekend | Onbekend |
|
Test of Gross Motor Development-2 AAA (subtest: object control)[185]
NB 3e versie is net verschenen |
3-10 | Niet omschreven | 6 items die behoren bij de subtest ‘object control’ | Onbekend | Niet onderzocht | Ja, echter, sommige onderdelen kunnen nog verbeterd worden | Onbekend |
|
Körperkoordinationstest für Kinder (KTK-NL)[194]
|
5-12 | Leerkrachten | 4 subtests gericht op grofmotorische ontwikkeling bij kinderen | 15 minuten | matig | Onbekend | |
|
Preschooler Gross Motor Quality Scale (PGMQ)[213],[214]
|
Preschoolers | Niet omschreven | 17 items in 3 subschalen: locomotie (8 items), object manipulatie (5 items) en balans (4 items) | Onbekend |
Ja (onderzocht met TGMd-2) |
– | Onbekend |
|
Children’s Activity and Movement in Preschool Study Motor Skills Protocol (CMSP)[215]
|
Pre-schoolers | Niet omschreven | Verdeeld over 2 subschalen: locomotor (6 vaardigheden) en object controle (6 vaardigheden) |
45 min. (4 trials per vaardig-heid) 25-30 min. (2 trials per vaardig-heid) |
Ja (onderzocht met TGMD-2) |
Ja | Onbekend |
| Fijne motoriek | |||||||
|
Writing Readiness Inventory Tool in Context (WRITIC)[198]
|
5-6 jaar | – | 3 domeinen die elk weer bestaan uit 2 subdomeinen: Kind (interesse en aandacht), Omgeving (fysieke omgeving en sociale omgeving) en Papier-potlood taken (taak prestatie en intensiteit van prestatie) | 20 min. |
Ja (onderzocht met Beery-Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration and the Nine-Hole Peg Test) |
Ja | Onbekend |
|
Nine-hole Peg Test[216]
|
5-10 jaar | – | Kinderen moeten zo snel mogelijk 9 pinnetjes in een pegboard plaatsen en verwijderen met één hand. | < 5 minuten | Ja (onderzocht met Purdue Pegboard Test) | Ja | Onbekend |
8.9 Bijlage 10 Kenmerken van vragenlijsten voor de beoordeling van de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen van 0-18 jaar
Vragenlijsten voor de algemene (niet-geselecteerde) populatie, zonder Nederlandse normwaarden.
| Vragenlijst | Leeftijd doelgroep | Wie neemt de test af? | Inhoud | Afname-duur | Valide? | Betrouwbaar? | Nederlandse normwaarden? |
| Totale motoriek | |||||||
|
Preschool Child Development Inventory (PCDI)[196]
|
3-6 jaar | Moeders | 208 statements verdeeld over 6 subtesten, waarvan 3 motorische testen: grove motoriek (27 statements), fijne motoriek (22 statements) en zelfhulp (25 statements) | Onbekend | Ja | Onbekend | Onbekend |
|
Toddler Language and Motor Questionnaire[197]
|
15-38 maanden |
Moeders
|
144 items verdeeld over 3 motorisch gerelateerde testen (grove motoriek, fijne motoriek en zelfhulp) en 2 taal gerelateerde testen | Onbekend | Ja (onder andere onderzocht met IJslandse versie van CDI en IJslandse versie van WPPSI-R) | Ja | Onbekend |
|
Infant Movement Motivation Questionnaire (IMMQ)[191]
|
0-12 maanden | Ouders | 27 items, bestaande uit 4 hoofdgroepen: Activiteit, Ontdekken, Motivatie en Aanpassingsvermogen | 21 min. | Onbekend | Test lijkt betrouwbaar, maar verder onderzoek is nodig | Onbekend |
|
Inventory to obtain information from mothers[195]
|
4-41 maanden | Moeders | 174 items verdeeld over 6 subtesten: grove motoriek, fijne motoriek, taalbegrip, taaluitdrukking, persoonlijke-sociale competentie en zelfhulp | Onbekend | Ja | Ja | Onbekend |
| Grove motoriek | |||||||
|
Maternal assessment[217]
|
0-3 jaar | Moeders | Vragen over de leeftijd waarop kinderen 8 belangrijke mijlpalen behalen | Onbekend | Niet onderzocht | Voldoende betrouwbaar | Onbekend |
| Fijne motoriek | |||||||
|
Contextual Fine Motor Questionnaire[218]
|
4-8 jaar |
Ouders, verzorgers, leerkrachten
|
Hiermee wordt vooral ADL getest; 24 vragen verdeeld over 5 categorieën (pencontrole, gebruik van eetgerei, aansluiten en scheiden, het openen van voorwerpen). Maximale score is 108 (hoe hoger de score, hoe slechter de fijnmotorische vaardigheid) | Onbekend | Ja | Ja | Onbekend |
8.10 Bijlage 11 Kenmerken van observatie-instrumenten voor de beoordeling van de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen van 0-18 jaar
Observatie-instrumenten voor de algemene (niet-geselecteerde) populatie, zonder Nederlandse normwaarden.
| Observatie instrument | Leeftijd doelgroep | Wie neemt de test af? | Inhoud | Afnameduur | Valide? | Betrouwbaar? | Nederlandse normwaarden? |
| Totale motoriek | |||||||
|
The Infant Motor Profile (IMP)[16],[199],[200]
|
3-18 maanden, of, bij langzame motorische ontwikkeling, tot de leeftijd dat het kind enkele maanden zelfstandig kan lopen. | Onbekend |
Spontaan motorisch gedrag (of uitgedaagd met speelgoed) wordt met een video opgenomen in de volgende condities: rugligging, buikligging, zitten met en zonder ondersteuning, staan met en zonder ondersteuning en zitten bij een ouder/verzorger op schoot. De IMP bestaat uit 80 items die onderverdeeld zijn in 5 subschalen: variabiliteit (repertoire; 25 items), variabiliteit (mogelijkheid tot het kunnen selecteren van de meest passende beweging; 15), vloeiend (7), symmetrisch (10) en prestatie (bereiken van mijlpalen; 23 items) |
15 min. filmen + beoorde-ling film |
Goede concurrent validiteit met de AIMS en neurologische test. Goede constructvaliditeit (vergeleken met prenatale, perinatale en neonatale variabelen) |
Ja | Onbekend |
|
Structured Observation of Motor Performance in Infants-I [201]
|
0-12 maanden | Verpleegkundigen |
Zowel de spontane- en vrijwillige bewegingen van kinderen in rugligging, buikligging, zittende houding, staande houding en tijdens het bewegen als de handfunctie worden geobserveerd en beoordeeld op niveau en kwaliteit. De score voor niveau loopt van 0-72 (hoe hoger hoe beter); de score voor kwaliteit loopt van 0-24 (hoe lager hoe beter).
|
Onbekend | Onbekend | Wel voor het bepalen van het niveau, maar niet voor het bepalen van de kwaliteit van motorische bewegingen. | Onbekend |
|
School version of the Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (School AMPS)[192]
|
Niet beschreven | Niet beschreven | Items zoals knippen en plakken worden geobserveerd in het klaslokaal. | Onbekend | De studie toont aan dat de test twee verschillende aspecten meet (school motorische vaardigheden en school proces vaardigheden) (onderzocht met de PDMS-FM) | Onbekend | Onbekend |
| Grove motoriek | |||||||
|
Gross Motor Rating Scale (GMRS)[219]
|
Niet beschreven | Leerkrachten | 20 items onderverdeeld in 3 categorieën: grofmotorische vaardigheden (10 items), fysieke kwaliteiten (7 items) en bewegingsmotivatie (3 items) | Onbekend |
Nee (onderzocht met o.a TGMD en M-ABC) |
Onbekend | Onbekend |
8.11 Bijlage 12 Gouden standaard bij onderzoek naar validiteit van motoriektesten
12.1 Movement Assessment Battery for Children
De Movement ABC is in 2007 vernieuwd (M-ABC-2) en bestaat uit een motorische test en een checklist. De motorische testen zijn geschikt voor kinderen in de leeftijd van 3-16 jaar, terwijl de checklist is ontwikkeld voor kinderen van 5 tot 11+ jaar. De M-ABC-2 wordt internationaal het meest frequent gebruikt als referentietest (gouden standaard). Hierbij wordt echter door meerdere geraadpleegde experts aangetekend dat de M-ABC eigenlijk niet geschikt is als gouden standaard, omdat de M-ABC weliswaar uitgebreid op stoornisniveau meet (8 domeinen) maar niet op participatieniveau (de mate waarin een kind, met eventuele motorische beperkingen, toch kan meedoen bijv. aan de activiteiten op school waarbij motorische vaardigheden gebruikt worden). Daarom omvat de M-ABC niet de totale motorische ontwikkeling van kinderenExpert opinion; projectgroep.
Inhoud en afname
De motorische test bestaat uit motorische taken, die onderverdeeld zijn in drie domeinen: handvaardigheid, mikken en vangen, en evenwicht. De scores op deze testen worden omgezet in standaardscores met bijbehorende percentielscores. Hiermee kan worden vastgesteld hoe een kind presteert ten opzichte van zijn leeftijdgenoten. De leeftijdsgroepen zijn opgedeeld in 3-6 jaar, 7-10 jaar en 11-16 jaar. De stoplichtmethode wordt gebruikt om te beoordelen of de prestaties van een kind in het
- Normale bereik vallen: scores in groene deel van de normtabel, boven het 16e percentiel,
- Licht afwijkend zijn: scores in het oranje deel van de normtabel, tussen 5e-15e percentiel,
- Afwijkend zijn: scores in het rode deel van de normtabel, beneden het 5e percentiel.
Er zijn Nederlandse normwaarden beschikbaar, gebaseerd op 3230 Vlaamse en Nederlandse kinderen. De onderzoekspopulatie was representatief voor de sociodemografische status (etniciteit, educatieniveau ouders, verdeling over de geografische regio’s). Het afnemen van de test duurt 20-40 minuten en dient te worden uitgevoerd door kinderfysiotherapeuten/ kinderoefentherapeuten, die hierin getraind zijn.
De checklist bestaat uit drie delen, waarbij deel A bestaat uit 15 vragen over functionele activiteiten in een stilstaande of voorspelbare omgeving, deel B uit 15 vragen over functionele activiteiten in een bewegende, onvoorspelbare omgeving, en deel C uit 13 vragen gerelateerd aan het gedrag dat van invloed kan zijn op de motoriek van het kind. De checklist wordt ingevuld door leerkrachten en/of ouders. De scores op deel A en B worden opgeteld tot een totaalscore en beoordeeld door middel van de stoplichtmethode (zie hiervoor) aan de hand van een normtabel. Hoe hoger de totaalscore, hoe slechter de motorische vaardigheden. Ook de checklist is voor Nederlandse kinderen genormeerd.
Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing
De betrouwbaarheid (interbeoordelaarsbetrouwbaarheid, test-hertestbetrouwbaarheid) en validiteit (soortgenotenvaliditeit) van de motorische test van de Movement ABC-2 zijn goed bevonden[108]. De psychometrische eigenschappen van de checklist zijn onderzocht bij een groep Nederlandse kinderen De onderzochte groep was representatief voor de sociodemografische status (etniciteit, educatie niveau ouders, verdeling over de geografische regio’s[127]). Voor het onderzoeken van de validiteit, sensitiviteit en specificiteit van de checklist van de M-ABC-2 zijn de motorische test van de M-ABC-2 en de Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire als referentietesten gebruikt. De interne consistentie van de items van de checklist is zeer goed gebleken. Dit betekent dat elke vraag van de checklist een bepaald aspect meet van het motorisch functioneren van kinderen. De validiteit van de checklist blijkt voldoende te zijn. Beide bevindingen blijken ook uit ander onderzoek bij verschillende leeftijdscategorieën[126]. De sensitiviteit van de checklist is echter vrij laag. Daarom wordt afgeraden om de checklist te gebruiken als screeningsinstrument in een basisschoolpopulatie[108],[128]. De vragenlijst zou in de toekomst, na nader onderzoek naar hiervoor geschikte indicaties, mogelijk wel op indicatie gebruikt kunnen worden binnen de JGZExpert opinion.
12.2 Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development
De Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development (Third edition, Nederlandse versie; Bayley-III NL) is een observatie-instrument om de vroegkinderlijke ontwikkeling in kaart te brengen bij kinderen vanaf 16 dagen tot en met 42 maanden en 15 dagen. De test bestaat uit de schalen cognitie, taal (taalbegrip en taalproductie) en motoriek (grove en fijne motoriek). Daarnaast bevat de test nog twee schalen die met behulp van een vragenlijst door ouders of verzorgers van het kind worden beoordeeld: het sociaal-emotionele gedrag en adaptief gedrag (conceptuele, sociale en praktische vaardigheden).
Inhoud en afname
Het motorische testgedeelte bestaat uit 66 items voor het beoordelen van de fijne motoriek en 72 items voor het beoordelen van de grove motoriek, welke worden beoordeeld door een in de Bayley getrainde instructeur die ervaring heeft in het omgaan met peuters en kleuters[136],[221]. Het afnemen van de totale test duurt 31-86 minuten, afhankelijk van de leeftijdsgroep[221].
Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing
De Bayley-III-NL blijkt een betrouwbaar en valide meetinstrument te zijn met goede psychometrische eigenschappen, waarvan ook Nederlandse normwaarden beschikbaar zijn[136],[221].
12.3 Alberta Infant Motor Scale
De Alberta Infant Motor Scale (AIMS) is een observatie-instrument met als doel het vroegtijdig identificeren van kinderen in de leeftijd van 0 tot 18 maanden met een vertraagde of afwijkende grofmotorische ontwikkeling[129].
Inhoud en afname
De motoriek van kinderen wordt gemeten in vier verschillende posities met in totaal 58 items. De grofmotorische vaardigheden worden beoordeeld in rugligging (21 items), buikligging (9 items), zittend (12 items) en staand (16 items)[108]. De afnameduur van de AIMS bedraagt 20-30 minuten[129]. De test kan afgenomen worden door kinderfysiotherapeuten/kinderoefentherapeuten die hierin geschoold zijn.
Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing
De betrouwbaarheid en validiteit van de AIMS zijn grondig onderzocht en blijken beiden goed te zijn[120],[129],[131]. De normwaarden voor kinderen die in Nederland wonen worden momenteel vastgesteld.
8.12 Bijlage 13 Overzichtsformulier motorische vaardigheden 4-vaardigheden scan
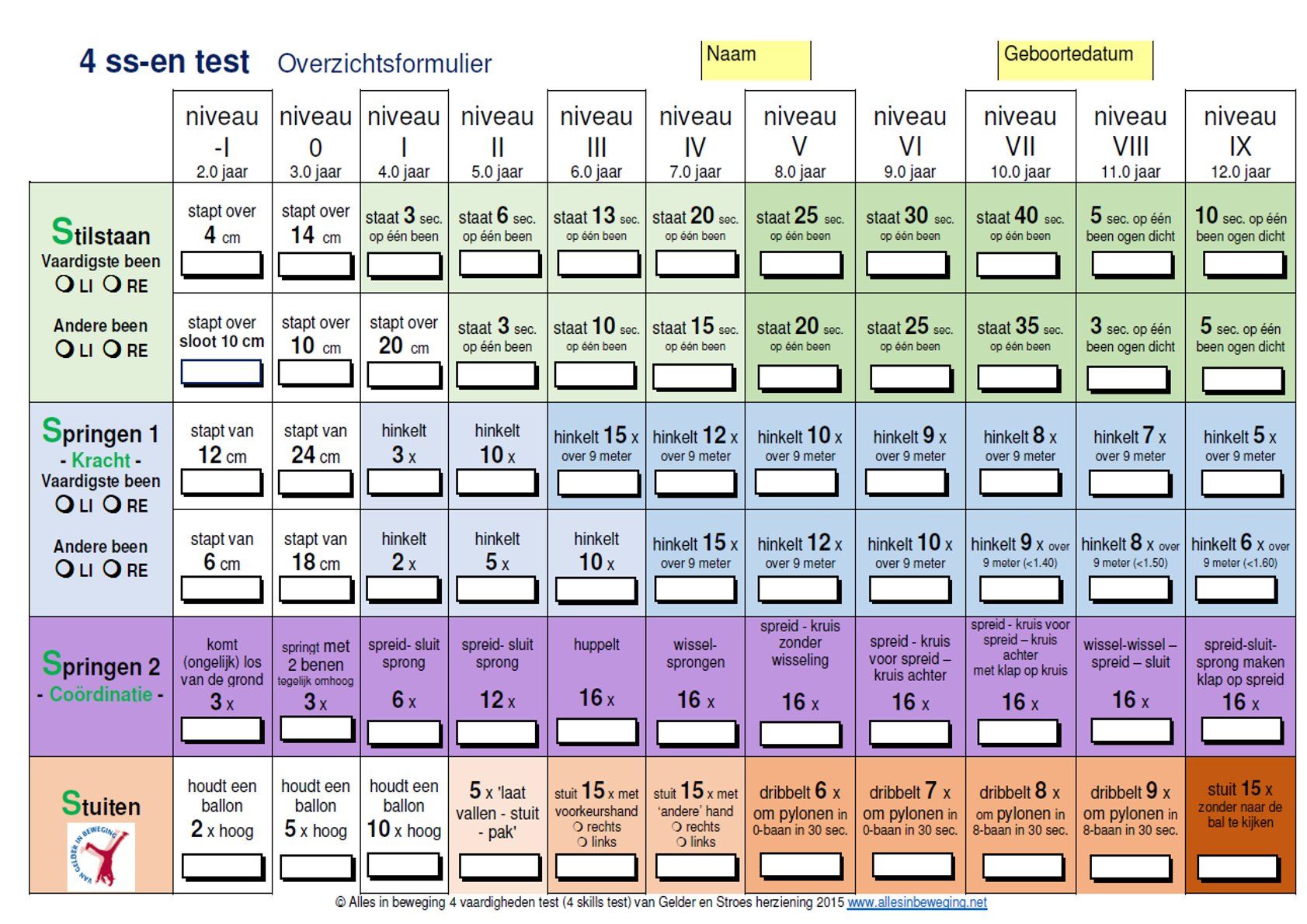
Voor elke vaardigheid wordt een ontwikkelingslijn aangegeven. Zo loopt bij de vaardigheidslijn ’Stuiten’ de lijn van ’het hooghouden van een ballon’ (indicatie groep 1) tot het ’dribbelen in tempo in een 8-baan’ (indicatie groep 8 en de brugklas). Elke vaardigheidslijn is gekoppeld aan niveaus en indien gewenst aan genormeerde leeftijdsindicaties; Voor elke vaardigheid zijn observatiecriteria aangegeven; Voor elke vaardigheid worden tips gegeven om efficiënt te observeren. Per vaardigheidslijn wordt in ieder geval beschreven: de situatie waarin geobserveerd wordt; de opdracht; de beoordeling aan de hand van niveaus en uitvoering; tips voor een effectieve observatie en registratie.
8.13 Bijlage 14 Groninger Motoriek Observatieschaal (GMO)
De GMO is ontwikkeld om kinderen die motorisch onhandig zijn en kinderen die een verhoogd risico hebben op Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) te identificeren aan de hand van een vragenlijst. Het meetinstrument is bedoeld voor kinderen in de leeftijd van 5-11 jaar[144]. De vragenlijst bevat 18 items (grove en fijne motoriek) die door leerkrachten zowel binnen als buiten het klaslokaal geobserveerd kunnen worden. De 18 items zijn onder te verdelen in twee onderwerpen; algemeen motorische functioneren en handschrift. Alle items worden gescoord op een schaal van 1 (niet van toepassing) tot 4 (wel van toepassing). De eindscore wordt bepaald door de scores van alle items bij elkaar op te tellen.
Per leeftijd zijn er aparte normscores opgesteld voor jongens en meisjes. De beoordeling van de motoriek valt op basis van percentielen naar leeftijd en geslacht in één van de drie categorieën:
- normaal (score > P15),
- licht afwijkend (score tussen P5 en P15),
- afwijkend (score < P5).
Bij categorie 2 en 3 is nader onderzoek nodig. De normering van de GMO is gebaseerd op 1919 basisschoolleerlingen van 5 tot en met 11 jaar[220]. De sensitiviteit van de GMO in een gemengde populatie (algemeen en geselecteerd) is 80,5% en de specificiteit 62%[144]. Voor alleen een algemene populatie is dit onbekend.
8.14 Bijlage 15 Coördinatie Vragenlijst voor Ouders
De Development Coordination Questionnaire (DCD-Q) heet in het Nederlands Coördinatie Vragenlijst voor Ouders (CVO). De CVO is ontwikkeld om kinderen die motorisch onhandig zijn en kinderen die een verhoogd risico hebben op Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) te identificeren aan de hand van een vragenlijst. Het meetinstrument is bedoeld voor kinderen in de leeftijd van 5 tot 15;6 jaar.
De vragenlijst bevat 15 items (grove, fijne motoriek en schrijven) die door ouders worden ingevuld. Alle items worden gescoord op een schaal van 1 (‘deze omschrijving klopt helemaal niet voor mijn kind’) tot 5 (‘deze omschrijving klopt helemaal voor mijn kind’). De eindscore wordt bepaald door de scores van alle items bij elkaar op te tellen.
De CVO is gevalideerd voor de algemene populatie en geselecteerde populatie. De psychometrische eigenschappen van de CVO bij de geselecteerde populatie zijn goed. Bij gebruik in een algemene populatie is de sensitiviteit en specificiteit onvoldoende gebleken en daarom wordt geadviseerd de CVO alleen bij een geselecteerde populatie te gebruiken. Er zijn geen aparte normeringen voor jongens en meisjes, wel voor kinderen 5 tot 7;11 jaar, voor kinderen van 8 tot 9;11 jaar en voor kinderen van 10 tot 15;6 jaar. Samen met de GMO wordt de CVO gebruikt bij de diagnostiek van DCD. De diagnose DCD mag nooit op basis van alleen de GMO en CVO worden gesteld, maar alleen als voldaan is aan alle daarvoor gestelde criteria.
8.15 Bijlage 16 Neurologische onderzoeken
Hierna volgen neurologische onderzoeken per leeftijdscategorie die in de tweede of derde lijn kunnen worden uitgevoerd of door een kinderfysiotherapeut (tabel 8.16.1).
16.1 Zuigelingen (0-1;6 jaar)
Op basis van de beschrijvingen van Touwen11 met betrekking tot de neurologische ontwikkeling van zuigelingen is er een gestandaardiseerd leeftijdsspecifieke neurologisch onderzoek ontstaan voor deze doelgroep: de Touwen Infant Neurological Examination (TINE). Zie tabel 8.16 (1) Het onderzoek richt zich met name op kleine neurologische dysfuncties en start met het observeren van het motorisch gedrag van het kind in rugligging, buikligging, zittend en tijdens het reiken en grijpen. Bij oudere kinderen wordt ook naar de motorische bewegingen gekeken tijdens het staan en lopen.
Tijdens het eerste gedeelte van het onderzoek worden ook het optrekken tot zit, de zijwaartse steunreactie, de houding tijdens buikligging en de houding tijdens het optillen geëvalueerd. Hierbij is de variabiliteit in houding en bewegingen erg belangrijk. Het laatste deel van het onderzoek bestaat uit een evaluatie van de hersenstamreacties, het visuomotorisch functioneren, de spiertonus en verschillende reflexen. Het afnemen van het onderzoek duurt 15-20 minuten en de interbeoordelaarsbetrouwbaarheid blijkt goed te zijn[223].
Baby’s tonen General Movements (GM’s). Zie hoofdstuk 1. Het beoordelen van GM’s zou informatie kunnen geven over het functioneren van het brein[222],[226]. Experts verschillen van mening over het nut van het beoordelen van GM’s door de JGZ. Enkele leden van de werkgroep en enkele geïnterviewde experts geven aan dat het beoordelen van de kwaliteit van GM’s zinvolle informatie geeft over de neurologische ontwikkeling van kinderen in de leeftijd van 0-3 maanden. Kinderen bij wie geen motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen worden geconstateerd op basis van het VWO, kunnen desondanks wel duidelijk afwijkende GM’s hebben op basis van een cerebrale parese. Door middel van het beoordelen van de GM’s zouden motorische ontwikkelingsproblemen vroegtijdig opgespoord kunnen worden waardoor interventies vroegtijdig gestart kunnen worden.
Voor een adequate beoordeling van de kwaliteit van deze GM’s wordt er gebruik gemaakt van video-opnames. Een kind wordt gedurende 3-5 minuten gefilmd terwijl het beweegt (liggend op de rug). Deze videobeelden worden achteraf beoordeeld waarbij met name gelet wordt op de variatie en complexiteit van de bewegingen die het kind laat zienexpert opinion. De prevalentie van ‘zeker’ abnormale GM’s in de algehele populatie is 3.7%, en dat van ‘milde’ abnormale GM’s 25%[224]. Wetenschappelijk bewijs voor de voorspellende waarde van GM’s voor een neurologische stoornis is alleen gevonden voor een hoogrisicopopulatie (bijvoorbeeld prematuren) en kan niet worden gegeneraliseerd naar de algehele populatie[224].
De leden van de projectgroep en enkele geïnterviewde experts geven aan dat het goed kunnen afnemen en beoordelenvan GM’s erg lastig is. Hiervoor is veel scholing (en tijd) vereist. Van de jeugdartsen mag niet worden verwacht dat ze deze test valide af kunnen nemen binnen een consult. Vaak zijn de prematuren, voor wie de afname van deze test het meest zinvol wordt geacht, al in beeld bij een ‘follow-up poli prematuren’ waar ze nauwlettend in de gaten worden gehouden. Het beoordelen van GM’s binnen de JGZ heeft volgens experts daarom geen meerwaarde. Wel is het goed dat de JGZ nagaat of de premature baby inderdaad naar een follow-up poli gaat. Ook vinden ze het zinvol dat de JGZ-professional zich bewust is van het feit dat GM’s beoordeeld kunnen worden. Verder zou de kennis die verkregen kan worden bij scholing in het beoordelen van GM’s, kunnen worden toegepast bij de beoordeling van het VWO en BFMT.
16.2 Peuters en kleuters (1;6-4 jaar)
Voor peuters en kleuters bestaat er ook een gestandaardiseerd neurologisch onderzoek[30]; zie tabel 8.16 (2). Het is een leeftijdsspecifieke methode om disfuncties te detecteren en om de neurologische ontwikkeling van peuters en kleuters te evalueren. Het neurologisch onderzoek bestaat voornamelijk uit het observeren van spontaan vertoond neuromotorisch gedrag in verschillende (speel)situaties[30],[153]. Hierbij wordt onder andere gekeken naar bewegingsaspecten gedurende het grijpen, zitten, kruipen, staan, en lopen. Daarnaast wordt gekeken naar het hoofd (het beoordelen van de hersenzenuwfuncties) en naar het sensomotorisch functioneren door middel van manipulatie[12]. De betrouwbaarheid en validiteit van dit onderzoek wordt momenteel in internationaal verband onderzocht. Het afnemen van het onderzoek duurt 30 minuten[12]. Om die reden is het praktisch niet uitvoerbaar in de JGZ.
16.3 Kinderen vanaf 4 jaar
Om neurologisch onderzoek bij kleuters vanaf 4 jaar uit te voeren, wordt het Modified Touwen onderzoek gebruikt[12], zie tabel 8.16 (3) Het is een gestandaardiseerd en leeftijdsspecifiek onderzoek dat zich met name richt op kleine neurologische afwijkingen (minor neurological disorders). Het onderzoek bestaat uit acht clusters: houding, reflexen, onwillekeurige bewegingen, geassocieerde bewegingen, coördinatieproblemen, problemen met fijne manipulatie, problemen met de sensoriek en problemen met betrekking tot de hersenzenuwen[12]. De betrouwbaarheid van dit onderzoek blijkt matig tot goed te zijn wanneer het onderzoek wordt uitgevoerd in een relatief gezonde populatie[225]. Het afnemen van het onderzoek duurt 30 minuten en is om die reden niet geschikt voor afname in de JGZ.
Tabel 8.16 Overzicht van neurologische onderzoeken per leeftijdscategorie die op indicatie uitgevoerd zouden kunnen worden in de 2e of 3e lijn, of door een kinderfysiotherapeut.
| Onderzoek | Doelgroep | Inhoud | Afgenomen door | Test-duur | Validiteit | Betrouw-baarheid | |
| 1 |
Touwen Infant Neurological Examination (TINE)[223]
|
Zuigelingen (0 – 1;5 jaar) |
De volgende onderdelen worden onderzocht: -Functioneren tijdens reiken en grijpen -Grof- motorisch functioneren -Functioneren van hersenstam – Visuomotorisch functioneren – Sensomotorisch functioneren |
Artsen en paramedici | 15-20 min. | Onbekend |
Goed
|
| 2 |
Hempel onderzoek [30],[227]
|
Peuters en kleuters (1;5 – 4 jaar) |
Bewegingsaspecten gedurende het grijpen, zitten, kruipen, staan, en lopen worden beoordeeld. Daarnaast wordt gekeken naar het hoofd (het beoordelen van de hersenzenuw functie) en naar het sensomotorisch functioneren door middel van manipulatie | Artsen en paramedici |
30 min.
|
Onbekend |
Inter-beoorde-laars-betrouw-baarheid:
voldoende |
| 3 |
Modified Touwen onderzoek[73]
|
Vanaf 4 jaar |
De volgende 8 clusters worden onderzocht: houding; reflexen; onwillekeurige bewegingen; geassocieerde bewegingen; coördinatieproblemen; problemen met fijne manipulatie; -problemen met de sensoriek; problemen met betrekking tot de hersenzenuw |
Artsen en paramedici | 30 min. | Onbekend | Matig-goed[225] |
8.16 Bijlage 17 Beweegrichtlijn
Voor jeugdigen (4-18 jaar) geeft de Beweegrichtlijn aan: dagelijks (zomer en winter) minimaal één uur tenminste matig intensieve lichamelijk activiteit van 5 MET (Metabolic Equivalent of Task) tot 8 MET (bijvoorbeeld hardlopen 8 km/uur), waarbij minimaal drie keer per week kracht-, lenigheid- en coördinatieoefeningen voor het verbeteren of handhaven van de lichamelijke fitheid[226],241 . Zie ook de website van het Voedingscentrum, waar concrete activiteiten met bijbehorende MET-waarden worden gegeven voor kinderen vanaf vier jaar.
In 2009 was het percentage inactieve (dat wil zeggen minder dan twee dagen per week ten minste 60 minuten matig actief) 4-17 jarigen 13,6%[226]. Inactiviteit neemt toe met de leeftijd: 9,3% van de 4-11 jarigen en 19,0% van de 12-17 jarigen voldoet niet aan de norm. Meisjes zijn vaker inactief dan jongens (17,1% vs. 13,3% inactieven). Ook niet-sporters zijn een risicogroep voor inactiviteit[226]. Een kanttekening bij dit onderzoek is de gehanteerde definitie van een sporter: iemand die ten minste één keer heeft gesport in de afgelopen 12 maanden.
In 2009 besteedden in Nederland kinderen van 4 tot 11 jaar op weekdagen buiten schooltijd gemiddeld rond de twee uur per dag aan zittende en liggende activiteiten waarvoor weinig energie (≤1,5 METS) nodig is. Dit wordt sedentair gedrag genoemd. Bij adolescenten (12-17 jaar) ligt het gemiddelde aantal uren sedentair gedrag na schooltijd net boven de drie uur per dag[226]. Vanuit het oogpunt van behoud van gezondheid en een gezond gewicht wordt voor kinderen en jongeren geadviseerd sedentair gedrag zo veel mogelijk te beperken en bewegen te stimuleren. Voor kinderen tot twee jaar wordt daarom het gebruiken van een computer/tablet en tv/dvd kijken ontraden[160]. Aan ouders van kinderen van 2-4 jaar wordt geadviseerd om hun kinderen niet meer dan één uur per dag een computer/tablet te laten gebruiken en/of tv/dvd te laten kijken.
8.17 Bijlage 18 Interventies ‘Veilig Groot worden’ en ‘Armoede en gezondheid’
De interventie Veilig groot worden is een combinatie van mondelinge, schriftelijke en digitale (app) voorlichting aan ouders van kinderen van 0-4 jaar oud over veilig opgroeien. Doel van de voorlichting is om ouders aan te zetten tot het nemen van veiligheidsmaatregelen. De folderreeks en de mobiele app bieden praktische informatie over de vaardigheden van het kind, de ongevalsrisico’s en de mogelijkheden om ongevallen te voorkomen. Tijdens het consult bespreekt de verloskundige, kraamverzorgende, de jeugdarts of de jeugdverpleegkundige met de ouders welke maatregelen zij voor hun kind het beste kunnen nemen. Zo worden ouders gestimuleerd tot veilig gedrag: voldoende toezicht, een veilige omgeving en een opvoeding die erop is gericht dat kinderen zich op een veilige manier leren bewegen. De interventie geeft ouders informatie over veiligheid op het moment dat het relevant is en sluit aan bij de leeftijd- en ontwikkelingsfase van het kind. De voorlichting is daarom gefaseerd van opzet (status interventie database CGL: goed onderbouwd). Zie verder: www.veiligheid.nl en www.loketgezondleven.nl.
De bedoeling van de interventie Armoede en gezondheid van kinderen is deprivaties terug te dringen die samenhangen met de gezondheid van kinderen. Deprivatie is een begrip uit de literatuur over armoede. Iemand is gedepriveerd als hij/zij om financiële redenen bepaalde zaken niet heeft of activiteiten niet kan doen. De interventie beoogt het beschikbaar komen van geoormerkte extra financiële middelen ten gunste van determinanten van gezondheid van het gedepriveerde kind. Het is een intersectorale interventie die wordt uitgevoerd door de JGZ in samenwerking met de gemeentelijke sociale dienst. De interventie is gericht op kinderen in de voorschoolse leeftijd en in de basisschoolleeftijd bij wie een gezondheidsrisico is gesignaleerd dat samenhangt met geldgebrek in het gezin en dat te beïnvloeden is met een financiële verstrekking.
Referenties
[1] Lubans DR, Morgan PJ, Cliff DP, Barnett LM, Okely AD. Fundamental movement skills in children and adolescents: review of associated health benefits. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) 2010;40(12):1019-35
http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/11536850-000000000-00000 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21058749[2] Smith LB, Thelen E. A Dynamic Systems Approach to the Development of Cognition and Action 1994
http://dx.doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/2524.001.0001 https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/2524.001.0001[3] Chow JY, Davids K, Button C, Renshaw I. Nonlinear Pedagogy in Skill Acquisition: An Introduction 2021
http://dx.doi.org/10.4324/9781003247456[4] Skinner RA, Piek JP. Psychosocial implications of poor motor coordination in children and adolescents. Human movement science 2001;20(1-2):73-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11471399[5] Emck C, Bosscher R, Beek P, Doreleijers T. Gross motor performance and self-perceived motor competence in children with emotional, behavioural, and pervasive developmental disorders: a review. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2009;51(7):501-17
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03337.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19538424[6] Chen H-F, Cohn ES. Social participation for children with developmental coordination disorder: conceptual, evaluation and intervention considerations. Physical & occupational therapy in pediatrics 2003;23(4):61-78
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14750309[7] Piek JP, Barrett NC, Allen LSR, Jones A, Louise M. The relationship between bullying and self-worth in children with movement coordination problems. The British journal of educational psychology 2005;75(Pt 3):453-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16238876[8] Losse A, Henderson SE, Elliman D, Hall D, Knight E, Jongmans M. Clumsiness in children--do they grow out of it? A 10-year follow-up study. Developmental medicine and child neurology 1991;33(1):55-68
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1704864[9] Delgado MR, Albright AL. Movement disorders in children: definitions, classifications, and grading systems. Journal of child neurology 2003;18 Suppl 1():S1-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13677567[10] Touwen B.C.L., Touwen-Eringa A1-2, Frese H.. De neurologische ontwikkeling van de zuigeling : ontwikkelingsgang en samenhang van de onderdelen van het neurologisch onderzoek 1984
[11] Touwen BC. How normal is variable, or how variable is normal? Early human development 1993;34(1-2):1-12
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8275868[12] Hadders-Algra M., Dirks JF.. de Motorische Ontwikkeling Van de Zuigeling: Variëren, Selecteren, Leren Adapteren 2000
https://books.google.be/books?id=AMtt8tOTRrsC[13] Hadders-Algra M, Maathuis KGB, Pangalila RF, Becher JG, de Moor J. Kinderrevalidatie. Assen: Van Gorcum 2015
[14] Hadders-Algra M. Variation and variability: key words in human motor development. Physical therapy 2010;90(12):1823-37
http://dx.doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20100006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20966209[15] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de Jeugdgezondheidszorg. Het Van Wiechenonderzoek. De Baecke-Fassaert Motoriektest. Van Gorcum. 2008
[16] Heineman KR, Bos AF, Hadders-Algra M. The Infant Motor Profile: a standardized and qualitative method to assess motor behaviour in infancy. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2008;50(4):275-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.02035.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18279412[17] Bailey DB, Hebbeler K, Scarborough A, Spiker D, Mallik S. First experiences with early intervention: a national perspective. Pediatrics 2004;113(4):887-96
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15060241[18] Gerber RJ, Wilks T, Erdie-Lalena C. Developmental milestones: motor development. Pediatrics in review 2010;31(7):267-76; quiz 277
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/pir.31-7-267 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20595440[19] Lüchinger AB, Hadders-Algra M, van Kan CM, de Vries JIP. Fetal onset of general movements. Pediatric research 2008;63(2):191-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18091359[20] Prechtl HFR. The importance of fetal movements. In: KJ Connolly & H Forssberg (Eds). Neurophysiology and neuropsychology of motor development. Clinics in Developmental Medicine. London: Mac Keith Press 1997
[21] Hadders-Algra M. Putative neural substrate of normal and abnormal general movements. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews 2007;31(8):1181-90
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17568672[22] Bilo RAC, Voorhoeve HWA. Kind in Ontwikkeling Uitgeversmaatschappij De Tijdstroom bv. 1990
[23] Davis BE, Moon RY, Sachs HC, Ottolini MC. Effects of sleep position on infant motor development. Pediatrics 1998;102(5):1135-40
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9794945[24] Crouchman M. The effects of babywalkers on early locomotor development. Developmental medicine and child neurology 1986;28(6):757-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3817314[25] Thelen E, Corbetta D, Kamm K, Spencer JP, Schneider K, Zernicke RF. The transition to reaching: mapping intention and intrinsic dynamics. Child development 1993;64(4):1058-98
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8404257[26] Largo RH, Molinari L, Weber M, Comenale Pinto L, Duc G. Early development of locomotion: significance of prematurity, cerebral palsy and sex. Developmental medicine and child neurology 1985;27(2):183-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3996775[27] Adolph KE, Vereijken B, Denny MA. Learning to crawl. Child development 1998;69(5):1299-312
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9839417[28] Yang JF, Stephens MJ, Vishram R. Infant stepping: a method to study the sensory control of human walking. The Journal of physiology 1998;507 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):927-37
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9508851[29] Van Dokkum NH, Kerstjens JM, Bos AF, Reijneveld SA, De Kroon MLA. Association between gestational age, attainment age of smiling and walking and development at school entry Abstract NVK-congres 2017
[30] Hempel MS. Neurological development during toddling age in normal children and children at risk of developmental disorders. Early human development 1993;34(1-2):47-57
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8275882[31] van Dokkum NH, de Kroon MLA, Bos AF, Reijneveld SA, Kerstjens JM. Attainment of gross motor milestones by preterm children with normal development upon school entry. Early human development 2018;119():62-67
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2018.03.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29579559[32] Pascal A, Govaert P, Oostra A, Naulaers G, Ortibus E, Van den Broeck C. Neurodevelopmental outcome in very preterm and very-low-birthweight infants born over the past decade: a meta-analytic review. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2018;60(4):342-355
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13675 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29350401[33] Pearsall-Jones JG, Piek JP, Levy F. Developmental Coordination Disorder and cerebral palsy: categories or a continuum? Human movement science 2010;29(5):787-98
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2010.04.006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20594606[34] Williams J, Hyde C, Spittle A. Developmental Coordination Disorder and Cerebral Palsy: Is There a Continuum? Current Developmental Disorders Reports 2014/06/01;1():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40474-014-0009-3[35] Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson BO, Damiano D, . Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2005;47(8):571-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16108461[36] Paneth N. Establishing the diagnosis of cerebral palsy. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology 2008;51(4):742-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/GRF.0b013e318187081a https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18981799[37] Wichers MJ, Odding E, Stam HJ, van Nieuwenhuizen O. Clinical presentation, associated disorders and aetiological moments in Cerebral Palsy: a Dutch population-based study. Disability and rehabilitation 2005;27(10):583-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16019867[38] Richtlijn Spastische cerebrale parese bij kinderen 2015
http://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/spastische_cerebrale_parese_bij_kinderen/diagnostiek_van_cerebr%20ale_parese.html[39] International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Children and Youth Version WHO 2007
[40] Becker H, Blank R, Jenni O, Linder-Lucht M, Polatajko H, Steiner F, Geuze R, Smits-Engelsman B, Wilson P. Aanbevelingen van de EACD. Duits-Zwitserse richtlijn voor de klinische praktijk. Definitie, diagnose, evaluatie en behandeling van Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD). Nederlandse vertaling en aanpassing door landelijke DCD netwerk. 2013
[41] Hafkamp-de Groen E, van den Bos L, Raat H. Motorische Ontwikkeling Programmeringsstudie 2012
[42] Zwicker JG, Missiuna C, Harris SR, Boyd LA. Developmental coordination disorder: a review and update. European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society 2012;16(6):573-81
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2012.05.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22705270[43] Aanbevelingen van de EACD; Definitie, diagnose, evaluatie en behandeling van DCD, versie juli 2011. Nederlandse vertaling en aanpassing door landelijke DCD netwerk European Academy of Childhood Disability (EACD) 2013
[44] Dutch consensus statement DCD. Vertaling van de Leeds Consensus Statement Development Coördination Disorder as a Specific Learning Difficulty ESRC Research Seminar Series, 2004-2005 2011
http://www.motoriek.nl/userfiles/file/Dutch_Consensus_Statement_DCD_2011_.pdf[45] Noordstar JJ, van der Net J, Jak S, Helders PJM, Jongmans MJ. The change in perceived motor competence and motor task values during elementary school: A longitudinal cohort study. The British journal of developmental psychology 2016;34(3):427-46
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bjdp.12142 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26989988[46] Noordstar JJ, Stuive I, Herweijer H, Holty L, Oudenampsen C, Schoemaker MM, Reinders-Messelink HA. Perceived athletic competence and physical activity in children with developmental coordination disorder who are clinically referred, and control children. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(12):3591-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.09.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25244693[47] Edwards J, Berube M, Erlandson K, Haug S, Johnstone H, Meagher M, Sarkodee-Adoo S, Zwicker JG. Developmental coordination disorder in school-aged children born very preterm and/or at very low birth weight: a systematic review. Journal of developmental and behavioral pediatrics : JDBP 2011;32(9):678-87
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0b013e31822a396a https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21900828[48] Zhu JL, Olsen J, Olesen AW. Risk for developmental coordination disorder correlates with gestational age at birth. Paediatric and perinatal epidemiology 2012;26(6):572-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3016.2012.01316.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23061693[49] www.spierziekten.nl geraadpleegd op 14-02-2016
http://www.spierziekten.nl[50] van Empelen R. R van Empelen, R. Nijhuis-van der Sanden & A Hartman (Eds.), Kinderfysiotherapie. 3e druk 2013 Reed Business. 2012
[51] Gijzen R, Zadoks J. Zorgstandaard Traumatisch Hersenletsel, Kinderen & Jongeren. In opdracht van de Hersenstichting 2016
[52] www.dehoogstraat.nl (Traumatologie, hoofdstuk 12). Geraadpleegd op 02-04-2016
http://www.dehoogstraat.nl/revalidatie/kinderen-en-jeugd/aandoening/niet-aangeboren-hersenletsel[53] Jelsma LD, Geuze RH, Klerks MH, Niemeijer AS, Smits-Engelsman BCM. The relationship between joint mobility and motor performance in children with and without the diagnosis of developmental coordination disorder. BMC pediatrics 2013;13():35
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-13-35 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23497034[54] de Boer RM, van Vlimmeren LA, Scheper MC, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MWG, Engelbert RHH. Is Motor Performance in 5.5-Year-Old Children Associated with the Presence of Generalized Joint Hypermobility? The Journal of pediatrics 2015;167(3):694-701.e1
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.06.034 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26190232[55] Engelbert RHH, Juul-Kristensen B, Pacey V, de Wandele I, Smeenk S, Woinarosky N, Sabo S, Scheper MC, Russek L, Simmonds JV. The evidence-based rationale for physical therapy treatment of children, adolescents, and adults diagnosed with joint hypermobility syndrome/hypermobile Ehlers Danlos syndrome. American journal of medical genetics. Part C, Seminars in medical genetics 2017;175(1):158-167
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31545 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28306230[56] Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, Layden J, Carnes BA, Brody J, Hayflick L, Butler RN, Allison DB, Ludwig DS. A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. The New England journal of medicine 2005;352(11):1138-45
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15784668[57] Thompson Coon J, Boddy K, Stein K, Whear R, Barton J, Depledge MH. Does participating in physical activity in outdoor natural environments have a greater effect on physical and mental wellbeing than physical activity indoors? A systematic review. Environmental science & technology 2011;45(5):1761-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/es102947t https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21291246[58] Gillberg C, Kadesjö B. Why bother about clumsiness? The implications of having developmental coordination disorder (DCD). Neural plasticity 2003;10(1-2):59-68
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14640308[59] Fliers E, Rommelse N, Vermeulen SHHM, Altink M, Buschgens CJM, Faraone SV, Sergeant JA, Franke B, Buitelaar JK. Motor coordination problems in children and adolescents with ADHD rated by parents and teachers: effects of age and gender. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 2008;115(2):211-20
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17994185[60] Lingam R, Golding J, Jongmans MJ, Hunt LP, Ellis M, Emond A. The association between developmental coordination disorder and other developmental traits. Pediatrics 2010;126(5):e1109-18
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-2789 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20956425[61] Kaplan B, Wilson B, Dewey D, Crawford S. DCD may not be a discrete disorder Human Movement Science 1998/08/01;17():471
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9457(98)00010-4[62] Dewey D, Kaplan BJ, Crawford SG, Wilson BN. Developmental coordination disorder: associated problems in attention, learning, and psychosocial adjustment. Human movement science 2002;21(5-6):905-18
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12620725[63] Njokiktjien C. Gedragsneurologie van het kind. Handboek voor ontwikkelingsneurologie, neuropsychiatrie en neuropsychologie, Amsterdam 2004
[64] Novak I, McIntyre S, Morgan C, Campbell L, Dark L, Morton N, Stumbles E, Wilson S-A, Goldsmith S. A systematic review of interventions for children with cerebral palsy: state of the evidence. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2013;55(10):885-910
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12246 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23962350[65] Missiuna C, Campbell W. Psychological Aspects of Developmental Coordination Disorder: Can We Establish Causality? Current Developmental Disorders Reports 2014/06/01;1():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40474-014-0012-8[66] Soleimani F, Badv RS, Momayezi A, Biglarian A, Marzban A. General movements as a predictive tool of the neurological outcome in term born infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Early human development 2015;91(8):479-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2015.05.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26070097[67] . Assessment of sex differences and heterogeneity in motor milestone attainment among populations in the WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992). Supplement 2006;450():66-75
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16817680[68] . WHO Motor Development Study: windows of achievement for six gross motor development milestones. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992). Supplement 2006;450():86-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16817682[69] Giagazoglou P, Kabitsis N, Kokaridas D, Zaragas C, Katartzi E, Kabitsis C. The movement assessment battery in Greek preschoolers: the impact of age, gender, birth order, and physical activity on motor outcome. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(6):2577-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.06.020 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21816567[70] Hardy LL, King L, Farrell L, Macniven R, Howlett S. Fundamental movement skills among Australian preschool children. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2010;13(5):503-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2009.05.010 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19850520[71] Kelly Y, Sacker A, Schoon I, Nazroo J. Ethnic differences in achievement of developmental milestones by 9 months of age: The Millennium Cohort Study. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2006;48(10):825-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16978462[72] Angulo-Barroso RM, Schapiro L, Liang W, Rodrigues O, Shafir T, Kaciroti N, Jacobson SW, Lozoff B. Motor development in 9-month-old infants in relation to cultural differences and iron status. Developmental psychobiology 2011;53(2):196-210
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/dev.20512 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21298634[73] Van Hus JW, Potharst ES, Jeukens-Visser M, Kok JH, Van Wassenaer-Leemhuis AG. Motor impairment in very preterm-born children: links with other developmental deficits at 5 years of age. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2014;56(6):587-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24926490[74] Taanila A, Murray GK, Jokelainen J, Isohanni M, Rantakallio P. Infant developmental milestones: a 31-year follow-up. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2005;47(9):581-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16138663[75] Jenni OG, Chaouch A, Caflisch J, Rousson V. Infant motor milestones: poor predictive value for outcome of healthy children. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2013;102(4):e181-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/apa.12129 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23289493[76] Mayson TA, Harris SR, Bachman CL. Gross motor development of Asian and European children on four motor assessments: a literature review. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2007;19(2):148-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17505292[77] Touwen BCL. Psychomotorische ontwikkelingen en stoornissen. In A.J.M. Bonnet-Breusers e.a. (Eds.), Handboek Jeugdgezondheidszorg 1990
http://dx.doi.org/Utrecht:%20Wetenschappelijke%20Uitgeverij%20Bunge[78] Gorga D, Stern FM, Ross G, Nagler W. The neuromotor behavior of preterm and full-term children by three years of age: quality of movement and variability. Journal of developmental and behavioral pediatrics : JDBP 1991;12(2):102-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2045482[79] Bouchard C, Malina RM. Genetics of physiological fitness and motor performance. Exercise and sport sciences reviews 1983;11():306-39
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6350021[80] Francks C, Fisher S, Marlow A, MacPhie I, Taylor K, Richardson A, Stein J, Monaco A. Familial and Genetic Effects on Motor Coordination, Laterality, and Reading-Related Cognition The American journal of psychiatry 2003/12/01;160():1970
http://dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.160.11.1970[81] Stromswold K, Rosenthal M, Patel K, Molnar D. Development of Visual-Motor Integration: The Role of Genetic & Environmental Factors Journal of Vision 2011;11(11):462
http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/11.11.462 https://doi.org/10.1167/11.11.462[82] Williams LR, Gross JB. Heritability of motor skill. Acta geneticae medicae et gemellologiae 1980;29(2):127-36
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7196128[83] Saccani R, Valentini NC. Cross-cultural analysis of the motor development of Brazilian, Greek and Canadian infants assessed with the Alberta Infant Motor Scale. Revista paulista de pediatria : orgao oficial da Sociedade de Pediatria de Sao Paulo 2013;31(3):350-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-05822013000300012 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24142318[84] Hwang A-W, Liao H-F, Granlund M, Simeonsson RJ, Kang L-J, Pan Y-L. Linkage of ICF-CY codes with environmental factors in studies of developmental outcomes of infants and toddlers with or at risk for motor delays. Disability and rehabilitation 2014;36(2):89-104
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2013.777805 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23594061[85] Golding J, Emmett P, Iles-Caven Y, Steer C, Lingam R. A review of environmental contributions to childhood motor skills. Journal of child neurology 2014;29(11):1531-47
http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0883073813507483 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24170258[86] Castetbon K, Andreyeva T. Obesity and motor skills among 4 to 6-year-old children in the United States: nationally-representative surveys. BMC pediatrics 2012;12():28
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-12-28 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22420636[87] Lopes VP, Stodden DF, Bianchi MM, Maia JAR, Rodrigues LP. Correlation between BMI and motor coordination in children. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2012;15(1):38-43
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2011.07.005 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21831708[88] Mond JM, Stich H, Hay PJ, Kraemer A, Baune BT. Associations between obesity and developmental functioning in pre-school children: a population-based study. International journal of obesity (2005) 2007;31(7):1068-73
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17471298[89] D'Hondt E, Deforche B, Gentier I, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Vaeyens R, Philippaerts R, Lenoir M. A longitudinal analysis of gross motor coordination in overweight and obese children versus normal-weight peers. International journal of obesity (2005) 2013;37(1):61-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.55 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22508339[90] Glascoe FP. Parents' concerns about children's development: prescreening technique or screening test? Pediatrics 1997;99(4):522-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9093291[91] Harris SR, Mickelson ECR, Zwicker JG. Diagnosis and management of developmental coordination disorder. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2015;187(9):659-665
http://dx.doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.140994 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26009588[92] Williams J, Lee KJ, Anderson PJ. Prevalence of motor-skill impairment in preterm children who do not develop cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(3):232-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03544.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20002114[93] Bakker I, Bakker C, van Dijke A, Terpstra L. Balansmodel Nederlands Instituut voor Zorg en Welzijn (NIZQ) O&O in perspectief 1998
[94] Kerstjens JM, de Winter AF, Bocca-Tjeertes IF, ten Vergert EMJ, Reijneveld SA, Bos AF. Developmental delay in moderately preterm-born children at school entry. The Journal of pediatrics 2011;159(1):92-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.12.041 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21324481[95] Rivilis I, Hay J, Cairney J, Klentrou P, Liu J, Faught BE. Physical activity and fitness in children with developmental coordination disorder: a systematic review. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(3):894-910
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.017 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21310588[96] Emery AE. Population frequencies of inherited neuromuscular diseases--a world survey. Neuromuscular disorders : NMD 1991;1(1):19-29
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1822774[97] Buijssen M, Jajou R, van Kessel FGB, Vonk Noordegraaf-Schouten MJM, Zeilmaker MJ, Wijga AH, van Rossum CTM. Health effects of breastfeeding: an update. Systematic literature review RIVM rapport, 043 2015
[98] Wilson JMG, Jungner G. Principles and practice of screening for disease World Health Organization. Public Health Paper 1968
[99] Een jeugdgezondheidszorg richtlijn voor screening van de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen: een haalbaarheidsstudie TNO-rapport 2008
[100] Grevinga M, van Harten L, Hofstetter H, Verkerk P, Detmar S. Het afnemen van de Van Wiechenkenmerken door ouders: een pilotonderzoek Manuscript draft JGZ Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 2018
[101] Schwartze P. Entwicklungsuntersuchung in der SPrechstunde. Arbeitsbuch nach dem revidierten Van-Wiechen-Schema Pädiatrie Grenzgebiete 1991;30():1
[102] Gesell A, Amatruda CS. Developmental diagnosis Hoeber, Harper & Row, New York 1947
[103] Gesell A, Amatruda CS, Knobloch H, Pasamanick B. Gesell and Amatruda's Developmental diagnosis : the evaluation and management of normal and abnormal neuropsychologic development in infancy and early childhood. 1974
[104] Touwen BCL. Ontwikkelingsneurologisch onderzoek. In: Verhulst en Verhey GV (red). Kinder- en jeugdpsychiatrie; onderzoek en diagnostiek Van Gorcum 1992
[105] Touwen BCL. De neurologische ontwikkeling van 0 tot 3 jaar. In: de Boer JE (red): Infantpsychiatrie II. Van Gorcum 1993
[106] Schlesinger-Was EA. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek van zuigelingen en kleuters op het consultatiebureau Proefschrift Rijksuniversiteit Leiden 1981
[107] Verkerk PH, Reerink JD, Herngreen WP. Evaluatie van het Van Wiechenschema - I: De overeenkomst tussen de referentiewaarden en waarnemingen in de praktijk Tijdschrift voor Jeugdgezondheidszorg 1993;25(5):71
[108] Schoemaker M, Ketelaar M, Reinders-Messelink H. Hoofdstuk 6: Meetinstrumenten - Voor de motorische ontwikkeling van kinderen. In: Kinderfysiotherapie. Van Empelen R, Nijhuis-van der Sanden & Hartman 1 (Eds). Springer Media B.V. 2013
[109] Baecke JAH, Boersma-Slütter WGM, van Heeswijk ALM. Ontwikkeling van een motoriektest voor kleuters: de betrouwbaarheid Tijdschrift voor de Sociale Gezondheidszorg 1984;62():38
[110] Dijkmans-Scheepstra D, Rietveld E. De constructvaliditeit van de Baecke-Fassaert motoriektest en de Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 Nederlandstalige versie Masterthesis. Transfergroep Rotterdam 2013
[111] De Kroon ML, van Kernebeek WG, Neve BF, ter Veer JM, Reijeveld SA, de Vet HCW, Toussaint HM. Validity and discriminative ability of Dutch motor tests in 5 to 6 year old children 2018
[112] Jacobusse G, Buuren S, Verkerk P. Ontwikkeling van de D-score : een samenvattende maat voor het Van Wiechenonderzoek 2008/01/01
[113] Hafkamp-de Groen E, Dusseldorp E, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Jacobusse GW, Oudesluijs-Murphy AM, Verkerk PH. Relatie tussen het Van Wiechenonderzoek en het intelligentieniveau op 5 jaar Tijdschrift voor Jeugdgezondheidszorg 2009;41():10
[114] Pilotstudie D-screening: screening op ontwikkelingsachterstand bij het jonge kind, uitgevoerd door de jeugdarts TNO-rapport 2011
[115] Dunnink G, Lijs-spek WJG. Activiteiten basistakenpakket jeugdgezondheidszorg 0-19 jaar per contactmoment. Geraadpleegd op 21-03-2016 2008
http://www.rivm.nl/Documenten_en_publicaties/Wetenschappelijk/Rapporten/2008/juli/Activit%20eiten_Basistakenpakket_Jeugdgezondheidszorg_0_19_jaar_per_Contactmoment[116] Baecke JAH, Fassaert YAH, van Rossum JHA, van de Kolk W. Motoriek bij kleuters: samenstelling en normering van een in de Jeugdgezondheidszorg hanteerbare test Tijdschrift voor Sociale Geneeskunde 1989;67():100
[117] Van Waelvelde H, Peersman W, Lenoir M, Smits Engelsman BCM. The reliability of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children for preschool children with mild to moderate motor impairment. Clinical rehabilitation 2007;21(5):465-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17613568[118] Blank R, Smits-Engelsman B, Polatajko H, Wilson P, . European Academy for Childhood Disability (EACD): recommendations on the definition, diagnosis and intervention of developmental coordination disorder (long version). Developmental medicine and child neurology 2012;54(1):54-93
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.04171.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22171930[119] Smits-Engelsman BCM, Niemeijer AS, van Waelvelde H. Is the Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2nd edition a reliable instrument to measure motor performance in 3 year old children? Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(4):1370-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.031 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21349686[120] Spittle AJ, Doyle LW, Boyd RN. A systematic review of the clinimetric properties of neuromotor assessments for preterm infants during the first year of life. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2008;50(4):254-66
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.02025.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18190538[121] Van Gelder W, Stroes H. Leerlingvolgsysteem bewegen en spelen. Over observeren, registreren en extra zorg 2010
[122] Van Kernebeek WG, de Schipper AW, Savelsbergh GJP, Toussaint HM. Inter-rater and test-retest (between-sessions) reliability of the 4-Skills Scan for dutch elementary school children. Measurement in Physical Education and Exercise Science 2018;22(2):129
[123] van Kernebeek WG, de Kroon MLA, Savelsbergh GJP, Toussaint HM. The validity of the 4-Skills Scan A double-validation study. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2018;28(11):2349-2357
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/sms.13231 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29858501[124] Runhaar J, Collard DCM, Singh AS, Kemper HCG, van Mechelen W, Chinapaw M. Motor fitness in Dutch youth: differences over a 26-year period (1980-2006). Journal of science and medicine in sport 2010;13(3):323-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2009.04.006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19592305[125] Schoffelmeer L, Toussaint H. De oogst van beweegarmoede in de jeugd; overgewicht en minder makkelijk bewegen Lichamelijke Opvoeding 2013;11():39
[126] Ellinoudis T, Evaggelinou C, Kourtessis T, Konstantinidou Z, Venetsanou F, Kambas A. Reliability and validity of age band 1 of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children--second edition. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(3):1046-51
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.035 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21333488[127] Schoemaker MM, Niemeijer AS, Flapper BCT, Smits-Engelsman BCM. Validity and reliability of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 Checklist for children with and without motor impairments. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2012;54(4):368-75
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04226.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22320829[128] Holm I, Tveter AT, Aulie VS, Stuge B. High intra- and inter-rater chance variation of the movement assessment battery for children 2, ageband 2. Research in developmental disabilities 2013;34(2):795-800
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2012.11.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23220056[129] Piper M.C., Darrah J.. Motor Assessment of the Developing Infant 1994
https://books.google.be/books?id=kdVsAAAAMAAJ[130] Neonatale Prematuren Follow-up (NPF) Richtlijn: Aanbeveling landelijke neonatale follow-up-NICU follow-up 2015
[131] Pin TW, de Valle K, Eldridge B, Galea MP. Clinimetric properties of the alberta infant motor scale in infants born preterm. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2010;22(3):278-86
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PEP.0b013e3181e94481 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20699776[132] Syrengelas D, Siahanidou T, Kourlaba G, Kleisiouni P, Bakoula C, Chrousos GP. Standardization of the Alberta infant motor scale in full-term Greek infants: Preliminary results. Early human development 2010;86(4):245-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.03.009 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20452736[133] Piper MC, Pinnell LE, Darrah J, Maguire T, Byrne PJ. Construction and validation of the Alberta Infant Motor Scale (AIMS). Canadian journal of public health = Revue canadienne de sante publique 1992;83 Suppl 2():S46-50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1468050[134] Van Baar AL, Steenis LJP, Verhoeven M, Hessen DJ. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development - Third Edition - Nederlandse versie (Bayler-III-NL). Geraadpleegd op 19-03-2016 2015
http://www.pearsonclinical.nl/bayley-3[135] Connolly BH, McClune NO, Gatlin R. Concurrent validity of the Bayley-III and the Peabody Developmental Motor Scale-2. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2012;24(4):345-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PEP.0b013e318267c5cf https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22965209[136] Steenis LJP, Verhoeven M, Hessen DJ, van Baar AL. Performance of Dutch children on the Bayley III: a comparison study of US and Dutch norms. PloS one 2015;10(8):e0132871
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132871 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26267907[137] Kroes M, Feron FJM, Sleijpen FAM, Vles JSH. De Maastrichtse Motoriek Test Tijdschrift van de NVFK 2006;18(51):3
[138] STIMULIZ Leerlingvolgsysteem 0-24 jaar. Geraadpleegd op 10-10-2017
https://stimuliz.com/[139] Hoeboer J, de Vies S. Big data in het bewegingsonderwijs Presentatie VvBN symposium 2015
[140] Jongbloed-Pereboom M, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MWG, Steenbergen B. Norm scores of the box and block test for children ages 3-10 years. The American journal of occupational therapy : official publication of the American Occupational Therapy Association 2013;67(3):312-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.5014/ajot.2013.006643 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23597689[141] Hornman J, Kerstjens JM, de Winter AF, Bos AF, Reijneveld SA. Validity and internal consistency of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire 60-month version and the effect of three scoring methods. Early human development 2013;89(12):1011-5
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2013.08.016 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24041814[142] Kerstjens JM, Bos AF, ten Vergert EMJ, de Meer G, Butcher PR, Reijneveld SA. Support for the global feasibility of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire as developmental screener. Early human development 2009;85(7):443-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2009.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19356866[143] van der Linde BW, van Netten JJ, Otten BE, Postema K, Geuze RH, Schoemaker MM. Psychometric properties of the DCDDaily-Q: a new parental questionnaire on children's performance in activities of daily living. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(7):1711-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.03.008 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24685097[144] Schoemaker MM, Flapper BCT, Reinders-Messelink HA, Kloet AD. Validity of the motor observation questionnaire for teachers as a screening instrument for children at risk for developmental coordination disorder. Human movement science 2008;27(2):190-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2008.02.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18346804[145] Caravale B, Baldi S, Gasparini C, Wilson BN. Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability and predictive validity of the Italian version of Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ). European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society 2014;18(3):267-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2013.11.009 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24332678[146] Caravale B, Baldi S, Capone L, Presaghi F, Balottin U, Zoppello M. Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ-Italian). Research in developmental disabilities 2015;36C():543-550
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.10.035 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25462515[147] Schoemaker MM, Flapper B, Verheij NP, Wilson BN, Reinders-Messelink HA, de Kloet A. Evaluation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire as a screening instrument. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2006;48(8):668-73
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16836779[148] Wilson BN, Crawford SG, Green D, Roberts G, Aylott A, Kaplan BJ. Psychometric properties of the revised Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire. Physical & occupational therapy in pediatrics 2009;29(2):182-202
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01942630902784761 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19401931[149] Martini R, St-Pierre M-F, Wilson BN. French Canadian cross-cultural adaptation of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire '07: DCDQ-FC. Canadian journal of occupational therapy. Revue canadienne d'ergotherapie 2011;78(5):318-27
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22338299[150] Kennedy-Behr A, Wilson BN, Rodger S, Mickan S. Cross-cultural adaptation of the developmental coordination disorder questionnaire 2007 for German-speaking countries: DCDQ-G. Neuropediatrics 2013;44(5):245-51
http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1347936 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23716299[151] Parmar A, Kwan M, Rodriguez C, Missiuna C, Cairney J. Psychometric properties of the DCD-Q-07 in children ages to 4-6. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(2):330-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.10.030 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24321562[152] Van Empelen R, Nijhuis-van der Sanden R, Hartman A. Kinderfysiotherapie Springer Media B.V. 2013
[153] Bender-de Haan S, Broer van Dijk-van der Hulst M, Hommes-Hospers HJ, van Wijlen-Hempel MS, Touwen BCL. Een neuromotorische onderzoekmethode voor de peuterleeftijd Tijdschrift Jeugdgezondheidszorg 1998;30():49
[154] Chagas PSC, Cunha RSM, Mancini MC, Magalhaes LC. There is no evidence to support or refute the effect of baby walkers on motor development in typically developing children. Geraadpleegd op 19-04-2016 2007
http://www.otcats.com/topics/CAT%20-%20%20Paula%20Chagas%202007.pdf[155] Abbott AL, Bartlett DJ. Infant motor development and equipment use in the home. Child: care, health and development 2001;27(3):295-306
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11350456[156] Fay D, Hall M, Murray M, Saatdjian A, Vohwinkel E. The Effect of Infant Exercise Equipment on Motor Milestone Achievement Pediatric Physical Therapy 2006/01/01;18():90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00001577-200601810-00039[157] Pin T, Eldridge B, Galea MP. A review of the effects of sleep position, play position, and equipment use on motor development in infants. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):858-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979866[158] Kuo Y-L, Liao H-F, Chen P-C, Hsieh W-S, Hwang A-W. The influence of wakeful prone positioning on motor development during the early life. Journal of developmental and behavioral pediatrics : JDBP 2008;29(5):367-76
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0b013e3181856d54 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18766114[159] Saccani R, Valentini NC, Pereira KR, Müller AB, Gabbard C. Associations of biological factors and affordances in the home with infant motor development. Pediatrics international : official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society 2013;55(2):197-203
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ped.12042 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23279095[160] Tremblay MS, Leblanc AG, Carson V, Choquette L, Connor Gorber S, Dillman C, Duggan M, Gordon MJ, Hicks A, Janssen I, Kho ME, Latimer-Cheung AE, Leblanc C, Murumets K, Okely AD, Reilly JJ, Spence JC, Stearns JA, Timmons BW, . Canadian Physical Activity Guidelines for the Early Years (aged 0-4 years). Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme 2012;37(2):345-69
http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/h2012-018 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22448608[161] Graf C, Koch B, Kretschmann-Kandel E, Falkowski G, Christ H, Coburger S, Lehmacher W, Bjarnason-Wehrens B, Platen P, Tokarski W, Predel HG, Dordel S. Correlation between BMI, leisure habits and motor abilities in childhood (CHILT-project). International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders : journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 2004;28(1):22-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14652619[162] Morgan PJ, Barnett LM, Cliff DP, Okely AD, Scott HA, Cohen KE, Lubans DR. Fundamental movement skill interventions in youth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2013;132(5):e1361-83
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2013-1167 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24167179[163] Kirk MA, Rhodes RE. Motor skill interventions to improve fundamental movement skills of preschoolers with developmental delay. Adapted physical activity quarterly : APAQ 2011;28(3):210-32
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21725115[164] Logan SW, Robinson LE, Wilson AE, Lucas WA. Getting the fundamentals of movement: a meta-analysis of the effectiveness of motor skill interventions in children. Child: care, health and development 2012;38(3):305-15
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2214.2011.01307.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21880055[165] Lai SK, Costigan SA, Morgan PJ, Lubans DR, Stodden DF, Salmon JO, Barnett LM. Do school-based interventions focusing on physical activity, fitness, or fundamental movement skill competency produce a sustained impact in these outcomes in children and adolescents? A systematic review of follow-up studies. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) 2014;44(1):67-79
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24122775[166] Smith GA, Bowman MJ, Luria JW, Shields BJ. Babywalker-related injuries continue despite warning labels and public education. Pediatrics 1997;100(2):E1
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9233972[167] van Wieringen JCM, Beckers MCB. Hoe krijgt de jeugdgezondheidszorg de jeugd in beweging Tijdschrift Jeugdgezondheidszorg 2015
[168] Riethmuller AM, Jones R, Okely AD. Efficacy of interventions to improve motor development in young children: a systematic review. Pediatrics 2009;124(4):e782-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0333 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19736263[169] Boonzajer Flaes SAM, Chinapaw MJM, Koolhaas CM, van Mechelen W, Verhagen EALM. More children more active: Tailored playgrounds positively affect physical activity levels amongst youth. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2016;19(3):250-254
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2015.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25846126[170] Cohen DA, Han B, Isacoff J, Shulaker B, Williamson S, Marsh T, McKenzie TL, Weir M, Bhatia R. Impact of park renovations on park use and park-based physical activity. Journal of physical activity & health 2015;12(2):289-95
http://dx.doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2013-0165 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24956608[171] Janssen M, Twisk JWR, Toussaint HM, van Mechelen W, Verhagen EALM. Effectiveness of the PLAYgrounds programme on PA levels during recess in 6-year-old to 12-year-old children. British journal of sports medicine 2015;49(4):259-64
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2012-091517 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23293007[172] Kriemler S, Meyer U, Martin E, van Sluijs EMF, Andersen LB, Martin BW. Effect of school-based interventions on physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents: a review of reviews and systematic update. British journal of sports medicine 2011;45(11):923-30
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2011-090186 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21836176[173] Wood C, Gladwell V, Barton JO. A repeated measures experiment of school playing environment to increase physical activity and enhance self-esteem in UK school children. PloS one 2014;9(9):e108701
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108701 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25264610[174] De Schipper A, Deerenberg H, Bouthoorn B, Toussaint H. Gymmen kleuters beter met een gymleraar? Sportgericht 2014;3(68):29
[175] Van Gelder W, Goedhart B, Janssen M. Het plein wacht...(1). Lichamelijke Opvoeding magazine 2015;103():26
[176] Van Gelder W, Goedhart B, Janssen M. Het plein wacht...(2). Lichamelijke Opvoeding magazine ;103():23
[177] Van Gelder W, Goedhart B, Janssen M. Het plein wacht...(3). Lichamelijke Opvoeding magazine ;103():19
[178] Jantje Beton - De Jantje Beton aanpak; samen met kinderen werken aan buitenspelen. Geraadpleegd op 22-03-2016 2013
http://www.jantjebeton.nl/gemeenten/de-jantje-betonaanpak/[179] Reddingsbrigade Nederland. 'Reddingsbrigade wil dat schoolzwemmen terugkomt'. Geraadpleegd op 22-03-2016 2015
http://www.nu.nl/werk-en-prive/4113093/reddingsbrigadewil-%20schoolzwemmen-terugkomt.html[180] Standpunt beweegstimulering door de jeugdgezondheidszorg RIVM/Centrum jeugdgezondheidszorg (Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu) 2009
[181] Kenniscentrum Sport. Evaluatie van kansrijke beweegprogramma's om lichaamsbeweging in de bevolking te bevorderen: fase 2. Geraadpleegd op 21-04-2016 2016
http://www.nivel.nl/sites/default/files/bestanden/Rapport-evaluatie-kansrijkebeweegprogrammas-%20fase2.pdf[182] Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, . GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2008;336(7650):924-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18436948[183] Delacy MJ, Reid SM, . Profile of associated impairments at age 5 years in Australia by cerebral palsy subtype and Gross Motor Function Classification System level for birth years 1996 to 2005. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2016;58 Suppl 2():50-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13012 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26777873[184] Goldet G, Howick J. Understanding GRADE: an introduction. Journal of evidence-based medicine 2013;6(1):50-54
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jebm.12018 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23557528[185] Barnett LM, Minto C, Lander N, Hardy LL. Interrater reliability assessment using the Test of Gross Motor Development-2. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2014;17(6):667-70
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2013.09.013 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24211133[186] Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, Dan B, Jacobsson BO. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Developmental medicine and child neurology. Supplement 2007;109():8-14
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17370477[187] Rosenbaum PL, Walter SD, Hanna SE, Palisano RJ, Russell DJ, Raina P, Wood E, Bartlett DJ, Galuppi BE. Prognosis for gross motor function in cerebral palsy: creation of motor development curves. JAMA 2002;288(11):1357-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12234229[188] Bruininks R, Bruininks B. Bruininks-Oseretsky test of motor proficiency (2nd ed.) Minneapolis, MN: NCS Pearson 2005
[189] Campbell SK, Swanlund A, Smith E, Liao P-J, Zawacki L. Validity of the TIMPSI for estimating concurrent performance on the test of infant motor performance. Pediatric physical therapy : the official publication of the Section on Pediatrics of the American Physical Therapy Association 2008;20(1):3-10
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PEP.0b013e31815f66a6 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18300928[190] De-Andrés-Beltrán B, Rodríguez-Fernández ÁL, Güeita-Rodríguez J, Lambeck J. Evaluation of the psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Denver Developmental Screening Test II. European journal of pediatrics 2015;174(3):325-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2410-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25164064[191] Doralp S, Bartlett D. Infant Movement Motivation Questionnaire: development of a measure evaluating infant characteristics relating to motor development in the first year of life. Infant behavior & development 2014;37(3):326-33
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2014.04.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24861943[192] Fingerhut P, Madill H, Darrah J, Hodge M, Warren S. Classroom-based assessment: validation for the school AMPS. The American journal of occupational therapy : official publication of the American Occupational Therapy Association 2002;56(2):210-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11905306[193] Folio MR, Fewell RR. Peabody Developmental Motor Scales, Second edition (PDMS-2) Occupational and Physical Therapy 2000
[194] Fransen J, D'Hondt E, Bourgois J, Vaeyens R, Philippaerts RM, Lenoir M. Motor competence assessment in children: convergent and discriminant validity between the BOT-2 Short Form and KTK testing batteries. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(6):1375-83
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.03.011 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24713517[195] GUDMUNDSSON EINAR, GRETARSSON SJ. Reliability and validity of mothers' developmental estimates for children between 4 and 41 months Scandinavian Journal of Psychology 1994;35(4):336
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.1994.tb00958.x https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.1994.tb00958.x[196] Gudmundsson E, Gretarsson SJ. Mothers' questionnaire of preschoolers' language and motor skills: a validation study. Child: care, health and development 2013;39(2):246-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2214.2011.01362.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22329598[197] Gudmundsson E. The Toddler Language and Motor Questionnaire: A mother-report measure of language and motor development. Research in developmental disabilities 2015;45-46():21-31
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26209772[198] van Hartingsveldt MJ, Cup EHC, de Groot IJM, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MWG. Writing Readiness Inventory Tool in Context (WRITIC): reliability and convergent validity. Australian occupational therapy journal 2014;61(2):102-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1440-1630.12082 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24689921[199] Heineman KR, La Bastide-Van Gemert S, Fidler V, Middelburg KJ, Bos AF, Hadders-Algra M. Construct validity of the Infant Motor Profile: relation with prenatal, perinatal, and neonatal risk factors. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(9):e209-15
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03667.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20477835[200] Heineman KR, Middelburg KJ, Bos AF, Eidhof L, La Bastide-Van Gemert S, Van Den Heuvel ER, Hadders-Algra M. Reliability and concurrent validity of the Infant Motor Profile. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2013;55(6):539-45
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12100 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23480426[201] Johansen K, Persson K, Sarkadi A, Sonnander K, Magnusson M, Lucas S. Can nurses be key players in assessing early motor development using a structured method in the child health setting? Journal of evaluation in clinical practice 2015;21(4):681-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jep.12366 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25958886[202] Kakebeeke TH, Caflisch J, Chaouch A, Rousson V, Largo RH, Jenni OG. Neuromotor development in children. Part 3: motor performance in 3- to 5-year-olds. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2013;55(3):248-56
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12034 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23278183[203] Kambas A, Venetsanou F. The Democritos Movement Screening Tool for Preschool Children (DEMOST-PRE©): development and factorial validity. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(7):1528-33
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.03.046 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24763377[204] Kambas A, Venetsanou F, Giannakidou D, Fatouros IG, Avloniti A, Chatzinikolaou A, Draganidis D, Zimmer R. The Motor-Proficiency-Test for children between 4 and 6 years of age (MOT 4-6): an investigation of its suitability in Greece. Research in developmental disabilities 2012;33(5):1626-32
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2012.04.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22543059[205] Tabatabainia MM, Ziviani J, Maas F. Construct validity of the Bruininks‐Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency and the Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Australian Occupational Therapy Journal 1995;42(1):3
[206] MacCobb S, Greene S, Nugent K, O'Mahony P. Measurement and prediction of motor proficiency in children using Bayley infant scales and the Bruininks-Oseretsky test. Physical & occupational therapy in pediatrics 2005;25(1-2):59-79
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15760824[207] Venetsanou F, Kambas A, Aggeloussis N, Serbezis V, Taxildaris K. Use of the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency for identifying children with motor impairment. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):846-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979863[208] Venetsanou F, Kambas A, Aggeloussis N, Fatouros I, Taxildaris K. Motor assessment of preschool aged children: A preliminary investigation of the validity of the Bruininks-Oseretsky test of motor proficiency - short form. Human movement science 2009;28(4):543-50
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2009.03.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19443065[209] Saraiva L, Rodrigues LP, Cordovil R, Barreiros J. Motor profile of Portuguese preschool children on the Peabody Developmental Motor Scales-2: a cross-cultural study. Research in developmental disabilities 2013;34(6):1966-73
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.03.010 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23584176[210] Reuben DB, Magasi S, McCreath HE, Bohannon RW, Wang Y-C, Bubela DJ, Rymer WZ, Beaumont J, Rine RM, Lai J-S, Gershon RC. Motor assessment using the NIH Toolbox. Neurology 2013;80(11 Suppl 3):S65-75
http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182872e01 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23479547[211] Pergami P, Seemaladinne N, Billings A. Validation of a computer application as a test of motor function in healthy children and adults. NeuroRehabilitation 2012;31(4):453-61
http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/NRE-2012-00816 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23232170[212] Westcott McCoy S, Bowman A, Smith-Blockley J, Sanders K, Megens AM, Harris SR. Harris Infant Neuromotor Test: comparison of US and Canadian normative data and examination of concurrent validity with the Ages and Stages Questionnaire. Physical therapy 2009;89(2):173-80
http://dx.doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20080189 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19131397[213] Sun S-H, Zhu Y-C, Shih C-L, Lin C-H, Wu SK. Development and initial validation of the Preschooler Gross Motor Quality Scale. Research in developmental disabilities 2010;31(6):1187-96
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2010.08.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20843658[214] Sun S-H, Sun H-L, Zhu Y-C, Huang L-C, Hsieh Y-L. Concurrent validity of Preschooler Gross Motor Quality Scale with Test of Gross Motor Development-2. Research in developmental disabilities 2011;32(3):1163-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.01.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21295441[215] Williams HG, Pfeiffer KA, Dowda M, Jeter C, Jones S, Pate RR. A Field-Based Testing Protocol for Assessing Gross Motor Skills in Preschool Children: The CHAMPS Motor Skills Protocol (CMSP). Measurement in physical education and exercise science 2009;13(3):151-165
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21532999[216] Smith YA, Hong E, Presson C. Normative and validation studies of the Nine-hole Peg Test with children. Perceptual and motor skills 2000;90(3 Pt 1):823-43
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10883762[217] Majewska R, Mrozek-Budzyn D, Kieltyka A, Augustyniak M. Usefulness of maternal assessment of children development based on reported age of achieved milestones. Przeglad epidemiologiczny 2013;67(3):487-90, 585-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24340566[218] Lin C-K, Meng L-F, Yu Y-W, Chen C-K, Li K-H. Factor analysis of the contextual fine motor questionnaire in children. Research in developmental disabilities 2014;35(2):512-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.11.007 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24374604[219] Netelenbos JB. Teachers’ ratings of gross motor skills suffer from low concurrent validity Human Movement Science 2005;24(1):116
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2005.02.001 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167945705000059[220] Schoemaker MM. Manual of the motor observation questionnaire for teachers Groningen: internal Publication, Center for Human Movement Sciences, In Dutch 2003
[221] Kerkmeer M, Zijlstra J, Dek J. Bayley-III-NL - Psychometrische eigenschappen Pearson Assesment and Information BV 2015
[222] Burger M, Louw QA. The predictive validity of general movements--a systematic review. European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society 2009;13(5):408-20
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2008.09.004 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19036618[223] Hadders-Algra M, Heineman KR, Bos AF, Middelburg KJ. The assessment of minor neurological dysfunction in infancy using the Touwen Infant Neurological Examination: strengths and limitations. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(1):87-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03305.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19549207[224] Bouwstra H, Dijk-Stigter GR, Grooten HMJ, Janssen-Plas FE, Koopmans AJ, Mulder CD, van Belle A, Hadders-Algra M. Predictive value of definitely abnormal general movements in the general population. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2010;52(5):456-61
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03529.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20002118[225] Peters LK, Maathuis KG, Kouw E, Hamming M, Hadders-Algra M. Test-retest, inter-assessor and intra-assessor reliability of the modified Touwen examination Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2008;12(4):328
[226] Trendrapport Bewegen en Gezondheid TNO. Onder redactie van: V.H. Hildebrandt, A.M.J. Chorus, J.H. Stubbe 2008
[227] Visser JD. Kinderorthopedie: Pluis of Niet Pluis. Een leidraad voor eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. 11e druk 2009
[228] Global recommendations on physical activity for health World Health Organization (WHO): Genève 2010
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackLET OP: print de JGZ-richtlijn in liggende afdrukstand!
Grote tabellen zijn niet volledig zichtbaar als de JGZ-richtlijn in staande afdrukstand geprint wordt. Om kleuren in de printversie goed door te laten komen, moet bij de printerinstellingen Achtergrondillustraties aangezet worden.
Disclaimer printversie JGZ-richtlijnen
De printversie van de JGZ-richtlijn bevat de algemene tekst inclusief de aanbevelingen. De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing is terug te vinden op de website, bij de aanbevelingen onder de link “Evidence”.