| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| Nicoline Schalij-Delfos (voorzitter van de werkgroep) | Hoogleraar kinderoogheelkunde | LUMC |
| Hein Raat (penvoerder) | Hoogleraar sectie jeugd van de afdeling Maatschappelijke Gezondheidszorg | Erasmus MC |
| Huib Simonsz | Kinderoogarts en hoogleraar van de afdeling oogheelkunde | Erasmus MC |
| Caren Lanting | Senior adviseur richtlijnontwikkeling en onderzoeker bij de afdeling Child Health | TNO |
| Frea Sloot | Promovendus en oogarts in opleiding van de afdeling oogheelkunde | Erasmus MC |
| Aya Sami | Orthoptist en junior onderzoeker van de afdeling oogheelkunde | Erasmus MC |
| Suzanne van den Toren | Junior onderzoeker sectie jeugd van de afdeling Maatschappelijke Gezondheidszorg | Erasmus MC |
4.3 Leden van de projectgroep
JGZ-richtlijn Opsporen oogafwijkingen
JGZ-richtlijn Opsporen oogafwijkingen
Let op: deze richtlijn is momenteel in herziening.
Dit betekent niet dat de inhoud van deze richtlijn incorrect is. Tot de herziening blijft de richtlijn leidend voor de praktijk. Wel bestaat er een kans dat een deel van de informatie verouderd is.
Heb je feedback over deze JGZ-richtlijn? Stuur jouw feedback naar onze servicedesk. Zoek het tekstgedeelte waarbij je suggesties voor verbetering hebt. Via de knop ‘Geef jouw feedback’ kun je voor deze JGZ-richtlijn en het specifieke hoofdstuk jouw suggesties doorgeven.
Richtlijn inhoudsopgave
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrond informatie
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
4 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 4 Totstandkoming richtlijn
5 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 5 Verantwoording
6 Bijlage 1: de uitvoering van oogonderzoeken in de praktijk Ga naar pagina over 6 Bijlage 1: de uitvoering van oogonderzoeken in de praktijk
7 Bijlage 2: nuttige websites en boeken Ga naar pagina over 7 Bijlage 2: nuttige websites en boeken
8 Bijlage 4: literatuuronderzoek naar de mogelijke rol van automatische meetapparatuur/fotoscreeners (PlusOptix vision screener) bij de opsporing van oogafwijkingen Ga naar pagina over 8 Bijlage 4: literatuuronderzoek naar de mogelijke rol van automatische meetapparatuur/fotoscreeners (PlusOptix vision screener) bij de opsporing van oogafwijkingen
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrond informatie
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
4 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 4 Totstandkoming richtlijn
5 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 5 Verantwoording
6 Bijlage 1: de uitvoering van oogonderzoeken in de praktijk Ga naar pagina over 6 Bijlage 1: de uitvoering van oogonderzoeken in de praktijk
7 Bijlage 2: nuttige websites en boeken Ga naar pagina over 7 Bijlage 2: nuttige websites en boeken
8 Bijlage 4: literatuuronderzoek naar de mogelijke rol van automatische meetapparatuur/fotoscreeners (PlusOptix vision screener) bij de opsporing van oogafwijkingen Ga naar pagina over 8 Bijlage 4: literatuuronderzoek naar de mogelijke rol van automatische meetapparatuur/fotoscreeners (PlusOptix vision screener) bij de opsporing van oogafwijkingen
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackSamenvattingskaart richtlijn Opsporing Oogafwijkingen
Introductiefilmpje richtlijn Opsporing oogafwijkingen
PP-presentatie voor de scholing Opsporing oogafwijkingen
Factsheet richtlijn Opsporing oogafwijkingen
Randvoorwaardelijke implicaties richtlijn Opsporing Oogafwijkingen
Rapportage praktijktest richtlijn Opsporing oogafwijkingen
BDS-registratie-protocol richtlijn Oogafwijkingen
Indicatoren richtlijn Opsporing oogafwijkingen
Video Werksessie RL Opsporen Oogafwijkingen
PP-presentatie over de richtlijn door Nicolien Schalij-oogarts
Bestelinformatie Visuskaarten update 12-06-2024
Randvoorwaarden en achtergrond van meten van de visus bij kinderen
[1] Argumentenfabriek. Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg. 2014
[2] Koninklijke Nederlandsche Maatschappij tot bevordering der Geneeskunst. KNMG-visie Versterking medische zorg aan jeugdigen 2013
http://knmg.artsennet.nl/[3] Graham PA. Epidemiology of strabismus. The British journal of ophthalmology 1974;58(3):224-31
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4834596[4] Holmes JM, Clarke MP. Amblyopia. Lancet (London, England) 2006;367(9519):1343-51
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16631913[5] Lee C-W, Fang S-Y, Tsai D-C, Huang N, Hsu C-C, Chen S-Y, Chiu AW-H, Liu CJ-L. Prevalence and association of refractive anisometropia with near work habits among young schoolchildren: The evidence from a population-based study. PloS one 2017;12(3):e0173519
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173519 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28273153[6] Urbanus-van Laar N. Ethnic inequalities in quality of care for children in the Netherlands [Proefschrift]. Amsterdam: Universiteit van Amsterdam 2007
[7] Nederlands Jeugdinstituut. Factsheet media in het gezin. 2015
[8] Neitz M, Neitz J. Molecular genetics of color vision and color vision defects. Archives of ophthalmology (Chicago, Ill. : 1960) 2000;118(5):691-700
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10815162[9] Xiong S, Sankaridurg P, Naduvilath T, Zang J, Zou H, Zhu J, Lv M, He X, Xu X. Time spent in outdoor activities in relation to myopia prevention and control: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta ophthalmologica 2017;95(6):551-566
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aos.13403 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28251836[10] Simons K. Preschool vision screening: rationale, methodology and outcome. Survey of ophthalmology 1996;41(1):3-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8827927[11] Tedja MS, Wojciechowski R, Hysi PG, Eriksson N, Furlotte NA, Verhoeven VJM, Iglesias AI, Meester-Smoor MA, Tompson SW, Fan Q, Khawaja AP, Cheng C-Y, Höhn R, Yamashiro K, Wenocur A, Grazal C, Haller T, Metspalu A, Wedenoja J, Jonas JB, Wang YX, Xie J, Mitchell P, Foster PJ, Klein BEK, Klein R, Paterson AD, Hosseini SM, Shah RL, Williams C, Teo YY, Tham YC, Gupta P, Zhao W, Shi Y, Saw W-Y, Tai E-S, Sim XL, Huffman JE, Polašek O, Hayward C, Bencic G, Rudan I, Wilson JF, , , , Joshi PK, Tsujikawa A, Matsuda F, Whisenhunt KN, Zeller T, van der Spek PJ, Haak R, Meijers-Heijboer H, van Leeuwen EM, Iyengar SK, Lass JH, Hofman A, Rivadeneira F, Uitterlinden AG, Vingerling JR, Lehtimäki T, Raitakari OT, Biino G, Concas MP, Schwantes-An T-H, Igo RP, Cuellar-Partida G, Martin NG, Craig JE, Gharahkhani P, Williams KM, Nag A, Rahi JS, Cumberland PM, Delcourt C, Bellenguez C, Ried JS, Bergen AA, Meitinger T, Gieger C, Wong TY, Hewitt AW, Mackey DA, Simpson CL, Pfeiffer N, Pärssinen O, Baird PN, Vitart V, Amin N, van Duijn CM, Bailey-Wilson JE, Young TL, Saw S-M, Stambolian D, MacGregor S, Guggenheim JA, Tung JY, Hammond CJ, Klaver CCW. Genome-wide association meta-analysis highlights light-induced signaling as a driver for refractive error. Nature genetics 2018;50(6):834-848
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0127-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29808027[12] Tideman JWL, Polling JR, van der Schans A, Verhoeven VJM, Klaver CCW. [Myopia, a growing health problem]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2016;160():D803
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27879184[13] TNO. Belang van buitenspelen. 2011
[14] Wright KW, Strube YNJ. Postnatal development. Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 2nd ed. New York. In: Springer-Verlag 2003
[15] Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4-5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England) 2008;12(25):iii, xi-194
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18513466[16] Chou R, Dana T, Bougatsos C. Screening for visual impairment in children ages 1-5 years: update for the USPSTF. Pediatrics 2011;127(2):e442-79
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-0462 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21282269[17] Eibschitz-Tsimhoni M, Friedman T, Naor J, Eibschitz N, Friedman Z. Early screening for amblyogenic risk factors lowers the prevalence and severity of amblyopia. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2000;4(4):194-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10951293[18] Groenewoud JH, Tjiam AM, Lantau VK, Hoogeveen WC, de Faber JTHN, Juttmann RE, de Koning HJ, Simonsz HJ. Rotterdam AMblyopia screening effectiveness study: detection and causes of amblyopia in a large birth cohort. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2010;51(7):3476-84
http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.08-3352 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20089868[19] Institut fuer Qualitaet und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen. Screening for visual impairment in children(Structured abstract). Health Technology Assessment Database 2008
[20] IQWIG. Screening for visual impairment in children younger than 6 years: rapid report (Structured abstract). Health Technology Assessment Database 2015
[21] Jonas DE, Amick HR, Wallace IF, Feltner C, Vander Schaaf EB, Brown CL, Baker C. No title 2017
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29561582[22] Magnusson G, Persson U. Screening for congenital cataracts: a cost-consequence analysis of eye examination at maternity wards in comparison to well-baby clinics. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2005;94(8):1089-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16188854[23] Mathers M, Keyes M, Wright M. A review of the evidence on the effectiveness of children's vision screening. Child: care, health and development 2010;36(6):756-80
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2214.2010.01109.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20645997[24] Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion. Effectiveness of vision screening programs for children aged one to six years. Queen's Printer for Ontario: Toronto 2016
[25] Powell C, Hatt SR. Vision screening for amblyopia in childhood. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2009
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005020.pub3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19588363[26] Powell C, Wedner S, Richardson S. Screening for correctable visual acuity deficits in school-age children and adolescents. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2005
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15654703[27] Sami A, Karaman H, Sloot F, Sjoerdsma T, Banjamins J, Simonsz HJ. Quality of eye screening examinations at Child Health Centers in the Netherlands assessed by semi-structured observations. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2014;55(432):
[28] Sloot F, Sami A, Karaman H, Benjamins J, Loudon SE, Raat H, Sjoerdsma T, Simonsz HJ. Effect of omission of population-based eye screening at age 6-9 months in the Netherlands. Acta ophthalmologica 2015;93(4):318-21
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aos.12556 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25270899[29] Sloot F, Sami A, Karaman H, Gutter M, Benjamins J, Sjoerdsma T, Simonsz HJ. Semistructured Observation of Population-based Eye Screening in The Netherlands. Strabismus 2017;25(4):214-221
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09273972.2017.1395596 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29182469[30] Schmucker C, Grosselfinger R, Riemsma R, Antes G, Lange S, Lagrèze W, Kleijnen J. Effectiveness of screening preschool children for amblyopia: a systematic review. BMC ophthalmology 2009;9():3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2415-9-3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19607693[31] Hull S, Tailor V, Balduzzi S, Rahi J, Schmucker C, Virgili G, Dahlmann-Noor A. Tests for detecting strabismus in children aged 1 to 6 years in the community. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2017;11(11):CD011221
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011221.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29105728[32] Tung IC, Tsai RK, Chang CH, Sheu MM. Comparison of Trained Kindergarten Teachers and Public Health Nurses in the Administration of Preschool Amblyopia and Strabismus Screening Tests. Journal of Tzu Chi Medical Sciences 2006;18(1):29
[33] West S, Williams C. Amblyopia. BMJ clinical evidence 2011;2011():
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21714945[34] Williams C, Northstone K, Harrad RA, Sparrow JM, Harvey I, . Amblyopia treatment outcomes after preschool screening v school entry screening: observational data from a prospective cohort study. The British journal of ophthalmology 2003;87(8):988-93
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12881342[35] Williams C, Harrad RA, Harvey I, Sparrow JM, . Screening for amblyopia in preschool children: results of a population-based, randomised controlled trial. ALSPAC Study Team. Avon Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood. Ophthalmic epidemiology 2001;8(5):279-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11922382[36] Adhikari S, Shrestha U. Validation of performance of certified medical assistants in preschool vision screening examination. Nepalese journal of ophthalmology : a biannual peer-reviewed academic journal of the Nepal Ophthalmic Society : NEPJOPH 2011;3(2):128-33
http://dx.doi.org/10.3126/nepjoph.v3i2.5264 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21876585[37] Awan M, Proudlock FA, Grosvenor D, Choudhuri I, Sarvanananthan N, Gottlob I. An audit of the outcome of amblyopia treatment: a retrospective analysis of 322 children. The British journal of ophthalmology 2010;94(8):1007-11
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2008.154674 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19955200[38] Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. The course of moderate amblyopia treated with atropine in children: experience of the amblyopia treatment study. American journal of ophthalmology 2003;136(4):630-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14516802[39] Becker R, Hübsch S, Gräf MH, Kaufmann H. Examination of young children with Lea symbols. The British journal of ophthalmology 2002;86(5):513-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11973243[40] Bertuzzi F, Orsoni JG, Porta MR, Paliaga GP, Miglior S. Sensitivity and specificity of a visual acuity screening protocol performed with the Lea Symbols 15-line folding distance chart in preschool children. Acta ophthalmologica Scandinavica 2006;84(6):807-11
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17083543[41] Bušić M, Bjeloš M, Petrovečki M, Kuzmanović Elabjer B, Bosnar D, Ramić S, Miletić D, Andrijašević L, Kondža Krstonijević E, Jakovljević V, Bišćan Tvrdi A, Predović J, Kokot A, Bišćan F, Kovačević Ljubić M, Motušić Aras R. Zagreb Amblyopia Preschool Screening Study: near and distance visual acuity testing increase the diagnostic accuracy of screening for amblyopia. Croatian medical journal 2016;57(1):29-41
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26935612[42] Chen P-L, Chen J-T, Tai M-C, Fu J-J, Chang C-C, Lu D-W. Anisometropic amblyopia treated with spectacle correction alone: possible factors predicting success and time to start patching. American journal of ophthalmology 2007;143(1):54-60
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17113556[43] Clarke MP, Wright CM, Hrisos S, Anderson JD, Henderson J, Richardson SR. Randomised controlled trial of treatment of unilateral visual impairment detected at preschool vision screening. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2003;327(7426):1251
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14644966[44] Engin O, Despriet DDG, van der Meulen-Schot HM, Romers A, Slot X, Sang MTF, Fronius M, Kelderman H, Simonsz HJ. Comparison of optotypes of Amsterdam Picture Chart with those of Tumbling-E, LEA symbols, ETDRS, and Landolt-C in non-amblyopic and amblyopic patients. Graefe's archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie 2014;252(12):2013-20
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2763-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25228066[45] Flynn JT, Woodruff G, Thompson JR, Hiscox F, Feuer W, Schiffman J, Corona A, Smith LK. The therapy of amblyopia: an analysis comparing the results of amblyopia therapy utilizing two pooled data sets. Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society 1999;97():373-90; discussion 390-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10703134[46] Friendly DS. Preschool visual acuity screening tests. Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society 1978;76():383-480
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/754379[47] Hussein MAW, Coats DK, Muthialu A, Cohen E, Paysse EA. Risk factors for treatment failure of anisometropic amblyopia. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2004;8(5):429-34
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15492734[48] Kvarnström G, Jakobsson P. Is vision screening in 3-year-old children feasible? Comparison between the Lea Symbol chart and the HVOT (LM) chart. Acta ophthalmologica Scandinavica 2005;83(1):76-80
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15715562[49] Lai Y-H, Tseng H-Y, Hsu H-T, Chang S-J, Wang H-Z. Uncorrected visual acuity and noncycloplegic autorefraction predict significant refractive errors in Taiwanese preschool children. Ophthalmology 2013;120(2):271-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.08.009 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23182455[50] Lithander J, Sjöstrand J. Anisometropic and strabismic amblyopia in the age group 2 years and above: a prospective study of the results of treatment. The British journal of ophthalmology 1991;75(2):111-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1995038[51] Lokesh H, Bindurani M. Management of amblyopia by occlusion therapy. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences 2015;6(4):972
[52] Mazow ML, Chuang A, Vital MC, Prager T. 1999 Costenbader Lecture. Outcome study in amblyopia: treatment and practice pattern variations. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2000;4(1):1-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10675864[53] NVvO NOG OVN. Plan geïntegreerde oogzorg. 2013
[54] Ore L, Garzozi HJ, Tamir A, Stein N, Cohen-Dar M. Performance measures of the illiterate E-chart vision-screening test used in Northern District Israeli school children. Journal of medical screening 2008;15(2):65-71
http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/jms.2008.007094 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18573773[55] Ore L, Garzozi HJ, Tamir A, Cohen-Dar M. Vision screening among northern Israeli Jewish and Arab schoolchildren. The Israel Medical Association journal : IMAJ 2009;11(3):160-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19544706[56] Schmucker C, Kleijnen J, Grosselfinger R, Riemsma R, Antes G, Lange S, Lagrèze W. Effectiveness of early in comparison to late(r) treatment in children with amblyopia or its risk factors: a systematic review. Ophthalmic epidemiology 2010;17(1):7-17
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09286580903312301 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20100095[57] Stewart CE, Fielder AR, Stephens DA, Moseley MJ. Treatment of unilateral amblyopia: factors influencing visual outcome. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2005;46(9):3152-60
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16123414[58] Telleman MAJ, Sloot F, Benjamins J, Simonsz HJ. High rate of failed visual-acuity measurements with the Amsterdam Picture Chart in screening at the age of 36 months. Acta ophthalmologica 2019;97(1):24-28
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aos.13898 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30284395[59] Tjiam AM, Groenewoud JH, Passchier J, Loudon SE, De Graaf M, Hoogeveen WC, Lantau VK, Juttmann RE, De Koning HJ, Simonsz HJ. Determinants and outcome of unsuccessful referral after positive screening in a large birth-cohort study of population-based vision screening. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2011;15(3):256-62
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2011.01.159 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21777799[60] Wallace DK, Lazar EL, Crouch ER, Hoover DL, Kraker RT, Tamkins SM, . Time course and predictors of amblyopia improvement with 2 hours of daily patching. JAMA ophthalmology 2015;133(5):606-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.6 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25695355[61] CEN. European Standard: Ophthalmic opties - Visual acuity testing - Standard symbool and its presentation 2018
[62] Sheedy JE, Bailey IL, Raasch TW. Visual acuity and chart luminance. American journal of optometry and physiological optics 1984;61(9):595-600
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6507580[63] NEN. European Standard: Ophthalmic opties - Visual acuity testing - Standard optotype and its presentation 2017
[64] Arnold RW, Armitage MD. Performance of four new photoscreeners on pediatric patients with high risk amblyopia. Journal of pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus 2014;51(1):46-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20131223-02 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24369683[65] Donahue SP, Arnold RW, Ruben JB, . Preschool vision screening: what should we be detecting and how should we report it? Uniform guidelines for reporting results of preschool vision screening studies. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2003;7(5):314-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14566312[66] Sanchez I, Ortiz-Toquero S, Martin R, de Juan V. Advantages, limitations, and diagnostic accuracy of photoscreeners in early detection of amblyopia: a review. Clinical ophthalmology (Auckland, N.Z.) 2016;10():1365-73
http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S93714 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/275557441 Inleiding
Dit document is bedoeld voor jeugdgezondheidszorg [JGZ] professionals en beoogt een richtlijn te zijn voor het handelen in hun contacten met individuele jeugdigen en hun ouders/verzorgers met betrekking tot de screening op oogafwijkingen. JGZ-professionals zijn jeugdartsen, verpleegkundig specialisten*, jeugdverpleegkundigen en doktersassistenten. De JGZ signaleert door systematisch onderzoek vroegtijdig afwijkingen aan het oog en het gezichtsvermogen, met als doel om slechtziendheid te voorkomen en gezondheidswinst te halen. Deze gezondheidswinst wordt met name behaald door het zo vroeg mogelijk opsporen van een amblyopie (lui oog) en andere oogafwijkingen, zoals cataract en tumoren in het oog, zodat effectieve behandeling mogelijk is. Deze richtlijn ‘Opsporen oogafwijkingen’ is een vervanging van de richtlijn ‘Opsporing Visuele stoornissen 0-19 jaar’ uit 2010 en beschrijft het hele opsporingsprogramma voor oogafwijkingen voor jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar. Basis voor de richtlijn zijn uitgangsvragen die zijn vastgesteld tijdens een knelpuntenanalyse onder JGZ-professionals, onder leiding van de Argumentenfabriek [1]. Cochrane Netherlands heeft waar mogelijk de uitgangsvragen beantwoord met wetenschappelijke literatuur. Het gehele rapport van Cochrane Netherlands is op te vragen bij de auteurs van de richtlijn.
De herziene richtlijn is door de Richtlijn Advies- en Autorisatie Commissie (RAC) op 01-04-2019 geautoriseerd voor gebruik in de JGZ. De RAC heeft bij haar beoordeling rekening gehouden met de inhoud van de richtlijn (wetenschappelijke onderbouwing, opzet) en de voor implementatie vereiste randvoorwaarden.
*De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en zij werkt op expertniveau. Zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
| Met de autorisatie van deze richtlijn is de JGZ-richtlijn ‘Opsporing visuele stoornissen 0-19 jaar’ (2010) komen te vervallen. |
1.1 Nieuw in deze herziening
- De leeftijden waarop oogonderzoek bij het kind wordt geadviseerd zijn: 1 maand, 2 maanden, 3 maanden, 6-9 maanden, 14-24 maanden, 36 maanden, 42-48 maanden en 54-66 maanden.
- Vanwege verschillen tussen JGZ-organisaties in de invulling van de contactmomenten worden het twee keer beoordelen of de rode fundusreflex aanwezig is en de visusmetingen in de leeftijdsperiode van 42-48 maanden en 54-66 maanden noodzakelijk geacht. De andere bovengenoemde momenten worden dringend aanbevolen.
- De inhoud van de uit te voeren onderzoeken is aangepast ten opzichte van de vorige richtlijn.
- In de leeftijdsperiode tussen 0 en 3 maanden worden de pupilreacties niet meer beoordeeld.
- In de leeftijdsperiode tussen 6 en 24 maanden worden de cornea lichtreflex, instelbeweging en monoculaire volgbeweging uitgevoerd.
- De oogstand wordt beoordeeld met de cornea lichtreflex en de instelbeweging van het niet afgedekte oog. De monoculaire volgbewegingen worden uitgevoerd als globale test om een verminderde visus vast te stellen.
- Op de leeftijd van 36 maanden wordt de visusmeting niet meer standaard, maar slechts op indicatie EN indien de JGZ-professional dit wenst, uitgevoerd.
- Het eerste moment waarop de visus bepaald wordt bij alle kinderen is in de leeftijdsperiode van 42-48 maanden en het tweede moment is in de leeftijdsperiode van 54-66 maanden, waarbij 66 maanden (5 1⁄2 jaar) de uiterste termijn is.
- De lichtkasten voor de visuskaart worden vanaf invoering van deze richtlijn niet meer gebruikt.
- De Amsterdamse Plaatjes Kaart (APK) wordt zo spoedig mogelijk, uiterlijk 1-1-2020, vervangen door de LEA Symbolen kaart.
- De Landolt-C kaart zal uiterlijk 1-1-2021 vervangen zijn door de logaritmische E-Haken kaart. Tot deze datum mag ook de transparante Landolt-C kaart zonder lichtkast gebruikt worden op een witte achtergrond, liefst met wit papier.
- Wanneer het kind de E-haken kaart, of indien nog niet vervangen de Landolt C kaart, niet kan uitvoeren, wordt de LEA-symbolen kaart als alternatief gebruikt.
- De verwijscriteria voor de visusmeting zijn aangepast aan wat internationaal gebruikelijk is, namelijk een drempel van 0.63 in de leeftijdsperiode van 42-48 maanden en een drempel van 0.8 in de leeftijdsperiode van 54-66 maanden .
- Bij de visusmeting in de leeftijdsperioden van 42-48 maanden en van 54-66 maanden wordt voor elk oog getest tot de hoogst haalbare visus, met een maximum van 1.0.
Informatie uitwisseling bij verwijzing
De KNMG stelt in haar visie ‘Versterking medische zorg aan jeugdigen’ dat artsen ieder voor zich en gezamenlijk verantwoordelijk zijn voor kwalitatief goede en samenhangende zorg. Dit houdt ook in dat zij per regio onderling afspraken maken over verwijzing, terugverwijzing, berichtgeving/gegevensuitwisseling en verdeling van verantwoordelijkheden [2].
Voor een optimale begeleiding is het van belang dat de JGZ op de hoogte is van de bevindingen en het beloop van de behandeling, en zo nodig actief naar recente informatie vraagt bij de behandelende specialist.
De verwijsbrief van jeugdarts of verpleegkundig specialist aan orthoptist/oogarts bevat naast de persoonsgegevens informatie over relevante risicofactoren, indien van toepassing uitslagen van eerder uitgevoerd oogonderzoek en de uitslag van het meest recent uitgevoerde oogonderzoek inclusief de visus per oog. Vermeld ook de naam en contactgegevens van de verwijzer zodat terug rapportage mogelijk is.
2 Definities en achtergrond informatie
2.1 Ontwikkeling van het oog en de visuele functies
In dit thema wordt achtergrondinformatie gegeven over de normale visuele ontwikkeling en over oogafwijkingen die een bedreiging kunnen zijn voor deze ontwikkeling.
Een goede gezichtsscherpte is van groot belang voor de algemene ontwikkeling. Op latere leeftijd kan een amblyoop (lui) oog de reden zijn dat iemand slechtziend wordt bij verlies van het goede oog (Rahi, 2002). Daarom is tijdige opsporing, accurate verwijzing en de juiste behandeling noodzakelijk om schade aan de visuele ontwikkeling te voorkomen of zoveel mogelijk te beperken. Daarnaast is tijdige detectie en verwijzing naar orthoptist/oogarts van groot belang bij maligniteiten en symptomen die duiden op systemische aandoeningen, syndromen of chromosomale afwijkingen.
Normale ontwikkeling
Vanaf de geboorte groeit het oog en ontwikkelen de visuele functies. Om afwijkingen vast te kunnen stellen is het van belang de normale ontwikkeling te kennen. Vanaf de leeftijd van 6 weken moet een baby gericht een object kunnen fixeren zoals een speeltje of de ogen van de ouders*. Vanaf 2 maanden kunnen de meeste kinderen vloeiende volgbewegingen maken. Scherpstellen dichtbij (accommoderen) en het tegelijkertijd bewegen van beide ogen richting de neus (convergeren) is mogelijk vanaf 3-4 maanden. Het driedimensionaal dieptezien (stereoscopisch zien) ontwikkelt zich tussen de leeftijd van 3-5 maanden en 3 jaar. Ook de gezichtsscherpte (visus) neemt in de loop van jaren langzaam toe van 0,05 bij de geboorte tot 1,0 rond de leeftijd van 6 jaar. Het oog zelf groeit in de loop van jaren uit naar volwassen afmetingen. Voor de screening op oogafwijkingen is van belang dat de horizontale diameter van het hoornvlies (de cornea) toeneemt van 9,5-10,5 mm bij geboorte tot 12 mm (volwassen waarde) op 7-jarige leeftijd. De gemiddelde pupildiameter is 4 mm. Bij meten van de refractie heeft het merendeel van de kinderen een +sterkte (hypermetropie) die gemiddeld +1.0 dioptrie (D) bij geboorte is, toeneemt tot de leeftijd van 7 jaar en dan weer afneemt om rond het 16e jaar de volwassen sterkte te bereiken [14].
Voor de beschrijving van de normale ontwikkeling van het oog wordt verwezen naar referenties in bijlage 2.
*In het Van Wiechenschema staat bij vier weken het item ‘ogen fixeren’ aangegeven. Wij houden in deze richtlijn zes weken aan, omdat een kind bij vier weken nog niet hoeft te fixeren.
Tabel 2.1: Normale visuele ontwikkeling
| Ontwikkeling van het zien | Vanaf leeftijd |
| Vaste fixatie | 6 weken |
| Vloeiende volgbewegingen | 2 maanden |
| Convergentie | 3 maanden |
| Accommodatie | 3-4 maanden |
| Stereoscopisch zien | 3-5 maanden tot 3 jaar |
2.1.1 Amblyopie en strabismus
Amblyopie is slechtziendheid ten gevolge van een onderbreking van de normale visuele ontwikkeling in de eerste levensmaanden of -jaren. De prevalentie is 1-4 % afhankelijk van de gebruikte definitie en de bestudeerde populatie [4](Friedman, 2009). Het kan éénzijdig of (in zeldzame gevallen) dubbelzijdig voorkomen. Oorzaken voor amblyopie zijn refractieafwijkingen, strabismus of deprivatie (bijvoorbeeld een mediatroebeling zoals cataract of een cornealitteken). Ook een combinatie van verschillende oorzaken komt met regelmaat voor. Als de hersenen een gestoord beeld aangeboden krijgen, zoals een dubbelbeeld bij scheelzien of een wazig of vervormd beeld bij een refractieafwijking of een mediatroebeling, dan wordt de normale visuele ontwikkeling van één oog belemmerd en wordt de gezichtsscherpte van dat oog slechter.
Oorzaken
Refractie amblyopie is het gevolg van brekingsafwijkingen of een verschil in brilsterkte tussen beide ogen (anisometropie). Een oog zonder brekingsafwijking is emmetroop . Voorkomende refractieafwijkingen zijn hypermetropie of verziendheid die gecorrigeerd wordt met een bril met plussterkte, en myopie of bijziendheid die gecorrigeerd wordt met een bril met minsterkte. Wanneer de breking niet in alle vlakken (horizontaal en verticaal) gelijk is, is er sprake van astigmatisme dat gecorrigeerd wordt met een cilinderglas. Astigmatisme komt vaak voor samen met hypermetropie of myopie.
Een refractieafwijking vormt een bedreiging voor de visuele ontwikkeling als het beeld dat aangeboden wordt aan de hersenen zo wazig is dat het onderdrukt wordt. Dit is vooral het geval bij hoge refractieafwijkingen, astigmatisme met een schuine as of anisometropie. Bij anisometropie is er een verschil in sterkte van meer dan 1.5D tussen de ogen. Het is in normale omstandigheden niet mogelijk met het ene oog meer te accommoderen dan met het andere oog. Bij kinderen, bij wie meestal sprake is van hypermetropie, betekent dit dat geaccommodeerd wordt tot 1 oog scherp ziet. Het beeld van het andere oog is dan wazig. Een hoge refractieafwijking aan beide ogen kan dubbelzijdige amblyopie veroorzaken. Refractie amblyopie wordt bij screening opgespoord met een visusmeting.
Strabismus-amblyopie (scheelziensamblyopie) ontstaat ten gevolge van scheelzien. Om dubbelzien, dat ontstaat als een oog scheel gaat kijken, te voorkomen wordt het beeld van het scheelstaande oog in de hersenen onderdrukt, waardoor de visuele ontwikkeling van dit oog achterblijft. Strabismus wordt in deze richtlijn met cornea lichtreflex en de instelbeweging opgespoord.
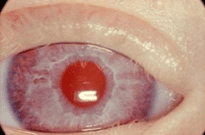
Deprivatie-amblyopie wordt veroorzaakt door een troebeling in de optische as die de beeldvorming in het oog belemmert, zoals cataract of een litteken van de cornea (figuur 1). Het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex zorgt ervoor dat troebelingen in het oog opgespoord worden. Deze troebelingen verhinderen goede beeldvorming op het netvlies en veroorzaken daardoor deprivatie amblyopie.
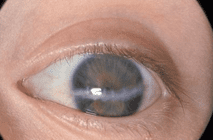
Figuur 1: Cornealitteken*
*Voor het gebruik van de foto’s in deze richtlijn is toestemming verleend
Behandeling
Behandeling van amblyopie start bij voorkeur voor de leeftijd van 6 jaar. Amblyopie veroorzaakt door strabismus of deprivatie is vaak ernstiger dan een amblyopie veroorzaakt door een refractie afwijking. Bij amblyopie die alleen veroorzaakt wordt door een refractieafwijking kan ook na het 6e jaar meestal nog succesvol behandeld worden. Na voltooiing van de visuele ontwikkeling rond het 10e jaar, is behandeling van amblyopie niet meer mogelijk. Niet of onvoldoende succesvol behandelde amblyopie heeft tot gevolg dat het oog permanent slechter ziet.
Het doel van amblyopiebehandeling is de gezichtsscherpte van het amblyope oog te verbeteren. Dit wordt gedaan door het goede oog een aantal uren per dag af te plakken met een occlusiepleister, zodat het amblyope oog gedwongen wordt te kijken. Indien nodig wordt daarnaast de refractieafwijking gecorrigeerd, meestal met een bril en in uitzonderlijke gevallen met een contactlens. Een mediatroebeling wordt, indien mogelijk, verwijderd. Als dit niet mogelijk is, kunnen gedurende de behandeling pupil-verwijdende druppels gegeven worden om het mogelijk te maken langs de troebeling te kijken en zo het oog te trainen.
Strabismus
Scheelzien of strabismus is een standsafwijking van de ogen waarbij de ogen niet gelijktijdig op hetzelfde punt gericht zijn. De incidentie is ± 5% [3]. Strabismus kan manifest (altijd) of latent (af en toe; op momenten dat de twee ogen tijdelijk niet goed samenwerken, bijvoorbeeld bij vermoeidheid) aanwezig zijn. Om te beoordelen of er sprake is van manifest scheelzien wordt gebruik gemaakt van de cornea lichtreflex, zie bijlage 1c . Bij iemand die niet scheel kijkt staan de lichtreflexbeeldjes op de cornea symmetrisch en iets nasaal van het midden van de pupil. Als in één oog het lichtreflex beeldje verschoven is, is dit een aanwijzing voor manifest scheelzien. Wanneer bij afdekken van één oog het niet afgedekte oog een instelbeweging maakt is dit een tweede aanwijzing dat er sprake is van manifest scheelzien.
Screening is gericht op opsporen van manifest strabismus, omdat dit kan leiden tot (diepe) amblyopie, vooral als altijd hetzelfde oog scheel staat. Latent scheelzien leidt zelden tot ernstige (‘diepe’) amblyopie. Actie is pas nodig als het leidt tot hoofdpijnklachten of een verminderde visus, hetgeen opgespoord wordt met de visusmeting.
Verschillende vormen van manifest strabismus worden onderscheiden (figuur 2):
- Esotropie (scheelstand naar binnen, verplaatsing van lichtreflex beeldje naar buiten/lateraal)
- Exotropie (scheelstand naar buiten, verplaatsing van lichtreflex beeldje naar binnen/nasaal)
- Hypertropie (scheelstand naar boven, verplaatsing van lichtreflex beeldje naar beneden)
- Hypotropie (scheelstand naar beneden, verplaatsing van lichtreflex beeldje naar boven)
- Mengvormen van horizontaal en verticaal strabismus.
Bijzondere vormen van manifest strabismus zijn:
- Strabismus waarbij de refractie invloed heeft op de oogstand: accommodatieve esotropie waarbij overmatige accommodatie bij kinderen met (hoge) hypermetropie leidt tot esotropie.
- Strabismus die soms wel en soms niet aanwezig is: intermitterend strabismus.
- Strabismus waarbij afwisselend het rechter of het linker oog scheel staat: alternerend strabismus.
- Strabismus waarbij de scheelzienshoek wisselt in verschillende blikrichtingen.
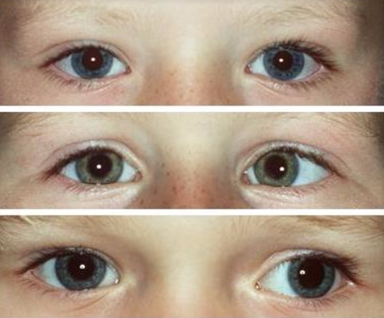
Figuur 2: Voorbeelden van manifest strabismus. De bovenste foto laat een rechte oogstand zien (symmetrische cornea lichtreflex), de middelste foto een esotropie van het linkeroog en de onderste foto een exotropie van het linker oog.
Een scheelziensoperatie kan uitgevoerd worden om de oogstand te verbeteren. In sommige gevallen kan de samenwerking tussen de ogen hersteld worden. Een scheelziensoperatie geeft geen verbetering van de visus.
Pseudostrabismus
Deze term wordt gebruikt voor de situatie waarbij er een scheelstand lijkt te zijn door bijvoorbeeld asymmetrie van het gelaat of de ooglidspleten, een brede neusbrug of epicanthus. Met de cornea lichtreflex kan onderscheid gemaakt worden tussen pseudo- en manifest strabismus. Bij pseudostrabismus zijn de reflex beeldjes op de cornea symmetrisch.
Epicanthus
Een extra huidplooi ter hoogte van de binnenste ooghoek waardoor aan de nasale zijde van de iris minder oogwit zichtbaar is dan aan de temporale zijde. Dit geeft de indruk van een esotropie (figuur 3).
Figuur 3: Epicanthus
2.1.2 Overige oogheelkundige afwijkingen
Oogleden
Ptosis: een afhangend bovenooglid. Congenitale ptosis is bij ± 80 % enkelzijdig- en bij ± 20% dubbelzijdig en komt vaak familiair (autosomaal-dominant) voor. Andere oorzaken voor ptosis bij kinderen zijn ontsteking (van oogleden en/of orbita (oogkas)), trauma en tumoren van het ooglid (hemangioom) (figuur 4), rhabdomyosarcoom gekenmerkt door snel progressieve proptosis (naar voren komen van oog) of ptosis). Meer zeldzame oorzaken zijn neurogeen (Hornersyndroom, n. oculomotorius (III) parese) of myogeen (myasthenie, mitochondriale aandoeningen).
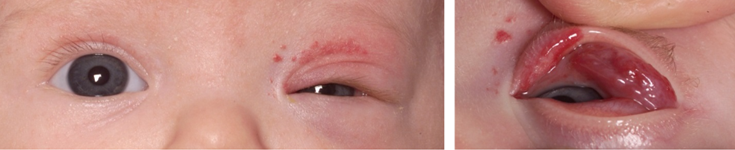
Figuur 4: Ptosis veroorzaakt door hemangioom linker ooglid
Indien het ooglid continu of regelmatig voor de pupil hangt is er een grote kans op het ontstaan van, vaak ernstige, amblyopie. Compensatiemechanismen om onder het ooglid door te kijken zijn optrekken van de wenkbrauwen door gebruik te maken de voorhoofdsspier om het ooglid omhoog te trekken of een torticollis (dwangstand van het hoofd) met de kin omhoog (figuur 5).
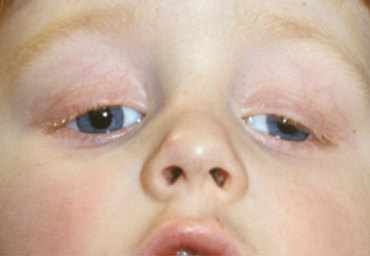
Figuur 5: Ptosis met opgetrokken wenkbrauwen en torticollis met kin omhoog (neusgaten zichtbaar)
Pupil
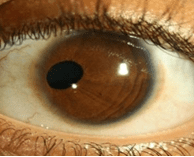
Anisocorie: een verschil in diameter van de pupillen, waarbij een anisocorie groter dan 1mm pathologisch kan zijn. Naast een verschil in diameter van de pupillen, wordt een pupil met een diameter kleiner dan 2 mm of groter dan 5 mm als afwijkend beschouwd.
Vormafwijking: de pupil is niet rond of niet in het centrum gelokaliseerd. Bij een coloboom van de iris is de pupil sleutelgatvormig naar onderen toe. Het is een sluitingsdefect van de oogbeker in de embryonale fase. Colobomen kunnen voorkomen in iris, lens, choroïdea (vaatvlies), retina (netvlies) en n. opticus (II). Een iriscoloboom kan dus een signaal zijn voor ernstige afwijkingen in de diepere lagen van het oog en slechtziendheid. Colobomen komen voor bij verschillende syndromen bijvoorbeeld trisomie 13 of CHARGE syndroom: Colobomen, Hartafwijkingen, Atresie van de choanen, Retardatie van groei en/of ontwikkeling, uroGenitale afwijkingen, externe en interne afwijkingen van het oor (Ear) en evenwichtsorgaan. Een oog met een coloboom kan te klein zijn: microphthalmus (figuur 6).
Figuur 6: Microphthalmus met Iriscoloboom
Bij chronische ontstekingen van het vaatvlies (uveitis) kan de pupil een grillige vorm krijgen door verkleving met de lens. De pupil wordt dan ook niet meer goed wijd.
Wanneer de pupil niet centraal in de iris zit, kan dit wijzen op congenitale afwijkingen van het voorsegment, die vaak gepaard gaan met verhoogde oogdruk (figuur 7).
Figuur 7: Pupil excentrisch
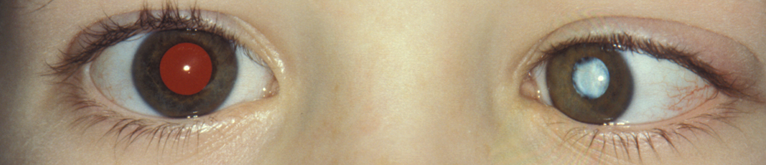
Kleurverandering-Leucocorie
De pupil is niet zwart maar witgrijs verkleurd. De rode of (bij donker gepigmenteerde mensen) geelbruine fundusreflex is niet egaal of (goed) zichtbaar (figuur 8). Daarnaast kan er een witte reflex zijn. De oorzaken van een witte pupil zijn divers en alle oorzaken zijn reden voor snelle verwijzing (zie bijlage 1, tabel B5 voor verwijstermijnen).
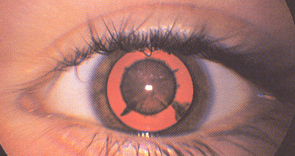
Figuur 8: verwijde pupil met rode fundusreflex die centraal gestoord is als gevolg van cataract (donkere vlek met uitlopertjes in het midden)
Meest voorkomende oorzaken van leukocorie:
Cataract: troebele ooglens waardoor er geen of slechte beeldvorming op de retina is. Kan enkel- (figuur 9) of dubbelzijdig voorkomen. Oorzaken zijn een aanlegstoornis van het oog (vaak ook microphthalmus), familiair, (intra-uteriene) infectie (TORCHES: Toxoplasmose, Rubella, CMV, Herpes simplex of Syphilis), stofwisselingsziekte of in kader van bijvoorbeeld Downsyndroom.
Figuur 9: leukocorie (en microphtalmus) linker oog bij cataract
Bij totaal, congenitaal cataract moet op zeer jonge leeftijd de lens operatief verwijderd worden: enkelzijdig cataract voor de 6e levensweek, dubbelzijdig cataract voor de leeftijd van 3 maanden. Bij dubbelzijdig cataract is de deprivatie van beide ogen gelijk. Na operatie zal de visuele ontwikkeling van beide ogen verder gaan. Na 3 maanden is de achterstand zo groot dat een ernstige visuele beperking onvermijdelijk is. Bij enkelzijdige staar is de visuele ontwikkeling van het oog zonder cataract normaal terwijl het oog met cataract zich niet ontwikkelt. Na 6 weken is dit proces al onomkeerbaar en zal het oog met cataract niet meer beter kunnen gaan zien na operatie.
Ook wanneer er geen sprake is van totaal cataract dient zo snel mogelijk verwezen te worden zodat de oogarts kan oordelen of behandeling geïndiceerd is.
Retinoblastoom: zeldzame maligne tumor uitgaande van de retina, die mits tijdig gedetecteerd en behandeld een goede prognose heeft. Kent een sporadische, enkelzijdige vorm (60 %) en een erfelijke, meestal dubbelzijdige vorm (40 %) waarbij de afwijking gevonden wordt op chromosoom 13. Kinderen met een familiaire belasting worden vanaf de geboorte, volgens een vast schema, gescreend. Screening en behandeling zijn in Nederland gecentraliseerd bij de afdeling oogheelkunde VUmc. Een retinoblastoom laat de pupil wit oplichten (figuur 10).
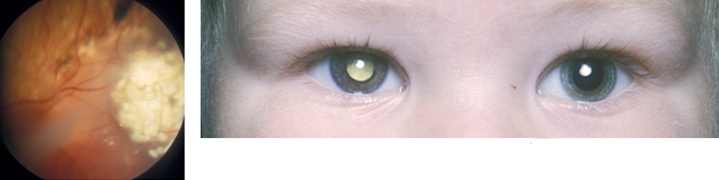
Figuur 10: Retinoblastoom
Andere oorzaken voor een leukocorie zijn bijvoorbeeld een groot chorioretinaal coloboom of een opticus coloboom, eindstadium prematurenretinopathie (aandoening van de retinale vaten bij prematuur geborenen ontstaan in de weken na de geboorte), congenitale toxoplasmose.
Congenitaal glaucoom
Kenmerkend zijn een te groot oog in combinatie met blepharospasme (knijpen), fotofobie (lichtgevoeligheid) en tranen. Vaak is het hoornvlies niet helder maar heeft een mat, grijzig aspect. De oogdruk is te hoog waardoor het oog opgerekt wordt. Congenitaal glaucoom kan één- en tweezijdig voorkomen (figuur 11) en wordt veroorzaakt door een embryonale membraan die de afvoer van oogkamerwater belemmert. Indien niet tijdig behandeld ontstaat irreversibele schade aan de oogzenuw met verlies van visus en gezichtsveld. De behandeling is operatief.
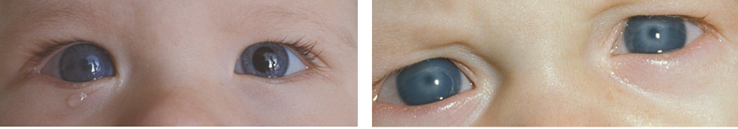
Figuur 11: Congenitaal glaucoom, enkelzijdig (rechter oog op linker foto) en dubbelzijdig (rechter foto)
Andere zeldzame oorzaken voor glaucoom zijn aanlegstoornissen van het voorsegment van het oog (bijvoorbeeld Rieger, aniridie), familiair juveniel glaucoom, Sturge Weber syndroom en secundair glaucoom na operatie vanwege congenitaal cataract. Deze vormen van glaucoom hebben meestal een normale corneadiameter en geen andere kenmerkende symptomen (tenzij er sprake is van afwijkingen aan het voorsegment (iris, pupil, cornea).
Afwijkende corneadiameter: de horizontale afmeting van de cornea die begrensd wordt door de overgang van de iris naar de sclera (oogwit) (figuur 11). Deze kan desgewenst gemeten worden door een liniaaltje boven of onder het oog te houden en te beoordelen of de diameter duidelijk groter of kleiner is dan 10mm (1 cm).
Een diameter bij geboorte < 9 mm is te klein. Dit kan duiden op een microphthalmus en/of een ontwikkelingsstoornis van het oog.
Een diameter bij geboorte > 10,5 à 11 mm is te groot. Dit kan duiden op congenitaal glaucoom (buphthalmus). Rond het 7e jaar is de volwassen waarde van 12mm bereikt.
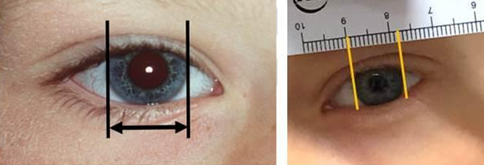
Figuur 12: Corneadiameter. Om een grove indruk te krijgen van de diameter kan een liniaaltje boven het oog gehouden worden. In dit voorbeeld is de diameter 12mm.
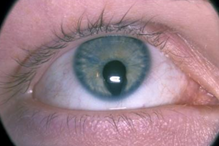
Iris
Heterochromie: kleurverschil van de ogen. Het komt zeer zelden voor, kan erfelijk zijn en is meestal onschuldig. Reden voor verwijzing is als het oog met de lichtste iris ook een kleinere pupil en een milde ptosis heeft. Dit is verdacht voor het syndroom van Horner. Andere oorzaken voor heterochromie zijn een voorgeschiedenis met trauma of operatie in het oog, chronische uveitis of gebruik van medicatie met prostaglandine-analogen die voorgeschreven worden bij glaucoom. Doorgaans is het kind dan al bekend bij de oogarts.
Irisdiafanie: door gebrek aan pigment van de iris wordt deze doorschijnend waardoor de rode reflex van het netvlies door de iris heen zichtbaar kan zijn (figuur 13). Irisdiafanie is een kenmerk van albinisme dat alleen aan het oog (oculair albinisme) of gegeneraliseerd (oculocutaan albinisme) voor kan komen. Bijkomende symptomen kunnen zijn fotofobie, slechte visus en nystagmus. Vaak komen hoge refractieafwijkingen, strabismus en amblyopie voor, die opgespoord en behandeld moeten worden om een zo goed mogelijke visus te behalen.
Figuur 13: Irisdiafanie
Vlekken of tumoren: iris naevi zijn pigmentvlekken die frequent voorkomen en indien zij niet van grootte of kleur veranderen onschadelijk zijn. Geel-roze, bruine of bleke tumoren dienen nader onderzocht te worden. De mate van groei is bepalend voor de snelheid van verwijzen.
Conjunctiva en sclera
Pigmentvlekken: bij mensen met een donkerder gepigmenteerde huid worden vaak pigmentvlekken gezien op de conjunctiva of het oogwit. Redenen voor verwijzing zijn: groei, verandering van pigmentatie, meerdere pigmentvlekken, dikke uitgezette vaten naar pigmentatie toelopend of chronisch recidiverende irritatie.
Blauwgrijze of zwarte vlekken: melanosis oculi. Wordt vaak gezien bij mensen met Aziatische achtergrond. Kleine vlekken hebben geen consequentie (figuur 14). Uitgebreide, grote vlekken zijn vaak geassocieerd met toename van pigmentatie in het oog, glaucoom en hyperpigmentatie van oogleden en huid. Vanwege de licht verhoogde kans op een oogmelanoom worden mensen met uitgebreide afwijkingen jaarlijks gescreend.
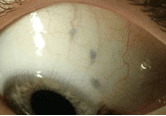
Figuur 14: Blauwgrijze vlekjes
Traanwegen
Congenitale traanwegstenose: een bij de geboorte aanwezige obstructie op de overgang van het traankanaal naar de neus (klep van Hasner) zorgt ervoor dat tranen niet weg kunnen lopen naar de neus. Door ophoping van tranen en bacteriën in de traanzak ontstaan klachten van tranen, slijmproductie en recidiverende infecties (figuur 15). Het oog zelf is doorgaans niet rood, maar bij een heftige ontsteking kan een conjunctivitis ontstaan. Aangezien de blokkade bij > 90 % van de kinderen spontaan open gaat voor de leeftijd van 9 maanden wordt geadviseerd de ogen schoon te houden (tissue of gaasje dat vochtig gemaakt is met lauw water) en de traanzak te masseren (met vinger de traanzak tegen het neusbot duwen en naar beneden (richting neusvleugel) en naar boven (richting nasale ooghoek) masseren).
Bij heftige recidiverende ontstekingen en wanneer de klachten na 9-12 maanden niet verdwenen zijn wordt een sondage verricht (doorprikken traankanaal onder narcose).
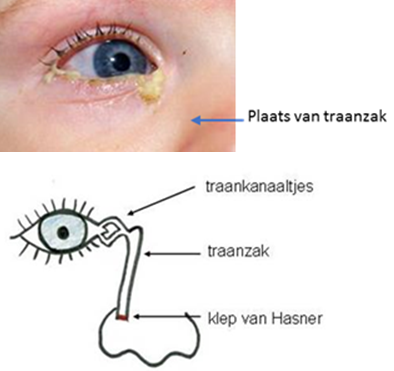
Figuur 15a: klinisch beeld van traanweg stenose
Figuur 15b: Plaats van traanweg stenose, schematisch
Let op: een forse ontsteking waarbij het oogwit rood is kan bij een pasgeborene (eerste 6 weken) duiden op een conjunctivitis neonatorum. Dit is een ernstige ontsteking, meestal op basis van gonorroe, chlamydia, herpes of stafylokokken en dient met spoed verwezen en behandeld te worden (figuur 16).
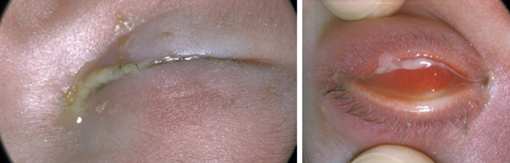
Figuur 16: Conjunctivitis
Nystagmus
Nystagmus: onwillekeurige, oscillatoire en ritmische bewegingen die horizontaal, verticaal en/of rotatoir kunnen zijn. Te onderscheiden zijn een ruknystagmus waarbij een snelle en een langzame fase gezien wordt en pendelnystagmus waarbij de ogen bewegen zonder snelle of langzame fase. Congenitale idiopatische nystagmus ontstaat meestal op de leeftijd van 6-8 weken en is vaak erfelijk. Andere oorzaken voor nystagmus zijn slechte visus en neurologische afwijkingen. Nystagmus is altijd een reden om te verwijzen. Zie voor de verwijscriteria bijlage 1, tabel B5.
Cerebrale Visuele stoornis
Dit is stoornis in het zien ten gevolge van beschadiging van het visuele systeem voorbij het chiasma opticum, waardoor de verwerking van beelden die aan de hersenen aangeboden worden niet goed verloopt. Dit leidt tot gestoorde waarneming (perceptie). Oorzaken zijn aanlegstoornissen of beschadiging in de perinatale periode van de hersenen, gecompliceerde zwangerschap, prematuriteit, trauma, epilepsie, hydrocephalus, stofwisselingsstoornissen en intracerebrale bloedingen in de voorgeschiedenis. Een deel van deze kinderen heeft tevens een verstandelijke beperking. Kinderen met CVI kunnen een normale of sterk verminderde visus hebben. Vaak is er ook sprake van strabismus, nystagmus en gezichtsvelddefecten. Voorbeelden van perceptiestoornissen zijn problemen met het herkennen van voorwerpen, vormen of gezichten, oriëntatie in de ruimte, vast kunnen houden van visuele aandacht, interpreteren van gelaatsuitdrukkingen, gelijktijdig herkennen van verschillende objecten en waarneming van diepte of bewegende objecten. Bij verdenking op CVI is verwijzing naar een oogarts geïndiceerd om oogheelkundige pathologie uit te sluiten. Voor uitgebreid onderzoek en begeleiding worden kinderen met CVI door de oogarts doorverwezen naar Visio of Bartiméus (instellingen voor mensen met een visuele beperking). Meer uitgebreide informatie is terug te vinden in de richtlijn ‘CVI, diagnostiek en verwijzing’ van het Nederlands Oogheelkundig Gezelschap (NOG) .
Kleurenzienstoornissen
Kleurenzien is een functie van de kegeltjes in het netvlies. Licht wordt door drie verschillende lichtgevoelige pigmenten (rood, groen en blauw) geabsorbeerd in de kegeltjes. Als kleuren minder goed onderscheiden worden doordat deze kleur waarnemingssystemen onvoldoende werken spreekt men van verminderd kleurenzien, bij totale uitval spreekt men van kleurenblindheid. De meest voorkomende vorm van gestoord kleurenzien is een rood-groen stoornis, waarbij geen goed onderscheid tussen rood en groen gemaakt kan worden. Dit is een X-gebonden erfelijke aandoening die voorkomt bij ongeveer 8 % van de mannen. Zeer zelden komt een rood-groen stoornis voor bij vrouwen (0,5 %) [8]. Rood-groen stoornissen kunnen getest worden, bijvoorbeeld met de Ishihara kleurenzientest. Veel zeldzamer zijn stoornissen in de geel-blauw waarneming. Bij ernstige vormen van kleurenzienstoornis kan de visus verlaagd zijn of kan nystagmus voorkomen. Een extreem voorbeeld hiervan is de zeldzame achromatopsie waarbij geen kleuren worden waargenomen.
Kleurenzien is mogelijk vanaf de leeftijd van twee tot zes weken, maar pas vanaf de leeftijd van 3 jaar kunnen kleuren actief vergeleken, onderscheiden en benoemd worden. Ongeveer 40 % van de jongeren met een kleurenzienstoornis is zich hiervan niet bewust. Als de kleurenzienstoornis klachten geeft wordt verwezen naar de oogarts.
2.1.3 Overige aandachtsgebieden
Bijziendheid (myopie) en ‘lifestyle’ adviezen
De interesse in het ontstaan van bijziendheid (myopie) is de laatste jaren sterk toegenomen. Ouders stellen de JGZ hierover vragen. Uit wetenschappelijk onderzoek [12][13][9] blijkt een beschermende rol van buitenspelen op de ontwikkeling van myopie. Een studie naar genetische factoren rapporteert dat licht, of juist het gebrek daaraan, een belangrijke trigger is voor het ontstaan van bijziendheid [11]. Veel en langdurig achter elkaar verrichten van dichtbijwerk, zoals kijken naar beeldschermen en lezen verhoogt het risico op bijziendheid bij kinderen. Naast het advies om tenminste 2 uur per dag buiten te spelen is een praktisch advies door oogartsen bedacht om na 20 minuten dichtbijwerk tenminste 20 seconden in de verte te kijken. Leefstijl is niet de enige mogelijke reden voor het ontstaan van bijziendheid, ook andere invloeden zoals erfelijkheid spelen mee [5]. In zijn algemeenheid, maar dus ook voor de ogen, geldt dat het voor een gezonde ontwikkeling aan te raden is dat kinderen buiten spelen en niet te veel tijd aaneengesloten achter computers of beeldschermen doorbrengen. Het Nederlands Jeugdinstituut heeft factsheets gemaakt met tips voor het gebruik van media in het gezin, bijvoorbeeld over te lang mediagebruik van kinderen en hoe daar het beste mee omgegaan kan worden [7].
Kinderen met een hoge of snel progressieve vorm van myopie worden in steeds meer oogheelkundige praktijken behandeld met oogdruppels, zoals Atropine in diverse concentraties, of speciale contactlenzen (ortho-K of multifocale lenzen) hetgeen afremming van progressie geeft. Kinderen komen vanaf de leeftijd van 4 jaar voor deze oogdruppels in aanmerking (consensus World Society of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus) [WSPOS] . Het gebruik van nachtlenzen bij jonge kinderen wordt door het NOG afgeraden vanwege de kans op visusbedreigende ooginfecties en het minstens zo effectieve alternatief atropine.
Kinderen met een verhoogd risico op oogafwijkingen
Er worden groepen kinderen onderscheiden die een verhoogde kans hebben op amblyopie, refractieafwijkingen en strabismus. Deze groepen zijn: ex-prematuren, dysmaturen, ’nieuwkomers in de JGZ’* en kinderen met (multiple) beperkingen of een gehoorstoornis. Bij twijfel over visus of oogstand bij deze groepen kinderen is het verstandig door te verwijzen naar orthoptist/oogarts. Opgemerkt moet worden dat kinderen uit gezinnen met een migratieachtergrond een verhoogde kans hebben om te laat of niet behandeld te worden voor amblyopie. Uit onderzoek bleek dat het voor kinderen met een niet-westerse herkomst, vooral kinderen met een Marokkaanse herkomst (58%) en kinderen met een Turkse herkomst (54%) minder waarschijnlijk was dan voor kinderen met een Nederlandse herkomst om een oogheelkundig centrum te consulteren. Dit gold ook voor Surinaamse kinderen. Als belangrijkste reden werd gebrekkige informatie-uitwisseling tussen arts en ouders aangegeven. [6]
*‘Nieuwkomers’ zijn jeugdigen die pas op latere leeftijd voor het eerst door de JGZ worden onderzocht. Dit kan diverse oorzaken hebben, zoals adoptie, gezinshereniging, een vlucht uit het eigen land of immigratie om andere redenen.
In Nederland worden de volgende groepen kinderen, buiten de JGZ, protocollair gescreend:
- Diabetes type 1: Bij detectie op jonge leeftijd eenmalig screenen op risicofactoren voor amblyopie. Vanaf puberteit jaarlijkse screening op diabetische retinopathie.
- Neurofibromatose: vanaf detectie jaarlijkse screening tot 10e jaar vanwege kans op opticusglioom.
- Syndroom van Down: vanaf geboorte onderzoeken op cataract, later ook refractieafwijkingen, accommodatiestoornis, strabismus, amblyopie. Richtlijn zie: .
- Syndroom van Marfan: vanaf detectie elke 2 jaar onderzoeken op refractieafwijkingen, (partiële) lensluxatie. Richtlijn zie: .
- Juveniele Idiopatische Artritis (JIA / Jeugdreuma): kinderen worden meerdere keren per jaar gescreend op uveitis
Bij kinderen met één van deze aandoeningen mag de screening bij de JGZ achterwege gelaten worden als het kind inderdaad volgens schema gecontroleerd wordt door een orthoptist / oogarts. De visusmeting bij de JGZ hoeft niet uitgevoerd te worden bij kinderen met diabetes wanneer het controle moment bij de JGZ vrijwel samenvalt (+/- 4 maanden) met de eenmalige screening.
Zie bijlage 3 voor een verklarende woordenlijst bij dit thema.
2.2 Verklarende woordenlijst
- Accommoderen: scherpstellen op een voorwerp dichtbij door automatische verandering van de bolling van de ooglens
- Astigmatisme: brilsterkte afwijking waarbij een cilinderglas nodig is voor correctie. Dit glas breekt niet in alle richtingen gelijk.
- Binoculaire volgbeweging: volgbeweging met beide ogen
- Conjunctiva: oppervlakkige bindvlies
- Convergeren: beide ogen gelijktijdig naar de neus draaien als een voorwerp dichtbij komt
- Cornea: hoornvlies. Belangrijk voor de beeldvorming in het oog.
- Cornea lichtreflex: reflex van fixatielampje op het hoornvlies.
- Cycloplegie: door middel van oogdruppels wordt het accommoderend vermogen van de lens uitgeschakeld waardoor de refractie gemeten kan worden zonder invloed van accommodatie op de uitkomst. Deze druppels geven ook pupilverwijding.
- Dysmatuur: kind met geboortegewicht dat te laag is voor de zwangerschapsduur. De Engelse term hiervoor is SGA (Small for Gestational Age).
- Fovea: centrum van de gele vlek in het netvlies en deel waarmee maximale visus bereikt kan worden. Bij rechte oogstand valt het beeld van het object waar je naar kijkt (bv een fixatielampje) in beide ogen op de fovea.
- Glasvocht: glasachtig lichaam: heldere gelei die de achterste holte van het oog vult
- Hypermetropie: brilsterkte afwijking waarbij een positieve (+) lens nodig is voor correctie (verziendheid)
- Lens: bevindt zich achter de iris en is nodig voor focussering van beelden op het netvlies.
- Neurogeen: afwijking veroorzaakt door een afwijking van één of meerdere zenuwen
- Monoculaire volgbeweging: volgbeweging met 1 oog
- Myogeen: afwijking veroorzaakt door een afwijking van de spieren
- Myopie: brilsterkte afwijking waarbij een negatieve (-) lens nodig is voor correctie (bijziendheid)
- OD: oculus dexter = rechter oog
- Optische as: de virtuele lijn die loopt door het centrum van de cornea, de pupil en de lens en eindigt bij de fovea (gele vlek).
- OS: oculus sinister = linker oog
- Prematuur: geboren voor de 37e week van de zwangerschap
- Pupil: zwarte, ronde opening in centrum van iris
- Retina: netvlies. Bevat staafjes en kegeltjes. De kegeltjes zijn belangrijk om scherp te kunnen zien en kleuren te kunnen waarnemen. De staafjes worden gebruikt om contouren te zien en in schemerdonker waar te kunnen nemen.
- Sclera: harde, witte omhulsel van het oog / oogwit
- Uvea: vaatvlies bestaande uit iris, corpus ciliare (straalvormig lichaam) en choroidea. De choroidea bevindt zich tussen retina en sclera.
- Voorste oogkamer: ruimte tussen cornea en iris-lens
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
3.1 Opsporing van oogafwijkingen bij kinderen in de leeftijdsperiode van 0-36 maanden
In dit thema (en bijlage 1) wordt besproken op welke wijze het oogonderzoek bij kinderen in de leeftijd van 0-36 maanden door de JGZ plaatsvindt. In dit thema worden zowel de aangeboren (congenitale) aandoeningen als de andere oogafwijkingen besproken. In thema 3 wordt het oogonderzoek met visusmeting bij kinderen in de leeftijd vanaf 36 maanden besproken.
Overwegingen
De werkgroep doet voorstellen voor het oogonderzoek op basis van het beschikbare bewijs uit de evidence synthese, aangevuld met artikelen die niet voldeden aan de zoekcriteria van de systematische review maar wel relevant bevonden werden zoals het observationele onderzoek van de uitvoering van het oogonderzoek [29], en praktijkervaring. Er is gekozen voor een zo efficiënt mogelijke combinatie van oogonderzoeken die de beste sensitiviteit en specificiteit hebben op de verschillende contactmomenten. Schrappen van onderdelen uit de combinatie van voorgestelde onderzoeken brengt het risico met zich mee dat kinderen met oogafwijkingen niet tijdig gedetecteerd worden en wordt dan ook ten zeerste afgeraden door de werkgroep.
Anamnese
Een gerichte anamnesevraag ondersteunt het onderzoek dat als doel heeft visusproblemen, scheelzien of andere afwijkingen aan het oog op te sporen. Ter ondersteuning voor de jeugdarts, jeugdverpleegkundige of verpleegkundig specialist* is, op basis van expert opinion, een set alarmsignalen ontwikkeld die indicatief kunnen zijn voor aanwezigheid van afwijkingen. Zie bijlage 1a.
*De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en zij werkt op expertniveau. Zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
Inspectie
Een uitwendige inspectie van de ogen is bedoeld om scheelzien en structurele afwijkingen aan de ogen op te sporen.
Contactmomenten
Contactmomenten in de leeftijdsperiode van 0 t/m 3 maanden
Opsporing van congenitale oogheelkundige aandoeningen is essentieel in deze periode. Hiervoor past de JGZ de volgende onderzoeken toe:
- Het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex
Uit de studie van Magnusson et al. (2005) bleek dat het kosteneffectief is als per jaar 3 kinderen met cataract opgespoord worden met behulp van het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex. Daarnaast wordt met het beoordelen van aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex niet alleen cataract opgespoord maar ook andere aandoeningen die snelle behandeling nodig hebben, zoals retinoblastoom. Daarom heeft de werkgroep besloten dat het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex gehandhaafd blijft en een noodzakelijk oogonderzoek is. Zie bijlage 1b voor de uitvoering van het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex
- Binoculaire volgbeweging
Op de leeftijd van 2 maanden wordt in het kader van het Van Wiechen onderzoek de binoculaire volgbeweging onderzocht. Hierbij wordt getest of een kind met hoofd en beide ogen tegelijk een object, bv het hoofd van de onderzoeker of een felgekleurd blokje, over een beperkte afstand kan volgen. Het is een complexe taak, waarbij vooral de ontwikkeling van de hersenen getest wordt. De test geeft aan of de coördinatie tussen zien, oogbewegingen en de spierbeheersing zo ver ontwikkeld is dat het kind in staat is om een voorwerp te volgen.
Contactmomenten in de leeftijdsperiode van 6-9 maanden en 14-24 maanden
In de leeftijdsperiode tussen 6 en 24 maanden worden de hieronder beschreven cornea lichtreflex, instelbeweging en monoculaire volgbeweging twee maal uitgevoerd, éénmaal op leeftijd 6-9 en éénmaal op leeftijd 14-24 maanden. Het uitvoeren van deze testen op beschreven momenten wordt dringend aanbevolen.
- Cornea lichtreflex
De studie van Tung et al. (2006) toonde aan dat de cornea lichtreflex een sensitiviteit heeft van 75 % en een specificiteit van 98.9 % in een screening setting. Bij de, in Nederland uitgevoerde, studies van Sloot et al. (2017) en Sami et al. (2014) werd de cornea lichtreflex bij 88 % van de kinderen goed uitgevoerd. Zie bijlage 1c voor een gedetailleerde beschrijving van de werkwijze.
- Monoculaire volgbeweging
Monoculaire volgbewegingen geven een indruk over de visus van elk oog afzonderlijk en zijn daarmee een grove maat voor een verschil in visus tussen de ogen. Bij de volgbeweging wordt onderzocht of het kind met een oog een lampje of een object vloeiend, niet vloeiend of helemaal niet volgt. In de studie van Sloot et al. (2015) werd deze test in de meeste gevallen (91%) goed uitgevoerd. Zie bijlage 1c voor een gedetailleerde beschrijving van de werkwijze.
- Pupilreacties, afdektest en oogmotiliteit
De pupilreacties, afdektest en oogmotiliteit (in de oude richtlijn stond bij het VOV-onderzoek “binoculaire volgbeweging” waar deze gebruikt werd om de “oogmotiliteit in alle richtingen” te testen) worden niet meer gedaan.
In de studie van Williams et al. (2001) bleek dat de afdektest een sensitiviteit lager dan 25 % (9-41 %) heeft op de leeftijd van 25 maanden, hoewel deze door orthoptisten in een screening setting uitgevoerd was.
In een observationeel onderzoek, dat is uitgevoerd door twee orthoptie studenten in de periode van februari tot april 2013 in Nederland, zijn er bij 25 jeugdartsen observaties verricht, waarbij de uitvoering van de fundusreflex, pupilreacties, cornea lichtreflex, afdektest, alternerende afdektest, oogmotiliteit en de visusmeting bij kinderen van 0 tot 45 maanden werd geëvalueerd [28][29]. Bij 239 kinderen, die 0-24 maanden oud waren, werden de pupilreacties bij slechts 14% beoordeeld, waarbij de pupilreactie bij 58% in een verlichte omgeving werd uitgevoerd, meestal omdat het licht niet uit kon. Volgens Sloot et al. (2017) werd de afdektest bij 65% van de kinderen uitgevoerd, bij 37% van de kinderen werden de ogen niet goed en/of te snel afgedekt. Daarnaast bleek uit een vragenlijst beantwoord door 56 jeugdartsen dat de afdektest ervaren wordt als het onderdeel van de VOV dat het moeilijkst uitvoerbaar is [28].
In hetzelfde onderzoek werd de oogmotiliteit bij 93% van de kinderen niet correct uitgevoerd [29][27].
Overig aandachtspunt: gebruik van fotoscreens bij het bepalen van de oogstand en brilsterkte
De laatste jaren wordt in sommige landen gebruik gemaakt van fotoscreeners, om de risicofactoren van een amblyopie op te sporen voordat een amblyopie zich ontwikkeld heeft. Fotoscreeners zijn apparaten waarmee de brilsterkte gemeten kan worden en die soms een waarschuwing geven dat de oogstand afwijkend is. Dit zijn risicofactoren voor het ontstaan van amblyopie. Om vast te stellen of er daadwerkelijk sprake is van amblyopie moet de visus gemeten worden. Er zijn een aantal vragen gesteld vanuit het veld over deze automatische meetapparatuur. Naar aanleiding van literatuuronderzoek door Cochrane Netherlands heeft de werkgroep besloten dat, met de huidige kennis van zaken, er geen aanleiding is om in de jeugdgezondheidszorg gebruik te maken van deze fotoscreeners bij het opsporen van amblyopie. Voor meer informatie kunt u de bijlage 4 van deze richtlijn raadplegen.
Aanbevelingen
3.2 Opsporing van oogafwijkingen bij kinderen vanaf de leeftijd van 36 maanden
In dit thema (en in bijlage 1) wordt besproken op welke wijze de opsporing van oogafwijkingen bij kinderen vanaf de leeftijd van 36 maanden door de JGZ het beste plaats kan vinden. In dit thema worden de oogonderzoeken besproken en de visusmetingen voor het opsporen van amblyopie.
Overwegingen
De belangrijkste parameters voor de keuze van de momenten waarop het oogonderzoek met een visusmeting plaats moet vinden zijn de uiterste leeftijd waarop amblyopie behandeling gestart kan worden en succesvol kan zijn en de leeftijd waarop het aantal fout positieve metingen, wat leidt tot onterechte verwijzingen, laag is. Op basis van de evidence synthese is geen antwoord gevonden op de vraag wat de beste leeftijd is om amblyopie op te sporen. Er zijn geen aanwijzingen gevonden dat er een voordeel is van opsporing en behandeling vóór de schoolleeftijd vergeleken met opsporing in de kleuterperiode (4 tot 5,5 jaar).
Om tot besluitvorming te komen over de momenten waarop de visus getest moet worden en de wijze waarop dat moet gebeuren heeft de werkgroep het beschikbare bewijs uit de evidence synthese aangevuld met artikelen die niet voldeden aan de zoekcriteria van de systematische review, maar wel relevant bevonden werden voor het onderwerp. Daarnaast is gekeken naar praktijkervaring.
De werkgroep heeft besloten om in twee leeftijdsperioden de visusmeting bij alle kinderen uit te voeren: ten eerste in de leeftijdsperiode van 42-48 maanden, samenvallend met een vaccinatie moment, en ten tweede in de leeftijdsperiode van 54-66 maanden (doorgaans in groep twee van de basisschool). Op 36 maanden wordt het visusonderzoek niet standaard uitgevoerd bij alle kinderen, maar alleen als daar indicatie voor is en indien de JGZ-professional dit wenst. Er wordt gericht geïnformeerd of de ouders klachten hebben over de ogen / het zicht van hun kind en er wordt uitwendige inspectie gedaan. Bij twijfel over de visus op deze leeftijd kan besloten worden deze te bepalen met de LEA Symbolen kaart.
Bij de overweging om de visusmeting op 36 maanden niet meer standaard uit te voeren bij alle kinderen, is meegewogen dat er op de leeftijd van 36 maanden een relatief hoog percentage mislukte en onvoldoende visusmetingen is, zowel met de APK als met de LEA Symbolen.
In Nederland zijn verschillende onderzoeken gedaan naar visusmeting op 36 maanden. De visusmeting met APK is geëvalueerd bij 8.337 kinderen. Na thuis oefenen van de APK-plaatjes mislukte de test, die afgenomen werd door een getrainde jeugdarts of jeugdverpleegkundige, bij 16.4% en scoorde 15.6% van de kinderen onvoldoende. Bij 40% van de kinderen met een onvoldoende testresultaat en 32% van de kinderen waarbij de test mislukte werd de geadviseerde hertest niet opnieuw gedaan, maar uitgesteld tot het screeningsmoment van 45 maanden [58]. In een onderzoek van Sloot et al. werd bij 322 kinderen de visus gemeten met E-haken (Sloot et al, 2016). Op de leeftijd van 36 maanden was het visusonderzoek niet uitvoerbaar bij 22% van de kinderen. Wanneer, op de leeftijd van 45 maanden, na het mislukken van de E-haken kaart vervolgens de LEA-symbolen afgenomen werden was het visusonderzoek nog maar bij 5% niet uitvoerbaar. Ook in de RAMSES studie was het aantal mislukte visusmetingen op 36 maanden hoog (Koning et al., 2013)[59]. Buitenlandse studies naar de uitvoerbaarheid van verschillende visusmetingen in relatie tot de testleeftijd laten vergelijkbare resultaten zien. De Diagnostic Test Accuracy studie van Friendly et al (1978) laat zien dat het aantal kinderen waarbij de visusmeting met E-haken geen bruikbare meting oplevert relatief groter is bij jonge kinderen. In een Duitse studie werd gevonden dat bij 44% de visusmeting met de E-haken op de leeftijd van 31-36 maanden en bij 24% op de leeftijd van 37-48 maanden mislukte. Belangrijkste oorzaak voor onvoldoende testresultaat was het gebrek aan medewerking van het kind, die duidelijk afnam met de leeftijd [39]. Een Zweedse studie vergeleek de uitvoerbaarheid van de HOTV en de LEA-symbolen. Deze was voor beide visus kaarten 80% op 36 maanden en 90% op 48 maanden [48].
In al deze studies is een duidelijke trend zichtbaar dat visusmeting succesvoller wordt met toename van de leeftijd.
Door een relatief hoog percentage mislukte visusmetingen op 36 maanden is de bruikbaarheid hiervan als screenend instrument beperkt: zowel herhalen van de visusmeting als een onterechte verwijzing is kostbaar en een hoog percentage mislukte visusmetingen bevordert het afwijken van de verwijscriteria in de richtlijn.
In de ontwikkelfase van deze richtlijn bleek bij sommige partijen echter behoefte om bij twijfel over de visus op 36 maanden niet altijd meteen door te verwijzen maar om eerst een visusmeting te kunnen doen om het aantal onnodige verwijzingen te beperken. De werkgroep heeft daarom besloten dat een facultatieve visusmeting op 36 maanden op indicatie kan worden gedaan.
In deze richtlijn is besloten om de Amsterdamse Plaatjes Kaart [APK] af te schaffen, waarbij de volgende overwegingen zijn meegenomen.
In de knelpuntenanalyse twijfelden de JGZ-professionals aan de toepasbaarheid van de APK. Deze twijfel aan de APK als meetinstrument werd in de studie van Engin et al. (2014) bevestigd: de optotypen van de APK meten naast het oplossend vermogen van het oog (resolutie van de visus) ook vormherkenning (recognitie van de visus). De 11 optotypen van de APK hebben elk een verschillende mate van vormherkenning. Zo wordt de auto het best herkend en het huis het slechtst. Als een plaatje door vormherkenning benoemd kan worden is de visusmeting, vooral bij amblyopie, minder betrouwbaar.
De visuskaart met LEA Symbolen werd daarom door de werkgroep gekozen voor een facultatieve visusmeting op indicatie op 36 maanden en als back-up test wanneer de E-Haken kaart bij een kind niet uitvoerbaar is. De test met LEA Symbolen heeft een sensitiviteit van 96% [41][40].
Ook is in deze richtlijn besloten tot een overgang van de Landolt-C kaart naar de E-Haken kaart.
De volgende overwegingen zijn hierin meegenomen. Bij de systematische review naar de sensitiviteit en de specificiteit van de verschillende visusmetingen is geen klinische evidence gevonden voor de Landolt-C, maar wel voor de E-haken. De E-haken test heeft een relatief hoge sensitiviteit en specificiteit van respectievelijk 92 en 76%, wanneer deze wordt uitgevoerd bij kinderen die jonger dan 60 maanden oud zijn [49]. De Landolt-C en de logaritmische E-Haken zijn goede visustesten omdat vormherkenning geen rol speelt. De vorm is steeds dezelfde, waarbij de richting van de opening benoemd moet worden. De verschillen met betrekking tot gemeten visus van beide kaarten zijn verwaarloosbaar [44]. De logaritmische E-Haken kaart heeft als voordeel dat deze 5 optotypen per regel heeft en zowel op 4 als op 5 meter kan worden afgenomen, waar dit bij de logaritmische Landolt-C kaart 3 in plaats van 5 optotypen per regel zijn*. In de praktijk blijken niet alle organisaties over een ruimte met een testafstand van 5 meter te beschikken. Geadviseerd wordt om per locatie één testafstand te gebruiken. Daarnaast is de ervaring uit de oogheelkundige praktijk dat E-haken voor kleine kinderen gemakkelijker te begrijpen zijn. Zie bijlage 1d voor een voorbeeld van de kaarten met de verwijscriteria . Ten slotte is een visuskaart gemiddeld vijf jaar te gebruiken, waarna vervanging nodig is. Er zijn om deze reden beperkte extra kosten verbonden aan de overgang van de Landolt-C naar de E-Haken ten opzichte van een overgang naar een nieuwe Landolt-C kaart vanwege veroudering.
In deze richtlijn zijn ook een aantal wijzigingen in de verwijscriteria gedaan. Zo wordt een visus van 0.5 beiderzijds op 42-48 maanden niet langer als voldoende geaccepteerd. De drempel is 0.63, zoals internationaal gangbaar. Het meetresultaat met de E-Haken en Landolt-C kaart is vergelijkbaar, mits de optotypen even groot zijn [44]. Dit betekent dat de verwijscriteria voor E-Haken en Landolt-C gelijk zijn. Zie tabel B7 voor de verwijscriteria op 42-48 maanden.
Bij de verwijscriteria van de visusmeting is de nadruk gelegd op een visus verschil tussen beide ogen van 2 logMAR regels als kenmerk van amblyopie. Dit is internationaal het criterium voor de diagnose amblyopie.
De verwijscriteria voor de tweede visusmeting op 54-66 maanden verschillen één logMAR regel ten opzichte van de criteria op 42-48 maanden omdat de visus in die periode met ongeveer een regel stijgt. Zie tabel B8 in de bijlage voor de verwijscriteria op 54-66 maanden . Bij onvoldoende visus wordt tot 10 jaar naar de orthoptist verwezen. Vanaf 10 jaar wordt verwezen naar een optometrist/optiekbedrijf.
Volgens de NHG Standaard Visusklachten en het addendum op het Plan Geïntegreerde Oogzorg dat is opgesteld door NOG (Nederlandse Oogheelkundig Gezelschap), NVvO (Nederlandse Vereniging van Orthoptisten) en OVN (Optometristen Vereniging Nederland) worden kinderen vanaf 8 jaar naar optometrist/optiekzaak verwezen, maar dient onder de leeftijd van 10 jaar altijd tenminste éénmaal refractie met cycloplegische oogdruppels gemeten te worden. Dit is de reden dat optometristen/optiekzaken er vaak de voorkeur aan geven kinderen tot 10 jaar door te verwijzen naar orthoptist/oogarts.
*De logaritmische E-Haken kaart is leverbaar voor gebruik op 4 meter. Omdat het een logaritmische kaart is betekent het dat er precies 1 regel verschil is in de gemeten visus als deze kaart op 5 meter gebruikt wordt. Goodlite heeft een aangepaste logaritmische E-Haken kaart gemaakt met links de decimale, lineaire visuswaarden bij gebruik op 4 meter en rechts de decimale, lineaire visuswaarden bij gebruik op 5 meter. De logaritmische visuskaarten met E-Haken die op dit moment beschikbaar zijn voor gebruik op 4 meter zijn: Good-Lite Tumbling E 4m #500044 en PrecisionVision Tumbling E 4m #2305.
Aanbevelingen
3.3 Randvoorwaarden voor het uitvoeren van de vroege opsporing van oogafwijkingen
In dit thema wordt besproken wat de randvoorwaarden zijn voor optimale opsporing van oogafwijkingen, waaronder de faciliteiten die nodig zijn voor het uitvoeren van de onderzoeken, het verwijzen, de informatie die moet worden gegeven aan ouders voorafgaand aan het onderzoek en de juiste scholing van JGZ-professionals. Daarnaast zijn goede samenwerking en afstemming tussen de verschillende disciplines die betrokken zijn bij de signalering, beoordeling en behandeling van kinderen met een (mogelijke) visuele stoornis, essentieel om de continuïteit in de zorg voor kind en ouders te waarborgen.
Overwegingen
Informatie aan de ouders
Wanneer ouders goed geïnformeerd worden over het belang van het oogonderzoek is de kans groter dat zij hun kind zullen laten onderzoeken op de aangegeven onderzoeksmomenten. Goede informatie over het verloop van het onderzoek en adviezen over voorbereiding van het kind zijn een voorwaarde voor het slagen van de test. Snip (2017) toonde aan dat vooraf oefenen van plaatjes of zien van een voorlichtingsfilmpje een positief effect heeft op het succesvol uitvoeren van het aantal onderzoeken. Onvoorbereid had 35.3% een onvoldoende testresultaat, na oefenen werd het aantal mislukte tests met ongeveer 25% gereduceerd.
Ouders ontvangen de informatie van JGZ-instellingen. Indien het oogonderzoek op school plaats vindt kan, in overleg, de school een rol spelen bij de voorbereiding. Ouders met een lage sociaal economische status (SES), of ouders met een niet-Nederlandse herkomst, kunnen moeite hebben met het gangbare schriftelijk materiaal en het taalgebruik van de hulpverlener. Het gaat om ouders met beperkte gezondheidsvaardigheden (health literacy). Veel folders, interventies en behandelingen gaan uit van taalvaardigheid en een abstractievermogen dat bij deze groep niet voldoende aanwezig is. Daarom moet de informatievoorziening door de JGZ professional ook aansluiten bij ouders met een lage SES en/of ouders met een beperkte beheersing van het Nederlands. Eventuele folders bij de richtlijn moeten geschreven zijn in begrijpelijke taal. Folders in meerdere talen of informatieverstrekking op een meer beeldende manier (filmpje, tekeningen) kunnen helpen bij de uitleg. Maak gebruik van de ‘teach back methode’: Laat de ouders of het kind aan jou terug vertellen wat de hoofdboodschap is. Een veelgebruikte zin daarvoor is: “Ik wil graag weten of ik het goed heb uitgelegd. Wil je mij vertellen wat we net hebben besproken?” Ook in het kader van doorverwijzen is dit heel belangrijk.
Stakeholders
Deze richtlijn kent een verscheidenheid aan stakeholders. Primaire stakeholders zijn ouders, kinderen, jeugdartsen, verpleegkundig specialisten, jeugdverpleegkundigen, jeugd-doktersassistenten en zorginstellingen. Secundaire stakeholders zijn relevante ketenpartners en indirect betrokken beroepsgroepen: huisartsen, orthoptisten, oogartsen, optometristen, opticiens, gemeenten, scholen en onderwijzers.
Aanbevelingen
4 Totstandkoming richtlijn
4.1 Doel
Deze richtlijn beoogt door systematisch onderzoek afwijkingen aan het oog en het gezichtsvermogen vroegtijdig op te sporen om gezondheidswinst te behalen en oogafwijkingen te voorkomen. Dit geldt vooral voor gezondheidswinst die wordt behaald door bij te dragen aan het vroeg opsporen van een amblyopie (lui oog), zodat effectieve behandeling mogelijk is. Hiervoor is het nodig dat medewerkers van de jeugdgezondheidszorg de meest optimale methoden op de meest optimale momenten hanteren.
4.2 Werkwijze
Op initiatief van het Erasmus MC (afdelingen maatschappelijke gezondheidszorg en oogheelkunde), TNO Leiden en het LUMC (afdeling oogheelkunde), is begin 2016 begonnen met de tweede herziening van de richtlijn ‘Opsporing visuele stoornissen 0-19 jaar’, welke in 2002 werd uitgegeven en in 2010 voor de eerste keer werd herzien. Voor de start van een project is een werkgroep samengesteld. Deze werkgroep is bij alle fasen van de ontwikkeling van de richtlijn betrokken geweest. De werkgroep is samengesteld uit experts op het gebied van visuele stoornissen en/of JGZ. Een overzicht van de werkgroepleden staat onder paragraaf c. Tijdens de eerste vergadering met de werkgroep zijn de uitgangsvragen besproken, gerubriceerd en waar nodig nader gespecificeerd. Voor een deel van de uitgangsvragen is een systematisch literatuuronderzoek (evidence synthese) verricht. De werkgroep heeft voor deze uitgangsvragen PICO’s gedefinieerd. De PICO-methode staat voor Patiënt, Interventie, Controle en Outcome; dit acroniem omschrijft de vier elementen van een specifieke klinische vraag waarmee kan worden gezocht in de wetenschappelijke literatuur. Alle documenten die betrekking hadden op de richtlijn waren voor de werkgroepleden inzichtelijk binnen een Teamwork platform. Deze documenten zijn via Teamwork en tijdens zes werkgroepvergaderingen bediscussieerd en waar nodig aangepast, en er zijn aanbevelingen opgesteld.
Tevens is een klankbordgroep samengesteld. Zie voor de deelnemers aan de klankbordgroep paragraaf d . De klankbordgroep is voor de start van de praktijktest geconsulteerd met de vraag om de conceptrichtlijn van commentaar te voorzien.
Het eerste concept van de richtlijn is in mei en juni 2017 van commentaar voorzien door de RAC en is op 12 juni 2017 besproken in een vergadering van de RAC. De RAC wilde op een aantal punten meer toelichting. Daarom is het eerste concept aangepast en wederom besproken in de RAC op 18 september 2017. Hierna is gestart met een praktijktest gedurende zes maanden bij 4 JGZ teams, om de bruikbaarheid van de richtlijn in de praktijk te onderzoeken. De conceptrichtlijn is in dezelfde periode verspreid voor de landelijke commentaarronde. Daarbij is ook gevraagd naar het commentaar van de adviescommissie ‘visus’ van het NCJ.
4.3 Leden van de projectgroep
| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| Nicoline Schalij-Delfos (voorzitter van de werkgroep) | Hoogleraar kinderoogheelkunde | LUMC |
| Hein Raat (penvoerder) | Hoogleraar sectie jeugd van de afdeling Maatschappelijke Gezondheidszorg | Erasmus MC |
| Huib Simonsz | Kinderoogarts en hoogleraar van de afdeling oogheelkunde | Erasmus MC |
| Caren Lanting | Senior adviseur richtlijnontwikkeling en onderzoeker bij de afdeling Child Health | TNO |
| Frea Sloot | Promovendus en oogarts in opleiding van de afdeling oogheelkunde | Erasmus MC |
| Aya Sami | Orthoptist en junior onderzoeker van de afdeling oogheelkunde | Erasmus MC |
| Suzanne van den Toren | Junior onderzoeker sectie jeugd van de afdeling Maatschappelijke Gezondheidszorg | Erasmus MC |
4.4 Leden van de werkgroep
| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| Regine van Riemsdijk | Jeugdarts | AJN |
| Margot van Denderen | Jeugdarts | AJN |
| Jet Linskens-Vinken | Verpleegkundig specialist preventie | V&VN |
| Anneke Driesen | Verpleegkundig specialist preventie | V&VN |
| Mathilde Buijs | Doktersassistente | NVDA |
| Yvonne van Straten | Doktersassistente | NVDA |
| Anky Morshuis | Orthoptist | NVvO |
| Pauline Heus* | Optometrist/orthoptist | OVN |
| Els van As, later overgenomen door Marlinda Stam | Teamleider JGZ | JGZ organisatie |
| Ilse Vermeer | Ouder | Oudervereniging |
| Trijntje Sjoerdsma | Orthoptist | Spinoza center, NCJ werkgroep visus |
| Wietze Eizenga (schriftelijk commentaar geleverd) | Huisarts |
*Pauline Heus was zowel lid van de werkgroep als één van de uitvoerenden van de evidence synthese vanuit Cochrane Netherlands
4.5 Leden van de klankbordgroep
| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| Hans van den Berg | Bovenschools manager | RVKO |
| Ria van Berlo | Jeugdarts | AJN |
| Marietta Stoel | Jeugdverpleegkundige | V&VN |
| Lien Wienen | Jeugdarts en werkend met kinderen met een ontwikkelingsachterstand | AJN |
| Silvia van Braak- de Graaf | Optometrist/orthoptist | OVN |
| Esther de Bekker-Grob | Gezondheidseconoom | |
| Hanny Groenewoud | RAMSES studie vertegenwoordiger | |
| René van Rijn | Oogarts | NOG |
| Mies van Genderen | Hoogleraar zeldzame visuele aandoeningen bij kinderen | Bartiméus / Visio |
5 Verantwoording
Tijdens de eerste werkgroepvergadering zijn de uitgangsvragen besproken, gerubriceerd en waar nodig nader gespecificeerd. Voor een deel van de uitgangsvragen is een systematisch literatuuronderzoek (evidence synthese) verricht. In de evidence synthese genaamd ‘Herziening JGZ-richtlijn Oogafwijkingen, evidence synthese’ is gerapporteerd over de werkwijze en de resultaten van dit systematische literatuuronderzoek. Deze evidence synthese is op te vragen bij de richtlijnontwikkelaars.
De werkgroep heeft de adviezen voor het onderzoek en de onderzoeksmomenten voor het opsporen van oogafwijkingen geformuleerd op basis van het beschikbare bewijs uit de evidence synthese, aangevuld met artikelen die niet voldeden aan de zoekcriteria van de systematische review maar wel relevant bevonden werden, en praktijkervaring van de leden van de werkgroep. In de werkgroep waren alle relevante groepen/‘stakeholders’ vertegenwoordigd door tenminste 1 afgevaardigde.
De projectgroep heeft het proces van de totstandkoming van de richtlijn begeleid, de documenten voor de richtlijn opgesteld en deze ter goedkeuring aangeboden aan de werkgroep alvorens deze naar buiten te brengen.
Geen van de leden van de werkgroep en de projectgroep heeft belangenverstrengeling aangegeven. Het voorstel tot herziening is voor advies voorgelegd aan de leden van de klankbordgroep. Ook was er een landelijke commentaarronde, die zo breed mogelijk is uitgevoerd. Daarbij is ook de adviescommissie ‘visus’ van het NCJ geraadpleegd. Ter goedkeuring is de richtlijn voorgelegd aan de Richtlijn Advies- en Autorisatie Commissie (RAC) van het Nederlands Centrum Jeugdgezondheid (NCJ).
6 Bijlage 1: de uitvoering van oogonderzoeken in de praktijk
In tabel B1 is een overzicht te vinden van leeftijden en leeftijdsperiodes waar oogonderzoek geadviseerd wordt.
Tabel B1. Acties ten behoeve van oogonderzoek per uitvoeringsmoment
|
Leeftijden en periodes |
Anamnese |
Inspectie |
Rode fundus-reflex |
Van Wiechen |
Cornea Lichtreflex |
Instel beweging |
Monoculaire volgbeweging |
Visusmeting |
| 1 maand |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
|
|
| 2 maanden |
x |
x |
• |
x |
|
|
|
|
| 3 maanden |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
|
|
| 6-9 maanden |
x |
x |
|
|
x |
x |
x |
|
| 14-24 maanden |
x |
x |
|
|
x |
x |
x |
|
| 36 maanden (3 jaar) |
x |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
* |
| 42-48 maanden (3,5-4 jaar) |
x |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
| 54-66 maanden (4,5-5,5 jaar) |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
| ≥ 84 maanden (7 jaar) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
*op indicatie
Contactmomenten 0-36 maanden
Tijdens alle contactmomenten waarop de opsporing van oogafwijkingen plaatsvindt gericht navraag gedaan aan ouders of er klachten zijn over de ogen / het zicht van hun kind en wordt het oog geïnspecteerd (zie bijlage 1a).
Opsporing van aangeboren (congenitale) oogheelkundige aandoeningen is essentieel in deze periode. Hiervoor verricht de JGZ de volgende onderzoeken: het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex, de drie onderdelen van het Van Wiechen-onderzoek (fixeren, binoculair volgen en naar eigen handen kijken, zie tabel B2), cornea lichtreflex, instelbeweging en de monoculaire volgbewegingen. Zie tabel B3 voor een overzicht van de onderzoeken, indicaties en acties bij kinderen tussen 0 en 36 maanden.
Tabel B2: Onderdelen Van Wiechen onderzoek
| Leeftijd | Ontwikkelingskenmerken | Verwijscriterium |
| 1 maand | Ogen fixeren | Een kind moet op de leeftijd van 6 weken gericht aan kunnen kijken, indien het kind dat niet doet → verwijzen |
| 2 maanden | Volgt met ogen en hoofd 30° ↔ 0° ↔ 30° |
Bij 2 maanden begint een kind te volgen, bij 3 maanden moet het kind vloeiend kunnen volgen, indien dat niet het geval is → verwijzen |
| 3 maanden | Kijkt naar eigen handen | Indien het gewenste gedrag niet kan worden geobserveerd en de ouder de vraag naar het gedrag ontkennend beantwoordt, kan dit mede afhankelijk van de overige bevindingen reden zijn voor verwijzing. |
Tabel B3: Acties bij onvoldoende of afwijkende bevindingen van oogonderzoek bij kinderen tot 36 maanden*
| Leeftijd of periode | Uit te voeren oogonderzoeken | Bevinding | Bijbehorende actie met verwijs- en herhaaltermijnen |
| 1 maand | Beoordelen van de rode fundusreflex |
Rode fundusreflex afwezig of afwijkend Rode fundusreflex niet te behoordelen of bij twijfel over de rode fundusreflex |
→ Verwijzen binnen 1 week → Binnen 4 weken herhalen (uiterlijk op de leeftijd van 2 maanden) |
| Van Wiechen onderdeel: fixeren | Zie tabel B2 | ||
| 2 maanden | Op indicatie beoordelen van de rode fundusreflex (als dit nog niet gelukt of gedaan was op de leeftijd van 1 maand) | Rode fundusreflex afwezig, afwijkend of niet te beoordelen |
→ Verwijzen binnen 1 week |
| Van Wiechen onderdeel: binoculaire volgbeweging | Zie tabel B2 | ||
| 3 maanden | Beoordelen van de rode fundusreflex | Rode fundusreflex afwezig, afwijkend of niet te beoordelen | → Verwijzen binnen 1 week |
| Van Wiechen onderdeel: naar eigen handen kijken | Zie tabel B2 | ||
| 6-9 en 14-24 maanden | Cornea lichtreflex | Asymmetrische cornea lichtreflex | → Verwijzen (scheelzien)** |
| Instelbeweging bij afdekken | Instelbeweging bij afdekken aanwezig | → Verwijzen (scheelzien)** | |
| Afweer bij afdekken | Afweer bij afdekken van het ene en niet bij afdekken van het andere oog | → Verwijzen binnen 1-2 weken | |
| Monoculaire volgbeweging | Volgt vloeiend met 1 oog en niet of zoekend/schokkerig met het andere oog | → Verwijzen binnen 1-2 weken | |
| Bij de vier bovengenoemde onderdelen | Bij twijfel | → Herhalen binnen 3 maanden |
*Zie bijlage 1 van de richtlijn voor een beschrijving van de uitvoering van het oogonderzoek bij kinderen tot de leeftijd van 36 maanden
** Zie tabel B5 voor bijbehorende verwijstermijnen
Contactmomenten vanaf 36 maanden
Een overzicht van de onderzoeken, indicaties en acties bij kinderen vanaf 36 maanden is via deze te vinden. Op de leeftijd van 36 maanden wordt anamnese afgenomen en inspectie van het uitwendige oog verricht. Op indicatie en indien de JGZ-professional dit wenst, kan een visusmeting worden gedaan. Voor de uitvoering wordt verwezen naar thema 3 van deze richtlijn.
Verwijscriteria 36 maanden: (zie tabel B6):
- Indien visus bepaald wordt:
- bij onvoldoende visus verwijzen
- bij voldoende visus wordt de visusmeting opnieuw gedaan op de leeftijd van 42-48 maanden
- Indien geen visus bepaald wordt:
- Een of meerdere symptomen die kunnen wijzen op een verminderd gezichtsvermogen met positieve familieanamnese: verwijzen
- Een of meerdere symptomen die kunnen wijzen op een verminderd gezichtsvermogen met negatieve familieanamnese: binnen 3 maanden opnieuw beoordelen tenzij ernst van klachten aanleiding is tot verwijzen (frequent aanwezig scheelzien of ernstige twijfel over visus).
- Een positieve familieanamnese zonder klachten: visusmeting op 42-48 maanden
Op de leeftijd van 42-48 maanden wordt de anamnesevraag gesteld en wordt inspectie van het oog verricht. Daarnaast wordt de visus met de E-Haken kaart (of de Landolt-C kaart tot vervanging) of, als dit niet lukt, met de LEA Symbolen gemeten. Bij twijfel opnieuw testen binnen 3 maanden. Bij twee keer twijfel doorverwijzen, zie tabel B7 voor verwijscriteria.
Op de leeftijd van 54-66 maanden wordt de visus met de E-Haken kaart (of de Landolt-C kaart tot vervanging) gemeten, ook wordt anamnese afgenomen. Bij twijfel over uitslag opnieuw onderzoeken binnen 3 maanden. Bij twee keer twijfel doorverwijzen, zie tabel B8
Tabel B4: Acties bij onvoldoende of afwijkende bevindingen van oogonderzoek met visusmeting bij kinderen vanaf 36 maanden*
| Leeftijd of periode | Uit te voeren oogonderzoeken met visusmetingen | Bevinding en bijbehorende actie | Verwijs- en herhaaltermijnen |
| 36 maanden = 3 jaar ** | Klachten met positieve familie anamnese | → Verwijzen | |
| Klachten met negatieve familie anamnese | → Afhankelijk van ernst klachten direct verwijzen of binnen 3 maanden opnieuw beoordelen | ||
| Facultatief: Visusmeting op indicatie met de LEA Symbolen kaart | Bij onvoldoende uitslag | → Verwijzen | |
| Bij voldoende visus | → Visusmeting op 42-48 maanden | ||
| 42-48 maanden = 3,5 tot 4 jaar** | Visusmeting met de E-Haken kaart (Als de visusmeting niet lukt met de E-Haken kaart, gebruik dan LEA Symbolen kaart). | Onvoldoende uitslag | → Verwijzen |
| Twijfel of met beide kaarten niet gelukt | → Visusmeting herhalen binnen 3 maanden | ||
| Twee keer twijfel | → Verwijzen | ||
| 54-66 maanden = 4,5 tot 5,5 jaar** | Visusmeting met E-Haken kaart | Onvoldoende uitslag of niet gelukt | → Verwijzen |
| Twijfel | → Visusmeting herhalen binnen 3 maanden | ||
| Twee keer twijfel | → Verwijzen | ||
| ≥ 84 maanden = 7 jaar | Visusmeting op indicatie met E-Haken kaart | Onvoldoende uitslag | → Onder de 10 jaar verwijzen naar orthoptist; vanaf 10 jaar naar optometrist / optiek bedrijf |
*Zie bijlage 1d voor een beschrijving van de uitvoering van de visusmetingen
**Zie Tabel 7A,B,C voor de verwijscriteria van de visusmeting op de leeftijd van 36 maanden en in de leeftijdsperiode tussen de 42 en 48 maanden en tussen de 54 en 66 maanden respectievelijk
6.1 Bijlage 1a: handleiding voor het voeren van het anamnesegesrpek en voor de inspectie van de ogen
Tijdens alle contactmomenten waarop de opsporing van oogafwijkingen plaatsvindt, wordt gerichte navraag gedaan naar afwijkingen van de ogen of het zien en wordt het oog geïnspecteerd (m.u.v. het visusonderzoek in de leeftijdsperiode van 54-66 maanden, waar geen inspectie plaatsvindt).
Eénmalig wordt een familieanamnese gericht op oogheelkundige afwijkingen uitgevraagd en opgenomen in dossier: komen hoge brilsterkte (een sterkte hoger dan +6 of -5) op basisschoolleeftijd, amblyopie, scheelzien, slechtziendheid of andere oogafwijkingen bij familieleden in de eerste en tweede graad voor? Een positieve familieanamnese op zich is geen reden tot verwijzing, maar ondersteunt de beslissing om door te verwijzen.
- Tijdens alle contactmomenten wordt:
- in elk geval één vraag gesteld die gericht is op het opsporen van mogelijke oogafwijkingen en visuele stoornissen van het kind en vindt inspectie van de ogen en oogleden plaats (m.u.v. het visusonderzoek in de leeftijdsperiode van 54-66 maanden, waar geen inspectie plaatsvindt). Aan de ouder(s) of verzorger(s) wordt gevraagd: Heeft u klachten over de ogen / het zien van uw kind?
- gevraagd of het kind een bril of contactlenzen draagt.
- gevraagd of het kind onder behandeling is van een orthoptist / oogarts en of een controletermijn is afgesproken. Als dit zo is, hoeft geen onderzoek plaats te vinden.
- Als nog niet geïnventariseerd: Komen hoge brilsterkte (een sterkte hoger dan +6 of -5) op basisschoolleeftijd, amblyopie, slechtziendheid, scheelzien of andere oogafwijkingen van familieleden in de eerste en tweede graad voor?
Symptomen die kunnen wijzen op een verminderd gezichtsvermogen:
- Bij baby’s tot en met 6 maanden
- Niet gericht aankijken (vanaf 6 weken)
- Niet naar bijvoorbeeld eigen handjes, mobiel of speelgoed kijken (vanaf 6-8 weken)
- Niet volgen van bijvoorbeeld het bewegende gezicht van de ouder of een speelgoedje (vanaf 2 maanden)
- Scheel kijken (vanaf 6-8 weken)
- Nystagmus (vanaf 6-8 weken): snelle ritmische- of dwaalbewegingen.
- Bij kinderen vanaf 6 maanden
- Knijpen met de ogen bij kijken op afstand
- Dingen altijd heel dichtbij houden om ernaar te kijken
- Veel knipperen en knijpen om objecten te kunnen zien
- Niet langere tijd met kleine voorwerpen kunnen spelen
- Plaatjes in een prentenboek niet kunnen zien (vanaf ± 3 jaar)
- Regelmatig hoofdpijn in loop van de dag (vanaf ± 3 jaar)
- Veel struikelen, zonder dat er sprake is van onbesuisd gedrag of een afwijkende grove- en/of fijne motorische ontwikkeling
- Dicht bij TV / spelcomputer zitten omdat het kind het niet kan zien als verder weg gezeten moet worden
- Letters niet kunnen lezen omdat ze te klein zijn
- Scheelzien: permanent of wisselend aanwezig.
- Nystagmus
Algemene inspectie van de ogen:
Bij de contactmomenten waarop oogonderzoek plaatsvindt wordt tot en met de leeftijdsperiode van 42-48 maanden het oog geïnspecteerd op afwijkingen. Hulpmiddel hierbij is een penlight, waarmee de onderdelen uit verwijstabel B4 onderzocht kunnen worden. Een meetlatje kan gebruikt worden om de diameter van de cornea te meten als er twijfel is of deze normaal is. Zie bijlage 1e, verwijzingstabel 1 e.1.
6.2 Bijlage 1b: handleiding voor het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex
Het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex wordt standaard uitgevoerd op de leeftijd van 1 en 3 maanden. Omdat totaal eenzijdig cataract voor de leeftijd van 6 weken en dubbelzijdig cataract voor de leeftijd van 3 maanden geopereerd moet worden, moet de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex voor die tijd in elk geval beoordeeld zijn. Mocht het onderzoek niet gelukt of gedaan zijn op de leeftijd van 1 maand, dan moet dit liefst zo snel mogelijk alsnog gebeuren, maar uiterlijk op de leeftijd van 2 maanden.
Het beoordelen van de aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex wordt gedaan door de jeugdarts of door de verpleegkundig specialist. Het onderzoek wordt uitgevoerd met een oogspiegel (ophthalmoscoop). De onderzoeker zit op een afstand van ongeveer 20 cm op ooghoogte met het kind. Als het kind ligt, buigt de onderzoeker zich over het kind heen, zodat recht in de ogen van het kind gekeken kan worden. Veel baby’s openen de ogen als ze op de schoot van de ouder / begeleider gelegd worden met het hoofdje op de knieën en de beentjes tegen de buik van ouder/begeleider. Het licht van de ophthalmoscoop wordt op het oog geprojecteerd zodat met doorvallend licht beoordeeld wordt of de fundus oplicht. Een normale bevinding is een egaal oplichtende, rode fundusreflex (of een geelbruine fundusreflex bij donkere kinderen).
De fundusreflex is afwijkend als de pupil niet oplicht, niet egaal is (deel van de pupil gemaskeerd door een troebeling) of (geel-)wit van kleur is. Een afwijkende rode fundusreflex is reden tot verwijzing.
6.3 Bijlage 1c: handleiding voor het uitvoeren van de cornea lichtreflex, de instelbeweging en de monoculaire volgbeweging
Bij kinderen in de leeftijd van 6-9 maanden en 14-24 maanden wordt de oogstand beoordeeld met de cornea lichtreflex en de instelbeweging. Om een indruk over de visus te krijgen wordt de monoculaire volgbeweging van elk oog gedaan en beoordeeld of er afweer bij occlusie is van één oog. Hieronder vindt u de beschrijving voor de praktische uitvoering van de afzonderlijke onderdelen.
De cornea lichtreflex, een test voor het opsporen van manifest scheelzien
Met de cornea lichtreflex kan onderscheid gemaakt worden tussen een rechte oogstand en manifest scheelzien. De oogstand is recht als bij fixatie van een lampje de afbeelding van het lampje in beide ogen op de fovea valt. De fovea is het centrum van de gele vlek of macula lutea en is het gedeelte van het netvlies waarmee men het scherpst ziet. Omdat bij een rechte oogstand de twee ogen allebei het lampje fixeren staan de cornea reflex beeldjes in beide ogen symmetrisch ten opzichte van elkaar (figuur B1 links). Bij manifest scheelzien (strabismus) zijn de cornea reflex beeldjes niet symmetrisch. In het afwijkende, schele oog valt de afbeelding naast de fovea. Het cornea reflex beeldje in het scheel staande oog is dan verschoven (figuur B1 rechts). Manifest scheelzien is een reden om te verwijzen (zie verwijstabel B4)
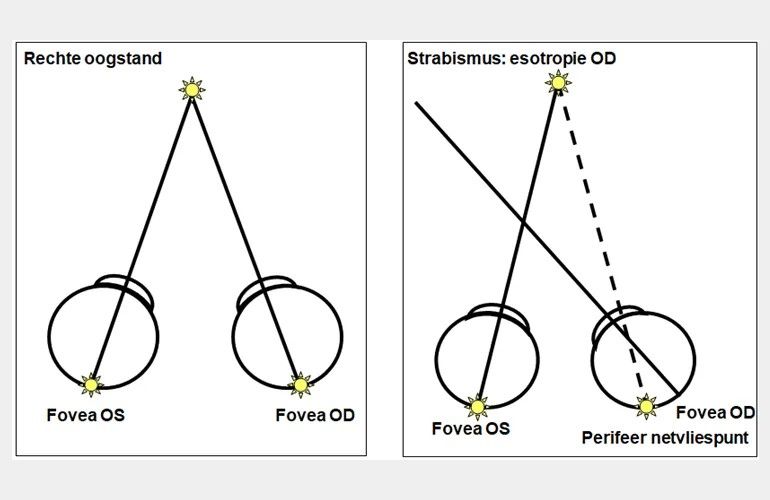
Figuur B1: schematische voorstelling van effect van strabismus op plaats van de cornea lichtreflex. OD = rechter oog, OS= linker oog.
Rechte oogstand: bij fixatie van het lampje valt de afbeelding van het lampje op de fovea van het rechter (OD) en linker oog (OS); de lichtreflex van het lampje op de cornea van beide ogen staat symmetrisch. Bij het afdekken van het rechter of linker oog blijft het andere oog het lampje fixeren en zal geen instelbeweging worden gemaakt. Voorwaarde voor het beoordelen van het wel of niet aanwezig zijn van een instelbeweging is dat het kind op het beoordelingsmoment het lampje fixeert.
Strabismus, in voorbeeld esotropie rechter oog: Beeld van het lampje valt op de fovea van linker oog en op een perifeer netvliespunt van het rechter oog. De lichtreflex op de cornea is niet symmetrisch. Omdat het rechter oog naar binnen gedraaid staat, is de lichtreflex op de cornea naar buiten (temporaal) verplaatst. Bij afdekken van het linker oog maakt het rechter oog een instelbeweging van nasaal naar temporaal om het lichtje te fixeren met de fovea. Dit is de instelbeweging en is een maat voor manifest strabismus.
Praktische uitvoering van de cornea lichtreflex
Voor dit onderzoek zit het kind op schoot bij de ouder. Het hoofd moet recht staan. De oppervlakte van de cornea werkt als een bolle spiegel, daardoor wordt een lampje als een kleine witte punt in de pupil van het kind afgebeeld. Het lampje, bij voorkeur een penlight met twee AA- of AAA batterijen, wordt voor de neusrug van de onderzoeker gehouden, op ooghoogte van het kind. Dit kan het beste gebeuren op armlengte afstand van het kind, ongeveer 40cm. Laat het kind naar het lampje kijken. Let op, de positie van de cornea lichtreflex mag alleen beoordeeld worden op de momenten dat het kind het lampje fixeert.
Bevindingen
Symmetrische cornea lichtreflex
Bij een rechte oogstand staat de cornea lichtreflex symmetrisch in het midden, of iets verplaatst naar de neuskant ten opzichte van het midden, in de pupilopening van beide ogen (figuur B2). De reden dat de reflex niet exact in het midden staat, is dat de gele vlek niet precies aan de achterkant van het oog zit, maar iets meer naar de kant van het oor geplaatst is.
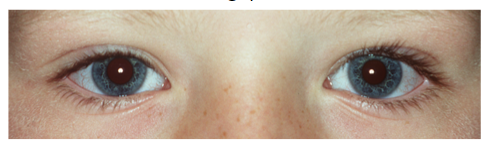
Figuur B2. Rechte oogstand. De cornealichtreflex staat symmetrisch, iets aan de neuskant van het midden van beide pupillen
Een symmetrische cornea lichtreflex is een goede indicatie van een rechte oogstand en helpt ook in het onderscheid maken tussen manifest en pseudostrabismus.

Figuur B3. Epicanthus van beide ogen
Het visuele effect van een epicanthus: door de epicanthus is in het linker oog aan de neuskant minder oogwit zichtbaar dan aan de kant van het oor en lijkt er een scheelzien naar binnen (esotropie) te bestaan, de cornea lichtreflex is echter symmetrisch (figuur B3).
Niet symmetrische cornea lichtreflex
Bij scheelzien is de plaats van de cornea lichtreflex niet symmetrisch in beide ogen, maar in 1 oog verschoven ten opzichte van het andere oog. Bij scheelzien naar binnen is de lichtreflex in het scheelziende oog verschoven naar de oorkant (temporaal), bij scheelzien naar buiten naar de neuskant (nasaal). Verticaal scheelzien komt veel minder vaak voor. Hierbij is de cornea lichtreflex naar beneden (hypertropie) of naar boven (hypotropie) verschoven ten opzichte van het midden van de pupil (figuur B4-8: vormen van manifest scheelzien).
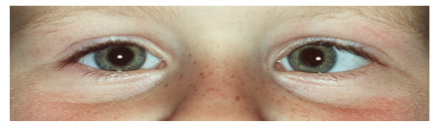
Figuur B4. Scheelzien naar binnen (esotropie) van het linker oog. In het linker oog staat de cornea lichtreflex aan de oorkant van de pupil en in het rechter oog, dat naar het lampje kijkt, iets aan de neuskant van het midden van de pupil. Het linker oog is naar de neus verschoven ten opzichte van het midden van de lidspleet.
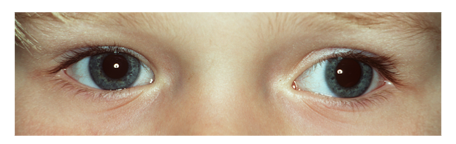
Figuur B5. Scheelzien naar buiten van het linker oog (exotropie)
In het linker oog staat de cornea lichtreflex in het scheelziende oog meer aan de neuskant van de pupil dan in het rechter oog, dat naar het lampje kijkt. Het oog zelf is naar temporaal verschoven ten opzichte van het midden van de lidspleet.
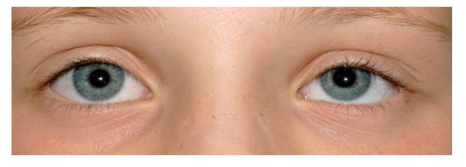
Figuur B6. Verticaal scheelzien van het linker oog waarbij het linker oog te hoog staat (hypertropie)
In het linker oog staat de cornea lichtreflex in het scheelziende oog lager dan in het rechter oog. In het rechter oog, dat naar het lampje kijkt, staat de cornea lichtreflex iets aan de neuskant van het midden van de pupil. Het linker oog is naar boven verschoven ten opzichte van het midden van de lidspleet.
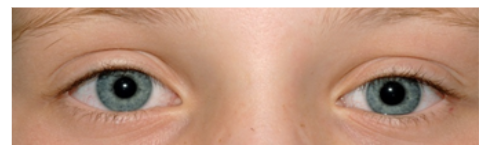
Figuur B7. Verticaal scheelzien van het linker oog waarbij het linker oog te laag staat (hypotropie). In het linker oog staat de cornea lichtreflex in het scheelziende oog hoger dan in het rechter oog. In het rechter oog, dat naar het lampje kijkt, staat de cornea lichtreflex iets aan de neuskant van het midden van de pupil. Het linker oog is naar onder verschoven ten opzichte van het midden van de lidspleet.
Wisselende cornea lichtreflex
Een bijzondere vorm van manifest scheelzien is alternerend scheelzien. Tijdens het onderzoek van de cornea lichtreflex wisselt het scheelzien af tussen het rechter en het linker oog. De plaats van de cornea lichtreflex verandert dan. Het ene moment staat het rechter oog scheel, het volgende moment het linker oog. Het kind kijkt afwisselend met het linker en het rechter oog naar het lampje (figuur B8).
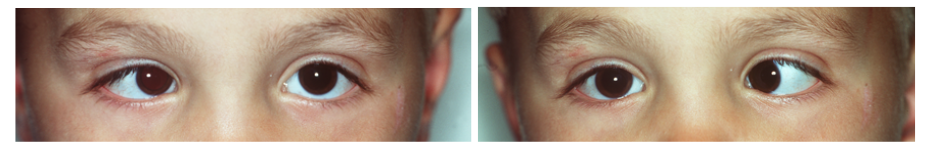
Figuur B8. Alternerend scheelzien waarbij op het linker plaatje het rechter oog scheel staat naar binnen (esotropie) en op het rechter plaatje het linker oog (esotropie).
Op het linker plaatje is de cornea lichtreflex van het rechter oog naar de oorkant verplaatst, op de rechter foto is de cornea lichtreflex van het linker oog naar de oorkant verplaatst.
Een kind jonger dan 3 maanden mag af en toe, niet dagelijks, scheel kijken. Als een kind langdurig of vaak scheel kijkt, of als de ouder aangeeft dat het kind soms scheel ziet (ook op oudere leeftijd als de oogstand recht lijkt maar de ouder zegt dat het kind regelmatig scheel kijkt) zal het kind door een orthoptist beoordeeld moeten worden.
Samenvatting oogstand
| Oog staat | Cornea lichtreflex staat | Manifest strabismus | |
| Naar neuskant | Naar oorkant | Scheelzien naar binnen | Esotropie |
| Naar oorkant | Naar neuskant | Scheelzien naar buiten | Exotropie |
| Naar boven | Naar beneden | Verticaal scheelzien | Hypertropie |
| Naar beneden | Naar boven | Verticaal scheelzien | Hypotropie |
Beoordelen van de instelbeweging bij afdekken van een oog
Het beoordelen van de instelbeweging bij het afdekken van een oog is een aanvulling op de cornea lichtreflex om te beoordelen of er sprake is van manifest scheelzien. De onderzoeker houdt het lampje op ooghoogte van het kind op ongeveer 40 cm afstand en houdt de hand waarmee afgedekt gaat worden klaar boven het hoofd van het kind. Op het moment dat het kind naar het lampje kijkt dekt de onderzoeker een oog af en beoordeelt of het andere oog een instelbeweging maakt. Dit wordt herhaald om de instelbeweging van het andere oog te onderzoeken. Als de oogstand recht is en beide ogen op het fixatielampje gericht zijn is de cornea lichtreflex symmetrisch en zal er geen instelbeweging gemaakt worden. Als een van beide ogen wel een instelbeweging maakt bij afdekken van een oog is er sprake van manifest scheelzien. De positie van de cornea lichtreflex moet passen bij de waargenomen instelbeweging. Er is dus sprake van manifest scheelzien als er asymmetrische lichtreflexen en een instelbeweging waargenomen zijn, hetgeen altijd reden is tot verwijzing.
- Als het oog een instelbeweging van de neuskant naar de oorkant maakt (van binnen naar buiten) is er sprake van een esotropie.
- Als het oog een instelbeweging van de oorkant naar de neuskant maakt (van buiten naar binnen) is er sprake van een exotropie.
- Als het oog een instelbeweging van boven naar beneden maakt, is er sprake van een hypertropie.
- Als het oog een instelbeweging van beneden naar boven maakt, is er sprake van een hypotropie.
Figuur B9. Esotropie OS
In figuur B9 is de lichtreflex van het linker oog verplaatst naar de oorkant. Bij afdekken van het rechter oog maakt het linker oog een instelbeweging naar het oor (buiten). De lichtreflex staat nu in het linker oog niet meer naast de pupil. Wanneer weer met twee ogen gekeken mag worden staat het linker oog weer naar binnen en staat de reflex weer aan de oorkant van de pupil.
Beoordelen van afweer bij afdekken van een oog als indicatie voor (verschil in) visus
Bij het afdekken van een oog kan het zijn dat het kind protesteert bijvoorbeeld door te huilen, door je hand weg te slaan of door om je hand heen probeert te kijken. Als dit steeds bij hetzelfde oog gebeurt, zou dat kunnen betekenen dat het oog dat niet afgedekt is slechter ziet dan het andere. Er is hoogstwaarschijnlijk sprake van een ernstige vermindering van de visus.
Als een kind probeert om je hand voor het oog weg te trekken of begint te huilen, stop dan niet met het onderzoek maar probeer het andere oog af te dekken. Als er een duidelijk verschil is tussen het afdekken van rechter- en linkeroog kan dit betekenen dat er een verschil in visus is.
Sommige kinderen willen absoluut niet dat je hun hoofd aanraakt en dan is het soms toch wel mogelijk om het kind met één oog te laten kijken door het andere oog met de hand af te dekken zonder dat je het hoofd aanraakt.
Een hulpmiddel bij het uitvoeren van de test is het kind een klein speelgoedje te laten pakken terwijl één oog afgedekt wordt. Een zoekende beweging of misgrijpen van het speelgoedje zou op een visusvermindering van dat oog kunnen duiden.
Van nystagmus is sprake als de ogen onwillekeurige ritmische bewegingen maken, meestal horizontaal. Een manifeste nystagmus valt meestal al direct op bij het onderzoek van de cornea lichtreflex, omdat dit permanent aanwezig is. Een andere vaak voorkomende vorm van nystagmus bij kinderen is latente nystagmus bij aangeboren scheelzien. Deze nystagmus treedt alleen op bij afdekken van één van beide ogen. Beide ogen hebben dan nystagmus waarbij de snelle beweging in de richting van het niet-afgedekte oog is. Als het andere oog afgedekt wordt slaat de nystagmus naar de andere kant. Een kind met een nystagmus, latent of manifest, moet meteen naar de orthoptist en oogarts verwezen worden.
De monoculaire volgbewegingen voor inschatting van de visus
De monoculaire volgbewegingen kunnen gebruikt worden om het gezichtsvermogen van beide ogen apart te bepalen.
In het Van Wiechen Schema worden op de leeftijd van 2 maanden de binoculaire volgbewegingen gebruikt om de cerebrale ontwikkeling te testen, maar daarmee kan niet een verschil in visus van beide ogen vastgesteld worden.
Amblyopie kan op jonge leeftijd, voordat de visus gemeten kan worden, opgespoord worden met de monoculaire volgbeweging: Als het kind met één oog een lampje of een voorwerp vloeiend volgt of niet protesteert bij afdekken en met het andere oog niet, niet vloeiend of zoekend volgt of protesteert bij afdekken, dan kan er sprake zijn van amblyopie en is er voldoende reden om te verwijzen.
Praktische uitvoering van de monoculaire volgbeweging
De monoculaire volgbeweging wordt voor ieder oog apart beoordeeld. Het doel van deze test is een indruk te krijgen van de visus van het niet-afgedekte oog. Bij de test worden alleen horizontale volgbewegingen onderzocht. Door de duim van de onderzoeker op de neusrug van het kind en de rest van de hand voor een oog te houden wordt het ene oog afgedekt terwijl het andere oog het lampje volgt. Het lampje wordt in de andere hand op ooghoogte voor het kind langzaam heen en weer bewogen op een afstand van ongeveer 40 cm. Om de aandacht zo goed mogelijk vast te houden kan ook een klein speelgoedje gebruikt worden in plaats van een lampje.
6.4 Bijlage 1d: het meten van de visus
Het meten van de visus bij kinderen
- Voor de visusbepaling zijn een logaritmische visuskaart met E-haken, een visuskaart met LEA Symbolen en een goede afdekbril nodig.
- Op de leeftijd van 42-48 maanden wordt de logaritmische E-Haken kaart gebruikt, bij onvoldoende medewerking de LEA Symbolen. Op 54-66 maanden wordt de E-Haken kaart gebruikt, alleen in bijzondere gevallen de LEA Symbolen.
- Tot 1-1-2021 mag de Landolt-C kaart met 5 symbolen op rij nog gebruikt worden als alternatief voor de logaritmische E-haken kaart. De transparante Landolt-C kaart mag tot vervanging nog gebruikt worden mits op een witte achtergrond, bij voorkeur wit papier . Lees bij verdere uitleg waar E haken staat steeds: en Landolt-C tot vervanging.
- De visus wordt monoculair bepaald door één oog af te dekken met een afdekbril. Het afdekken van het oog door de begeleider wordt afgeraden, omdat hierbij het risico bestaat dat tussen de vingers door gekeken wordt.
- Bij alle visusmetingen is het mogelijk de kinderen die niet mondeling willen / kunnen benoemen te laten wijzen met vingers, hand of arm of te matchen met kaartjes (LEA Symbolen) of een E/C op een stokje of als vorm van hout of dik, zwart papier dat in de hand gehouden wordt.
Eisen aan omgeving en materiaal
- De visus wordt afgenomen in een normaal verlichte spreekkamer. Het is niet toegestaan om een lichtkast te gebruiken of om de visuskaart met spotjes te belichten.
- De afdekbril sluit het afgedekte oog zo goed af, dat spieken niet mogelijk is.
- De visuskaarten bevatten tenminste 10 logaritmisch geordende regels met symbolen voor de decimale visuswaarden 0.125, 0.16, 0.2, 0.25, 0.32, 0.4, 0.5, 0.63, 0.8 en 1.0. Voor deze waarden moeten op elke regel tenminste 5 symbolen staan.
- De visuskaart wordt op 1.5 meter van de grond opgehangen tegen een witte achtergrond. .
- De afstand tussen de ogen van het kind en de kaart is voor de E-Haken kaart 4 of 5 meter, zonder gebruik van spiegels. Per locatie wordt één testafstand gebruikt: 4 of 5 meter.
- De LEA Symbolen kaart wordt op 4 of 5 meter afgenomen, waarbij het voorkeur heeft om bij de jongste kinderen voor de kortere afstand van 4 meter te kiezen. Dit kan op 2 manieren gedaan worden en is afhankelijk van de keuze om 1. de visuskaarten aan de muur te hangen of 2. de stoel waarop kind met begeleider zit op een vaste plek te laten staan. In het eerste geval hangt de kaart aan de muur en zit het kind bij begeleider op schoot waarbij de afstand van de ogen van het kind tot de kaart 4 meter is. In het tweede geval staat de stoel op dezelfde plek als voor afname van de E-haken en staat de onderzoeker op 4 meter afstand en houdt de kaart in de hand voor zich. De keuze wordt bepaald door de lokale mogelijkheden.
- De afstand tot de visuskaart moet voor LEA en E-haken worden gemarkeerd op de vloer.
Voorbereiding en instructies
Het is raadzaam om, bij de uitnodiging voor het consult, afbeeldingen van de E-Haken en de LEA Symbolen toe te voegen zodat de ouders thuis kunnen oefenen. Dit vermindert het aantal mislukte metingen.
Het kind zit op schoot van de begeleider, oudere kinderen mogen zelf zitten of staan. Het kind mag niet vooroverbuigen of op het puntje van de stoel zitten. Leg het kind in begrijpelijke bewoordingen uit wat er van hem verwacht wordt. Oefen dit eerst zonder afdekken van één van de ogen (binoculair) op korte afstand, bijvoorbeeld 40 cm, om te zien of het kind de opdracht begrijpt. Daarna begint u met de test per oog (monoculair). Blijf het kind tijdens het aanwijzen van de symbolen aankijken en ga nooit met uw rug naar het kind staan.
Uitvoering
- Zet het kind de afdekbril op.
- Begin met het rechteroog , tenzij het een herhalingsonderzoek betreft, dan wordt begonnen met het ‘slechtste’ oog bij de vorige visusmeting.
- Wijs de symbolen aan met een vinger of een zwarte pen. Zorg ervoor dat het hele symbool goed zichtbaar is voor het kind. Eenmalig omcirkelen van het symbool is toegestaan, maar niet om de omliggende symbolen af te dekken, omdat dan bij een lui oog een te hoge visus gemeten wordt.
- Begin bij de bovenste regel. Wijs steeds één symbool van afnemende stapgrootte aan. Het symbool mag maximaal 10 seconden aangeboden worden (Europese Richtlijn). Ga bij een juist antwoord naar de volgende regel. Wijs bij een fout antwoord op dezelfde regel nog een symbool aan. Wordt ook dit symbool niet goed gezien ga dan 1 regel terug. Worden op die regel 3 symbolen goed aangegeven, ga dan verder naar de volgende regel. Als drie van de vijf symbolen op die rij goed beantwoord worden, ga dan naar de volgende regel. Ga door tot de laatste regel waarbij drie van de vijf symbolen goed beantwoord worden. Dat is dan de gemeten visus.
- Benader het kind positief, zeg nooit dat een antwoord fout is.
Notatie
- Vermeld welke kaart gebruikt is: E-Haken of LEA Symbolen.
- Noteer de gemeten visus als decimaal getal per oog.
6.5 Bijlage 1e: verwijscriteria
6.5.1 Contactmomenten 0-36 maanden
Tussen de leeftijd van 0 en 3 maanden wordt twee keer beoordeeld of de rode fundusreflex aanwezig is. De eerste keer is op de leeftijd van 1 maand en de tweede keer op de leeftijd van 3 maanden. De aanwezigheid van de rode fundusreflex moet zo snel mogelijk opnieuw beoordeeld worden als het op 1 maand niet gelukt of gedaan is, uiterlijk op de leeftijd 2 maanden, omdat totaal eenzijdig cataract, in principe, voor de leeftijd van 6 weken en dubbelzijdig cataract voor de leeftijd van 3 maanden geopereerd moet worden. De controle op de leeftijd van 2 maanden wordt gedaan door de verpleegkundige. Het onderzoek van de rode fundusreflex wordt in principe door de jeugdarts gedaan of door een verpleegkundig specialist*. Zie tabel B5 voor een overzicht van de verwijstermijnen bij afwijkende bevindingen tijdens de inspectie van het oog.
*De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en zij werkt op expertniveau. Zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
6.5.2 Contactmoment 36 maanden
Op deze leeftijd wordt anamnese a fgenomen en inspectie van het uitwendige oog verricht. Klik op deze voor de uitvoering. Zie tabel B5 voor een overzicht van de verwijstermijnen bij afwijkende bevindingen tijdens de inspectie van het oog.
- Tijdens alle contactmomenten wordt gecheckt of familie anamnese uitgevraagd is en in elk geval één vraag gesteld die gericht is op het opsporen van mogelijke oogafwijkingen en visuele stoornissen van het kind en vindt inspectie van de ogen plaats. Aan de ouder(s) of verzorger(s) wordt gevraagd: Heeft u klachten over de ogen / het zien van uw kind? (Zie overzicht van symptomen die kunnen wijzen op een verminderd gezichtsvermogen (bijlage 1a).
- Indien nog niet geïnventariseerd: Komen hoge brilsterkte (een sterkte hoger dan +6 of -5) op basisschoolleeftijd, amblyopie, slechtziendheid, scheelzien of andere oogafwijkingen van familieleden in de eerste en tweede graad voor?
Bij twijfel over de visus mag een visusmeting met LEA symbolen gedaan worden.
Verwijscriteria bij visusmeting op indicatie op 36 maanden: (zie bijlage 1a):
- Indien visus bepaald:
- bij onvoldoende visus verwijzen, zie tabel B6
- bij voldoende visus wordt opnieuw getest op de leeftijd van 42-48 maanden
- Indien geen visus bepaald wordt:
- Een of meerdere symptomen die kunnen wijzen op een verminderd gezichtsvermogen met positieve familieanamnese: verwijzen
- Een of meerdere symptomen die kunnen wijzen op een verminderd gezichtsvermogen met negatieve familieanamnese: binnen 3 maanden herbeoordelen tenzij ernst van klachten aanleiding is tot verwijzen (frequent aanwezig scheelzien of ernstige twijfel over visus).
- Een positieve familieanamnese zonder klachten: visusmeting op 42-48 maanden
Tabel B5. Acties naar aanleiding van afwijkende bevindingen tijdens inspectie van het oog
| Deel van het oog | Aandoening of afwijking | Extra aanwijzingen | Uiterste termijn voor afspraak bij orthoptist/oogarts |
| Ooglid | Hangend ooglid (ptosis), pupil bedekt door ooglid Hangend ooglid (ptosis), pupil niet bedekt door ooglid | Wanneer kind jonger is dan 6 maanden (Kind mag bij beoordeling torticollis hebben) | 1 week < 6 weken |
| Hangend ooglid (ptosis), pupil bedekt door ooglid Hangend ooglid (ptosis), pupil niet bedekt door ooglid | Wanneer kind ouder is dan 6 maanden (Kind mag bij beoordeling torticollis hebben) | < 6 weken Regulier* |
|
| Rode vlek (naevus flammeus) / capillair hemangioom V1-V2 (= gebied rond het oog) | Wanneer het ooglid betrokken is: naar oogarts, anders naar kinderarts | Regulier* | |
| Als ook corneadiameter te groot (zie cornea) | 1 week | ||
| Pupil | Anisocorie (grootte verschil > 1mm) | 4 weken | |
| Afwijkende vorm (bv sleutelgat – coloboom) | 4 weken | ||
| Afwijkende kleur (wit – leucocorie) | 1 week | ||
| Geen rode fundusreflex | Wanneer kind jonger is dan 6 maanden Wanneer kind ouder is dan 6 maanden |
1 week
2 weken |
|
| Geen egale rode fundusreflex | 2 weken | ||
| Cornea | Diameter te groot (>10.5-11mm bij geboorte / 1e jaar) Diameter te klein (< 9mm) |
1 week
4 weken |
|
| Cornea niet helder | 1 week | ||
| Iris | Heterochromie (kleurverschil ogen) | ||
| Lichtdoorschijnend – albinisme | Wanneer kind jonger is dan 6 maanden Wanneer kind ouder is dan 6 maanden |
4 weken
Regulier* |
|
| Sclera/oogwit | Pigmentvlekken, bruin | Donkere huid, geen groei of geen toename in aantal Lichte huid of heel veel pigmentvlekken |
Niet verwijzen Regulier* |
| Blauwzwarte vlekken (melanosis) | Meerdere vlekken | Regulier* | |
| Aandoening of afwijking | Achtergrondinformatie | Extra aanwijzingen | Uiterste termijn voor afspraak bij orthoptist/oogarts |
| Tumoren/vlekken | Ooglid, conjunctiva of iris | Snel groeiend Niet of langzaam groeiend |
1 week 4 weken |
| Niet fixeren | Niet/onvoldoende fixeren | Vanaf de leeftijd van 6 weken | 1-2 weken |
| Onvoldoende /schokkerig / zoekend volgen met één of twee ogen | Vanaf de leeftijd van 8 weken | 1-2 weken | |
| Onvoldoende of niet volgen | Niet/onvoldoende /schokkerig / zoekend volgen met één of twee ogen | Vanaf de leeftijd van 8 weken | 1-2 weken |
| Onrustige oogbewegingen | Nystagmus /dwalende oogbewegingen | Acuut ontstaan Langer bestaand |
1-2 weken 4 weken |
| Tranen in combinatie met terugkerende (recidiverende) ontsteking | Vanaf geboorte aanwezig, oog zelf niet rood (congenitale traanwegstenose) | Wanneer deze ontsteking niet voorbij is op de leeftijd van 9 maanden | Regulier* |
| Later ontstaan | 4 weken | ||
| Scheelzien | Altijd aanwezig (manifest) en acuut ontstaan Altijd aanwezig (manifest) en langer bestaand |
Alle leeftijden Wanneer kind jonger is dan 6 maanden Wanneer kind ouder is dan 6 maanden |
1-2 weken 4 weken Regulier* |
| Niet altijd aanwezig (intermitterend) | Regulier* |
*Regulier = afspraak zodra er plaats is
NB: groei of verandering zijn vaak goed te beoordelen met behulp van foto’s.
Achtergrond over de aandoeningen: zie sectie 2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie.
Tabel B6 verwijscriteria visus met LEA Symbolen op 36 maanden (facultatief en op indicatie)
|
VOD |
≤0.12 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.63 | 0.8 | 1.0 | |
| VOS | |||||||||||
| ≤0.12 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.16 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.2 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.25 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.3 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.4 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.5 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.63 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | V | V | O | |
| 0.8 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | V | V | V | |
| 1.0 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | V | V |
V = voldoende visus
O = onvoldoende visus
*Bij elk kind en elk oog doortesten tot hoogst haalbare visus met een maximum van 1.0, dus niet stoppen bij een visus van 0.63
6.5.3 Contactmomenten 42-48 maanden
Visus verwijsindicaties
Op deze leeftijd wordt de visus met de E-Haken kaart (of Landolt-C kaart tot vervanging) gemeten, waarnaast ook anamnese en inspectie plaatsvinden. Bij twijfel opnieuw testen binnen 3 maanden. Bij twee keer twijfel doorverwijzen, zie tabel B7 voor verwijscriteria .
Tabel B7 Verwijscriteria visus met E-haken en LEA Symbolen op 42-48 maanden
|
|
VOD | ≤0.12 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.63 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| VOS | |||||||||||
| ≤0.12 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.16 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.2 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.25 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.3 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.4 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.5 | O | O | O | O | O | O | T | T | T | O | |
| 0.63 | O | O | O | O | O | O | T | V | V | T | |
| 0.8 | O | O | O | O | O | O | T | V | V | V | |
| 1.0 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | T | V | V |
V= Voldoende visus
O= Onvoldoende visus, verwijzen
T= Twijfel visus, binnen 3 maanden visus herhalen. Bij twee keer twijfel het kind verwijzen.
*Bij elk kind en elk oog doortesten tot hoogst haalbare visus met een maximum van 1.0, dus niet stoppen bij visus van 0.63.
Bij een hertest vanwege twijfel over de visus: beide ogen herhalen maar starten met oog met slechtste visus bij 1e onderzoek.
6.5.4 Contactmoment 54-66 maanden
Visus verwijsindicaties
Op deze leeftijd wordt de visus met de E-Haken kaart (of Landolt–C kaart tot vervanging) uitgevoerd, waarnaast ook anamnese wordt gedaan. Bij twijfel over uitslag opnieuw testen binnen 3 maanden. Bij twee keer twijfel doorverwijzen, zie tabel B8 .
In de volgende situaties wordt, gezien de noodzaak om indien nodig op tijd te kunnen starten met amblyopiebehandeling, bij twijfel over de uitslag van de visusmeting niet opnieuw testen, maar meteen doorverwezen: Symptomen die kunnen wijzen op een verminderd gezichtsvermogen
- Knijpen met de ogen bij kijken op afstand
- Dingen altijd heel dichtbij houden om ernaar te kijken
- Veel knipperen en knijpen om objecten te kunnen zien
- Niet langere tijd met kleine voorwerpen kunnen spelen
- Regelmatig hoofdpijn in loop van de dag
- Veel struikelen, zonder dat er sprake is van onbesuisd gedrag of een afwijkende grove- en/of fijne motorische ontwikkeling
- Dicht bij TV/spelcomputer/boek zitten omdat het kind het niet kan zien als verder weg gezeten moet worden
- Scheelzien: permanent of wisselend aanwezig.
- Nystagmus
- Amblyopie bij familielid in 1e of 2e graad
- Hoge myopie (> -6) of hypermetropie (> +5) bij familielid
- Ex-prematuren, dysmaturen en kinderen met (multiple) beperkingen of een gehoorstoornis
Tabel B8 Verwijscriteria visus met E-Haken en LEA Symbolen op 54-66 maanden
|
|
VOD | ≤0.12 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.63 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| VOS | |||||||||||
| ≤0.12 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.16 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.2 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.25 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.3 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.4 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.5 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | |
| 0.63 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | T | T | T | |
| 0.8 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | T | V | V | |
| 1.0 | O | O | O | O | O | O | O | T | V | V |
V= Voldoende visus
O= Onvoldoende visus, verwijzen
T= Twijfel visus, binnen 3 maanden visus herhalen. Bij twee keer twijfelen het kind verwijzen.
*Bij elk kind en elk oog doortesten tot hoogst haalbare visus met een maximum van 1.0, dus niet stoppen bij visus van 0.8
Bij hertest vanwege onvoldoende visus: beide ogen herhalen maar starten met oog dat slechtste visus had bij het vorige onderzoek.
6.5.5 Kinderen vanaf 7 jaar
Bij kinderen vanaf zeven jaar wordt een visusmeting verricht wanneer aan één of meer van de volgende criteria is voldaan, maar het kind niet bekend is bij een oogarts of orthoptist:
- verzoek ouders, kind of school vanwege twijfel over visus;
- geen eerdere visusmeting verricht;
- regelmatig hoofdpijnklachten;
- leer- en/of leesproblemen;
- beide ouders brildragend of bekend bij oogarts
Vanaf 10 jaar mag ook verwezen worden naar een optometrist/optiek bedrijf.
7 Bijlage 2: nuttige websites en boeken
- Oogheelkunde
- Orthoptisten
- Eyewiki
- NVK-Leidraad voor de medische begeleiding van kinderen met neurofibromatose type 1.
- Protocol screening Down-syndroom (verwijzing naar NVK-richtlijn)
- Multidisciplinaire richtlijn voor de medische begeleiding van kinderen met Downsyndroom
- Protocol screening Marfan-syndroom (verwijzing naar NVK-richtlijn)
- JIA screening
- Richtlijn CVI
- Richtlijn Nachtlenzen bij kinderen
Tan H, van der Pol B.A.E., Stilma J.S. Leerboek oogheelkunde (2013). Hoofdstuk 1 Anatomie en fysiologie (Imhof S.M., Bleys R.L.A.W.), Hoofdstuk 2 (t/m 2.2.1): Anamnese en algemeen oogheelkundig onderzoek (Cruysberg L.P.J.) en Hoofdstuk 6: Oogheelkundige problemen op de kinderleeftijd (Schalij-Delfos N.E.)
8 Bijlage 4: literatuuronderzoek naar de mogelijke rol van automatische meetapparatuur/fotoscreeners (PlusOptix vision screener) bij de opsporing van oogafwijkingen
Met automatische meetapparatuur/fotoscreeners (zoals de PlusOptix vision screener) wordt amblyopie niet opgespoord. Ze worden in een aantal landen wel gebruikt bij de opsporing van risicofactoren op amblyopie. Eind 2017 is een door ZonMw gesubsidieerde studie in Nederland naar de PlusOptix, uitgevoerd door TNO, afgerond. De wetenschappelijke publicaties over deze studie zijn nog niet verschenen. In juni 2018 heeft Kind en Gezin Vlaanderen besloten de Plusoptix fotoscreener niet meer te gebruiken bij de oogscreening. Hieronder volgt de beoordeling op basis van de systematische review van Sanchez en collega’s [66] en de overwegingen op basis van andere relevante artikelen en ervaring uit de praktijk.
Aanbevelingen
Fotoscreeners zullen geen rol spelen in de opsporing van oogafwijkingen zoals geformuleerd in deze richtlijn.
De studie “Can vision screening in Dutch Youth Health Care (YHC) be improved by adding PlusOptix – a feasibility study” van TNO is afgerond. Er is meer gedetailleerd onderzoek nodig voordat invoering in het landelijk screeningsprogramma overwogen kan worden.
Uitgangsvraag
Wat is de diagnostische accuratesse van de PlusOptix Vision Screener voor het vroegtijdig opsporen van (risicofactoren voor) amblyopie bij kinderen van 0-4 jaar?
Deze uitgangsvraag is uitgewerkt via de volgende PICO:
P: kinderen van 0-4 jaar, bij voorkeur in algemene populatie / screening setting
I: PlusOptix fotoscreener (type S08, S09, A09, S12), ongedilateerd onderzoek
C: volledige oogheelkundig onderzoek
O: aantallen terecht positief, terecht negatief, fout positief, fout negatief, sensitiviteit, specificiteit, voorspellende waarden, succesvolle amblyopiebehandeling.
3. Methode
De systematische review van Sanchez en collega’s, aangedragen door de richtlijnwerkgroep, werd als uitgangspunt genomen [66]. De zoekactie voor deze systematische review van diagnostische accuratesse studies (in de databases Medline en PubMed) omvatte Engelstalige publicaties tot januari 2016. Omdat in deze systematische review meerdere typen PlusOptix Vision Screeners werden opgenomen en de resultaten onvoldoende gedetailleerd beschreven werden, werd besloten de voor onze vraag relevante studies uit de review te selecteren. Op 13 september 2016 werd vervolgens voor de periode vanaf januari 2016 een zoekactie gedaan naar diagnostische accuratessestudies in de databases Medline en Embase. Na het sluiten van de systematische literatuurstudie van Cochrane Netherlands is nog een review verschenen van de U.S. Preventive Services Taskforce [21]. Deze review blijkt geen nieuwe inzichten te geven en heeft dus geen consequenties voor deze richtlijn.
4. Onderbouwing
Er werd één referentie geïncludeerd [64]. Het betreft een diagnostische accuratesse studie van de PlusOptix S 09 Vision Screener voor het opsporen van risicofactoren op amblyopie bij 108 kinderen van 9 tot 146 maanden oud. Deelnemers werden onderzocht met de PlusOptix S09 Vision Screener en kregen vervolgens een oogheelkundig onderzoek bestaande uit een visusmeting, onderzoek van oogstand, motiliteit (bewegingen) en voorste oogsegment, en een cycloplegische refractie. Of er daadwerkelijk risicofactoren voor amblyopie aanwezig waren (en dus een terechte doorverwijzing voor een oogheelkundig onderzoek), werd beoordeeld aan de hand van de AAPOS 2003 criteria (een anisometropie van groter dan 1.0 dioptrieën (D); hypermetropie van groter dan 3.5D; een astigmatisme van meer dan 1.5D axiaal of 1.0D schuin; myopie van groter dan 3.0D of een aanwezigheid van manifest strabismus) [65]. De kans vooraf op één van deze risicofactoren was 56% in de studiepopulatie. De sensitiviteit, specificiteit en positief voorspellende waarde werden bepaald. De resultaten voor 62 kinderen van 0 tot 4 jaar oud werden in de studie afzonderlijk gerapporteerd. De sensitiviteit, specificiteit en positief voorspellende waarde waren respectievelijk 74%, 92% en 89%. Bij 21% van de kinderen lukte het niet om een bruikbare meting te verkrijgen.
5. Kwaliteit van bewijs
Vanwege imprecisie met betrekking tot de effectschatting werd de kwaliteit van het bewijs als laag ingeschat.
6. Conclusies
| laag (GRADE) | Bij kinderen met een hoog risico op amblyopie in de leeftijdscategorie 0-4 jaar zal bij het gebruik van de PlusoptiX S09 Vision Screener 26% van de kinderen met een daadwerkelijke risicofactor voor amblyopie ten onrechte niet verwezen worden en zal 8% van de kinderen zonder daadwerkelijke risicofactor voor amblyopie ten onrechte verwezen worden. In 21% van de gevallen zal geen bruikbare meting worden verkregen. [64] |
Referenties
[1] Argumentenfabriek. Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg. 2014
[2] Koninklijke Nederlandsche Maatschappij tot bevordering der Geneeskunst. KNMG-visie Versterking medische zorg aan jeugdigen 2013
http://knmg.artsennet.nl/[3] Graham PA. Epidemiology of strabismus. The British journal of ophthalmology 1974;58(3):224-31
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4834596[4] Holmes JM, Clarke MP. Amblyopia. Lancet (London, England) 2006;367(9519):1343-51
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16631913[5] Lee C-W, Fang S-Y, Tsai D-C, Huang N, Hsu C-C, Chen S-Y, Chiu AW-H, Liu CJ-L. Prevalence and association of refractive anisometropia with near work habits among young schoolchildren: The evidence from a population-based study. PloS one 2017;12(3):e0173519
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173519 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28273153[6] Urbanus-van Laar N. Ethnic inequalities in quality of care for children in the Netherlands [Proefschrift]. Amsterdam: Universiteit van Amsterdam 2007
[7] Nederlands Jeugdinstituut. Factsheet media in het gezin. 2015
[8] Neitz M, Neitz J. Molecular genetics of color vision and color vision defects. Archives of ophthalmology (Chicago, Ill. : 1960) 2000;118(5):691-700
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10815162[9] Xiong S, Sankaridurg P, Naduvilath T, Zang J, Zou H, Zhu J, Lv M, He X, Xu X. Time spent in outdoor activities in relation to myopia prevention and control: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta ophthalmologica 2017;95(6):551-566
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aos.13403 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28251836[10] Simons K. Preschool vision screening: rationale, methodology and outcome. Survey of ophthalmology 1996;41(1):3-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8827927[11] Tedja MS, Wojciechowski R, Hysi PG, Eriksson N, Furlotte NA, Verhoeven VJM, Iglesias AI, Meester-Smoor MA, Tompson SW, Fan Q, Khawaja AP, Cheng C-Y, Höhn R, Yamashiro K, Wenocur A, Grazal C, Haller T, Metspalu A, Wedenoja J, Jonas JB, Wang YX, Xie J, Mitchell P, Foster PJ, Klein BEK, Klein R, Paterson AD, Hosseini SM, Shah RL, Williams C, Teo YY, Tham YC, Gupta P, Zhao W, Shi Y, Saw W-Y, Tai E-S, Sim XL, Huffman JE, Polašek O, Hayward C, Bencic G, Rudan I, Wilson JF, , , , Joshi PK, Tsujikawa A, Matsuda F, Whisenhunt KN, Zeller T, van der Spek PJ, Haak R, Meijers-Heijboer H, van Leeuwen EM, Iyengar SK, Lass JH, Hofman A, Rivadeneira F, Uitterlinden AG, Vingerling JR, Lehtimäki T, Raitakari OT, Biino G, Concas MP, Schwantes-An T-H, Igo RP, Cuellar-Partida G, Martin NG, Craig JE, Gharahkhani P, Williams KM, Nag A, Rahi JS, Cumberland PM, Delcourt C, Bellenguez C, Ried JS, Bergen AA, Meitinger T, Gieger C, Wong TY, Hewitt AW, Mackey DA, Simpson CL, Pfeiffer N, Pärssinen O, Baird PN, Vitart V, Amin N, van Duijn CM, Bailey-Wilson JE, Young TL, Saw S-M, Stambolian D, MacGregor S, Guggenheim JA, Tung JY, Hammond CJ, Klaver CCW. Genome-wide association meta-analysis highlights light-induced signaling as a driver for refractive error. Nature genetics 2018;50(6):834-848
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0127-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29808027[12] Tideman JWL, Polling JR, van der Schans A, Verhoeven VJM, Klaver CCW. [Myopia, a growing health problem]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2016;160():D803
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27879184[13] TNO. Belang van buitenspelen. 2011
[14] Wright KW, Strube YNJ. Postnatal development. Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 2nd ed. New York. In: Springer-Verlag 2003
[15] Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4-5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England) 2008;12(25):iii, xi-194
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18513466[16] Chou R, Dana T, Bougatsos C. Screening for visual impairment in children ages 1-5 years: update for the USPSTF. Pediatrics 2011;127(2):e442-79
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-0462 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21282269[17] Eibschitz-Tsimhoni M, Friedman T, Naor J, Eibschitz N, Friedman Z. Early screening for amblyogenic risk factors lowers the prevalence and severity of amblyopia. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2000;4(4):194-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10951293[18] Groenewoud JH, Tjiam AM, Lantau VK, Hoogeveen WC, de Faber JTHN, Juttmann RE, de Koning HJ, Simonsz HJ. Rotterdam AMblyopia screening effectiveness study: detection and causes of amblyopia in a large birth cohort. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2010;51(7):3476-84
http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.08-3352 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20089868[19] Institut fuer Qualitaet und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen. Screening for visual impairment in children(Structured abstract). Health Technology Assessment Database 2008
[20] IQWIG. Screening for visual impairment in children younger than 6 years: rapid report (Structured abstract). Health Technology Assessment Database 2015
[21] Jonas DE, Amick HR, Wallace IF, Feltner C, Vander Schaaf EB, Brown CL, Baker C. No title 2017
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29561582[22] Magnusson G, Persson U. Screening for congenital cataracts: a cost-consequence analysis of eye examination at maternity wards in comparison to well-baby clinics. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2005;94(8):1089-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16188854[23] Mathers M, Keyes M, Wright M. A review of the evidence on the effectiveness of children's vision screening. Child: care, health and development 2010;36(6):756-80
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2214.2010.01109.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20645997[24] Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion. Effectiveness of vision screening programs for children aged one to six years. Queen's Printer for Ontario: Toronto 2016
[25] Powell C, Hatt SR. Vision screening for amblyopia in childhood. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2009
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005020.pub3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19588363[26] Powell C, Wedner S, Richardson S. Screening for correctable visual acuity deficits in school-age children and adolescents. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2005
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15654703[27] Sami A, Karaman H, Sloot F, Sjoerdsma T, Banjamins J, Simonsz HJ. Quality of eye screening examinations at Child Health Centers in the Netherlands assessed by semi-structured observations. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2014;55(432):
[28] Sloot F, Sami A, Karaman H, Benjamins J, Loudon SE, Raat H, Sjoerdsma T, Simonsz HJ. Effect of omission of population-based eye screening at age 6-9 months in the Netherlands. Acta ophthalmologica 2015;93(4):318-21
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aos.12556 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25270899[29] Sloot F, Sami A, Karaman H, Gutter M, Benjamins J, Sjoerdsma T, Simonsz HJ. Semistructured Observation of Population-based Eye Screening in The Netherlands. Strabismus 2017;25(4):214-221
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09273972.2017.1395596 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29182469[30] Schmucker C, Grosselfinger R, Riemsma R, Antes G, Lange S, Lagrèze W, Kleijnen J. Effectiveness of screening preschool children for amblyopia: a systematic review. BMC ophthalmology 2009;9():3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2415-9-3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19607693[31] Hull S, Tailor V, Balduzzi S, Rahi J, Schmucker C, Virgili G, Dahlmann-Noor A. Tests for detecting strabismus in children aged 1 to 6 years in the community. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2017;11(11):CD011221
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011221.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29105728[32] Tung IC, Tsai RK, Chang CH, Sheu MM. Comparison of Trained Kindergarten Teachers and Public Health Nurses in the Administration of Preschool Amblyopia and Strabismus Screening Tests. Journal of Tzu Chi Medical Sciences 2006;18(1):29
[33] West S, Williams C. Amblyopia. BMJ clinical evidence 2011;2011():
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21714945[34] Williams C, Northstone K, Harrad RA, Sparrow JM, Harvey I, . Amblyopia treatment outcomes after preschool screening v school entry screening: observational data from a prospective cohort study. The British journal of ophthalmology 2003;87(8):988-93
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12881342[35] Williams C, Harrad RA, Harvey I, Sparrow JM, . Screening for amblyopia in preschool children: results of a population-based, randomised controlled trial. ALSPAC Study Team. Avon Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood. Ophthalmic epidemiology 2001;8(5):279-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11922382[36] Adhikari S, Shrestha U. Validation of performance of certified medical assistants in preschool vision screening examination. Nepalese journal of ophthalmology : a biannual peer-reviewed academic journal of the Nepal Ophthalmic Society : NEPJOPH 2011;3(2):128-33
http://dx.doi.org/10.3126/nepjoph.v3i2.5264 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21876585[37] Awan M, Proudlock FA, Grosvenor D, Choudhuri I, Sarvanananthan N, Gottlob I. An audit of the outcome of amblyopia treatment: a retrospective analysis of 322 children. The British journal of ophthalmology 2010;94(8):1007-11
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2008.154674 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19955200[38] Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. The course of moderate amblyopia treated with atropine in children: experience of the amblyopia treatment study. American journal of ophthalmology 2003;136(4):630-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14516802[39] Becker R, Hübsch S, Gräf MH, Kaufmann H. Examination of young children with Lea symbols. The British journal of ophthalmology 2002;86(5):513-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11973243[40] Bertuzzi F, Orsoni JG, Porta MR, Paliaga GP, Miglior S. Sensitivity and specificity of a visual acuity screening protocol performed with the Lea Symbols 15-line folding distance chart in preschool children. Acta ophthalmologica Scandinavica 2006;84(6):807-11
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17083543[41] Bušić M, Bjeloš M, Petrovečki M, Kuzmanović Elabjer B, Bosnar D, Ramić S, Miletić D, Andrijašević L, Kondža Krstonijević E, Jakovljević V, Bišćan Tvrdi A, Predović J, Kokot A, Bišćan F, Kovačević Ljubić M, Motušić Aras R. Zagreb Amblyopia Preschool Screening Study: near and distance visual acuity testing increase the diagnostic accuracy of screening for amblyopia. Croatian medical journal 2016;57(1):29-41
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26935612[42] Chen P-L, Chen J-T, Tai M-C, Fu J-J, Chang C-C, Lu D-W. Anisometropic amblyopia treated with spectacle correction alone: possible factors predicting success and time to start patching. American journal of ophthalmology 2007;143(1):54-60
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17113556[43] Clarke MP, Wright CM, Hrisos S, Anderson JD, Henderson J, Richardson SR. Randomised controlled trial of treatment of unilateral visual impairment detected at preschool vision screening. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2003;327(7426):1251
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14644966[44] Engin O, Despriet DDG, van der Meulen-Schot HM, Romers A, Slot X, Sang MTF, Fronius M, Kelderman H, Simonsz HJ. Comparison of optotypes of Amsterdam Picture Chart with those of Tumbling-E, LEA symbols, ETDRS, and Landolt-C in non-amblyopic and amblyopic patients. Graefe's archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie 2014;252(12):2013-20
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2763-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25228066[45] Flynn JT, Woodruff G, Thompson JR, Hiscox F, Feuer W, Schiffman J, Corona A, Smith LK. The therapy of amblyopia: an analysis comparing the results of amblyopia therapy utilizing two pooled data sets. Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society 1999;97():373-90; discussion 390-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10703134[46] Friendly DS. Preschool visual acuity screening tests. Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society 1978;76():383-480
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/754379[47] Hussein MAW, Coats DK, Muthialu A, Cohen E, Paysse EA. Risk factors for treatment failure of anisometropic amblyopia. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2004;8(5):429-34
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15492734[48] Kvarnström G, Jakobsson P. Is vision screening in 3-year-old children feasible? Comparison between the Lea Symbol chart and the HVOT (LM) chart. Acta ophthalmologica Scandinavica 2005;83(1):76-80
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15715562[49] Lai Y-H, Tseng H-Y, Hsu H-T, Chang S-J, Wang H-Z. Uncorrected visual acuity and noncycloplegic autorefraction predict significant refractive errors in Taiwanese preschool children. Ophthalmology 2013;120(2):271-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.08.009 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23182455[50] Lithander J, Sjöstrand J. Anisometropic and strabismic amblyopia in the age group 2 years and above: a prospective study of the results of treatment. The British journal of ophthalmology 1991;75(2):111-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1995038[51] Lokesh H, Bindurani M. Management of amblyopia by occlusion therapy. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences 2015;6(4):972
[52] Mazow ML, Chuang A, Vital MC, Prager T. 1999 Costenbader Lecture. Outcome study in amblyopia: treatment and practice pattern variations. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2000;4(1):1-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10675864[53] NVvO NOG OVN. Plan geïntegreerde oogzorg. 2013
[54] Ore L, Garzozi HJ, Tamir A, Stein N, Cohen-Dar M. Performance measures of the illiterate E-chart vision-screening test used in Northern District Israeli school children. Journal of medical screening 2008;15(2):65-71
http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/jms.2008.007094 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18573773[55] Ore L, Garzozi HJ, Tamir A, Cohen-Dar M. Vision screening among northern Israeli Jewish and Arab schoolchildren. The Israel Medical Association journal : IMAJ 2009;11(3):160-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19544706[56] Schmucker C, Kleijnen J, Grosselfinger R, Riemsma R, Antes G, Lange S, Lagrèze W. Effectiveness of early in comparison to late(r) treatment in children with amblyopia or its risk factors: a systematic review. Ophthalmic epidemiology 2010;17(1):7-17
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09286580903312301 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20100095[57] Stewart CE, Fielder AR, Stephens DA, Moseley MJ. Treatment of unilateral amblyopia: factors influencing visual outcome. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2005;46(9):3152-60
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16123414[58] Telleman MAJ, Sloot F, Benjamins J, Simonsz HJ. High rate of failed visual-acuity measurements with the Amsterdam Picture Chart in screening at the age of 36 months. Acta ophthalmologica 2019;97(1):24-28
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aos.13898 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30284395[59] Tjiam AM, Groenewoud JH, Passchier J, Loudon SE, De Graaf M, Hoogeveen WC, Lantau VK, Juttmann RE, De Koning HJ, Simonsz HJ. Determinants and outcome of unsuccessful referral after positive screening in a large birth-cohort study of population-based vision screening. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2011;15(3):256-62
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2011.01.159 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21777799[60] Wallace DK, Lazar EL, Crouch ER, Hoover DL, Kraker RT, Tamkins SM, . Time course and predictors of amblyopia improvement with 2 hours of daily patching. JAMA ophthalmology 2015;133(5):606-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.6 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25695355[61] CEN. European Standard: Ophthalmic opties - Visual acuity testing - Standard symbool and its presentation 2018
[62] Sheedy JE, Bailey IL, Raasch TW. Visual acuity and chart luminance. American journal of optometry and physiological optics 1984;61(9):595-600
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6507580[63] NEN. European Standard: Ophthalmic opties - Visual acuity testing - Standard optotype and its presentation 2017
[64] Arnold RW, Armitage MD. Performance of four new photoscreeners on pediatric patients with high risk amblyopia. Journal of pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus 2014;51(1):46-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20131223-02 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24369683[65] Donahue SP, Arnold RW, Ruben JB, . Preschool vision screening: what should we be detecting and how should we report it? Uniform guidelines for reporting results of preschool vision screening studies. Journal of AAPOS : the official publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2003;7(5):314-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14566312[66] Sanchez I, Ortiz-Toquero S, Martin R, de Juan V. Advantages, limitations, and diagnostic accuracy of photoscreeners in early detection of amblyopia: a review. Clinical ophthalmology (Auckland, N.Z.) 2016;10():1365-73
http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S93714 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27555744Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackLET OP: print de JGZ-richtlijn in liggende afdrukstand!
Grote tabellen zijn niet volledig zichtbaar als de JGZ-richtlijn in staande afdrukstand geprint wordt. Om kleuren in de printversie goed door te laten komen, moet bij de printerinstellingen Achtergrondillustraties aangezet worden.
Disclaimer printversie JGZ-richtlijnen
De printversie van de JGZ-richtlijn bevat de algemene tekst inclusief de aanbevelingen. De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing is terug te vinden op de website, bij de aanbevelingen onder de link “Evidence”.
