Lees meer in de onderliggende hoofdstukken.
5 Begeleiden en behandelen
JGZ-richtlijn Heupdysplasie
JGZ-richtlijn Heupdysplasie
Let op: deze richtlijn is momenteel in herziening.
Dit betekent niet dat de inhoud van deze richtlijn incorrect is. Tot de herziening blijft de richtlijn leidend voor de praktijk. Wel bestaat er een kans dat een deel van de informatie verouderd is.
Heb je feedback over deze JGZ-richtlijn? Stuur jouw feedback naar onze servicedesk. Zoek het tekstgedeelte waarbij je suggesties voor verbetering hebt. Via de knop ‘Geef jouw feedback’ kun je voor deze JGZ-richtlijn en het specifieke hoofdstuk jouw suggesties doorgeven.
Richtlijn inhoudsopgave
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definitie en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definitie en achtergrond informatie
3 Risicofactoren en beschermende factoren Ga naar pagina over 3 Risicofactoren en beschermende factoren
4 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen van DDH Ga naar pagina over 4 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen van DDH
5 Begeleiden en behandelen Ga naar pagina over 5 Begeleiden en behandelen
6 Communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ-professionals Ga naar pagina over 6 Communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ-professionals
7 Samenwerken Ga naar pagina over 7 Samenwerken
8 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 8 Totstandkoming richtlijn
9 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 9 Verantwoording
10 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 10 Bijlagen
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definitie en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definitie en achtergrond informatie
3 Risicofactoren en beschermende factoren Ga naar pagina over 3 Risicofactoren en beschermende factoren
4 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen van DDH Ga naar pagina over 4 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen van DDH
5 Begeleiden en behandelen Ga naar pagina over 5 Begeleiden en behandelen
6 Communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ-professionals Ga naar pagina over 6 Communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ-professionals
7 Samenwerken Ga naar pagina over 7 Samenwerken
8 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 8 Totstandkoming richtlijn
9 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 9 Verantwoording
10 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 10 Bijlagen
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackSamenvattingskaart richtlijn Heupdysplasie
PP-presentatie voor de scholing Heupdysplasie
Randvoorwaardelijke implicaties richtlijn Heupdysplasie
Rapportage praktijktest richtlijn Heupdysplasie
BDS-registratieprotocol richtlijn Heupdysplasie
Bijlage 6 Cliëntfolder richtlijn Heupdysplasie
Veel gestelde vragen over richtlijn Heupdysplasie
Bijlage 3 Screenings- handelings- en verwijsprotocol 0 t/m 6 maanden
Bijlage 4 Onderzoeks- en verwijsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen vanaf 7 maanden
Bijlage 5 Activiteiten per contactmoment in de leeftijdsperiode 0 t/m 6 maanden richtlijn heupdysplasie
Bijlage 1 Anamnese op basis van risicofactoren
[1] Klisic PJ. Congenital dislocation of the hip--a misleading term: brief report. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1989;71(1):136
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2914985[2] CBO en De Argumentenfabriek, Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg. 2014
[3] Boere-Boonekamp M.M., Mostert A.K.. Dysplastische heupontwikkeling, in Basisboek Jeugdgezondheidszorg in Nederland. 2010, Elsevier Gezondheidszorg: Maarssen. p. 139-52 2010
[4] Hasegawa Y, Iwata H, Mizuno M, Genda E, Sato S, Miura T. The natural course of osteoarthritis of the hip due to subluxation or acetabular dysplasia. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery 1992;111(4):187-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1622705[5] Wedge JH, Wasylenko MJ. The natural history of congenital dislocation of the hip: a critical review. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1978
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/743823[6] Kingma M.J.. Nederlands Leerboek der orthopedie. 1977, Utrecht: Bohn, Scheltema & Holkema. 1977
[7] Boere-Boonekamp M, Ikkink A., E S, L V, Hurts M., Koornstra G., Roodbergen J., D S, Vriezen J., Wensing-Souren C.. Landelijke Eerstelijns Samenwerkings Afspraak Dysplastische HeupOntwikkeling Huisarts En Wetenschap 2010/01/01
[8] Graf R. [Hip ultrasonography. Basic principles and current aspects]. Der Orthopade 1997;26(1):14-24
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9082298[9] Graf R. Hip Sonography: Diagnosis and Management of Infant Hip Dysplasia 2006: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2006
[10] Graf R. Essentials of Infant Hip Sonography - According to Graf (manual). 2014: Stozalpe. 2014
[11] Graf R. Sonographie der Säuglingshüfte und therapeutische Konsequenzen. 2000, Stutgart: Georg Thieme Verlag. 2000
[12] Tönnis D., Brunken D.. Eine Abgrenzung normaler und pathologischer Hüftpfannendachwinkel zur Diagnose der Hüftdysplasie Archiv für orthopädische und Unfall-Chirurgie, mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Frakturenlehre und der orthopädisch-chirurgischen Technik 1968;64(3):197
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02171260 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02171260[13] Boere-Boonekamp M.M.. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip (dissertation). 1996. 1996
[14] Jackson JC, Runge MM, Nye NS. Common questions about developmental dysplasia of the hip. American family physician 2014;90(12):843-50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25591184[15] de Hundt M, Vlemmix F, Bais JMJ, Hutton EK, de Groot CJ, Mol BWJ, Kok M. Risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a meta-analysis. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology 2012;165(1):8-17
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.06.030 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22824571[16] Ortiz-Neira CL, Paolucci EO, Donnon T. A meta-analysis of common risk factors associated with the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. European journal of radiology 2012;81(3):e344-51
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.11.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22119556[17] American Academy of Pediatrics, Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: recommendation statement. Pediatrics 2006;117(3):898-902
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16510673[18] Shaw ED, Beals RK. The hip joint in Down's syndrome. A study of its structure and associated disease. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1992
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1532929[19] Broughton NS, Menelaus MB, Cole WG, Shurtleff DB. The natural history of hip deformity in myelomeningocele. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1993;75(5):760-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8376434[20] Lonstein JE, Beck K. Hip dislocation and subluxation in cerebral palsy. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1986;6(5):521-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3760161[21] Sharrard WJ, Allen JM, Heaney SH. Surgical prophylaxis of subluxation and dislocation of the hip in cerebral palsy. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1975;57(2):160-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1141282[22] Tönnis D.. Congenital Dysplasia and Dislocation of the Hip in Children and Adults. 1987
[23] Visser J.D.. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerste lijn gezondheidszorg. 2012
[24] Ziegler J, Thielemann F, Mayer-Athenstaedt C, Günther K-P. [The natural history of developmental dysplasia of the hip. A meta-analysis of the published literature]. Der Orthopade 2008;37(6):515-6, 518-24
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00132-008-1238-0 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18483804[25] Scharft A., Boere-Boonekamp M.M., Van der Kaap H.. Onderzoek naar de gezondheidsgerelateerde kwaliteit van leven bij (jong)volwassen (vrouwen) met dysplastische heupontwikkeling (bachelorscriptie). 2008
[26] Blom R.. Inbakeren brengt rust. Een handleiding voor het inbakeren van je kind. 2011
[27] Panagiotopoulou N, Bitar K, Hart WJ. The association between mode of delivery and developmental dysplasia of the hip in breech infants: a systematic review of 9 cohort studies. Acta orthopaedica Belgica 2012;78(6):697-702
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23409562[28] Blom R.. Regelmaat en inbakeren. 2010: Uitgeverij Christofoor. 2010
[29] Guner SI, Guner S, Peker E, Ceylan MF, Guler A, Turktas U, Kaki B. Are consanguineous marriage and swaddling the risk factors of developmental dysplasia of the hip? The Journal of membrane biology 2013;246(2):115-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9509-4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23080296[30] Li L.S., Zhang L., Zhao Q., Cheng X., Dang Y.. Heritability and sibling recurrent risk of developmental dysplasia of the hip in Chinese population. European journal of clinical investigation, 2013. 43(6): p. 589-594.
[31] Rühmann O, Konermann W, Lazović D, Vitek L, Bouklas P. [Ultrasound neonatal screening: the effect of anamnestic risk factors on hip dysplasia]. Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und ihre Grenzgebiete 1998;136(6):492-500
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10036736[32] Rühmann O, Lazović D, Bouklas P, Gossé F, Franke J. [Ultrasound hip joint screening in newborn infants. Correlation of anamnestic risk factors and hip dysplasia]. Klinische Padiatrie 1999;211(3):141-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10412123[33] Peterlein CD, Penner T, Schmitt J, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Fölsch C. [Sonographic screening of the newborn hip at the university hospital Marburg--a long-run analysis]. Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und Unfallchirurgie 2014;152(3):234-40
http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1368446 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24960091[34] Patterson C.C.K., Mollan R.A., Haugh P.E., Trainor B.P.. High incidence of congenital dislocation of the hip in Northern Ireland. Paediatric and perinatal epidemiology, 1995. 9(1): p. 90-97. 1995
[35] Uludag S, Seyahi A, Orak MM, Bilgili MG, Colakoglu B, Demirhan M. The effect of gestational age on sonographic screening of the hip in term infants. The bone & joint journal 2013;95-B(2):266-70
http://dx.doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.95B2.30798 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23365040[36] Partenheimer A, Scheler-Hofmann M, Lange J, Kühl R, Follak N, Ebner A, Fusch C, Stenger R, Merk H, Haas JP. [Correlation between sex, intrauterine position and familial predisposition and neonatal hip ultrasound results]. Ultraschall in der Medizin (Stuttgart, Germany : 1980) 2006;27(4):364-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16596510[37] von Deimling U, Brähler JM, Niesen M, Wagner UA, Walpert J. [Effect of birth weight on hip maturation in the newborn infant]. Klinische Padiatrie 1998;210(3):115-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9629544[38] Boere-Boonekamp M.M.. Diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. The significance of anamnestic data and findings on physical examination. Huisarts en Wetenschap, 1997. 40(6): p. 236-243. 1997
[39] Shi D, Dai J, Ikegawa S, Jiang Q. Genetic study on developmental dysplasia of the hip European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2012;42(10):1121
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2012.02682.x https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2012.02682.x[40] Ibrahim T, Riaz M, Hegazy A. The prevalence of developmental dysplasia of the hip in idiopathic clubfoot: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International orthopaedics 2015;39(7):1371-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2757-z https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25846795[41] Harcke HT, Karatas AF, Cummings S, Bowen JR. Sonographic Assessment of Hip Swaddling Techniques in Infants With and Without DDH. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2016;36(3):232-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000446 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25851676[42] Chaarani M.W., Al Mahmeid M.S., Salman A.M.. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip before and after increasing community awareness of the harmful effects of swaddling. Qatar Medical Journal, 2002. 11(1): p. 40-43.
[43] Moosa NK, Kumar PT, Mahmoodi SM. Incidence of developmental dysplasia of the hip in Dubai. Saudi medical journal 2009;30(7):952-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19618014[44] van Sleuwen BE, Engelberts AC, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Kuis W, Schulpen TWJ, L'Hoir MP. Swaddling: a systematic review. Pediatrics 2007;120(4):e1097-106
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17908730[45] Sahin F, Aktürk A, Beyazova U, Cakir B, Boyunaga O, Tezcan S, Bölükbaşi S, Kanatli U. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: results of a 7-year follow-up study. Pediatrics international : official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society 2004;46(2):162-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15056242[46] Chan A, McCaul KA, Cundy PJ, Haan EA, Byron-Scott R. Perinatal risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 1997;76(2):F94-100
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9135287[47] Burke SM, Roberts JM, Johnston C. Congenital dislocation of the hip in the American black. Clin Orthop Relat Res., 1985. 192: p. 120-3. 1985
[48] Rühmann O, Lazović D, Bouklas P, Rössig S. [Ultrasound hip joint screening in newborn infants. Is twin pregnancy a risk factor for dysplasia?]. Ultraschall in der Medizin (Stuttgart, Germany : 1980) 1998;19(2):64-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9654671[49] Orak MM, Onay T., Gümüştaş SA, Gürsoy T., Muratlí HH. Is prematurity a risk factor for developmental dysplasia The Bone & Joint Journal 2015;97-B(5):716
http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B5.34010 https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B5.34010[50] Holen KJ, Tegnander A, Terjesen T, Johansen OJ, Eik-Nes SH. Ultrasonographic evaluation of breech presentation as a risk factor for hip dysplasia. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 1996;85(2):225-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8640055[51] Quan T, Kent AL, Carlisle H. Breech preterm infants are at risk of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Journal of paediatrics and child health 2013;49(8):658-63
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jpc.12250 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23758088[52] Hill LM. Prevalence of breech presentation by gestational age. American journal of perinatology 1990;7(1):92-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2403797[53] Hickok DE, Gordon DC, Milberg JA, Williams MA, Daling JR. The frequency of breech presentation by gestational age at birth: a large population-based study. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 1992;166(3):851-2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1550152[54] Fox AJS, Chapman MG. Longitudinal ultrasound assessment of fetal presentation: a review of 1010 consecutive cases. The Australian & New Zealand journal of obstetrics & gynaecology 2006;46(4):341-4
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16866797[55] Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2000
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10796122[56] Hofmeyr GJ. Interventions to help external cephalic version for breech presentation at term. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2004
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14973948[57] Lambeek AF, De Hundt M, Vlemmix F, Akerboom BMC, Bais JMJ, Papatsonis DNM, Mol BWJ, Kok M. Risk of developmental dysplasia of the hip in breech presentation: the effect of successful external cephalic version. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2013;120(5):607-12
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12013 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23145903[58] Anderssen SIE, Soukup M., Andersen AE. Congenital hip dysplasia in Ostfold 1990-96. Tidsskrift for den Norske laegeforening : tidsskrift for praktisk medicin, ny raekke, 2000. 120(29): p. 3530-3533. 2000
[59] Chan AKA, Cundy PJ, Haan EA, Byron-Scott R.. Perinatal risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Archives of disease in childhood.Fetal and neonatal edition, 1997. 76(2): p. F94-100. 1997
[60] CBO Kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg, Evidence-based Richtlijnontwikkeling. Handleiding voor werkgroepleden. 2007
[61] Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging (NOV) and Stichting LROI, Orthopedische implantaten in beeld. 2014
[62] Nederlandse Vereniging voor Obstetrie en Gynaecologie, Richtlijn Stuitligging. 2001
[63] Walsh JJ, Morrissy RT. Torticollis and hip dislocation. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1998;18(2):219-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9531405[64] Minihane KJJ, Simmons TD, Seshadri R., Wysocki RW, Sarwark JF. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants with congenital muscular torticollis. American journal of orthopedics (Belle Mead, N.J.), 2008. 37(9): p. E155-8; discussion E158. 2008
[65] Tien YC, Su JY, Lin GT, Lin SY. Ultrasonographic study of the coexistence of muscular torticollis and dysplasia of the hip. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2001;21(3):343-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11371818[66] Cheng JC, Tang SP, Chen TM. Sternocleidomastoid pseudotumor and congenital muscular torticollis in infants: a prospective study of 510 cases. The Journal of pediatrics 1999;134(6):712-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10356139[67] Castelein RM. [Physical diagnosis--Ortolani's manoeuvre]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2002;146(23):1077-80
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12085556[68] Patel H, . Preventive health care, 2001 update: screening and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2001;164(12):1669-77
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11450209[69] Paton RW. Screening for hip abnormality in the neonate. Early human development 2005;81(10):803-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16226409[70] American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Detection and nonoperative managment of pediatric developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants up to six months of age. 2014
[71] Paton RW, Srinivasan MS, Shah B, Hollis S. Ultrasound screening for hips at risk in developmental dysplasia. Is it worth it? The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1999;81(2):255-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10204931[72] Beentjes M, Weersma R., Koch W., Offringa A., Verduijn M, Mensink P., Wiersma T., Goudswaard L.. NHG-Standaard Zwangerschap en kraamperiode (tweede herziening) (NHG-Quality Standard Pregnancy and postnatal period (second revision)) Huisarts & Wetenschap 2012/01/01;55():1112
[73] Engelberts AC, Koerts B, Waelkens JJ, Wit JM, Burger BJ. [Measuring the length of newborn infants]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2005;149(12):632-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15813430[74] TNO, Groeidiagrammen 2010. Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen. 2010
[75] Omeroğlu H, Koparal S. The role of clinical examination and risk factors in the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a prospective study in 188 referred young infants. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery 2001;121(1-2):7-11
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11195123[76] Roposch A, Liu LQ, Hefti F, Clarke NMP, Wedge JH. Standardized diagnostic criteria for developmental dysplasia of the hip in early infancy. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 2011;469(12):3451-61
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-2066-9 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21952742[77] Stoffelen D, Urlus M, Molenaers G, Fabry G. Ultrasound, radiographs, and clinical symptoms in developmental dislocation of the hip: a study of 170 patients. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 1995;4(2):194-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7670989[78] Castelein RM, Korte J. Limited hip abduction in the infant. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2001;21(5):668-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11521039[79] Choudry Q, Goyal R, Paton RW. Is limitation of hip abduction a useful clinical sign in the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip? Archives of disease in childhood 2013;98(11):862-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2012-303121 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23946334[80] Jari S, Paton RW, Srinivasan MS. Unilateral limitation of abduction of the hip. A valuable clinical sign for DDH? The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 2002;84(1):104-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11837813[81] Senaran H, Ozdemir HM, Ogün TC, Kapicioglu MIS. Value of limited hip abduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatrics international : official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society 2004;46(4):456-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15310313[82] van Hees-van der Laan Z.J., Huttinga-Edens M.M.. Congenitale dysplasie van het heupgewricht bij zuigeligen; een onderzoek op consultatiebureaus in Groningen. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde, 1981. 125(47): p. 1913-1917. 1981
[83] Boere-Boonekamp MM, Kerkhoff TH, Schuil PB, Zielhuis GA. Early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip in The Netherlands: the validity of a standardized assessment protocol in infants. American journal of public health 1998;88(2):285-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9491024[84] Boere-Boonekamp MM, Verkerk PH. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip Seminars in Neonatology 1998;3(1):49
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1084-2756(98)80148-6 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084275698801486[85] Donnelly KJ, Chan KW, Cosgrove AP. Delayed diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip in Northern Ireland: can we do better? The bone & joint journal 2015;97-B(11):1572-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B11.35286 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26530663[86] Mudge AJ, Bau KV, Purcell LN, Wu JC, Axt MW, Selber P, Burns J. Normative reference values for lower limb joint range, bone torsion, and alignment in children aged 4-16 years. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2014;23(1):15-25
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e328364220a https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23852035[87] Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging (NOV). Systematische screening naar dysplastische heupontwikkeling bij een primaire idiopathische klompvoet. 2014; Geraadpleegd op 9 oktober 2017 2014
http://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/primaire_idiopathische_klompvoet/klompvoet_en_dysplas%20%20tische_heupontwikkeling.html#verantwoording.%20[88] Shipman SA, Helfand M, Moyer VA, Yawn BP. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a systematic literature review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics 2006;117(3):e557-76
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16510634[89] Roovers E.A.. Post-neonatal ultrasound screening for developmental dysplasie of the hip. A study on cost-effectiveness in the Netherlands (dissertation). 2004
[90] Ramwadhdoebe S.. Screening for developmental dysplkasie of the hip in primary care. Implementation by simulation (dissertation). 2010
[91] Witting M. Towards effective implementation strategies for ultrasound hip screening in child health care Tijdschrift voor Kindergeneeskunde 2012;80(2):49
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12456-012-0013-7 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12456-012-0013-7[92] . Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: recommendation statement. American family physician 2006;73(11):1992-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16770931[93] Clinical practice guideline: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics 2000;105(4 Pt 1):896-905
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10742345[94] Rosendahl K, Dezateux C, Fosse KR, Aase H, Aukland SM, Reigstad H, Alsaker T, Moster D, Lie RT, Markestad T. Immediate treatment versus sonographic surveillance for mild hip dysplasia in newborns. Pediatrics 2010;125(1):e9-16
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0357 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20026501[95] Bache CHK, Dickens DR, Donnan L., Johnson MB, Nattrass G., O'Sullivan M., Torode IP. Ligamentum teres tenodesis in medial approach open reduction for developmental dislocation of the hip. Journal of pediatric orthopedics, 2008. 28(6): p. 607-613. 2008
[96] Danielsson L. Late-diagnosed DDH: a prospective 11-year follow-up of 71 consecutive patients (75 hips). Acta orthopaedica Scandinavica 2000;71(3):232-42
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10919293[97] Fukiage K, Futami T, Ogi Y, Harada Y, Shimozono F, Kashiwagi N, Takase T, Suzuki S. Ultrasound-guided gradual reduction using flexion and abduction continuous traction for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a new method of treatment. The bone & joint journal 2015;97-B(3):405-11
http://dx.doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B3.34287 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25737526[98] Harding MG, Harcke HT, Bowen JR, Guille JT, Glutting J. Management of dislocated hips with Pavlik harness treatment and ultrasound monitoring. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1997;17(2):189-98
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9075094[99] Inoue T, Naito M, Nomiyama H. Treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip with the Pavlik harness: factors for predicting unsuccessful reduction. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2001;10(3):186-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11497359[100] Kitoh H, Kawasumi M, Ishiguro N. Predictive factors for unsuccessful treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip by the Pavlik harness. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2009;29(6):552-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181b2f200 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19700982[101] Zamzam MM, Kremli MK, Khoshhal KI, Abak AA, Bakarman KA, Alsiddiky AMM, Alzain KO. Acetabular cartilaginous angle: a new method for predicting acetabular development in developmental dysplasia of the hip in children between 2 and 18 months of age. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2008;28(5):518-23
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31817c4e6d https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18580365[102] Eidelman M, Katzman A, Freiman S, Peled E, Bialik V. Treatment of true developmental dysplasia of the hip using Pavlik's method. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2003;12(4):253-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12821841[103] Bialik GM, Eidelman M, Katzman A, Peled E. Treatment duration of developmental dysplasia of the hip: age and sonography. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2009;18(6):308-13
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e32832f12ba https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19593215[104] Lerman JA, Emans JB, Millis MB, Share J, Zurakowski D, Kasser JR. Early failure of Pavlik harness treatment for developmental hip dysplasia: clinical and ultrasound predictors. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2001;21(3):348-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11371819[105] Westacott DJ, Mackay ND, Waton A, Webb MSL, Henman P, Cooke SJ. Staged weaning versus immediate cessation of Pavlik harness treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2014;23(2):103-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0000000000000025 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24322535[106] Phelan NJ, Fox C., O'Daly BJ, O'Beirne J.. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: incidence and treatment outcomes in the Southeast of Ireland. Irish journal of medical science, 2015. 184(2): p. 411-415. 2015
[107] Shipman SM, Moyer VA, Yawn BP. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a systematic literature review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics, 2006. 117(3): p. e557-76. 2006
[108] Shorter D, Hong T, Osborn DA. Screening programmes for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborn infants. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2011;2011(9):CD004595
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004595.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21901691[109] Coussement C., Meulemans B.. Betere pijnbeheersing doet ouders vaccinatiekalender respecteren JGZ Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 2016/05/25;48():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12452-016-0061-y[110] Shendurnikar N, Thakkar PA. Communication skills to ensure patient satisfaction. Indian journal of pediatrics 2013;80(11):938-43
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12098-012-0958-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23378053[111] Barbosa CD, Balp M-M, Kulich K, Germain N, Rofail D. A literature review to explore the link between treatment satisfaction and adherence, compliance, and persistence. Patient preference and adherence 2012;6():39-48
http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S24752 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22272068[112] Berkenbosch TS, Ronde T., Konijnendijk AAJ, Boere-Boonekamp MM. Dysplastische heupontwikkeling: ervaringen van ouders met de screening door de jeugdgezondheidszorg JGZ Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 2016;48(3):57
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12452-016-0059-5 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12452-016-0059-5[113] Berkenbosch TR, Konijnendijk AAJ, Boere-Boonekamp MM. Tevredenheid van ouders met de screening op en de voorlichting en begeleiding bij dysplastische heupontwikkeling door de jeugdgezondheidszorg (bacheloropdracht). 2015
[114] Braun DD, Mansfield P.. How helping works. Towards a shared model of process. 2006, Londen: Parentline Plus. 2006
[115] Muller L.. Scholing: opvoedingsondersteuning vanuit het consultatiebureau. 2001: Centrum voor Advies en Training Luud Muller & Co. 2001
[116] Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, Boers M, Andersson N, Hamel C, Porter AC, Tugwell P, Moher D, Bouter LM. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC medical research methodology 2007;7():10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17302989[117] Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, DeBeer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of clinical epidemiology 2011;64(4):383-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21195583[118] Familie (verwanten) Wikipedia z.d. Geraadpleegd op 5 oktober 2017
https://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Familie_(verwanten)#Medisch_gebruik_van_de_familiegraden[119] van Ballegooijen M, de Kok IMCM, Habbema JDF. [Unequal discounting of health care costs and effects causes confusion]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2010;154():A1970
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20619050[120] JGZ Valent, Aangeboren heupafwijkingen. 2009
[121] Thuiszorg West-Brabant, Werkinstructie signaleren dysplastische heupontwikkeling. 2009
[122] GGD Gooi & Vechtstreek afdeling Jeugdgezondheidszorg, Protocol Dysplastische Heuptontwikkeling. 2006
[123] Thuiszorg Pantein Divisie JGZ, Protocol signaleren dysplastische heupontwikkeling. 2008
1 Inleiding
Deze richtlijn geeft handvatten voor het handelen van Jeugdgezondheidszorg (JGZ)-professionals tijdens contactmomenten met individuele kinderen van 0 tot 18 jaar* en hun ouders**. JGZ-professionals zijn jeugdartsen, verpleegkundig specialisten, jeugdverpleegkundigen en doktersassistenten. Daar waar in de richtlijn ‘jeugdarts’ staat, kan ook ‘verpleegkundig specialist’*** worden gelezen.
Internationaal wordt sinds begin jaren ‘90 van de twintigste eeuw in plaats van de term ‘heupdysplasie’ de term ‘Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip’ (DDH) gebruikt om het dynamische karakter van de aandoening te benadrukken [1]. In deze richtlijn wordt de Engelse afkorting DDH gehanteerd. Deze afkorting wordt ook door orthopeden en radiologen in Nederland gebruikt. Eenheid van taal is wenselijk wanneer verschillende zorgverleners samenwerken rondom een kind met (mogelijke) DDH. In de communicatie met ouders wordt de term heupdysplasie (met of zonder luxatie) gebruikt.
Onbehandeld kan DDH leiden tot ernstige invaliditeit en vroege coxartrose (slijtage van de heup). Daarom is vroege opsporing en tijdige behandeling essentieel. Late behandeling (voor DDH met luxatie na de leeftijd van 3 maanden, voor DDH zonder luxatie na de leeftijd van 6 maanden) is meestal langduriger, invasiever en minder effectief dan vroegtijdige behandeling. De JGZ heeft een belangrijke rol bij de opsporing van DDH.
Vanwege haar unieke positie binnen de Nederlandse gezondheidszorg is de JGZ bij uitstek geschikt de opsporing van DDH uit te voeren. In Nederland bestaan op dit moment echter de nodige verschillen in signalering van zuigelingen met DDH. Er worden verschillende definities gebruikt voor risicofactoren, signaleringsinstrumenten worden niet uniform toegepast, en het ontbreekt aan eenduidig beleid over wanneer en naar wie moet worden doorverwezen. Naast de belangrijke rol bij de signalering en verwijzing, kan de JGZ ook een rol spelen bij de begeleiding en nazorg van kinderen met DDH. Een heldere richtlijn kan de JGZ in deze taken ondersteunen.
Deze richtlijn is gebaseerd op de knelpuntanalyse uitgevoerd door het Centraal BegeleidingsOrgaan (CBO) [2]. Deelnemers aan de knelpuntenanalyse hebben uitgangsvragen opgesteld die in deze richtlijn worden beantwoord. Een projectgroep van medewerkers van de Universiteit Twente en TNO (Nederlandse Organisatie voor toegepast-natuurwetenschappelijk onderzoek) heeft de teksten voor de richtlijn geschreven in samenwerking met een werkgroep van deskundigen op het gebied van DDH en/of JGZ (zie onderdeel ‘Totstandkoming richtlijn’. De richtlijn is op 13 november 2017 geautoriseerd door de Richtlijn Advies- en Autorisatie Commissie (RAC) voor gebruik in de JGZ.
*Kinderen met syndromen of aandoeningen waarbij DDH relatief vaak voorkomt (zie paragraaf epidemiologie in de inleiding) vallen buiten de doelgroep van deze richtlijn. Het onderzoek naar DDH vindt bij deze kinderen plaats door de behandelaar.
**Daar waar in de richtlijn ‘ouder’ staat, kan ook ‘verzorger’ worden gelezen.
***De verpleegkundig specialist is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied. Zij werkt op expertniveau en is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ-team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
1.1 Leeswijzer
Deze richtlijn start met een inleiding over DDH.
De sectie Definitie en achtergrond informatie biedt informatie over o.a. beeldvormende diagnostiek, het natuurlijk beloop en de gevolgen. Ook de algemene aspecten van de behandeling worden hier beschreven.
De richtlijn beschrijft in de sectie Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen achtereenvolgens de anamnese over risicofactoren voor DDH en de methoden van lichamelijk onderzoek die betrouwbaar en door de JGZ toepasbaar zijn voor de opsporing van DDH.
De uit de literatuur verzamelde informatie leidde samen met de mening van deskundigen tot het opstellen van een protocol voor screening bij zuigelingen (leeftijdsperiode 0 t/m 6 maanden), signalering bij oudere kinderen (vanaf 7 maanden) en verwijzing bij aanwezige risicofactoren of afwijkende bevindingen. Dit protocol wordt beschreven in de subsectie Onderzoeks-, handelings en verwijsprotocol. Tot slot geeft de Sectie ook een samenvatting van alle aandachtspunten bij prematuriteit en DDH.
De sectie Begeleiden en behandelen beschrijft verder de aandachtspunten voor JGZ tijdens behandeling
De sectie Communicatie gaat in op de communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ professionals over screening en eventuele verwijzing en behandeling.
De sectie Samenwerken gaat ten slotte in op samenwerking tussen de JGZ en andere betrokken zorgverleners uit de eerste lijn (het JGZ-team, de huisarts, een diagnostisch centrum met expertise op het gebied van (echografisch) heuponderzoek bij kinderen (indien aanwezig), de kinderfysiotherapeut en de verloskundig zorgverlener) en de tweede/derde lijn (radioloog met expertise op het gebied van (echografisch) heuponderzoek bij kinderen, de (kinder)orthopeed, de klinisch verloskundig zorgverlener en de kinderarts) over onder andere verwijzing, behandeling en begeleiding.
2 Definitie en achtergrond informatie
Dit onderdeel geeft een introductie op developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). De tekst in deze introductie is grotendeels gebaseerd op informatie uit het basisboek JGZ [3].
2.1 Definitie
Bij DDH is sprake van een dysplasie (onderontwikkeling) van het heupgewricht. Dit leidt ertoe dat de heupkom de heupkop onvoldoende overdekt. DDH kan heupinstabiliteit veroorzaken of in ernstige gevallen leiden tot luxatie (ontwrichting van de heupkop uit de heupkom). Onbehandeld kan DDH leiden tot ernstige invaliditeit en vroege coxartrose (slijtage van de heup) [4][5].
De aandoening DDH kan op verschillende tijdstippen ontstaan en kent verschillende graderingen. Allereerst kan bij de geboorte sprake zijn van instabiele, luxeerbare heupen. Bij dergelijke luxeerbare heupen sluit de heupkop onvoldoende aan bij de heupkom. Meestal zullen deze heupen in de eerste weken spontaan herstellen. Ze kunnen echter ook op verschillende tijdstippen daarna (soms pas als het kind gaat lopen) (sub)luxeren. Bij subluxatie heeft de heupkop de heupkom slechts gedeeltelijk verlaten. Bij luxatie bevindt de heupkop zich volledig buiten de heupkom.
Het is ook mogelijk dat, hoewel bij de geboorte sprake is van stabiele heupen (zie A in figuur 1), er toch een verstoring van de normale ontwikkeling van het gewricht is opgetreden tijdens de zwangerschap of na de bevalling. Dit kan leiden tot een te steile en ondiepe heupkom, en een abnormaal naar ventraal gedraaide heupkop (dysplasie zonder luxatie, zie B in figuur 1). Als sprake is van een dergelijke discongruentie tussen heupkop en heupkom, kan de heupkop gemakkelijk uit de ondiepe kom glijden (dysplasie met subluxatie, zie C in figuur 1). De meest ernstige vorm van DDH is dysplasie met luxatie (D in figuur 1).
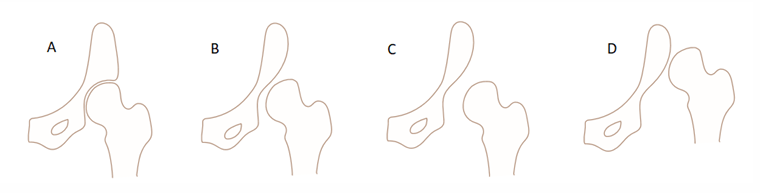
Figuur 1. Vereenvoudigde weergave van de verschillende graderingen van DDH [6].
2.2 Beeldvormende diagnostiek
De diagnose DDH wordt gesteld met behulp van aanvullend beeldvormend onderzoek: echografie of röntgenonderzoek. Welk type aanvullend onderzoek wordt aangevraagd bij vermoeden van DDH is afhankelijk van de leeftijd van het kind. Deze punten worden verder uitgewerkt in Onderzoeks- handelings- en verwijsprotocol en Samenwerken.
Echografie
Echografie is het onderzoek van eerste keus in de eerste 6 levensmaanden. Hiermee kunnen vanaf de geboorte de vroege ontwikkeling van zowel kraakbenige en benige structuren als de weke delen en de positie en de beweging van de heupkop in de heupkom in beeld worden gebracht [7]. In Nederland wordt vooral de methode van Graf gehanteerd en de bijbehorende classificering (zie tabel 1) [8], [9], [10]. Dit is voor de JGZ-professional van belang voor het interpreteren van uitslagen. Op sommige plaatsen in Nederland blijft echografie ook na de leeftijd van 6 maanden eerste keus en worden (ook) andere methoden van heupechografie gebruikt.
Tabel 1. Classificering van echografische heuptypes volgens Graf [9], [10]. De alpha-hoek en bèta-hoek geven informatie over de overdekking van de heupkop door respectievelijk het benige pandak (acetabulum) en het kraakbenige dak (labrum); deze hoekmetingen worden verricht in het standaardvlak (bij type III en IV heupen doorgaans niet mogelijk).
| Type | Leeftijd | Benig pandak | Benige erker | Kraakbenig dak | Alpha | Bèta | |
| I | Uitgerijpt heupgewricht | elke leeftijd | goed | hoekig/stomp | overdekkend | ≥ 60° | |
| IIa | Fysiologisch onrijp | 0-5 weken | voldoende | rond* | overdekkend | 50-59° | |
| IIa+ | Passend bij leeftijd | 6-12 weken | voldoende | rond* | overdekkend | 50-59° | |
| IIa- | Rijpingsachterstand | 6-12 weken | gebrekkig | rond* | overdekkend | 50-59° | |
| IIb | Vertraagde verbening | >12 weken | gebrekkig | rond* | overdekkend | 50-59° | |
| IIc | Kritische range: stabiel of instabiel | elke leeftijd | zeer gebrekkig | rond tot vlak | overdekkend | 43-49° | < 77° |
| D | Luxerende heup | elke leeftijd | zeer gebrekkig | rond tot vlak | verplaatst | 43-49° | ≥ 77° |
| III | Geluxeerde heup | elke leeftijd | slecht | vlak | naar craniaal verplaatst; en soms met structurele veranderingen | < 43° | |
| IV | Geluxeerde heup | elke leeftijd | slecht | vlak | verplaatst naar beneden-mediaal | < 43° |
* Er kan sprake kan zijn van secundaire verbening waardoor de benige erker hoekig oogt.
Type l betreft normale heupen (A in figuur 1). De typeringen IIa+ en lla- worden alleen gebruikt onder de leeftijd van 3 maanden om nog onvoldoende uitgerijpte heupen aan te duiden. De typering llb wordt gebruikt na de leeftijd van 3 maanden en betekent dat sprake is van dysplasie zonder luxatie (B in figuur 1). Type llc en D wijzen op dysplasie met subluxatie (C in figuur 1) en bij de types lll en lV is sprake van luxatie (D in figuur 1). De echografische typering van de heupen vindt plaats onafhankelijk van de zwangerschapsduur bij geboorte. Voor prematuriteit wordt echter wel gecorrigeerd als besloten moet worden of wel of niet behandeld gaat worden [11].
Röntgenonderzoek
Vanwege de toenemende verbening van de femurkop wordt het in de tweede helft van het eerste levensjaar geleidelijk lastiger om met echografie de heupkom goed af te beelden. In dat geval is röntgenonderzoek de aangewezen methode voor diagnostiek.
Het maken van een röntgenfoto wordt met name gedaan voor diagnostiek bij zuigelingen van circa 6 maanden en ouder. De waarde van een röntgenfoto is in de eerste 3 tot 5 levensmaanden beperkt, omdat niet alle delen van het heupgewricht verbeend zijn. Wel is het vanaf de geboorte mogelijk om röntgenfoto’s te maken om de centrering van de heupkop te beoordelen (voor-achterwaartse opname, Lauenstein opname) en daarmee een (sub)luxatie vast te stellen [7].
Op de voor-achterwaartse röntgenfoto is de hellingshoek van het acetabulum de belangrijkste parameter. Een goede positionering van het kind is voor het maken van een dergelijke voor achterwaartse opname essentieel; draaiing en kanteling van het bekken hebben direct invloed op de hoekmetingen. Bij de beoordeling van de acetabulumhoek wordt vaak gebruik gemaakt van een tabel met normale waardes (zie tabel 2) [12]. De afkappunten in deze tabel worden volgens de huidige opvattingen minder streng aangehouden (expertopinie werkgroep). Naast de acetabulumhoek zijn morfologische elementen zoals de vorm en sclerose van het acetabulum en de (a)symmetrie in verbening van de femurkopkern van belang voor de beoordeling.
Tabel 2. Classificering van DDH met behulp van röntgenonderzoek: grenswaarden in booggraden van de acetabulumhoek. Voor meisjes en jongens van verschillende leeftijdsgroepen zijn de afkapwaardes voor lichte en sterke dysplasie weergegeven (respectievelijk gemiddelde waardes (x) plus 1 en 2 standaarddeviaties (sd)) [12].
| Leeftijd | Meisje | Jongen | ||||||
| Licht dysplastisch (x + sd) | Sterk dysplastisch (x + 2 sd) | Licht dysplastisch (x + sd) | Sterk dysplastisch (x + 2 sd) | |||||
| Rechts | Links | Rechts | Links | Rechts | Links | Rechts | Links | |
| 1-2 mnd | 35,8 | 36,1 | 41,6 | 41,6 | 27,7 | 31,2 | 31,8 | 35,2 |
| 3-4 mnd | 31,4 | 33,2 | 36,3 | 38,7 | 27,9 | 29,1 | 32,4 | 33,7 |
| 5-6 mnd | 27,3 | 29,3 | 31,8 | 34,1 | 24,2 | 26,8 | 29,0 | 31,6 |
| 7-9 mnd | 25,3 | 26,9 | 29,4 | 31,3 | 24,6 | 25,4 | 28,9 | 29,5 |
| 10 mnd – 1 jr | 24,7 | 27,1 | 28,6 | 31,4 | 23,2 | 25,2 | 27,0 | 29,1 |
| 1 jr, 1 mnd – 1 jr, 3 mnd | 24,6 | 26,9 | 29,0 | 31,7 | 23,1 | 24,0 | 27,5 | 27,7 |
| 1 jr, 4 mnd – 1 jr, 6 mnd | 25,0 | 26,1 | 29,3 | 30,4 | 23,8 | 25,8 | 28,1 | 30,0 |
| 1 jr, 7 mnd – 2 jr | 24,1 | 26,4 | 28,4 | 30,8 | 20,6 | 23,2 | 24,4 | 27,3 |
| 2 jr, 1 mnd – 3 jr | 21,8 | 23,3 | 25,6 | 27,1 | 21,0 | 22,7 | 25,3 | 26,9 |
| 3 jr, 1 mnd – 5 jr | 17,9 | 21,2 | 21,3 | 25,8 | 19,2 | 19,8 | 23,5 | 23,8 |
| 5 jr, 1 mnd – 7 jr | 19,3 | 19,8 | 23,4 | 23,8 | 16,8 | 19,3 | 20,9 | 23,2 |
2.3 Natuurlijk beloop
DDH is een dynamische aandoening, die zich op diverse manieren kan presenteren en ontwikkelen. DDH kan al in utero ontstaan, maar ook pas in de zuigelingen- of peutertijd. Daarnaast kan zowel spontaan herstel optreden als verslechtering tijdens de eerste levensmaanden.
Neonataal luxeerbare heup
Het natuurlijke beloop van de neonataal luxeerbare heup is in de meeste gevallen gunstig. Ongeveer 60 80% herstelt zich spontaan. De overige gevallen gaan zonder behandeling over in een dysplasie en eventueel in een (sub)luxatie [23].
Dysplasie zonder luxatie
Het natuurlijke beloop van een dysplasie van de heup zonder (sub)luxatie is meestal ongunstig: ongeveer 70% ontwikkelt op volwassen leeftijd vroegtijdige slijtage, ofwel coxartrose [4], [5], [24].
Dysplasie met (sub)luxatie
Het natuurlijk beloop van de ge(sub)luxeerde heup is vrijwel altijd ongunstig. Als de baby 2 à 3 maanden oud is, treden al veranderingen ten gevolge van de (sub)luxatie op. De belangrijkste verandering is een verkorting van de heupadductoren. Zonder behandeling kunnen later ernstige complicaties op treden, zoals coxartrose of een ‘valse heupkom’ (een heupkom boven de plaats waar deze zou moeten zijn) [3].
2.4 Gevolgen
Gevolgen voor het dagelijks leven
Onbehandeld kan DDH leiden tot ernstige invaliditeit. Bij luxatie van één heup ontstaat een verschil in beenlengte, uiteindelijk tot circa 6 centimeter. Het kind zal gaan trekken met een been en mank lopen.
Bij een dubbelzijdige luxatie ontwikkelt het kind een holle rug en gaat het door de heupen ‘zwikken’ (eendengang of waggelgang). Het kind zal zich een groot aantal activiteiten op het gebied van sport en spel moeten ontzeggen.
Op (jong)volwassen leeftijd zullen meestal pijn en invalidering optreden door coxartrose [4], [5], [14]. De kans op coxartrose is lager wanneer kinderen vroeg worden behandeld voor DDH.
Sommige volwassenen met een dubbelzijdige luxatie, of met een enkelzijdige luxatie, maar daarbij een goed ontwikkelde kom boven de plaats waar de kom zou moeten zijn (‘valse heupkom’), hebben een geringere functiebeperking [3].
Uit Nederlands onderzoek onder (jong)volwassen vrouwen blijkt dat vrouwen met DDH met name op het fysieke domein (o.a. fysiek functioneren, pijn, algemene gezondheidsbeleving en vitaliteit), maar ook op het psychosociale domein (sociaal functioneren) een lagere kwaliteit van leven ervaren dan vrouwen zonder DDH [25].
2.5 Behandeling algemene aspecten
Algemene aspecten van behandeling van DDH
De behandeling van een DDH zonder (sub)luxatie bij zuigelingen bestaat uit het in flexie- en spreidstand houden van de heupen, waardoor de heupkop goed in de heupkom wordt geplaatst. Hiervoor wordt een spreidmiddel gebruikt. Het spreidmiddel moet aanvankelijk tenminste 23 uur per dag worden gedragen. Meestal duurt de spreidbehandeling meerdere maanden. De behandeling met een spreidmiddel wordt zelden voortgezet nadat het kind 1 jaar oud is.
Als een dysplasie gepaard gaat met een (sub)luxatie van de heupkop, zal eerst repositie van de heupkop moeten plaatsvinden. In het eerste half jaar kan hiertoe behandeling plaatsvinden met een spreidmiddel. Ook kan tractiebehandeling plaatsvinden, waarna een gipsbroek wordt aangelegd. Soms kan repositie onder narcose noodzakelijk zijn. Repositie wordt gevolgd door stabilisatie van de heupen in flexie en abductie gedurende enige maanden met een gipsbroek. Daarna kan nog langdurige spreidbehandeling plaatsvinden [3]. Wanneer een dysplasie op latere leeftijd wordt ontdekt, of wanneer sprake is van restdysplasie na behandeling van een luxatie, kan vaak alleen nog door een bekkenosteotomie een goede overdekking van de heupkop worden verkregen, over het algemeen pas na de leeftijd van 3 jaar [3]. Bezoek voor meer algemene informatie en afbeeldingen van spreidmiddelen de website van de Vereniging Afwijkende Heupontwikkeling (www.heupafwijkingen.nl).
2.6 Afkortingenlijst
| AAOS | American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons |
| AJN | Jeugdartsen Nederland |
| AMC-UvA | Academisch Medisch Centrum-Universiteit van Amsterdam |
| AMSTAR | A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews |
| BI | Betrouwbaarheidsinterval |
| BIG | (wet op de) Beroepen in de Individuele Gezondheidszorg |
| CBO | Centraal BegeleidingsOrgaan |
| CINAHL | Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature |
| CMT | congenitale musculaire torticollis |
| DDH | Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip |
| DES | Discrete Event Simulation |
| DHO | Dysplastische HeupOntwikkeling |
| EBRO | Evidence-Based RichtlijnOntwikkeling |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation |
| JGZ | Jeugdgezondheidszorg |
| KNMG | Koninklijke Nederlandsche Maatschappij tot bevordering der Geneeskunst |
| LESA | Landelijke Eerstelijns SamenwerkingsAfspraak |
| LROI | Landelijke Registratie Orthopedische Implantaten |
| NBOT | Nederlandse Beroepsvereniging Orthopedisch Technologen |
| NCJ | Nederlands Centrum Jeugdgezondheid |
| NHG | Nederlands Huisarts Genootschap |
| NOV | Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging |
| NVFK | Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kinderfysiotherapie |
| NVK | Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde |
| NVvR | Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PICO | Patient, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome |
| RAC | Richtlijn Advies- en Autorisatie Commissie |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| RR | Risk Ratio |
| SD | Standaarddeviatie |
| TNO | Nederlandse Organisatie voor toegepast-natuurwetenschappelijk onderzoek |
| VAH | Vereniging Afwijkende Heupontwikkeling |
| V&VN | Verpleegkundigen & Verzorgenden Nederland |
| VGGM | Veiligheids- en Gezondheidsregio Gelderland-Midden |
| WKO | Werkgroep Kinderorthopaedie Nederland |
3 Risicofactoren en beschermende factoren
Voor de vroegsignalering van DDH in de JGZ is het belangrijk dat jeugdartsen en jeugdverpleegkundigen de risicofactoren goed kennen. Inzicht in de risicofactoren helpt bij het identificeren van kinderen die een groter risico hebben op DDH, zodat deze kinderen tijdig kunnen worden verwezen voor diagnostiek en eventuele behandeling.
Uiteraard betekent de aanwezigheid van één of meerdere risicofactoren (anders dan het meisje-zijn), niet dat er dan altijd een DDH zal zijn of ontstaan; 1-10% van de kinderen met één of meer risicofactoren heeft DDH [17]. Dit geldt ook andersom: de afwezigheid van risicofactoren betekent niet dat er geen sprake kan zijn van een DDH; 10-27% heeft een of meer risicofactoren [17]. Het lichamelijk onderzoek tijdens de screening en onderzoek op indicatie bij vragen of ongerustheid van ouders blijft belangrijk.
3.1 Epidemiologie
DDH is een veel voorkomende aandoening bij jonge kinderen. In Nederland ontwikkelt 1 tot 4% van de zuigelingen in de leeftijdsperiode tot 6 maanden DDH [13]. Bij ongeveer 20% van de gevallen is sprake van dubbelzijdige DDH [14].
DDH komt 2,5 tot 3,8 keer zo vaak voor bij meisjes als bij jongens [15] [16]. Van alle zuigelingen met DDH heeft een minderheid (10-27%) één of meer risicofactoren anders dan vrouwelijk geslacht [17].
Ook hebben kinderen met het syndroom van Down [18], het syndroom van Ehlers-Danlos, arthrogryposis, of een neuromusculaire stoornis die zich kenmerkt door spierzwakte of spasticiteit (b.v. spina bifida [19] en cerebrale parese [20], [21]) een verhoogd risico op DDH.
De linkerheup is ongeveer 1,5 keer zo vaak aangedaan als de rechterheup [16]. Dit wordt toegeschreven aan de meest voorkomende ligging in de baarmoeder, waardoor de linkerheup in adductie tegen de moederlijke wervelkolom wordt gedrukt [3][22].
3.2 Risicofactoren
Risicofactoren voor DDH zijn:
- belaste familieanamnese (d.w.z. DDH en/of coxartrose voor de leeftijd van 50 jaar bij eerste- of tweedegraads familieleden)
- stuitligging vastgesteld na week 32 van de zwangerschap ongeacht de duur en periode van de stuitligging
- stuitligging bij de bevalling
- het strak inbakeren van het onderlichaam met de heupen en de knieën gestrekt.
Zie ook de Samenvatting van de literatuur inclusief Tabel 3 over kindfactoren en factoren rond zwangerschap en bevalling.
Lees verder in de Sectie Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen van DDH met de subsectie Anamnese over risicofactoren en Bijlage 1.
3.2.1 Risicofactoren (samenvatting literatuur)
Samenvatting van de literatuur
DDH wordt gezien als een multifactoriële aandoening waarbij zowel genetische factoren als omgevingsfactoren een rol spelen [12]. Genetische factoren zouden tot een verhoogde gevoeligheid van het heupgewricht voor DDH leiden. Omgevingsfactoren betreffen zowel hormonale als mechanische factoren. Bij hormonale factoren wordt als achterliggend mechanisme de grotere soepelheid van het kapsel en de banden rond het heupgewricht onder invloed van oestrogenen beschreven, die leidt tot hypermobiliteit. Mechanische factoren die bij het ontstaan van DDH een rol spelen, hebben als gezamenlijk kenmerk dat zij de fysieke ruimte beperken die de baby heeft tijdens of na de zwangerschap en tijdens de bevalling. Heel specifiek kan het daarbij gaan om de beperking van de ruimte die de heup(en) heeft (hebben) door de ligging die het kind in de zwangerschap heeft aangenomen of door het oprekken van kapsel en de banden van het heupgewricht tijdens het passeren van het geboortekanaal [27]. Ook kan het gaan om het beperken van de bewegingsmogelijkheden van de baby door ‘onveilig’ inbakeren, d.w.z. strak inbakeren van het onderlichaam met de heupen en knieën gestrekt, waardoor het kunnen spreiden van de benen in opgetrokken stand (‘kikkerstand’) en het volledig kunnen strekken van de benen niet mogelijk zijn [28].
De literatuur is samengevat in 2 hoofdgroepen: kindfactoren en factoren rond zwangerschap en bevalling.
Kindfactoren
Geslacht
De 2 recente systematische reviews met meta-analyses zijn eenduidig over de risicofactor geslacht. DDH komt 2,5 tot 3,8 keer zo vaak voor bij meisjes als bij jongens [15], [16] (Ortiz-Neira* 2012: gepoolde Odds Ratio (OR) 2,54; 95% Betrouwbaarheidsinterval (BI) 2,11–3,05; De Hundt 2012: gepoolde OR 3,8; 95% BI 3,0–4,6). Van de 8 geïncludeerde onderzoeken die niet in de reviews van 2012 zijn opgenomen, laten er 5 ORs (significant) zien variërend van 1,91 tot 4,0 [29], [30], [31], [32], 2 presenteren OR uitschieters van 11 en 28 [34], [35], en van één studie is geen OR te berekenen [36]. De studies vertonen een grote heterogeniteit; er zijn vooral verschillen in de gebruikte definities voor DDH.
Rangnummer kind
De literatuur naar rangnummer in relatie tot het voorkomen van DDH laat tegenstrijdige resultaten zien. De meta-analyse van Ortiz-Neira [16] beschrijft op basis van 5 geïncludeerde studies een verhoogd risico op DDH voor eerstgeborenen van 1,44 (95% BI 1,12-1,86). De meta-analyse van de Hundt [15] concludeerde echter op basis van 5 studies (waarvan 1 studie ook in de meta-analyse van Ortiz-Neira was opgenomen) dat geen associatie bestaat tussen rangnummer en DDH (gepoolde OR 1,55; 95 BI 0,96 2,5). Een niet in de meta-analyses opgenomen onderzoek vindt geen verband tussen rangnummer kind en de kans op heupluxatie [34].
Geboortegewicht
De meta-analyse van De Hundt [15] laat een beschermend effect zien van een geboortegewicht lager dan 2500 gram (4 studies; gepoolde OR 0,28; 95% BI 0,24-0,33) en geen verhoogd risico bij een geboortegewicht hoger dan 4000 gram (één studie). Daarbij dient te worden opgemerkt dat er geen correctie voor zwangerschapsduur plaatsvond. Eén van de 2 niet in de review opgenomen studies [34] liet een beschermend effect zien van een laag geboortegewicht voor heupluxatie (< 3000 gram versus >3000 gram; 93% a terme geboren kinderen) met een OR (significant) van 0,7 (95% BI 0,5-1,0). In het andere onderzoek [37] wordt een dosisrespons effect beschreven: de prevalentie van DDH (type IIc-D) in de groepen met laag (onder het tiende percentiel), gemiddeld (tussen tiende en negentigste percentiel) en hoog (boven negentigste percentiel) geboortegewicht voor de zwangerschapsduur was respectievelijk 2,35%, 3,51%, en 6,11%. Het verschil in prevalentie tussen de groepen met laag en gemiddeld geboortegewicht was significant. Ten slotte laat een studie uit 2013 onder a terme geboren kinderen geen verband zien tussen geboortegewicht en DDH [35].
Belaste familieanamnese voor heupaandoeningen
De literatuur naar het familiair voorkomen van DDH kan grofweg in 2 soorten worden ingedeeld. Allereerst is er het klassieke onderzoek naar de mate waarin DDH voorkomt bij kinderen die familiair belast zijn in vergelijking met kinderen die niet familiair belast zijn. De 2 beschikbare meta-analyses zijn eenduidig in hun conclusies dat een belaste familieanamnese voor DDH geassocieerd is met DDH bij het kind: De Hundt [15] presenteert een gepoolde OR van 4,8 (95% BI 2,8–8,2), gebaseerd op 15 onderzoeken; Ortiz-Neira [16] een relatief risico (RR) van 1,39 (95% BI 1,23–1,57), gebaseerd op 4 studies. Een kanttekening die in de meta-analyse van de Hundt wordt gemaakt is dat verschillende definities voor familiaire belasting worden gebruikt: in 10 studies geeft men geen definitie, in de overige 5 studies varieert de definitie van ‘een familielid’, een ‘eerstegraads familielid’, een ‘eerste- tot vierdegraads familielid’, ‘ten minste 1 eerstegraads of 2 tweedegraads familieleden’. Een Nederlandstalig artikel over de cohortstudie van Boere-Boonekamp [38] beschrijft de ORs bij gespecificeerde familiaire belasting: eerstegraads (ouders, broers/zusjes) OR 4,9 (95% BI 4,0-11,3), tweedegraads (grootouders, ooms/tantes) 4,3 (95% BI 1,9-9,2) en derde- en/of vierdegraads 2,6 (95% BI 1,2-5,3). Uit een nadere analyse van de resultaten van deze meest recente Nederlandse cohortstudie (n=1968) blijkt dat van de 157 kinderen (8,0%) met een belaste familieanamnese (eerste en/of tweede graad) er 23 een DDH hadden (positief voorspellende waarde 14,6%) [13], [38].
Behalve de 2 reviews (beiden uit 2012) zijn nog 3 artikelen geïncludeerd die niet in de review waren opgenomen: de 2 studies van Ruhmann vinden een 1,7 [32] en 2,4 [31] keer zo hoog risico op DDH als er sprake is van familiaire belasting; de studie van Partenheimer [36] stelt geen significant verhoogd risico vast. Ten slotte zijn nog 2 artikelen die in of na 2012 zijn verschenen geïncludeerd. Li [30] stelde in een onderzoek in China vast dat 87 van de 628 broertjes/zusjes van DDH-patiënten DDH hadden (radiologisch vastgesteld) (prevalentie 13,85%; 95% BI 10,94–16,76) en 14 van de 889 broertjes/zusjes van een controle populatiekinderen zonder DDH (prevalentie 1,57%; 95% BI 0,75–2,40) hetgeen een 10,05 keer zo hoog risico inhoudt (95% BI 5,66–17,85). Guner [29] vond in Turkije 3,13 (95% BI 1,190 8,24) keer zo vaak op de leeftijd van 4 weken een Graf Type II, III of IV als er een belaste familieanamnese voor DDH was.
Naast bovengenoemd klassiek onderzoek vindt er sinds begin van deze eeuw onderzoek plaats naar de rol van genetische factoren bij personen met een DDH. Dit betreft patiënt-controleonderzoeken waarbij DNA in het bloed van volwassenen met DDH en van gezonde controles is onderzocht op bepaalde genetische factoren. De review van Shi [39] beschrijft verscheidene DDH loci met kwetsbare genen die te maken hebben met de ontwikkeling van de botten en gewrichten, maar algemene conclusies zijn (nog) niet te trekken.
Voetafwijkingen
De meta-analyse van De Hundt [15] meldt op basis van 5 geïncludeerde studies een circa 3 keer verhoogde kans op DDH als tevens een voetafwijking aanwezig is (gepoolde OR 3,24; 95% BI 0,88-11,97), maar dit verband is niet significant. Een probleem bij de interpretatie is dat sommige studies verschillende typen voetafwijkingen onderscheiden (congenitale talipes calcaneovalgus, (congenitale) talipes equinovarus, metatarsus adductus) en in andere studies alle voetafwijkingen bij elkaar worden genomen. De studiepopulatie wordt bij studies die zich richten op één type voetafwijking klein, en het samennemen van alle voetafwijkingen leidt tot grote heterogeniteit van de populatie. De meta-analyse van De Hundt [15] includeerde alleen studies met een gelijktijdige controlegroep; de overige beschreven studies deden dit niet. Een recente systematische review en meta-analyse van Ibrahim [40] naar de prevalentie van DDH bij kinderen met een idiopathische klompvoet laat voor de 12 geïncludeerde studies (1964-2013) een prevalentie van DDH variërend van 0,6 tot 16,8% zien. Gevoeligheidsanalyses lieten een geschatte gepoolde prevalentie zien van 3,5% (95 % BI 1,1–10,8%) en 3,8% (95% BI 1,0–13,7%) als respectievelijk echografie (7 studies) of behandeling met een Pavlik harnas (5 studies) werd gebruikt als criterium voor de diagnose DDH. De auteurs concluderen dat de prevalentie van DDH bij kinderen met een idiopathische klompvoet vergelijkbaar is met die in de algemene populatie en dat het beschikbare bewijs een associatie tussen DDH en klompvoet niet ondersteunt.
Inbakeren
Er zijn aanwijzingen dat kinderen die strak worden ingebakerd met de heupen en knieën gestrekt een verhoogd risico hebben op DDH [41]. In het verleden werd een hoge incidentie van DDH beschreven bij volkeren (Navajo-indianen, Laplanders) die de gewoonte hadden jonge zuigelingen in gestrekte houding in te bakeren, waarbij de heupen langdurig in extensie en adductie werden gehouden [3]. In Oost-Europa en het Midden-Oosten worden frequent kinderen ingebakerd [42], [43]. Ook in Nederland vindt inbakeren in toenemende mate plaats, bijvoorbeeld door ouders met een migratie-achtergrond (Turkse, Marokkaanse ouders), door op antroposofie georiënteerde ouders of door ouders met een huilbaby (zie de JGZ-richtlijn Excessief huilen).
In een verhalende review van Van Sleuwen uit 2007 [44] wordt beschreven dat inbakeren een risicofactor is voor DDH. Deze conclusie is gebaseerd op 11 geïncludeerde studies, waarvan er 2 na 1995 zijn verschenen. De review beschrijft dat uit diermodellen en observaties bij pasgeborenen blijkt dat wanneer de heup en knie geforceerd gestrekt worden gehouden (luier, kleding, doeken) dit tot subluxatie of zelfs luxatie kan leiden. Uit onderzoek naar de incidentie van DDH blijkt dat in culturen waar zuigelingen verzorgd worden/werden met de heupen in flexiestand de prevalentie van DDH veel lager is/was dan in culturen waarbij de benen juist worden gestrekt (bijvoorbeeld ingebakerd op een wasbord). Geconcludeerd wordt dat strak inbakeren van het onderlichaam het ontstaan van DDH kan bevorderen. Om deze reden wordt in Nederland deze vorm van strak inbakeren ‘onveilig’ inbakeren genoemd; op indicatie kan een ‘veilige’ manier van inbakeren toegepast worden d.w.z. alleen strak rond het bovenlichaam en de armen, en losjes rond de heupen en benen (zie het boek ‘Inbakeren brengt rust’ door Ria Blom [26]).
De studies naar de rol van inbakeren als risicofactor voor DDH die na 1995 beschikbaar zijn gekomen, geven geen consistente resultaten. Wel gaat het in deze studies om het strak inbakeren met de heupen en knieën gestrekt. Uit een prospectief onderzoek van Guner van 2013 [29] in Turkije blijkt dat de ingebakerde kinderen een 2,65 (95% BI 1,004–7,00) keer zo hoog risico op DDH (Graf type II of hoger) hebben als niet-ingebakerde kinderen. Een groter onderzoek van Sahin [45], eveneens in Turkije, laat geen betrouwbare conclusies toe.
Etniciteit
Hoewel over de factor ‘etniciteit’ geen literatuur is gevonden die voldeed aan de inclusiecriteria, zijn er aanwijzingen dat de prevalentie van DDH tussen verschillende rassen verschilt en dat er ook regionale verschillen binnen een land kunnen bestaan. Gerapporteerde prevalenties uit niet-vergelijkende studies variëren van 0,1 per 1000 onder Chinezen in Hong Kong, tot 1-2 per 1000 in Engeland en Zweden, 10-40 per 1000 in Nederland en 75 per 1000 in Servië. Ook onder Griekse, Italiaanse, Libanese en Poolse populaties worden hoge prevalenties gemeld [46]. In Afrikaanse en Afro-Amerikaanse populaties [47] zou DDH daarentegen zeldzaam zijn. De variaties kunnen berusten op genetische factoren, omgevingsfactoren, verzorgingsfactoren, leeftijd van de onderzochte populatie, opsporingsmethode, ervaring van de onderzoeker, gebruikte definities voor DDH en gebrekkige registratie.
Factoren rond zwangerschap en bevalling
Meerlingzwangerschap
De meta-analyse (3 studies) van De Hundt [15] vindt geen verschil in risico tussen kinderen geboren uit een meerlingzwangerschap vergeleken met kinderen geboren uit een eenlingzwangerschap. Ook de 4 geïncludeerde studies [31], [32], [34], [48] die niet in de review van 2012 zijn opgenomen vinden geen verhoogd risico.
Zwangerschapsduur
In de meta-analyse van De Hundt [15] zijn 5 studies geïncludeerd, die de factor prematuriteit onderzoeken; geconcludeerd wordt dat de kans van prematuur geboren kinderen op DDH niet verschilt van die van niet-prematuur geboren kinderen (OR 0,53; 95% BI 0,23-1,2). De 6 geïncludeerde onderzoeken die niet in de review van de Hundt van 2012 zijn opgenomen [31], [32], [34], [35], [36], [49], laten geen van allen een associatie zien tussen de zwangerschapsduur (prematuriteit, a terme of serotiniteit) en het optreden van DDH.
Oligohydramnion
De meta-analyse van de Hundt [15] beschrijft een 2,5 (95% BI 0,75–8,2) keer zo hoog risico voor DDH als er sprake is van weinig vruchtwater (oligohydramnion). De bevinding is echter niet significant. De conclusie is gebaseerd op 3 geïncludeerde prospectieve cohortonderzoeken die geen details geven over de gebruikte definitie en meetmethode voor oligohydramnion en over de zwangerschapsduur bij diagnosestelling. Een in 2013 gepubliceerd onderzoek van Guner laat eveneens geen relatie zien tussen oligohydramnion en DDH [29] (OR 0,32; 95% BI 0,04-2,78).
Vaginale bevalling of keizersnede
De meta-analyses van de Hundt [15] en Ortiz-Neira [16] laten geen verschil in risico op DDH zien tussen kinderen die via vaginale bevalling worden geboren en kinderen die via keizersnede worden geboren. Eén van de 3 na 2012 gepubliceerde studies laat een 1,5 keer zo hoog risico zien na een keizersnede (p<0,05), maar het is onduidelijk of keizersnedes bij stuitliggingen zijn geëxcludeerd [34]. De andere 2 studies stellen geen verband vast [31], [32].
Stuitligging baby in zwangerschap en tijdens geboorte
De 2 meta-analyses zijn eenduidig over de risicofactor stuitligging. Ortiz-Neira (15 studies) komt op een verhoogd risico bij stuitligging/stuitbevalling van 3,75 (95% BI 2,25–6,24) [16]; De Hundt (22 studies) komt op een verhoogd risico van 5,7 (95% BI 4,4-7,4) [15]. Er werden 6 studies gevonden die niet in de meta-analyses zijn opgenomen. Vier van deze 6 studies laten significant verhoogde risico’s van stuitligging/stuitbevalling zien (ORs van 2,5 tot 4,5) [31], [32], [34], [48], 2 laten geen significant verband zien [29], [36]. Uit een nadere analyse van de resultaten van de meest recente Nederlandse cohortstudie (n=1968) blijkt dat van de 102 kinderen (6%) die in stuitligging lagen in het laatste trimester van de zwangerschap (na de 27e zwangerschapsweek) en/of bij de bevalling er 13 een DDH hadden (positief voorspellende waarde 12,7%) [13], [38]. Zowel de studies die in de meta-analyses zijn opgenomen als die daar niet in zitten, vertonen een grote heterogeniteit; er zijn vooral verschillen in de gebruikte definities voor DDH; verder wordt vaak geen onderscheid gemaakt tussen stuitligging in de zwangerschap en stuitbevalling.
Volkomen of onvolkomen stuitligging
De leerboeken zeggen dat baby’s die in onvolkomen stuitligging lagen, met de benen gestrekt omhoog langs het lichaam, een speciale hoog-risico groep voor DDH vormen [22]. Uit een onderzoek van Holen [50] onder 408 pasgeborenen die in stuit lagen bij de geboorte (141 vaginaal geboren, 267 via keizersnede) blijkt dat neonatale heupinstabiliteit vaker voorkwam bij de pasgeborenen die tijdens de geboorte in onvolkomen stuit lagen (9,3%) dan bij de pasgeborenen die in volkomen stuit lagen (3,8%); dit verschil is significant (p=0,038). De betekenis van deze bevinding is niet duidelijk omdat neonatale instabiliteit meestal spontaan herstelt. Voor de associatie van de aard van de stuitligging met DDH na de neonatale periode is geen onderzoek beschikbaar.
Stuitligging bij prematuren of bij a terme geboren kinderen
Quan [51] onderzocht 256 kinderen die in stuitligging lagen en ofwel prematuur (< 37 weken; n=129) ofwel a terme (≥ 37 weken; n=163) in stuit geboren werden. Van de prematuren hadden 3 kinderen een DDH; deze waren geboren na respectievelijk 29, 36 en 36 weken zwangerschapsduur; van de a terme geboren kinderen hadden ook 3 kinderen een DDH. Deze prevalenties van 2,3% en 1,8% verschilden niet significant. De associatie tussen stuitligging en DDH lijkt dus niet anders voor a terme geboren kinderen of prematuren.
Wel/niet met succes uitwendig draaien van stuitligging naar hoofdligging
Bij het begin van het derde trimester (week 28) ligt 22-25% van de kinderen in stuit [52], [53], [54], bij week 32 is dit 7-15% [53], terwijl 3 – 4% van de kinderen in de a terme periode in stuit ligt [52], [53]. In principe kan het kind, mits er voldoende vruchtwater is, vanaf een zwangerschapsduur van 36-37 weken tot aan de bevalling gedraaid worden middels uitwendige versie. De kans op een succesvolle uitwendige versie is ongeveer 60% [55], [56].
Lambeek [57] onderzocht in een observationeel prospectief onderzoek onder 498 kinderen die in de zwangerschap in stuitligging lagen of het risico op DDH verschilde voor kinderen die met succes uitwendige versie ondergingen en kinderen waar de uitwendige versie mislukte. In deze groepen was de prevalentie van behandelde DDH respectievelijk 2,8% en 9,3%. Dit betekent een 3,55 keer zo hoog risico op DDH als de uitwendige versie niet slaagde in vergelijking met als deze wel slaagde (p<0,01). Kinderen met andere risicofactoren voor DDH waren uitgesloten voor deelname aan dit onderzoek. De auteurs concluderen dat de prevalentie van DDH van 2,8% in de groep met een geslaagde uitwendige versie waarschijnlijk nog steeds hoger is dan de prevalentie in een algemene populatie zonder risicofactoren (1%); zij pleiten voor herhaling in een grote cohortstudie en adviseren om nog geen onderscheid te maken in het beleid voor kinderen die in stuitligging lagen en al dan niet een geslaagde uitwendige versie ondergingen.
Andersen [58] onderzocht 257 kinderen die in stuitligging lagen na 36 weken zwangerschap. Van deze groep werden er 62 vaginaal geboren na een geslaagde uitwendige versie en 195 via een keizersnede (waarvan 75 na een niet-geslaagde uitwendige versie en 120 waar geen uitwendige versie was geprobeerd). In beide groepen werden uiteindelijk 2 kinderen behandeld voor DDH (verschil niet significant).
Vaginale bevalling of keizersnede bij een stuitligging
In de meta-analyse van De Hundt [15] zijn 5 studies geïncludeerd, die onderzoeken of het risico voor kinderen die in stuitligging liggen, verschilt voor diegenen die vaginaal worden geboren en diegenen die per keizersnede worden geboren. Er werd geen verband gevonden tussen de aard van de bevalling en het voorkomen van DDH (gepoolde OR voor vaginale bevalling 1,1, 95% BI 0,97–1,3). In een andere systematische review van Panagiotopoulou [27] zijn 9 studies geïncludeerd. Acht hiervan rapporteerden een vermindering van het risico op DDH bij keizersnede bij stuitligging, één een zeer geringe verhoging van het risico. De gepoolde OR was 0,87 (95% BI 0,78-0,97); dit betekent dat het risico op DDH na keizersnede iets lager is.
Twee andere studies rapporteren over de aard van de bevalling bij stuitligging. Lambeek [57] vond juist een verhoogd risico op DDH (criterium: wel/niet behandeling) na een keizersnede bij stuitligging (OR 2,5, 95% BI 1,06-4,37); na correctie voor verstorende variabelen bleek de OR echter 1,38 (95% BI 0,56-3,23) en niet meer significant. Chan [59] vond ten slotte in een groot patiënt-controle onderzoek dat, vergeleken met kinderen die in hoofdligging lagen, het risico op DDH voor kinderen in stuitligging die via een vaginale bevalling of via een keizersnede werden geboren significant hoger was, met ORs van respectievelijk 17,15 (95% BI 12,79-22,99) en 10,03 (95% BI 8,58-11,72); het verschil tussen deze ORs was significant.
Tabel 3: Overzicht van de uitkomsten van het literatuuronderzoek naar factoren die mogelijk een verhoogd risico op DDH zouden geven.
| Kindfactoren | Factoren rond zwangerschap en bevalling | |
| Factoren waarvoor een verhoogd risico op DDH is aangetoond, aannemelijk of waarschijnlijk is, of waarvoor aanwijzingen bestaan |
|
|
| Factoren waarvoor geen verhoogd risico op DDH aangetoond, aannemelijk of waarschijnlijk is, of waarvoor geen aanwijzingen bestaan |
|
|
| Factoren waarover geen onderzoek, dat voldeed aan de inclusiecriteria, gevonden is in relatie tot DDH |
|
|
*Voor de leesbaarheid wordt steeds alleen de eerste auteur van een artikel genoemd.
**Hier kan geen exacte definitie voor stuitligging worden gegeven, bv. over periode in de zwangerschap, alleen in de zwangerschap of alleen bij de bevalling of de combinatie, of de duur van de stuitligging, omdat deze verschillen in de beschikbare literatuur niet worden gemaakt.
***Voor geboortegewicht lager dan 2500 gram is een verlaagd risico aangetoond.
Conclusies*
Kindfactoren
|
Niveau** |
Conclusie*** |
Literatuur**** |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat DDH 2,5 tot 3,8 keer zo vaak voorkomt bij meisjes als bij jongens. | A1 [15], [16] A2 [36] B [29], [30], [31], [32], [33], [34], [35] |
| 1 | Het is niet aangetoond dat eerstgeboren kinderen een verhoogd risico op DDH hebben vergeleken met kinderen met een hoger rangnummer. | A1 [15], [16] B [34] |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat kinderen met een geboortegewicht lager dan 2500 gram een lager risico op DDH hebben vergeleken met kinderen met een hoger geboortegewicht. | A1 [15] B [34], [35], [37] |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat kinderen met een belaste familieanamnese voor DDH een 1,4 tot 4,8 keer zo groot risico op DDH hebben vergeleken met kinderen zonder belaste familieanamnese. | A1 [15], [39] A2 [36] B [29], [30], [31], [32] |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat er geen verband is tussen voetafwijkingen en DDH. | A1 [15], [40] |
| 3 | Er zijn aanwijzingen dat kinderen, bij wie het onderlichaam strak wordt ingebakerd met de heupen en knieën gestrekt, een verhoogd risico hebben op DDH. | B [29], [45] |
Factoren rond zwangerschap en bevalling
|
Niveau |
Conclusie |
Literatuur |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat er geen verband is tussen meerlingzwangerschap en DDH. | A1 [15] B [31], [32], [34], [48] |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat er geen verband is tussen zwangerschapsduur en DDH. | A1 [15] A2 [36] B [31], [32], [34], [35], [49] |
| 1 | Het is niet aangetoond dat er een verband is tussen oligohydramnion en DDH. | A1 [15] B [29] |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat er geen verband is tussen aard van de bevalling (vaginaal of keizersnede) en DDH. | A1 [15], [16] B [31], [32], [34] |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat DDH 2,5 tot 5,7 keer zo vaak voorkomt bij kinderen die in stuitligging lagen tijdens de zwangerschap en/of bij de bevalling***** vergeleken met kinderen die niet in stuitligging lagen. | A1 [15], [16] A2 [36] B [29], [31], [32], [34], [48] |
| 3 | Er zijn aanwijzingen dat het risico op DDH voor kinderen die als prematuur in stuitligging geboren worden niet anders is dan voor kinderen die a term in stuit geboren worden. | B [57], [59] |
| 3 | Er zijn aanwijzingen dat als een uitwendige versie bij een stuitligging in de zwangerschap niet is geslaagd er 3,6 keer zo vaak DDH voorkomt als wanneer de uitwendige versie wel is geslaagd (prevalentie resp. 9,3% en 2,8%). | B [38], [57] |
| 1 | Het is aangetoond dat kinderen die in stuitligging liggen en vaginaal geboren worden een licht verhoogd risico op DDH hebben in vergelijking met kinderen die via een keizersnede worden geboren******. | A1 [15], [27] B [57], [59] |
* In geval ORs uit meta-analyses beschikbaar zijn, worden alleen deze waarden gepresenteerd vanwege de grotere precisie in vergelijking met empirische studies.
** Zie voor het bepalen van het niveau van de conclusie en de literatuur het hoofdstuk Verantwoording.
*** Niveau 1: Het is aangetoond dat…. Niveau 2: Het is aannemelijk/waarschijnlijk dat…. Niveau 3: Er zijn aanwijzingen/het lijkt waarschijnlijk dat…. Niveau 4: De deskundigen/werkgroep zijn/is van mening dat….[60].
**** Zie voor de uitleg over de indeling van methodologische kwaliteit van individuele studies tabel 5 in het hoofdstuk Verantwoording.
***** Hier kan geen onderscheid worden gemaakt tussen alleen zwangerschap, alleen bevalling, of de combinatie, omdat dit verschil in de beschikbare literatuur niet wordt gemaakt.
****** Hoewel slechts 1 van de 2 reviews significante bevindingen rapporteert over het verband tussen het risico voor kinderen die in stuitligging lagen op DDH en de wijze van geboorte (vaginaal of per keizersnede), heeft de projectgroep ervoor gekozen de conclusie op deze manier te formuleren, omdat de resultaten van beide studies in dezelfde richting wijzen.
Overige overwegingen
Belaste familieanamnese voor coxartrose voor de leeftijd van 50 jaar
Het bepalen of wel of niet sprake is van een belaste familieanamnese betreft op de eerste plaats het navragen of eerste- of tweedegraads familieleden een DDH hebben gehad. Het vaststellen of sprake is van een belaste familieanamnese voor coxartrose is niet altijd gemakkelijk. Wel kunnen de ouders vertellen dat zijzelf of andere eerste- of tweedegraads familieleden op jonge leeftijd heupklachten hadden, die soms al vóór de leeftijd van 50 jaar resulteerde in een heupoperatie. Anamnestisch kunnen andere oorzaken dan DDH voor de heupklachten (trauma, polio, ontsteking, ziekte van Perthes) meestal worden uitgesloten, maar niet altijd. Uit de gegevens van de Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging en Stichting LROI [61] blijkt dat in 2014 17,0% van de mensen jonger dan 50 jaar oud en 6,5% van de mensen jonger dan 60 jaar oud die een totale heupprothese kregen, deze heupprothese kregen vanwege dysplasie. De enige beschikbare review naar het natuurlijk beloop van DDH [24] geeft aan dat 1) DDH met (sub)luxatie zonder behandeling altijd tot coxartrose leidt, en 2) er onvoldoende bewijs is (uit prospectief epidemiologisch onderzoek) dat persisterende milde dysplasie een etiologisch belangrijke factor is voor coxartrose. Om deze redenen adviseert de werkgroep om bij de familieanamnese te vragen naar heupklachten, begonnen vóór de leeftijd van 50 jaar.
Stuitligging
Er zijn veel publicaties over onderzoeken naar de risicofactor stuitligging in de zwangerschap en/of bij de bevalling in relatie tot het optreden van DDH. De publicaties beschrijven vaak niet hoeveel weken de baby in stuitligging lag. Ook beschrijven deze publicaties vaak niet tijdens welke weken van de zwangerschap de stuitligging werd vastgesteld. Soms wordt ook niet gespecificeerd of het om stuitligging in de zwangerschap of bij de bevalling ging. Verder vindt de werkgroep het bewijs voor een daling van het verhoogde risico naar lagere waarden na met succes toegepaste uitwendige versie van een stuitligging in de laatste weken van de zwangerschap te mager. Aan het begin van het derde trimester is de ligging van het kind in de baarmoeder nog erg wisselend: in week 28 ligt 22-25% van de kinderen in stuit [52], [53], [54], bij week 32 is dit 7-15% [53], [62]. De wisselende ligging wijst op veel bewegingsruimte voor het kind in de baarmoeder en daarmee op de afwezigheid van veel mechanische druk door de stuitligging op het zich ontwikkelende heupgewricht. Vanwege deze inhoudelijke reden, het gebrek aan wetenschappelijke onderbouwing en om veel fout-positieve uitkomsten door een hoog aantal verwijzingen voor beeldvormend onderzoek te vermijden, acht de werkgroep het gerechtvaardigd dat de risicofactor stuitligging bij de verwijscriteria wordt gespecificeerd als ‘stuitligging, vastgesteld na week 32 van de zwangerschap ongeacht de duur en periode van de stuitligging’ en/of ‘stuitligging bij de bevalling’.
Vrouwelijk geslacht
Uit alle literatuur blijkt dat DDH 2,5 tot 3,8 keer zo vaak voorkomt bij meisjes als bij jongens [15], [16]. De werkgroep heeft besloten dat alleen het ‘meisje-zijn’ geen reden is voor verwijzing aangezien dat tot minimaal 50% verwijzingen zou leiden.
Inbakeren
Op basis van wetenschappelijk onderzoek bestaan er aanwijzingen dat het strak inbakeren van het onderlichaam van het kind met de heupen en knieën gestrekt het risico op DDH verhoogt. Deze manier van onveilig inbakeren is echter als enige bevinding geen indicatie om te verwijzen voor beeldvormend onderzoek (expert opinie). De argumentatie hiervoor is dat onveilig inbakeren een veranderbare risicofactor betreft; het verhoogde risico verdwijnt zeer waarschijnlijk nadat de jeugdarts of jeugdverpleegkundige adviezen over veilig inbakeren heeft gegeven, die door de ouders worden opgevolgd.
Het strak inbakeren van het onderlichaam van het kind met de heupen en knieën gestrekt is een reden om het lichamelijk onderzoek extra alert uit te voeren. Extra alert wil zeggen dat de onderzoeker geen twijfel mag hebben over de betrouwbaarheid van het onderzoek (abductie en kniehoogte) en zo nodig laagdrempelig een extra contactmoment ter controle afspreekt.
Draagzakken en –doeken
Er is een korte (geen systematische) literatuursearch gedaan naar het verband tussen (langdurig) dragen door middel van een draagzak en/of draagdoek en het risico op heupdysplasie. Wetenschappelijke literatuur specifiek naar de manier van dragen van een baby is niet gevonden. Van Sleuwen [44] beschrijft in haar review over inbakeren dat uit diermodellen en observaties bij pasgeborenen blijkt dat het geforceerd gestrekt houden van de heup en knie (luier, kleding, doeken) tot subluxatie of zelfs luxatie kan leiden. In Afrikaanse en Afro-Amerikaanse populaties [47], waarin het dragen van baby’s met de heupen in spreidstand gebruikelijk is, zou DDH zeldzaam zijn; hier kunnen echter veel andere verklaringen aan ten grondslag liggen, bv. genetische factoren, gebruikte definities voor DDH, methode van opsporing en registratie. In de orthopedische wereld is de heersende opvatting dat de flexie spreidstand van de heupen tot een betere ontwikkeling van de heupkommen leidt dan een stand waarbij de heupen geforceerd worden gestrekt (expert opinie). Op basis van expert opinion adviseert de werkgroep zo veel mogelijk te kiezen voor een manier van dragen in een draagzak of draagdoek die gunstig is voor de heupontwikkeling d.w.z. met de heupen in flexie-spreid stand. Het is van belang om met name een jonge baby niet langdurig te dragen op een manier waarbij de heupen niet gebogen en gespreid kunnen worden. De werkgroep adviseert het vermijden van deze ongunstige draagmethode nog eens extra bij kinderen met risicofactoren voor DDH.
Congenitale musculaire torticollis
Er zijn 4 studies gevonden die het verband tussen torticollis en DDH onderzochten. Echter ontbreken gegevens over de prevalentie van DDH in gelijktijdige controlegroepen zonder torticollis, en voldeden deze studies zodoende niet aan de gestelde inclusiecriteria. Het betreft 3 retrospectieve dossieronderzoeken en 1 prospectief onderzoek van klinische populaties van kinderen met congenitale musculaire torticollis (CMT). De prevalenties van DDH (criterium: behandeling) varieerden in deze selecte populaties van 2,9% [63], 4,5% [64], 8,5% [65], tot 11,6% [66]. Mogelijke verklaringen voor deze variatie in prevalentie zijn de meer of minder strikte definitie voor CMT en DDH, maar ook variatie in de achtergrondprevalentie van DDH tussen populaties.
Klinische instabiliteit vastgesteld met de handgrepen van Barlow en Ortolani
Kort na de geboorte kunnen de handgrepen van Ortolani en Barlow worden uitgevoerd voor de vroege opsporing van respectievelijk geluxeerde en luxeerbare heupen [67]. De handgrepen zijn gericht op het vaststellen van abnormale beweeglijkheid van de heupkop ten opzichte van de heupkom en zijn dus tests voor instabiliteit [3]. De reproduceerbaarheid is afhankelijk van de vaardigheid en ervaring van de onderzoeker [68]. Deze methoden zijn vooral in de eerste 48 uur accuraat [69]. De handgrepen kunnen alleen in de eerste weken na de geboorte worden uitgevoerd [68]. De evidence-based richtlijn van de American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) [70] benoemt klinische instabiliteit vastgesteld met de handgrepen van Barlow en Ortolani als risicofactor voor geluxeerde heupen. De richtlijnontwikkelaars van deze AAOS richtlijn baseren zich op de studie van Paton [71]. Aangezien de handgrepen van Ortolani en Barlow minder valide zijn op de leeftijd van 4 weken, zijn deze tests minder geschikt voor toepassing van de JGZ tijdens dit contactmoment. In Nederland vindt volgens de NHG standaard ‘Zwangerschap en kraamperiode’ [72] direct na de geboorte geen onderzoek van de heupen plaats. Ook bij in de tweede lijn geboren kinderen vindt geen systematisch heuponderzoek plaats. Deze risicofactor is daarom niet relevant voor de Nederlandse situatie en is om die reden niet meegenomen in het literatuuronderzoek naar risicofactoren voor DDH in deze JGZ-richtlijn.
Lengtemeting bij zuigelingen
Er bestaan geen aanwijzingen dat de lengtemeting van de jonge zuigeling nadelig is voor diens heupontwikkeling en het risico op heupdysplasie met of zonder luxatie verhoogt. De lengte van zuigelingen kan bij ieder contactmoment, zowel bij premature als voldragen pasgeborenen, op een veilige wijze gemeten worden [73]. Het uitvoeren van de lengtemeting van een liggend kind is beschreven in het boekje ‘Groeidiagrammen 2010. Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen’, uitgegeven door TNO [74].
Informatie over risicofactoren ontbreekt of komt pas beschikbaar na de screeningsleeftijd
Wanneer er geen informatie is over risicofactoren of wanneer informatie over 1 of meerdere risicofactoren pas beschikbaar komt na de leeftijd van 6 maanden hoeft alleen verwijzing plaats te vinden voor aanvullend onderzoek als er afwijkende bevindingen bij lichamelijk onderzoek zijn.
Anamnese
Voor de vroegsignalering van DDH in de JGZ is het belangrijk dat jeugdartsen en jeugdverpleegkundigen de risicofactoren goed kennen. Inzicht in de risicofactoren helpt bij het identificeren van kinderen die een groter risico hebben op DDH, zodat deze kinderen tijdig kunnen worden verwezen voor diagnostiek en eventuele behandeling. Uiteraard betekent de aanwezigheid van één of meerdere risicofactoren (anders dan het meisje-zijn), niet dat er dan altijd een DDH zal zijn of ontstaan; 1-10% van de kinderen met één of meer risicofactoren heeft DDH [17]). Dit geldt ook andersom: de afwezigheid van risicofactoren betekent niet dat er geen sprake kan zijn van een DDH; 10-27% heeft een of meer risicofactoren [17]. Het lichamelijk onderzoek tijdens de screening en onderzoek op indicatie bij vragen of ongerustheid van ouders blijft belangrijk.
De werkgroep adviseert de volgende werkwijze met betrekking tot het uitvragen van de risicofactoren:
- De jeugdverpleegkundige neemt bij de intake van de zuigeling de anamnese af. Dit is meestal tijdens het huisbezoek in de tweede levensweek. In sommige situaties zal de anamnese later worden afgenomen, bijvoorbeeld in geval van ziekenhuisopname na de geboorte, wanneer een kind wordt gevolgd op de prematurenpoli, bij verhuizing, adoptie, etc.
- Tijdens het eerste contactmoment bij de jeugdarts loopt deze de anamnese na en vult deze zo nodig aan. Dit geldt met name voor de anamnese naar het voorkomen van DDH en/of coxartrose voor de leeftijd van 50 jaar in de naaste familie (eerste- en tweedegraads familieleden [LINK]?). Ouders hebben dit soms extra nagevraagd in de familie naar aanleiding van de vraag van de jeugdverpleegkundige tijdens de intake.
- De JGZ-professional neemt de anamnese over risicofactoren mondeling af. De ligging bij de bevalling kan de JGZ-professional meestal ook uit de overdrachtspapieren van de verloskundig zorgverlener en kraamzorg halen.
- Ten slotte interpreteert de jeugdarts tijdens het eerste contactmoment of sprake is van een risicofactor die reden is voor verwijzing.
- Voor het afnemen en interpreteren van de risicofactoren stelt de JGZ-professional de vragen zoals beschreven in Bijlage 1 en worden de erbij vermelde omschrijvingen gehanteerd. Pas de formulering van vragen zo nodig aan aan het begripsniveau van de ouders. Bij registratie is het belangrijk te noteren of een risicofactor wel of niet vóórkomt ofwel dat deze niet bekend is, bijvoorbeeld vanwege taalbarrière, adoptiekinderen, uithuisplaatsingen of omdat de JGZ-professional het (nog) niet heeft nagevraagd.
4 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen van DDH
Het onderzoek door de JGZ in het kader van de vroegtijdige opsporing van DDH bestaat uit anamnese en lichamelijk onderzoek. De anamnese betreft het identificeren van risicofactoren.
Inzicht in de risicofactoren helpt bij het identificeren van kinderen die een groter risico lopen op DDH. Deze kinderen kunnen ofwel tijdig worden verwezen voor diagnostiek en eventuele behandeling, ofwel advies en instructie krijgen over het vermijden van de risicofactor. In dit thema wordt beschreven op welke wijze de JGZ anamnese en lichamelijk onderzoek voor de opsporing van DDH uitvoert en wat de indicaties voor verwijzing zijn.
Zie ook de sectie Risico- en beschermende factoren.
4.1 Anamnese over risicofactoren
Op welke manier en op welk tijdstip kan de anamnese over risicofactoren voor de opsporing van DDH bij zuigelingen het beste worden afgenomen?
Aanbevelingen
4.1.1 Werkwijze anamnese
Op welke manier en op welk tijdstip kan de anamnese over risicofactoren voor de opsporing van DDH bij zuigelingen het beste worden afgenomen?
Anamnese
Voor de vroegsignalering van DDH in de JGZ is het belangrijk dat jeugdartsen en jeugdverpleegkundigen de risicofactoren goed kennen. Inzicht in de risicofactoren helpt bij het identificeren van kinderen die een groter risico hebben op DDH, zodat deze kinderen tijdig kunnen worden verwezen voor diagnostiek en eventuele behandeling. Uiteraard betekent de aanwezigheid van één of meerdere risicofactoren (anders dan het meisje-zijn), niet dat er dan altijd een DDH zal zijn of ontstaan; 1-10% van de kinderen met één of meer risicofactoren heeft DDH [17]). Dit geldt ook andersom: de afwezigheid van risicofactoren betekent niet dat er geen sprake kan zijn van een DDH; 10-27% heeft een of meer risicofactoren [17]. Het lichamelijk onderzoek tijdens de screening en onderzoek op indicatie bij vragen of ongerustheid van ouders blijft belangrijk.
De werkgroep adviseert de volgende werkwijze met betrekking tot het uitvragen van de risicofactoren:
- De jeugdverpleegkundige neemt bij de intake van de zuigeling de anamnese af. Dit is meestal tijdens het huisbezoek in de tweede levensweek. In sommige situaties zal de anamnese later worden afgenomen, bijvoorbeeld in geval van ziekenhuisopname na de geboorte, wanneer een kind wordt gevolgd op de prematurenpoli, bij verhuizing, adoptie, etc.
- Tijdens het eerste contactmoment bij de jeugdarts loopt deze de anamnese na en vult deze zo nodig aan. Dit geldt met name voor de anamnese naar het voorkomen van DDH en/of coxartrose voor de leeftijd van 50 jaar in de naaste familie (eerste- en tweedegraads familieleden). Ouders hebben dit soms extra nagevraagd in de familie naar aanleiding van de vraag van de jeugdverpleegkundige tijdens de intake.
- De JGZ-professional neemt de anamnese over risicofactoren mondeling af. De ligging bij de bevalling kan de JGZ-professional meestal ook uit de overdrachtspapieren van de verloskundig zorgverlener en kraamzorg halen.
- Ten slotte interpreteert de jeugdarts tijdens het eerste contactmoment of sprake is van een risicofactor die reden is voor verwijzing.
- Voor het afnemen en interpreteren van de risicofactoren stelt de JGZ-professional de vragen zoals beschreven in Bijlage 1 en worden de erbij vermelde omschrijvingen gehanteerd. Pas de formulering van vragen zo nodig aan aan het begripsniveau van de ouders. Bij registratie is het belangrijk te noteren of een risicofactor wel of niet vóórkomt ofwel dat deze niet bekend is, bijvoorbeeld vanwege taalbarrière, adoptiekinderen, uithuisplaatsingen of omdat de JGZ-professional het (nog) niet heeft nagevraagd.
4.2 Lichamelijk onderzoek
Aanbevelingen
4.2.1 Aandachtspunten bij het uitvoeren van het lichamelijk onderzoek
Het heuponderzoek wordt uitgevoerd in een warme omgeving met warme handen, zodat de spieren van het kind zoveel mogelijk ontspannen zijn. Het onderzoek van het kind dient plaats te vinden op een vlakke, warme en stevige onderlaag, bijvoorbeeld een harde (yoga)mat van ongeveer 1 cm dik met daarop een handdoek; een zacht (aankleed)kussen dient te worden verwijderd. Het kind is volledig ontkleed en de luier is verwijderd. Het kind ligt ontspannen. De onderzoeker staat aan het voeteneind van het kind [3], [23].
4.2.2 Uitvoering lichamelijk onderzoek (samenvatting)
Samenvatting van de literatuur
Leeftijdsperiode van 4 weken t/m 6 maanden: screening
Inspectie huidplooien in het bil- en liesgebied
In het prospectieve cohortonderzoek van Boere-Boonekamp [38] in een algemene populatie van 1968 zuigelingen bleek 24,2% van de kinderen tijdens één of meerdere onderzoeken asymmetrische bil- of liesplooien te hebben. De positief voorspellende waarde hiervan voor DDH was slechts 9%. In het Turkse onderzoek van Omeroglu [75] werd ook de symmetrie van huidplooien in het bil- en liesgebied meegenomen. Het is te verwachten dat de testeigenschappen van het aspect van de bil- en liesplooien in de voorgeselecteerde populatie van dit onderzoek (verwezen kinderen) gunstiger zijn dan in een algemene populatie kinderen. De sensitiviteit en specificiteit van asymmetrie van de plooien betrof in Omeroglu’s onderzoek respectievelijk 52% en 82%; de positief voorspellende waarde was 38%.
Abductie van de heupen
De zuigeling ligt op de rug, geheel recht, het gezicht in de middenpositie. Het kind kijkt naar boven/voren, uitgelokt door de onderzoeker of eventueel door de ouder die aan het hoofdeinde boven het kind de aandacht vangt. Bij het uitvoeren van de abductietest worden de benen in de heupen 90 graden en in de knieën maximaal gebogen. De handen van de onderzoeker omvatten de knieën van het kind, met de duimen aan de binnenkant van de dijen. De knieën worden voorzichtig geabduceerd (gespreid). Figuur 2 toont een meisje van 3 maanden met een abductiebeperking aan de rechterheup, waarbij de abductietest wordt uitgevoerd. Ten behoeve van het nemen van de foto omvatten de handen van de onderzoeker de onderbenen in plaats van de knieën van het kind.
Figuur 2. Abductie van de heupen bij een meisje van 3 maanden met een abductiebeperking aan de rechterheup. Ten behoeve van het nemen van de foto omvatten de handen van de onderzoeker de onderbenen in plaats van de knieën van het kind. Bron: Visser, J.D., Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerste lijn gezondheidszorg. 2012 [23].
In de literatuur worden verschillende afkappunten voor abductiebeperking vermeld: 60 graden of minder [14], [76], [77], [78] of 70 graden of minder [3], [7], [23]. Daarnaast wordt als afkappunt voor abductieverschil gebruikt: een verschil van 10 graden of meer [3], [7] of een verschil van 20 graden of meer [76], [77], [78], [79], [80]. Daarbij dient opgemerkt te worden dat bij ongeveer 20% van de gevallen sprake is van bilaterale DDH, waardoor mogelijk geen abductieverschil bestaat tussen beide zijden [14].
In een prospectief cohortonderzoek (1992-1993) in Twente werd de waarde van de abductietest vastgesteld [13], [38]. De sensitiviteit en specificiteit van de abductietest uitgevoerd tijdens 1 tot 4 heuponderzoeken in de eerste 6 levensmaanden waren respectievelijk 51% en 90%. De positief voorspellende waarde was in deze algemene populatie 16%. Vijf andere studies, 1 uitgevoerd in Nederland, 2 in Engeland, en 2 in Turkije, hebben de testeigenschappen en voorspellende waardes van enkel de abductietest onderzocht [75], [78], [79], [80], [81]. Al deze studies zijn uitgevoerd in een selecte populatie van kinderen die waren verwezen vanwege een vermoeden van DDH, met een prevalentie variërend van 7,6 tot 33,1%. Het is te verwachten dat de testeigenschappen van de abductietest in dergelijke voorgeselecteerde populaties gunstiger zijn dan in de algemene populatie van kinderen.
Het Nederlandse onderzoek richtte zich op de waarde van de abductietest voor het opsporen van DDH bij kinderen van 3-10 maanden oud door een orthopedisch chirurg in het ziekenhuis [78]. De prevalentie van DDH in deze hoog-risico populatie was 33,1% (Graf type IIb tot IV). De sensitiviteit en de specificiteit van de abductietest (criterium: abductie < 60 graden of abductieverschil van 20 graden) bleken respectievelijk 69% en 54%; bij 1 op de 3 zuigelingen met DDH was de abductie dus normaal. Daarnaast had de helft van de zuigelingen zonder DDH wel een abductiebeperking.
Het eerste onderzoek uit Engeland [79] is ook uitgevoerd in een ziekenhuissetting (kinderen ouder dan 8 weken). Hier was de prevalentie van DDH 7,6% (Graf type II tot IV). De sensitiviteit van de abductietest (criterium niet gespecificeerd) voor het opsporen van de ernstige gevallen van DDH (Graf type lll of IV) was 78%; de specificiteit was 93%.
Het tweede Engelse onderzoek [80] includeerde kinderen vanwege neonatale instabiliteit en risicofactoren; bij vermoeden van instabiele heupen volgde echografisch onderzoek na 1-2 weken, bij risicofactoren na 6-9 weken. De sensitiviteit en specificiteit van de abductietest (criterium: abductieverschil van 20 graden, eenzijdig) voor het opsporen van eenzijdige DDH (Graf type ll tot IV) waren respectievelijk 70% en 90%.
Het eerste onderzoek in Turkije [75] betrof 188 naar de kinderorthopedie verwezen kinderen. Bij 17% werd een DDH vastgesteld (Graf type IIa- tot IV). De sensitiviteit en specificiteit van een abductiebeperking (criterium: abductie < 70 graden) bedroegen respectievelijk 70% en 89% (berekend op heupniveau in plaats van op kindniveau).
De laatste studie betreft onderzoek in Turkije [81] bij kinderen van 30 tot 120 dagen, die verwezen waren vanuit kinderklinieken vanwege een abductiebeperking. De prevalentie van DDH bedroeg 9,3% (Graf type II tot IV). De sensitiviteit van een (opnieuw vastgestelde) eenzijdige abductiebeperking (criterium: abductieverschil van 20 graden) voor DDH was 42%, de specificiteit 98%; voor tweezijdige abductiebeperking waren deze waardes respectievelijk 30% en 65%.
Beoordelen kniehoogte
De zuigeling ligt op de rug, geheel recht, het gezicht in de middenpositie. Het kind kijkt naar boven/voren, uitgelokt door de onderzoeker of eventueel door de ouder die aan het hoofdeinde boven het kind de aandacht vangt. De kniehoogte wordt beoordeeld met de handgreep van Galeazzi. Het bekken ligt daarbij recht en wordt zo nodig door de ouder gefixeerd [82]. De benen worden in de heupen 90 graden en in de knieën maximaal gebogen. Bij een beweeglijk kind kan men de voeten eventueel laten steunen op de onderlaag (figuur 3). De hoogte van de knieën wordt vergeleken. Bij een ge(sub)luxeerde heup is de heupkop naar boven zijwaarts verplaatst, wat leidt tot een schijnbaar lagere kniehoogte aan de aangedane zijnde. Een positieve Galeazzi (kniehoogteverschil) is een aanwijzing voor de mogelijke aanwezigheid van een eenzijdig ge(sub)luxeerde heup [3], [23]. Vanzelfsprekend hoeft er bij een dubbelzijdige DDH geen verschil in kniehoogte te zijn.
Figuur 3. Onderzoek van de kniehoogte bij hetzelfde kind als getoond in figuur 2. Het kind moet bij de beoordeling van de kniehoogte idealiter naar boven/voren kijken. Bron: Visser, J.D., Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerste lijn gezondheidszorg. 2012 [23].
Er is 1 Nederlands en 1 Turks onderzoek gevonden dat de testeigenschappen en voorspellende waardes van het vergelijken van beenlengte en/of kniehoogte onderzocht. In het prospectieve cohortonderzoek van Boere-Boonekamp [13], [38] in een algemene populatie zuigelingen bleek de aanwezigheid van een beenlengteverschil een 11,9 (95% BI 7,7-18,3) keer zo grote kans op DDH te betekenen en een kniehoogteverschil een 10,9 (95% BI 7,1-17,0) keer zo grote kans. Het onderzoek geeft onvoldoende uitsluitsel over de testeigenschappen van het uitgevoerde beenlengte- en kniehoogte-onderzoek apart, omdat de onderzoeken direct na elkaar werden uitgevoerd. De sensitiviteit en specificiteit van een verschil in kniehoogte vastgesteld tijdens 1 tot 4 heuponderzoeken in de eerste 6 levensmaanden waren respectievelijk 33% en 97%. De positief voorspellende waarde was in deze algemene populatie 28% [13]. Het Turkse onderzoek [75] uitgevoerd in een voorgeselecteerde populatie, rapporteert specifiek over de testeigenschappen en voorspellende waarde van de aanwezigheid van een kniehoogteverschil. Een positieve Galeazzi kwam voor bij 6 van de 43 DDH heupen van een groep van 188 kinderen die naar de kinderorthopeed waren verwezen, hetgeen een sensitiviteit van 14% betekent.
Meerdere onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek samen
De meest relevante studie naar de waarde van lichamelijk onderzoek bij zuigelingen betreft een prospectief cohortonderzoek (1992-1993) uitgevoerd in Twente [83], [84]. Het onderzoek bestond uit een anamnese voor risicofactoren en een lichamelijk onderzoek van de heupen. De uitvoering van het lichamelijk onderzoek komt sterk overeen met de huidige werkwijze door de JGZ. Het lichamelijk onderzoek bestond steeds uit de observatie van de plaats en diepte van de huidplooien in het bil- en liesgebied, de abductietest, en het beoordelen van de beenlengte en kniehoogte. De prevalentie van DDH in deze algemene populatie zuigelingen was 3,7% (criterium: echografie plus röntgenonderzoek plus beoordeling orthopedisch chirurg). De studie toont aan dat het onderzoek als geheel, door de jeugdarts, uitgevoerd op de leeftijd van 1, 3, 4 en 5 maanden (gemiddeld 3,6 onderzoeken; range 1-5), een beperkte validiteit heeft [83]. Met dit protocol werden 6 op de 7 zuigelingen met DDH door de JGZ opgespoord, en 1 op de 7 niet (sensitiviteit 86%). Daarnaast werd 1 op de 6 zuigelingen zonder DDH op basis van het onderzoek verwezen voor aanvullende diagnostiek (specificiteit 82%). Van de onderzochte kinderen met een positieve testuitslag werd bij 16% daadwerkelijk de diagnose DDH gesteld. Daarnaast bleek dat 99% van de kinderen met een negatieve testuitslag ook daadwerkelijk geen DDH had. Een publicatie in Huisarts en Wetenschap [38] over ditzelfde onderzoek beschrijft de waarde van alleen het lichamelijk onderzoek in meer detail; van de honderd kinderen met een afwijkend heuponderzoek hadden er 83 geen en slechts 17 wel DDH (positief voorspellende waarde 17%). Oftewel, van de zes verwezen kinderen heeft 1 kind DDH.
Aantal screeningsmomenten
Er is geen kwalitatief goed onderzoek gevonden dat 1 moment van lichamelijk onderzoek in de leeftijdsperiode 0 t/m 6 maanden vergelijkt met meerdere screeningsmomenten. Door Donnelly [85] is één retrospectief cohortonderzoek gepubliceerd dat evalueerde op welk moment de diagnose voor DDH gesteld werd wanneer op 3 momenten een lichamelijk onderzoek (handgrepen van Barlow en Ortolani vlak na de geboorte door een kinderarts, en beenlengteverschil plus abductietest door een health visitor bij 6-10 weken en bij 4 maanden) plaatsvond. Dit onderzoek liet zien dat de helft van de gevallen van DDH (51%) gediagnosticeerd was wanneer het kind tussen de 3 en 5 maanden oud was. Ook het prospectieve cohortonderzoek van Boere-Boonekamp [13] in de algemene populatie zuigelingen onderzocht op welke leeftijd de screeningsonderzoeken de beste voorspellende waardes hadden. Bij 0 tot 6 weken was de voorspellende waarde 45% (5 gevallen van DDH uit elf verwijzingen), bij 7-12 weken 21% (5/24), bij 13-18 weken 15% (29/199), bij 19-24 weken 10% (11/87) en bij 25-30 weken 24% (4/17). Een mogelijke verklaring voor de hoge voorspellende waarde bij verwijzingen van kinderen van 0 tot 6 weken is dat dit onderzoek kinderen met evidente klinische afwijkingen betrof. Van de kinderen met een DDH was de helft verwezen op basis van alleen een afwijkend lichamelijk onderzoek. Driekwart van de diagnoses werd gesteld na verwijzingen op de leeftijd van 13 tot 24 weken.
Leeftijdsperiode vanaf 7 maanden tot 18 jaar: casefinding
Eén op van de 7 zuigelingen met DDH wordt niet door de JGZ opgespoord [83]. Het is belangrijk dat de JGZ in de leeftijdsperiode vanaf 7 maanden en ouder de heupen onderzoekt om kinderen met DDH op te sporen die niet bij de screening vóór de leeftijd van 7 maanden zijn gevonden. Er is dan geen sprake meer van screening ten behoeve van vroege opsporing, maar van zogeheten casefinding. Over de toepasbaarheid van methoden van lichamelijk onderzoek in de leeftijdsperiode van 7 maanden en ouder is geen literatuur gevonden. Voor deze tekst is gebruik gemaakt van informatie uit leerboeken, grijze literatuur en de mening van de werkgroep.
In de leeftijdsperiode 7 maanden tot 2 jaar wordt het heuponderzoek als vast onderdeel van het algemeen lichamelijk onderzoek uitgevoerd, als de jeugdarts lichamelijk onderzoek verricht. Na de leeftijd van 2 jaar vindt onderzoek plaats op indicatie naar aanleiding van vragen van de ouders of observaties van de jeugdarts, jeugdverpleegkundige of verpleegkundig specialist. De jeugdverpleegkundige let tijdens de contactmomenten bij haar observaties op symmetrie (bijvoorbeeld in het looppatroon), reageert adequaat op vragen van ouders, registreert observaties en vragen, en verwijst zo nodig naar de jeugdarts.
Naarmate het kind ouder wordt, neemt de abductie in een niet-afwijkende (niet-geluxeerde) heup af [23], [86]. Een verschil in abductie wordt minder uitgesproken en is moeilijker te zien. Wat meer uitgesproken wordt is het beenlengte- en kniehoogteverschil, maar vanzelfsprekend alleen bij enkelzijdige DDH [23].
Totdat het kind goed los loopt, onderzoekt de jeugdarts de abductie van de heupen en de kniehoogte bij het liggende kind op gestandaardiseerde wijze zoals eerder beschreven bij de screening, rekening houdend met de zojuist beschreven veranderingen. Vanaf het moment dat het kind zelfstandig loopt vindt allereerst onderzoek in staande houding plaats van het looppatroon, de luchtfiguur onder het perineum, en de lendenlordose (beenlengte vanaf de leeftijd van 2 jaar). Bij afwijkende bevindingen of bij specifieke klachten wordt het onderzoek uitgebreid met onderzoek van de abductie en kniehoogte in liggende houding. Afbeeldingen van methoden voor lichamelijk onderzoek zijn bijvoorbeeld te vinden in het boek ‘Pluis of niet Pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerste lijn gezondheidszorg’ [23].
Abductie en kniehoogte
Zie voor de manier van uitvoeren de beschrijving bij ‘Leeftijdsperiode van 0 t/m 6 maanden: screening’.
Looppatroon
Bij een eenzijdige luxatie kan sprake zijn van manklopen. Waggelend lopen kan wijzen op een dubbelzijdige luxatie.
Beenlengte (vanaf de leeftijd van 2 jaar)
Het onderzoek van de beenlengte en vaststellen van de mogelijke oorzaak van een verschil in beenlengte is niet gemakkelijk, vooral op de peuterleeftijd. Vanaf de peuter-kleuterleeftijd kan een verschil in beenlengte in staande houding zichtbaar worden.
Differentiëren tussen structureel en functioneel beenlengteverschil is lastig. Een structureel beenlengteverschil is gelegen in een daadwerkelijk lengteverschil van de individuele botten (femur, tibia). Bij een functioneel beenlengteverschil is de oorzaak gelegen in een posturele afwijking (op basis van een afwijking boven het bovenbeen), dus in een heupluxatie of een flexie adductiestand in een van de benen.
Om te onderzoeken of sprake is van een bekkenscheefstand, onderzoekt men het kind in zittende houding op de onderzoekstafel. Met de duimen palpeert men de spinae iliaca anteriores superiores en men beoordeelt of deze op gelijke hoogte staan. Is dit niet het geval, dan is sprake van een bekkenscheefstand.
Wanneer de onderzoeker zeker is dat de oorzaak van een vastgesteld beenlengteverschil niet in het onderbeen is gelegen (d.w.z. dat bij onderzoek in buikligging met de knieën 90 graden gebogen de voetzolen op gelijke hoogte staan), is er een indicatie voor een röntgenfoto van het bekken.
Luchtfiguur onder het perineum
Een verbrede luchtfiguur onder het perineum wordt veroorzaakt doordat de dijbeenkoppen bij een dubbelzijdige (sub)luxatie behalve naar achter-boven ook naar lateraal zijn verplaatst. Dit is zichtbaar als men het kind ontbloot laat staan en lopen. Figuur 4 toont een kind met een verbrede luchtfiguur onder het perineum.
Figuur 4. Verbreed luchtfiguur onder het perineum bij een meisje van 2 jaar en 3 maanden oud met een dubbelzijdige heupluxatie.
Bron: Visser, J.D., Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerste lijn gezondheidszorg. 2012 [23].
Lendenlordose
Een dubbelzijdige (sub)luxatie van de heupen gaat veelal ook gepaard met een versterkte lendenlordose. Er is dan sprake van een holle rug, veroorzaakt door een vooroverkanteling van het bekken door de flexiecontractuur, veroorzaakt door heupluxatie.
Aantal onderzoeken
In de leeftijdsperiode 7 maanden tot 2 jaar wordt het heuponderzoek (zie thema 1.3 [LINK] ) als vast onderdeel van het algemeen lichamelijk onderzoek uitgevoerd, als de jeugdarts lichamelijk onderzoek verricht. Na de leeftijd van 2 jaar vindt onderzoek van de heupen door de jeugdarts alleen op indicatie plaats, dat wil zeggen als er vragen, zorgen, klachten of opvallende observaties zijn van ouders/kind en/of jeugdverpleegkundige en/of jeugdarts.
Conclusies
Testeigenschappen en voorspellende waardes van het lichamelijk onderzoek door de JGZ
Meerdere onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek samen
|
Niveau* |
Conclusie** |
Literatuur |
| 2 | Het is aannemelijk dat een screening van de algemene populatie zuigelingen bij wie de heupen tussen 1 en 6 maanden gemiddeld 3,6 keer lichamelijk worden onderzocht door de jeugdarts een sensitiviteit van 86% en een specificiteit van 82% heeft. De positief voorspellende waarde van een afwijkend lichamelijk onderzoek van de heupen in een dergelijk protocol voor het opsporen van DDH is 17%. | A2 [83] |
Asymmetrie huidplooien
|
Niveau |
Conclusie |
Literatuur |
| 2 | Het is aannemelijk dat asymmetrie van de plooien wordt gevonden bij bijna een kwart van de algemene populatie zuigelingen op enig moment in de eerste 6 levensmaanden. Bij toepassing van deze test in de algemene populatie is de positief voorspellende waarde voor DDH 9%. | A2 [38], [75] |
Abductietest
|
Niveau |
Conclusie |
Literatuur |
| 2 | Het is aannemelijk dat de sensitiviteit en specificiteit van de abductietest uitgevoerd tijdens 1 tot 4 heuponderzoeken (gemiddeld 3,6) in de eerste 6 levensmaanden respectievelijk 51% en 90% is. Bij toepassing van deze test in de algemene populatie is de positief voorspellende waarde voor DDH 16%. | A2 [13], [38] |
| 2 | Het is aannemelijk dat de sensitiviteit en specificiteit van de abductietest voor het opsporen van DDH (Graf type ll of hoger), toegepast door een klinisch specialist in een populatie van naar het ziekenhuis verwezen kinderen hoger is dan in de algemene populatie (sensitiviteit 42-78% en specificiteit 90-93%). Voor eenzijdige abductiebeperking zijn de sensitiviteit en specificiteit gunstiger dan voor tweezijdige abductiebeperking. | A2 [75], [78], [81] |
Beenlengte- en kniehoogteverschil
|
Niveau |
Conclusie |
Literatuur |
| 2 | Het is aannemelijk dat bij een verschil in beenlengte vastgesteld tijdens 1 tot 4 heuponderzoeken (gemiddeld 3,6) in de eerste 6 levensmaanden de kans op een DDH circa 12 keer verhoogd is. Bij toepassing van deze test in de algemene populatie is de positief voorspellende waarde voor DDH 28%. | A2 [13], [38] |
| 2 | Het is aannemelijk dat de sensitiviteit en specificiteit van een verschil in kniehoogte vastgesteld tijdens 1 tot 4 heuponderzoeken (gemiddeld 3,6) in de eerste 6 levensmaanden respectievelijk 33% en 97% zijn. Bij toepassing van deze test in de algemene populatie is de positief voorspellende waarde voor DDH 28%. | A2 [13], [38] |
Aantal screeningsmomenten
|
Niveau |
Conclusie |
Literatuur |
| 3 | Er zijn aanwijzingen dat, indien er 3 tot 4 onderzoeksmomenten in de eerste 6 levensmaanden zijn, en kinderen met alleen risicofactoren bij 3 maanden aanvullend onderzoek krijgen, 50% tot 75% van de gevallen van DDH tussen 3 en 6 maanden worden vastgesteld. | B [13], [85] |
*Zie voor het bepalen van het niveau van de conclusie en de literatuur het hoofdstuk Verantwoording.
**Niveau 1: Het is aangetoond dat…. Niveau 2: Het is aannemelijk/waarschijnlijk dat…. Niveau 3: Er zijn aanwijzingen/het lijkt waarschijnlijk dat…. Niveau 4: De deskundigen/werkgroep zijn/is van mening dat…. [60].
Overige overwegingen
Neonataal onderzoek: handgrepen van Barlow en Ortolani
Kort na de geboorte kunnen de handgrepen van Ortolani en Barlow worden uitgevoerd voor de vroege opsporing van respectievelijk geluxeerde en luxeerbare heupen [67]. Deze methoden zijn vooral in de eerste 48 uur accuraat [69]. De handgrepen kunnen alleen in de eerste weken na de geboorte worden uitgevoerd [68]. Aangezien pasgeborenen pas na ongeveer 4 weken door de jeugdarts worden onderzocht, zijn de handgrepen van Ortolani en Barlow niet geschikt voor toepassing door de JGZ. De handgrepen zijn gericht op het detecteren van abnormale beweeglijkheid van de heupkop ten opzichte van de heupkom en zijn dus tests voor instabiliteit [3]. In Nederland vindt volgens de NHG standaard ‘Zwangerschap en kraamperiode’ [72] direct na de geboorte geen onderzoek van de heupen plaats. Ook bij kinderen die zijn geboren in de tweede lijn vindt geen systematisch heuponderzoek plaats.
Waarde lichamelijk onderzoek 1-6 maanden
De waarde van de verschillende onderdelen van het lichamelijk onderzoek van de heupen apart en gezamenlijk als onderdeel van het protocol voor screening op DDH is beperkt. In overleg met de werkgroep is gekozen om inspectie van huidplooien in het bil- en liesgebied niet op te nemen in het verwijsprotocol, vanwege de lage positief voorspellende waarde. Het onderzoek naar beenlengteverschil is bij jonge zuigelingen lastig; een vastgesteld verschil kan zowel op een verschil in lengte van het onderbeen als van het bovenbeen berusten. De literatuur geeft onvoldoende uitsluitsel over de testeigenschappen van onafhankelijk van elkaar uitgevoerd beenlengte- en kniehoogte-onderzoek. De werkgroep raadt aan om alleen een verschil in kniehoogte aan te houden als verwijsindicatie.
De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing voor afkapwaarden om te bepalen of sprake is van een abductiebeperking of een kniehoogteverschil is beperkt. Binnen de werkgroep is ervoor gekozen om te spreken van een afwijkend lichamelijk onderzoek wanneer sprake is van een abductiebeperking, d.w.z. een abductie < 70 graden, of een abductieverschil van ≥ 20 graden, en/of een duidelijk zichtbaar kniehoogteverschil.
Als men naar de waarde van het lichamelijk onderzoek van de heupen als geheel kijkt, dat wil zeggen onderzoek van abductie en kniehoogte gemiddeld 3,6 keer uitgevoerd in de leeftijd van 1 tot 6 maanden, blijkt dat van de honderd kinderen die men vanwege een afwijkend onderzoek verwijst er 83 geen DDH en slechts 17 wel DDH hebben (positief voorspellende waarde 17%). Oftewel, van de zes verwezen kinderen heeft 1 kind DDH. Een afwijkende abductietest heeft als enige indicatie voor verwijzing een matige voorspellende waarde (16%). De abductietest is bovendien bij circa de helft van de kinderen met een DDH niet afwijkend. Als onderdeel van het totale protocol maakt het de screening echter wel een stuk sensitiever.
Waarde screeningsprotocol 1-6 maanden
Het screeningsonderzoek dat de JGZ in Nederland uitvoert, bestaat naast het lichamelijk onderzoek van de heupen uit het identificeren van risicofactoren (familieanamnese, stuitligging). De werkgroep vindt dat dit protocol als geheel een zeer matige validiteit heeft: sensitiviteit 86%, specificiteit 82% [83]. Dit betekent dat bij toepassing in een algemene populatie zuigelingen, bij 14% van de kinderen met DDH de screeningstest niet positief is (dus geen vroege opsporing) en bij slechts 16% van de kinderen met een positieve screeningstest na aanvullend onderzoek daadwerkelijk de diagnose DDH wordt gesteld. Daarnaast wordt 1 op de 6 zuigelingen zonder DDH op basis van de screeningstest verwezen, en ondergaat dus ten onrechte aanvullend onderzoek. Vanwege de beperkte invasiviteit van het aanvullend onderzoek (echografie) dat na een positieve screeningsuitslag moet plaatsvinden, raadt de werkgroep aan de huidige screening voorlopig te blijven uitvoeren.
Voetafwijkingen
In de richtlijn primaire idiopathische klompvoet voor orthopeden [87] is geconcludeerd dat er een verhoogd risico op DDH bestaat bij kinderen met klompvoeten. Op basis van deze conclusie is in de betreffende richtlijn de aanbeveling opgenomen dat kinderen met idiopathische klompvoet gescreend worden op DDH door middel van echo of röntgenonderzoek. In de literatuursearch (2000-2012) ontbrak de recente review en meta-analyse van Ibrahim uit 2015 [40]. Deze studie van Ibrahim toonde aan dat er geen verband bestaat tussen voetafwijkingen en DDH, en was doorslaggevend in de beslissing voetafwijkingen in deze JGZ-richtlijn niet op te nemen als verwijscriterium voor beeldvormend onderzoek.
Wie voert het lichamelijk onderzoek uit?
Er is geen literatuur over wie het lichamelijk onderzoek het beste kan uitvoeren. In de praktijk vindt het lichamelijk onderzoek van de heupen vrijwel overal plaats door een jeugdarts, soms door een verpleegkundig specialist. Beiden hebben een gedegen opleiding, zowel gericht op uitvoering van het onderzoek als op kritische interpretatie van de resultaten. Vanwege de matige testeigenschappen van het heuponderzoek raadt de werkgroep aan het onderzoek door een jeugdarts of verpleegkundig specialist te laten uitvoeren.
Echografie
In diverse Europese landen (Duitsland, Oostenrijk) wordt in de neonatale periode gescreend m.b.v. de handgrepen van Barlow en Ortolani in combinatie met echografische screening (bij alle kinderen of alleen bij kinderen met risicofactoren). Een Cochrane review concludeerde in 2013 dat o.b.v. de beschikbare evidentie geen aanbevelingen kunnen worden gegeven voor screening met behulp van echografie; deze review beperkte zich echter tot pasgeborenen in de eerste 6 weken [88].
De projectgroep voerde een korte evaluatie uit van de beschikbare literatuur over de waarde van echografie als methodiek voor screening op DDH door de JGZ. In de afgelopen 15 jaar zijn in Nederland twee studies naar echografische screening in de tweede tot vierde levensmaand verricht (Soundchec 1 en 2). De resultaten waren niet eenduidig. Hoewel de resultaten van de eerste kosteneffectiviteitsstudie veelbelovend waren [89] bracht een bredere implementatie van de methodiek in de praktijk van de JGZ de nodige problemen aan het licht [90]. Allereerst waren er forse verschillen in opkomstpercentage voor de screening. Verder leidde de uitvoering van de heupechografie door een beperkt aantal, speciaal opgeleide, echografisten (jeugdartsen, jeugdverpleegkundigen, radiologisch laboranten) tot grote variatie in het aantal opgespoorde gevallen van DDH (3,6% in stedelijke regio vs. 10,2% in plattelandsregio). Deze verschillen konden niet worden verklaard. Ouders bleken overigens zeer tevreden over de echografische screening [91].
De US Preventive Services Task Force voerde in 2006 een review uit [88], [92] naar de waarde van screening op DDH in de periode 0-6 maanden; de conclusie was dat de voordelen van screening op DDH (lichamelijk onderzoek en/of echografie) niet duidelijk zijn. Mede gebaseerd hierop adviseren zowel de Canadian Task Force on Preventive Care [68] als de American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) [93] om geen algemene echografische screening te implementeren.
4.3 Onderzoeks-, handelings- en verwijsprotocol
De leeftijd van verwijzing is van belang als deze invloed heeft op het resultaat van behandeling. Om deze reden is gezocht naar literatuur over de effectiviteit van behandeling van DDH gerelateerd aan de leeftijd bij het starten van de behandeling.
Wanneer geen screening voor DDH zou worden uitgevoerd door de JGZ, zouden aanzienlijk meer kinderen met DDH laat gediagnosticeerd worden, waarna hoge kosten worden gemaakt voor behandeling (zie Bijlage 2).
In Bijlage 3 wordt het screeningsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud schematisch weergegeven.
In Bijlage 4 wordt het onderzoeks- en verwijsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen vanaf 7 maanden oud weergegeven.
Bijlage 5 toont voor deze leeftijdsperiode welke discipline, op welk moment, welke activiteit uitvoert.
Lees in de sectie Samenwerken meer over de samenwerking met huisartsen en ziekenhuizen bij verwijzing.
Aanbevelingen
4.4 Prematuriteit en DDH
Hieronder worden de aanbevelingen en overwegingen over de signalering van DDH bij prematuur geboren kinderen (zwangerschapsduur <37 weken) bij elkaar gepresenteerd.
4.4.1 Lichamelijk onderzoek prematuren
Er is geen literatuur beschikbaar die de aanbeveling over het wel of niet corrigeren van prematuriteit bij het uitvoeren van het lichamelijk onderzoek onderbouwt.
De werkgroep adviseert bij prematuren te streven naar 3 onderzoeken voor de gecorrigeerde leeftijd van 7 maanden, en bij langdurige ziekenhuisopname 2 onderzoeken, in samenspraak met kinderarts en ouders.
Zie subsectie Onderzoeks-, handelings- en verwijsprotocol en Bijlage 3 Screeningsprotocol en verwijs- en handelingsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud.
4.4.2 Verwijzing
De werkgroep adviseert om bij prematuren bij risicofactoren en afwijkende bevindingen beeldvormend onderzoek te laten verrichten op de gecorrigeerde leeftijd van 3 maanden, of binnen 2 weken bij een kind ouder dan de gecorrigeerde leeftijd van 3 maanden.
Bij vermoeden van een heupluxatie vindt de werkgroep dat het kind op dat moment moet worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed met het verzoek het kind binnen 2 weken te onderzoeken, zodat behandeling zo nodig tijdig kan worden ingezet.
De overwegingen voor aanvullend onderzoek op de gecorrigeerde leeftijd van 3 maanden zijn dat ook bij prematuur geboren kinderen de heup nog moet uitrijpen. Daarnaast bezoeken ouders en prematuur geboren kinderen na ontslag uit het ziekenhuis meerdere keren het ziekenhuis. Een extra ziekenhuisbezoek voor aanvullend onderzoek kan een extra belasting zijn voor ouders en kind, en onrust geven in het gezin. Met name erg prematuur geboren kinderen zijn bovendien erg kwetsbaar en lopen makkelijker infecties op, waardoor ziekenhuisbezoeken bij voorkeur beperkt worden.
De werkgroep benoemt dat bij risicofactoren en/of een vermoeden van dysplasie zonder luxatie de casemanager (kinderarts, jeugdarts of huisarts; zie JGZ-richtlijn ‘Vroeg en/of small for gestational age (SGA) geboren kinderen (2013)’ samen met de ouders beslist op welk moment de verwijzing plaatsvindt, waarbij naar de specifieke omstandigheden van het kind wordt gekeken. Bij de beslissing spelen de belastbaarheid van kind en ouders, mate van prematuriteit en ernst van de afwijkende bevindingen een rol. Bij een vermoeden van dysplasie met luxatie verwijst de jeugdarts op dat moment naar de (kinder)orthopeed met het verzoek het kind binnen 2 weken te onderzoeken.
5 Begeleiden en behandelen
5.1 Aandachtspunten voor JGZ tijdens behandeling
Wanneer een kind wordt behandeld voor DDH is het belangrijk dat JGZ-professionals hiermee rekening houden.
Meten en wegen
Bij een kind dat spreidbehandeling krijgt, wordt afgezien van het strekken van de benen en dus het meten van de lengte. Wegen kan zonder spreidmiddel wanneer de (kinder)orthopeed heeft aangegeven dat dit mag en anders mét spreidmiddel. Het uitvoeren van de lengtemeting van een liggend kind is beschreven in het boekje ‘Groeidiagrammen 2010. Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen’, uitgegeven door TNO [74].
Vaccineren
De wijze van behandeling kan invloed hebben op de keuze waar te vaccineren. De eerste voorkeursplaats voor injecties bij zuigelingen in de leeftijd van 0 tot 12 maanden is het dijbeen (musculus vastus lateralis). Als dit niet mogelijk is, kan in de bovenarm (musculus deltoideus of musculus triceps) gevaccineerd worden. Boven de leeftijd van 12 maanden is er geen voorkeur voor het dijbeen of de bovenarm. Een gipsbroek kan niet worden afgenomen en de bovenarm is in dat geval de aangewezen plek voor de vaccinatie. Bij een afneembare spreidmiddelbehandeling gaat de voorkeur uit naar het bovenbeen als plek voor de vaccinatie [109], maar de plek (bovenbeen of bovenarm) waar de vaccinatie plaatsvindt wordt, na het geven van uitleg, in overleg met ouders bepaald.
Aanbevelingen
6 Communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ-professionals
In dit thema staat de communicatie en samenwerking tussen ouders en JGZ-professionals centraal. Wanneer JGZ-professionals zorgen uiten over de heupontwikkeling van een kind of wanneer ouders zorgen of vragen hebben over hun kind, is aandacht voor goede communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ professionals van wezenlijk belang.
Het is belangrijk om aandacht te besteden aan de tevredenheid van ouders over de uitvoering van de screening (anamnese en lichamelijk onderzoek), de eventuele verwijzing en de zorg bij een kind met (mogelijke) DDH. Goede communicatie tussen JGZ-professionals en ouders vergroot de tevredenheid van ouders. Dit zal leiden tot positieve concrete ervaringen van ouders met de zorg. Patiënttevredenheid of oudertevredenheid leidt tot een hogere therapietrouw [110] [111]. Naar verwachting geldt dit ook voor de JGZ: door de betrokkenheid en tevredenheid van ouders te vergroten zal de kwaliteit en effectiviteit van de JGZ worden verbeterd.
In deze sectie wordt uitgewerkt welke informatie JGZ-professionals in de screeningsperiode (leeftijd kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud) aan ouders moeten geven over signaleren, uitslagen van de screening, verwijzen, behandelen en begeleiden, en op welke wijze dat het beste kan gebeuren. Daarnaast wordt aandacht besteed aan de communicatie na de screeningsperiode tot de leeftijd van 4 jaar oud. In deze periode is communicatie van groot belang voor zogeheten ‘casefinding’ (zie de Subsectie Onderzoeks- handelings- en verwijsprotocol[LINK?]).
Aanbevelingen
7 Samenwerken
Goede samenwerking en afstemming tussen de verschillende disciplines die in de eerste en tweede lijn betrokken zijn bij de signalering, verwijzing, diagnosticering, behandeling en nazorg van kinderen met een DDH is essentieel. Dit garandeert namelijk de continuïteit in de zorg voor kind en ouders. Daarnaast komen goede samenwerking en afstemming ten goede aan de kwaliteit, toegankelijkheid en betaalbaarheid van de zorg. Na de autorisatie van deze richtlijn komt de Landelijke Eerstelijns Samenwerkings Afspraak (LESA) te vervallen [7].
De uitgangsvragen zijn beantwoord op basis van expertopinie (mening werkgroepleden) en grijze literatuur, zoals de Landelijke Eerstelijns Samenwerkings Afspraak (LESA) HeupOntwikkeling [7].
Aanbevelingen
8 Totstandkoming richtlijn
8.1 Werkwijze
De eerste stap in de ontwikkeling van de JGZ-richtlijn betrof de inventarisatie van knelpunten rondom de screening op DDH door de JGZ en de bijbehorende voorlichting en begeleiding [2]. Aan deze inventarisatie namen de volgende disciplines deel: 2 jeugdartsen, een jeugdverpleegkundige, een verpleegkundig specialist, een stafarts jeugdgezondheidszorg, een bestuurslid van de Vereniging Afwijkende Heupontwikkeling (VAH), een kinderfysiotherapeut, 2 orthopedisch chirurgen met aandachtsgebied kinderorthopedie en een huisarts. De knelpunten zijn geanalyseerd en geprioriteerd. Uiteindelijk zijn 10 uitgangsvragen beschreven, waar de nieuwe JGZ-richtlijn Heupdysplasie antwoord op geeft.
De richtlijn is ontwikkeld volgens de methode van evidence-based richtlijnontwikkeling (EBRO) [60]. De volgende stappen zijn daarbij gezet. Na het vaststellen van de uitgangsvragen is een projectomgeving ingericht. De projectomgeving wordt gevormd door een projectgroep, een werkgroep, een indicatoren referentengroep, een klankbordgroep en 4 JGZ-organisaties die aan de praktijktest deelnemen.
De werkgroep is 4 keer bij elkaar gekomen. In de eerste bijeenkomst (november 2015) is het eerste deel van de uitgangsvragen aangescherpt. In de tweede bijeenkomst (december 2015) zijn de aangescherpte uitgangsvragen vastgesteld en de overige nog niet besproken uitgangsvragen aangescherpt en tevens vastgesteld. Vervolgens vond in februari 2016 een schriftelijke meeleesronde plaats waarbij concept richtlijnteksten zijn becommentarieerd. De commentaren zijn verwerkt in een nieuwe versie van de richtlijntekst, die tijdens de derde werkgroepbijeenkomst (maart 2016) is behandeld. In deze derde werkgroepbijeenkomst is daarnaast input gevraagd op uitgangsvragen die practice-based worden beantwoord. De vierde werkgroepbijeenkomst (september 2016) stond in het teken van bespreking en goedkeuring van het definitieve concept van de richtlijn voor gebruik in de praktijktest.
De projectgroep- en werkgroepleden hebben de uitgangsvragen aangescherpt en definitief vastgesteld. Daarbij is ook bepaald of de uitgangsvraag evidence-based kan worden beantwoord of dat een practice based benadering nodig is. De projectgroep heeft vervolgens richtlijnteksten geschreven. Op basis van het beschikbare bewijs in de wetenschappelijke literatuur, grijze literatuur (waaronder bestaande richtlijnen), handboeken en expertopinie, zijn concrete aanbevelingen geformuleerd voor de praktijk. De richtlijnteksten zijn meerdere keren door de werkgroep becommentarieerd. De klankbordgroep heeft de richtlijnteksten daarna van commentaar voorzien en aangevuld. In oktober 2016 is een eerste conceptversie vastgesteld. Deze is voorgelegd aan de Richtlijn Advies- en Autorisatie Commissie (RAC) van het Nederlands Centrum Jeugdgezondheid (NCJ) en ZonMw in december 2016. Naar aanleiding van de opmerkingen vanuit de RAC is de inhoud van de richtlijn opnieuw bijgesteld en is een versie vastgesteld waarmee een praktijktest kan worden uitgevoerd. In februari tot en met april 2017 is de definitieve conceptrichtlijn getest bij 4 praktijkorganisaties.
8.2 Betrokkenen
Projectgroep
De projectgroep is verantwoordelijk voor het organiseren van de bijeenkomsten van de werk- en klankbordgroep en het schrijven van de richtlijntekst. De projectgroep wordt gevormd door de volgende personen:
- Magda Boere-Boonekamp, arts Maatschappij en Gezondheid, senior onderzoeker bij Universiteit Twente;
- Annelies Broerse, bewegingswetenschapper en psycholoog, senior onderzoeker en projectleider bij TNO, afdeling Child Health;
- Jacqueline Deurloo, arts Maatschappij en Gezondheid, jeugdarts, wetenschappelijk medewerker bij TNO, afdeling Child Health; tevens werkzaam bij GGD Hollands Noorden;
- Annemieke Konijnendijk, gedragswetenschapper, onderzoeker bij Universiteit Twente;
- Caren Lanting, arts en epidemioloog, senior onderzoeker en projectleider bij TNO, afdeling Child Health.
Werkgroep
De werkgroep was verantwoordelijk voor de inhoud van de richtlijn. Bij de formatie van de werkgroep is gelet op een goede balans tussen wetenschappers, JGZ-professionals, inhoudelijke deskundigen en afgevaardigden van de Vereniging Afwijkende Heupontwikkeling (VAH). Bij de selectie van JGZ-professionals is rekening gehouden met verschillen in diversiteit van de populatie waarmee zij werken. De volgende 9 personen namen deel aan de werkgroep:
- Liesbeth Achterberg, Jeugdarts KNMG in de JGZ 0-4, werkzaam bij Icare Jeugdgezondheidszorg tot 31-12-2015 en sinds 1-1-2016 bij Veiligheids- en Gezondheidsregio Gelderland-Midden (VGGM); afgevaardigde namens Jeugdartsen Nederland (AJN);
- Margret Foreman-van Drongelen, Jeugdarts KNMG met staftaken en met aandachtsgebied DDH en tevens heupechografist, werkzaam bij ZuidZorg en Diagnostiek voor U (eerstelijns diagnostisch centrum); afgevaardigde namens AJN;
- Sanne Hamer, verpleegkundig specialist, werkzaam bij Icare Jeugdgezondheidszorg; afgevaardigde namens Verpleegkundigen & Verzorgenden Nederland (V&VN);
- Renske Pereboom, ervaringsdeskundige en secretaris van de VAH; afgevaardigde namens VAH;
- Sandra Prins, kinderarts en neonatoloog, werkzaam bij VU Medisch Centrum; afgevaardigde namens Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde (NVK);
- Renée van der Sluijs, arts maatschappij en gezondheid met aandachtsgebied DDH, werkzaam bij GGD regio Utrecht; afgevaardigde namens AJN;
- Anne Smets, kinderradioloog, werkzaam bij Academisch Medisch Centrum-Universiteit van Amsterdam (AMC-UvA); afgevaardigde namens Nederlandse Vereniging voor Radiologie (NVvR);
- Merel van Veen-Wagensveld, ervaringsdeskundige en bestuurslid VAH; afgevaardigde namens VAH;
- Adhiambo Witlox, orthopedisch chirurg met aandachtsgebied kinderorthopedie, werkzaam bij Maastricht UMC+ en bestuurslid van de Werkgroep Kinderorthopaedie Nederland (WKO); afgevaardigde namens WKO.
Alle leden van de werkgroep hebben een belangenverklaring ingevuld. Eén van de werkgroepleden is werkzaam bij Diagnostiek voor U, een eerstelijns diagnostisch centrum, en verricht daar heupecho’s bij jonge zuigelingen. Verder had geen van de werkgroepleden belangen die van belang zijn voor het ontwikkelen van de JGZ-richtlijn Dysplastische heupontwikkeling.
Klankbordgroep
De klankbordgroep was verantwoordelijk voor het becommentariëren en aanvullen van conceptteksten vanuit ieders eigen ervaring en expertise. De klankbordgroep heeft schriftelijk gereageerd in augustus 2016. De reacties van de klankbordgroep zijn verwerkt door de projectgroep en besproken met de werkgroep. De klankbordgroep bestond uit de volgende personen:
- Rosa de Boer, kinderfysiotherapeut en klinisch epidemioloog, namens Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kinderfysiotherapie (NVFK)
- Eric Boldingh, revalidatiearts, werkzaam bij Tyltylcentrum “De Witte Vogel”, Sophia Revalidatie
- Leonie Graat, jeugdverpleegkundige, werkzaam bij GGD Hart voor Brabant
- Bianca Klein, CB-assistente, werkzaam bij Icare jeugdgezondheidszorg
- Bart Looman, programmamanager Jeugd, Pharos (Expertisecentrum Gezondheidsverschillen)
- Davey van der Moolen, jeugdverpleegkundige, werkzaam bij Icare jeugdgezondheidszorg
- Irina de Niet-Muravjova, jeugdarts KNMG, werkzaam bij JGZ Kennemerland
- Sjoerd Verwaaijen, Orthopedisch adviseur OIM orthopedie, namens Nederlandse Beroepsvereniging Orthopedisch Technologen (NBOT)
- Laura de Vries, huisarts en wetenschappelijk medewerker bij het Nederlands Huisartsen Genootschap (NHG)
- Melinda Witbreuk, orthopedisch chirurg met aandachtsgebied kinderorthopedie, Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis/VU Medisch Centrum en voorzitter van de WKO
JGZ-organisaties die deelnamen aan de praktijktest
De JGZ-organisaties die deelnamen aan de praktijktest waren verantwoordelijk voor het testen van de richtlijn in de praktijk en het aansluiten van de richtlijn bij het werkveld. Het betrof de volgende JGZ organisaties:
- TWB Thuiszorg met Aandacht;
- Zuidzorg;
- JGZ Zuid Holland West;
- GGD Groningen.
8.3 Belangenverstrengeling
Voor de ontwikkeling van deze richtlijn is financiering verkregen van ZonMw. Alle werkgroepleden hebben een verklaring belangenverstrengeling ingevuld. De werkgroepleden hebben verklaard in de laatste 3 jaar (tot op heden) geen relatie of bemoeienis te hebben gehad met bedrijven of organisaties, zoals sponsors, farmaceutische industrie, belangenvereniging, of werkzaamheden te ontplooien vanuit een eigen bedrijf of (mede) methoden, instrumenten e.d. te ontwikkelen op het gebied van DDH, waardoor een belangenconflict zou kunnen ontstaan met de werkzaamheden in de richtlijnwerkgroep.
9 Verantwoording
9.1 Beantwoording van uitgangsvragen
De basis voor de richtlijn is een samenvatting van het beschikbare bewijs in de wetenschappelijke literatuur. Het literatuuronderzoek is uitgevoerd volgens de procedure beschreven in hoofdstuk 5 van de Evidence Based RichtlijnOntwikkeling (EBRO)-handleiding [60]. Uitgangsvragen die aan de hand van wetenschappelijke literatuur beantwoord konden worden, zijn geformuleerd in zogenaamde PICO vraagstellingen (Patient, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome). Voor elke PICO-vraag is een aparte search in de wetenschappelijke literatuur uitgevoerd. Uitgangsvragen die zich niet leenden voor beantwoording met wetenschappelijke literatuur zijn op basis van practice-based kennis of op basis van consensus onder deskundigen beantwoord.
De knelpuntenanalyse resulteerde in 10 uitgangsvragen. Deze zijn door de projectgroep gegroepeerd in 6 clusters:
- Definities voor DDH
- Risicofactoren voor DDH
- Waarde van het lichamelijk onderzoek op de zuigelingenleeftijd
- Beleid voor screening/verwijzing vanwege vermoeden DDH
- Informatievoorziening naar ouders
- Samenwerkingsafspraken
De project- en werkgroepleden hebben de uitgangsvragen aangescherpt. Hieronder is weergegeven op welke manier de uitgangsvragen per cluster zijn beantwoord.
Definities voor DDH
Het beantwoorden van de uitgangsvraag over definities is gedaan aan de hand van handboeken en overzichtsartikelen/reviews van de laatste 20 jaar. Daarnaast is gebruik gemaakt van expertopinie.
Risicofactoren voor DDH
De uitgangsvraag over het identificeren van risicofactoren zijn beantwoord via de PICO-methode. De uitgangsvraag over de manier en het tijdstip waarop de anamnese over risicofactoren voor de opsporing van DDH bij zuigelingen moet plaatsvinden, is beantwoord via raadpleging van handboeken, overzichtsartikelen/reviews en grijze literatuur van de laatste 20 jaar. Grijze literatuur betrof (inter)nationale literatuur over protocollen/richtlijnen op het gebied van DDH en nationale niet-peer review vakbladen (b.v. Medisch contact, Tijdschrift JGZ, proefschriften). Daarnaast werd gebruik gemaakt van expertopinie.
Waarde van lichamelijk onderzoek op de zuigelingenleeftijd voor de opsporing van DDH
De uitgangsvraag over de beschikbare methoden voor lichamelijk onderzoek is beantwoord via raadpleging van handboeken, overzichtsartikelen/reviews en grijze literatuur van de laatste 20 jaar; daarnaast werd gebruik gemaakt van expertopinie. De uitgangsvraag over de reproduceerbaarheid, validiteit en toepasbaarheid van methoden van lichamelijk onderzoek door de JGZ voor de vroege opsporing van DDH is in een PICO-vraag geformuleerd en beantwoord aan de hand van beschikbaar bewijs in de wetenschappelijke literatuur.
Beleid voor screening/verwijzing vanwege vermoeden DDH
De uitgangsvraag over het screenings-/verwijsbeleid bij een vermoeden van DDH door de JGZ is beantwoord via een PICO-vraagstelling, waarna wetenschappelijk literatuur is verzameld. De uitgangsvraag over de kenmerken van het screenings- en verwijsprotocol werd beantwoord via expertopinie. Tot slot werden de daaraan verbonden vragen over de kosten van het toepassen van het screening- en verwijsprotocol, en de kenmerken van het onderzoeks- en verwijsprotocol bij het kind na de leeftijdsperiode t/m 6 maanden beantwoord via raadpleging van handboeken en overzichtsartikelen/reviews van de afgelopen 20 jaar.
Communicatie tussen ouders en JGZ-professionals
De uitgangsvragen over informatievoorziening naar ouders zijn beantwoord via expertopinie. Met name de inbreng van de Vereniging Afwijkende Heupontwikkeling (VAH) was daarbij van grote waarde. Daarnaast is grijze literatuur geraadpleegd, waaronder een bachelor scriptie en een artikel daarover naar de tevredenheid van ouders met de screening op DDH en de bijbehorende begeleiding en voorlichting [112], [113].
Samenwerkingsafspraken
De uitgangsvragen over samenwerkingsafspraken tussen de eerste en tweede lijn werden beantwoord via expertopinie en grijze literatuur (waaronder de Landelijke Eerstelijns Samenwerkings Afspraak (LESA)).
9.2 Wetenschappelijke bewijsvoering
In totaal zijn 4 PICO-vragen geformuleerd, binnen de clusters 2-4. De PICO-vragen lenen zich voor beantwoording met bewijs beschreven in wetenschappelijk literatuur. Voor deze vragen is daarom systematisch literatuuronderzoek gedaan:
- In welke mate is de prevalentie van DDH hoger voor zuigelingen 0 t/m 6 maanden met < aanwezige risicofactoren > in vergelijking met zuigelingen zonder deze risicofactor?
- Met betrekking tot stuit- en dwarsligging:
- Verschilt het verhoogde risico op DDH van zuigelingen die tijdens de zwangerschap in stuit- of dwarsligging lagen tussen zuigelingen die kort (< 4 weken) en zuigelingen die langdurig (> 4 weken) in deze ligging lagen?
- Verschilt het verhoogde risico op DDH van zuigelingen die tijdens de zwangerschap in stuit /dwarsligging lagen, tussen zuigelingen die t/m week 37 van de zwangerschap in stuit- of dwarsligging lagen en zuigelingen die na de zevenendertigste week tot aan de bevalling in stuit /dwarsligging lagen?
- Verschilt het verhoogde risico op DDH tussen zuigelingen die tijdens de zwangerschap in stuitligging lagen en vervolgens via een vaginale stuitbevalling werden geboren en zuigelingen die vervolgens via een keizersnede werden geboren?
- Verschilt het verhoogde risico op DDH tussen zuigelingen die in volkomen stuitligging lagen en zuigelingen die in onvolkomen stuitligging lagen tijdens de zwangerschap?
- Verschilt het verhoogde risico op DDH tussen zuigelingen die spontaan of door uitwendige versie zijn gedraaid van stuitligging naar hoofdligging tijdens de zwangerschap en zuigelingen die niet spontaan zijn gedraaid van stuitligging naar hoofdligging?
- Met betrekking tot de validiteit van verschillende onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek voor DDH zoals toegepast in de JGZ bij zuigelingen (inclusief prematuren) van circa 1 t/m 6 maanden:
- Wat zijn de sensitiviteit, specificiteit en voorspellende waarde van als screeningsinstrument in een algemene populatie zuigelingen van circa 1 t/m 6 maanden?
- Wat zijn de sensitiviteit, specificiteit en voorspellende waarde van als screeningsinstrument bij prematuur geboren zuigelingen in de leeftijd van circa 1 t/m 6 maanden?
- Worden bij zuigelingen van circa 1 t/m 6 maanden meer kinderen met een DDH terecht opgespoord als in deze periode op meerdere momenten lichamelijk onderzoek wordt verricht volgens in vergelijking met één moment van afname van het lichamelijk onderzoek volgens ?
- Met betrekking tot de timing van behandeling:
- Is de prognose van DDH beter als de behandeling van dysplasie bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud op een eerder tijdstip wordt gestart in vergelijking met een behandeling die later start?
- Is de prognose van DDH beter als de behandeling van luxatie bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud op een eerder tijdstip wordt gestart in vergelijking met een behandeling die later start?
Selectie van literatuur
Per PICO-vraag zijn specifieke zoekstrategieën en inclusie- en exclusiecriteria (zie onder) gedefinieerd. De searches zijn uitgevoerd in december 2015.
De volgende inclusiecriteria golden voor alle PICO-vraagstellingen:
- Studies met de volgende studie designs: randomized controlled trial (RCT), patiënt-controle onderzoek, prospectief of retrospectief cohortonderzoek, cross-sectioneel onderzoek, systematische reviews die literatuur beschrijven die voldoen aan de eerdergenoemde studie designs.
- Datum publicatie artikelen ≥ 1995
- Onderzoeksdata zijn verzameld in het jaar 1985 of later.
- Databases: Cochrane Collaboration, Pubmed.
- Taal: Engels, Nederlands en Duits.
De volgende inclusiecriteria golden voor specifieke PICO’s:
- PICO 4: De database Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) is ook geraadpleegd. De zoekactie in CINAHL leverde zeer weinig bruikbare literatuur op. Vanwege de beperkte tijd die de richtlijnontwikkelaars hebben en de verwachte lage opbrengst is CINAHL niet als database ingezet voor het zoeken naar artikelen voor PICO 1-3.
De gehanteerde zoekstrategieën in Pubmed en CINAHL en de bijbehorende resultaten worden hier weergegeven.
Selectie en beoordeling van literatuur op basis van abstracts
De in- en exclusiecriteria bij de selectie en beoordeling van abstracts verschilden per PICO. De criteria worden hieronder weergegeven:
PICO 1:
- Populatie: Bij cohortonderzoek moet het gaan over onderzoek in een algemene populatie van kinderen waarin over het voorkomen van de risicofactor en over het voorkomen van de aandoening wordt gerapporteerd. Bij patiënt-controleonderzoek betreft het onderzoek onder patiënten met DDH en controles. Het aantal personen dat is onderzocht is gelijk aan of groter dan 100. Een uitzondering betreft onderzoek naar erfelijke factoren als risico; daarvoor is het minimale aantal van 50 verwante personen gehanteerd.
- Alle risicofactoren voor DDH zijn onderzocht. De zijde van het lichaam waar DDH vaker voorkomt – in de literatuur soms beschreven als risicofactor – wordt door de richtlijnontwikkelaars gezien als een kenmerk van DDH (net als b.v. het eenzijdig of dubbelzijdig vóórkomen) en om die reden niet als risicofactor onderzocht.
PICO 2:
- Populatie: het aantal personen dat is onderzocht is gelijk aan of groter dan 100. De populatie bestaat uit personen die tijdens de zwangerschap of bij de bevalling in stuitligging lagen. Wanneer het onderzoeksdesign een cohortstudie betreft, moet dit aantal minimaal 300 zijn, of moet het aantal personen met vastgestelde DDH groter zijn dan, of gelijk zijn aan, 10.
- Voor PICO 2 geldt als exclusiecriterium met betrekking tot populatie: personen die via een keizersnede zijn geboren.
PICO 3:
- Populatie: onderzoek in een algemene populatie van kinderen waarin over het lichamelijk onderzoek en het voorkomen van de aandoening wordt gerapporteerd, óf onderzoeken onder patiënten met DDH en controles, óf onderzoek van een selecte populatie kinderen die zijn verwezen voor aanvullend (beeldvormend) onderzoek vanwege risicofactoren of afwijkend lichamelijk onderzoek. Vanuit de selecte groep kinderen met risicofactoren of een afwijkend lichamelijk onderzoek kan een positief voorspellende waarde worden berekend.
- Populatie: het aantal kinderen dat is onderzocht is gelijk aan of groter dan 100, tussen circa 1 t/m 6 maanden oud tijdens het uitvoeren van het lichamelijk onderzoek.
- De studie beschrijft de sensitiviteit, specificiteit en/of voorspellende waarde van ten minste 1 onderdeel van het lichamelijk onderzoek.
- De onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek die zijn bestudeerd betreffen: abductietest, beenlengteverschil, beenlengte- en kniehoogteverschil en asymmetrie van huid- en bilplooien. Onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek die zijn geëxcludeerd betreffen de handgrepen van Ortolani en Barlow. Deze onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek worden in de neonatale periode uitgevoerd, en worden derhalve niet toegepast in de JGZ. In sommige onderzoeken wordt naast de door ons geïncludeerde onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek, óók de handgrepen van Ortolani en/of Barlow meegenomen. Wanneer de sensitiviteit, specificiteit en/of voorspellende waarde van de door ons geïncludeerde onderdelen van lichamelijk onderzoek niet apart te berekenen zijn, worden deze artikelen geëxcludeerd.
- Specifieke criteria voor sub-PICO’s:
- Voor PICO 3a en 3b: beschrijving van sensitiviteit, specificiteit en/of voorspellende waarde van ten minste 1 onderdeel van lichamelijk onderzoek.
- Voor PICO 3b: alleen onderzoek dat zich richt op prematuur geboren kinderen wordt geïncludeerd.
- Voor PICO 3c: de studie hoeft niet perse een vergelijking te bevatten tussen verschillende momenten van afnamen van lichamelijk onderzoek. Ten minste 1 moment van afname van ten minste 1 onderdeel van lichamelijk onderzoek moet beschreven zijn.
PICO 4:
- Populatie: kinderen met DDH, t/m 6 maanden oud bij start behandeling.
- Populatie: het aantal personen dat is onderzocht is gelijk aan of groter dan 40.
- DDH is vastgesteld met behulp van echografie of radiologie. Geëxcludeerd zijn studies waarbij DDH enkel klinisch is vastgesteld (b.v. alleen met de handgrepen van Ortolani en Barlow). Het enkel op basis van lichamelijk onderzoek vaststellen van DDH is geen good practice.
- Behandelingen die zijn geëxcludeerd: breed luieren, open repositie met osteotomie (bv. volgens Salter). Breed luieren is een verouderde techniek die in Nederland niet als nuttig wordt ervaren. Open repositie met osteotomie wordt niet voor de leeftijd van 6 maanden uitgevoerd.
- De behandeling van DDH moet gestart zijn tussen de eerste en zesde levensmaand.
Het zoeken naar literatuur via zoektermen en het toepassen van inclusiecriteria bij de eerste zoekactie leverde in totaal 1150 abstracts op voor de 4 PICO’s samen. Sommige abstracts zijn daarbij dubbel geteld, omdat ze bij meerdere PICO’s gevonden werden. Vier referenties betroffen systematische reviews, inclusief meta-analyse. De referentielijsten van deze 3 reviews zijn bekeken op referenties die niet met de PICO-zoektermen geïdentificeerd waren als relevant, maar wel relevant leken en voldeden aan de gestelde in- en exclusiecriteria. Het betrof 15 referenties bij PICO 1 en 10 referenties bij PICO 2. Voor alle 1175 geïncludeerde artikelen zijn eerst de abstracts gelezen. Twee personen (MB en AK) hebben deze onafhankelijk van elkaar beoordeeld op relevantie voor het beantwoorden van de uitgangsvragen en de hierboven geformuleerde in- en exclusiecriteria. De beoordelingen zijn met elkaar vergeleken. Wanneer er geen overeenstemming was over inclusie, werd overlegd totdat overeenstemming werd bereikt. Deze eerste beoordeling leidde tot de inclusie van in totaal 319 artikelen.
Beoordeling van volledige artikelen
De 319 geselecteerde artikelen zijn volledig gelezen en achtereenvolgens beoordeeld op relevantie, kwaliteit van het onderzoek en methodologische kwaliteit. Elk beoordelingscriterium (en de uitkomsten daarvan) wordt in de navolgende alinea’s beschreven. De beoordelingen werden ook hier weer door 2 personen (MB en AK) onafhankelijk van elkaar uitgevoerd. Het oordeel van beide personen werd vergeleken en gezamenlijk werd besloten over de inclusie van artikelen waarover de beoordelaars een verschillend oordeel hadden.
Relevantie
Voor elk artikel is eerst gekeken of de uitkomsten de (sub-)PICO vraag beantwoordden. Wanneer bij de selectie op basis van de abstracts niet duidelijk werd of de studie voldeed aan de daarvoor geldende in- en exclusiecriteria, zijn de volledige artikelen daarop nagekeken. Daarnaast golden de volgende aanvullende in- en exclusiecriteria:
- De onderzoeksdata zijn verzameld in het jaar 1985 of later. De resultaten van onderzoeken waarin de onderzoeksdata verzameld zijn in de jaren vóór 1985 zijn weinig relevant, omdat sindsdien de diagnostiek verbeterd is en de resultaten daardoor mogelijk niet meer gelden voor de huidige situatie;
- Het artikel is in volledige vorm beschikbaar voor de onderzoekers;
- Wanneer 2 of meerdere onderzoeken dezelfde onderzoeksresultaten beschrijven, is 1 artikel meegenomen: het artikel dat in het meest klinische tijdschrift is gepubliceerd.
Kwaliteit van onderzoek
Elk geselecteerd artikel moest voldoen aan de volgende kwaliteitscriteria om geïncludeerd te blijven:
- Er moest een heldere casusdefinitie zijn (wanneer is er sprake van DDH?);
- Studies waarbij de diagnose DDH alleen gebaseerd is op lichamelijk onderzoek (en waar dus geen beeldvormend onderzoek is gedaan) werden geëxcludeerd. De diagnose op basis van enkel lichamelijk onderzoek is onvoldoende betrouwbaar;
- Wat betreft PICO 1: Het artikel moest de risicofactor(en) helder definiëren;
- Wat betreft PICO 2: Het artikel moest helder beschrijven of het om stuitligging in de zwangerschap of om stuitbevalling gaat.
Tabel 4 toont het aantal artikelen dat in elke fase van het selectie- en beoordelingsproces geïncludeerd is. Uiteindelijk zijn voor alle PICO-vraagstellingen samen 89 artikelen meegenomen.
Tabel 4. Aantal geïncludeerde artikelen per PICO-vraagstelling.
| PICO | Inclusie op basis van zoektermen en inclusiecriteria | Selectie na beoordeling abstracts op basis van relevantie en in- en exclusiecriteria | Selectie na beoordeling op relevantie van volledige artikelen | Selectie op basis van kwaliteit onderzoek |
| 1 | 360 | 160 | 60 | 56 |
| 2 | 114 | 45 | 11 | 11 |
| 3 | 334 | 50 | 9 | 9 |
| 4 | 367 | 64 | 13 | 13 |
| Totaal | 1175 | 319 | 93 | 89 |
Methodische kwaliteit
Voor het beoordelen van de methodologische kwaliteit werd gebruik gemaakt van de EBRO-systematiek [60]. Tabel 5 geeft de indeling van methodologische kwaliteit van individuele studies en niveau van conclusies weer.
Tabel 5. Indeling van methodologische kwaliteit van individuele studies [60]
| Interventie | Diagnostische accuratesse onderzoek | Schade/bijwerking*, etiologie, prognose | |
| A1 | Systematische review van ten minste 2 onafhankelijk van elkaar uitgevoerde onderzoeken van A2-niveau | ||
| A2 | Gerandomiseerd dubbelblind vergelijkend klinisch onderzoek van goede kwaliteit van voldoende omvang | Onderzoek ten opzichte van een referentietest (een gouden standaard) met tevoren gedefinieerde afkapwaarden en onafhankelijke beoordeling van de resultaten van test en gouden standaard, betreffende een voldoende grote serie van opeenvolgende patiënten die alleen de index- en referentietest hebben gehad. | Prospectief cohort onderzoek van voldoende omvang en follow-up, waarbij adequaat gecontroleerd is voor ‘confounding’ en selectieve follow-up voldoende is uitgesloten. |
| B | Vergelijkend onderzoek, maar niet met alle kenmerken als genoemd onder A2 (hieronder valt ook patiënt-controle onderzoek, cohortonderzoek) | Onderzoek ten opzichte van een referentietest, maar niet met alle kenmerken die onder A2 zijn genoemd. | Onderzoek ten opzichte van een referentietest, maar niet met alle kenmerken die onder A2 zijn genoemd. |
| C |
Niet-vergelijkend onderzoek |
||
| D |
Mening van deskundigen |
||
*Deze classificatie is alleen van toepassing in situaties waarin om ethische of andere redenen gecontroleerde trials niet mogelijk zijn. Zijn die wel mogelijk, dan geldt de classificatie voor interventies.
De kwaliteit van de 4 geïncludeerde systematische reviews [15, 16, 27, 39, 40] is beoordeeld aan de hand van de AMSTAR-methode (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews) [116]. Het AMSTAR hulpmiddel, een korte vragenlijst, brengt de methodologische kwaliteit van systematische reviews in kaart. De vragenlijst vraagt onderzoekers de review op 10 aspecten van methodologische kwaliteit te beoordelen.
Vervolgens is voor alle PICO’s afgewogen of het toepassen van de GRADE-methodiek (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) [117] zinvol is. GRADE is een methode die per uitkomstmaat van een interventie een gradering aan de kwaliteit van bewijs toekent op basis van de mate van vertrouwen in de schatting van de effectgrootte. Een meerwaarde van GRADE-methode ten opzichte van de EBRO-methode is dat de GRADE-methode bij het beoordelen van de kwaliteit van de bewijskracht zowel met het type onderzoeksdesign rekening houdt als met specifieke factoren die de kwaliteit van de bewijskracht verhogen of verlagen. Een beperking van de GRADE-methodiek is dat deze ontwikkeld is voor het beoordelen van onderzoek dat interventies vergelijkt. Hierdoor is de methodiek minder toepasbaar op etiologisch en prognostisch onderzoek. De uitgangsvragen waarop de richtlijn Heupdysplasie gebaseerd is, omvatten vrijwel alleen vragen die enkel via observationeel onderzoek te onderzoeken zijn. De GRADE-methodiek is daarom uiteindelijk niet toegepast.
Evidentietabellen
Voor elke sub-PICO is een evidentietabel gemaakt. De evidentietabel beschrijft voor elk geïncludeerd artikel de methodische kwaliteit volgens de EBRO-systematiek. Verder worden de verschillende kenmerken en de uitkomsten van de studie beschreven. Indien van toepassing worden risk ratio’s (RRs) of odds ratio’s (ORs) gerapporteerd. De studies met het hoogste niveau van conclusie bovenaan in de tabel. Wanneer een artikel was opgenomen in één van de geïncludeerde reviews, is die studie niet als aparte studie beschreven in een evidentietabel. Evidentietabellen zijn op te vragen bij de richtlijnontwikkelaar.
Eindoordeel
De onderbouwing van de richtlijnaanbevelingen is vaak gebaseerd op conclusies uit meerdere onderzoeken. Bij elke conclusie wordt de methodologische kwaliteit van elk artikel vermeld, uitgedrukt volgens de EBRO-systematiek (tabel 5). Daarnaast wordt aan elke conclusie een eindoordeel verbonden voor de methodologische kwaliteit van alle studies samen waarop de onderbouwing is gebaseerd (tabel 6).
Tabel 6. Indeling van het eindoordeel (conclusie) [60].
| Niveau | Conclusie gebaseerd op: | Formulering conclusie |
| 1 | Onderzoek van niveau A1 of tenminste 2 onafhankelijke van elkaar uitgevoerde onderzoeken van niveau A2 | Het is aangetoond dat… |
| 2 | 1 onderzoek van niveau A2 of tenminste 2 onafhankelijk van elkaar uitgevoerde onderzoeken van niveau B | Het is aannemelijk/waarschijnlijk dat… |
| 3 | 1 onderzoek van niveau B of C | Er zijn aanwijzingen/het lijkt waarschijnlijk dat… |
| 4 | Mening van deskundigen | De deskundigen/werkgroep zijn/is van mening dat…. |
9.3 Overwegingen
De overwegingen van de werkgroep zijn per onderwerp opgenomen in Sectie 1 t/m 7.
9.4 Kennislacunes
- Er is onvoldoende wetenschappelijke kennis beschikbaar over de rol van de volgende factoren bij het ontstaan van DDH:
- Kindfactoren: congenitale musculaire torticollis, etniciteit, neurologische afwijkingen, voorkeurshouding, draagzakken en -doeken.
- Factoren rond zwangerschap en bevalling: dwarsligging, onvolkomen versus volkomen stuitligging, duur stuitligging, periode in de zwangerschap waarin deze stuitligging bestond, uitwendige versie bij stuitligging.
- Er is onvoldoende kennis over de kosteneffectiviteit van screening voor DDH bij kinderen, en over de benodigde randvoorwaarden. Met name ontbreekt betrouwbare informatie over het aantal verwijzingen en het aantal gediagnosticeerde en behandelde kinderen met DDH. Zie bijlage 2 voor een overzicht van de beschikbare literatuur over kosten voor de JGZ van toepassing van het screenings- en verwijsprotocol voor opsporing van DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud.
- Er is onvoldoende wetenschappelijke onderbouwing voor concrete en leeftijdsafhankelijke afkapwaarden van afwijkend lichamelijk onderzoek voor wat betreft de abductie van de heupen en de kniehoogte die indicatie zijn voor verwijzing voor aanvullend beeldvormend onderzoek of verwijzing naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
- Er is geen wetenschappelijke literatuur beschikbaar over welke JGZ-professional het heuponderzoek het beste kan uitvoeren.
- Een systematische review van literatuur over de effectiviteit en uitvoerbaarheid van echografische screening op DDH in de JGZ is geïndiceerd.
10 Bijlagen
- Bijlage 1 – Anamnese op basis van risicofactoren
- Bijlage 2 – Kosten JGZ screenings- en verwijsprotocol 0 t/m 6 maanden
- Bijlage 3 – Screenings- handelings- en verwijsprotocol 0 t/m 6 maanden
- Bijlage 4 – Onderzoeks- en verwijsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen vanaf 7 maanden
- Bijlage 5 – Activiteiten per contactmoment in de leeftijdsperiode 0 t/m 6 maanden
- Bijlage 6 – Tekst cliëntenfolder
- Bijlage 7 – Afkortingen lijst (zie sectie Definitie)
10.1 Anamnese op basis van risicofactoren
Familieanamnese
Vraag:
Zijn er familieleden die:
- een aangetoonde heupdysplasie of -(sub)luxatie hebben gehad?
- als kind een spalk, beugel, tractiebehandeling, operatie en/of gips hebben (gehad) voor de heupen?
- mank/scheef lopen of hebben gelopen ten gevolge van de heupen?
- vóór of rond het 50e jaar versleten heupen hebben (gehad)? Dit kan blijken uit ernstige pijn- of functieklachten ten gevolge van artrose van de heup.
- vóór of rond hun 50e jaar geopereerd zijn aan de heupen? Indien positief, dan andere oorzaken zoals trauma, polio, ontsteking, ziekte van Perthes, voor zover mogelijk uitsluiten.
Interpretatie:
Eén of meerdere familieleden van het kind met DDH en/of coxartrose voor de leeftijd van 50 jaar in de eerste graad (ouders, zussen, broers) of tweede graad (grootouders, tantes, ooms) betekent een belaste familieanamnese. Een belaste familieanamnese is een risicofactor voor DDH.
Er is een verschil tussen de familiaire graden in medisch en juridisch gebruik. In medisch gebruik gaat het om de kans op gelijke persoonskenmerken. Een eerstegraads familielid van een kind is een familielid dat ca. 50% van zijn genen met het betreffende kind deelt, d.w.z. ouders en broers/zussen. Een tweedegraads familielid is een familielid dat in ca. 25% van de genen overeenkomt, dus grootouders en broers/zussen van de ouders van het kind (ooms/tantes). Zie figuur 5 voor verduidelijking van de familiaire graden volgens medisch gebruik.
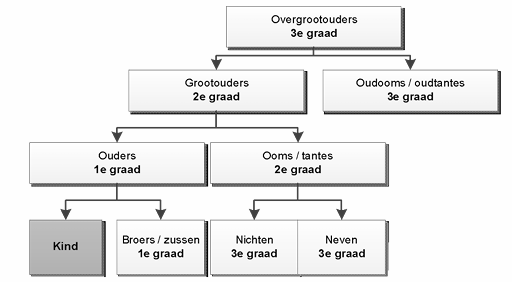
Figuur 5. Familiaire graden volgens medisch gebruik [118].
Ligging in de baarmoeder na week 32 van de zwangerschap
Vraag:
Hoe lag uw kind in de baarmoeder na week 32 van de zwangerschap? In hoofdligging, stuitligging of anders?
Interpretatie:
Stuitligging tijdens de zwangerschap na week 32 is een risicofactor voor DDH. Er is onvoldoende wetenschappelijke literatuur beschikbaar waardoor het nader specificeren naar periode en duur van de risicofactor ‘stuitligging in de zwangerschap’ niet mogelijk is. De keuze voor het criterium ‘na week 32’ is op basis van expert opinion gemaakt. In het begin van het derde trimester (zwangerschapsduur 27 weken) ligt 22-25% van de kinderen in stuit, bij 32 weken is dat 7-15%, terwijl 3 – 4% van de kinderen in de a terme periode in stuit ligt. De prevalentie van DDH in de groep met een geslaagde uitwendige versie is waarschijnlijk nog steeds hoger dan de prevalentie in een algemene populatie zonder risicofactoren. Het verwijsbeleid is bij geslaagde en niet geslaagde uitwendige versie hetzelfde.
Ligging in de baarmoeder bij de bevalling
Vraag:
Hoe lag uw kind in de baarmoeder op het moment dat u ging bevallen? In hoofdligging, stuitligging of anders?
Interpretatie:
Stuitligging op het moment van de bevalling is een risicofactor voor DDH. Het risico is hoger als het kind via een vaginale stuitbevalling werd geboren; echter ook als een keizersnede is verricht, geldt de stuitligging als risicofactor voor DDH. Het verhoogde risico hangt niet af van de aard van de stuitligging: volkomen, d.w.z. met de voeten naar beneden, of (half) onvolkomen, d.w.z. met (een of) beide benen omhoog. Ook hangt het verhoogde risico niet af van de zwangerschapsduur op het tijdstip van de bevalling.
Inbakeren
Vraag:
Wordt het onderlichaam van uw kind ingebakerd? Zo ja, is aan u uitgelegd hoe u uw kind het beste kan inbakeren? Zo ja, door wie?
Interpretatie:
Er zijn aanwijzingen dat kinderen bij wie het onderlichaam strak wordt ingebakerd met de heupen en knieën gestrekt een verhoogd risico hebben op DDH. In het verleden werd een hoge incidentie van DDH beschreven bij volkeren (Navajo-indianen, Laplanders) die de gewoonte hadden jonge zuigelingen in gestrekte houding in te bakeren, waarbij de heupen langdurig in extensie en adductie werden gehouden [3]. In Oost-Europa en het Midden-Oosten worden veel kinderen ingebakerd [42], [43]. Ook in Nederland vindt dit in toenemende mate plaats, bijvoorbeeld door ouders met een migratie-achtergrond (Turkse, Marokkaanse ouders), door op antroposofie georiënteerde ouders of door ouders met een huilbaby (zie de JGZ-richtlijn ‘Excessief huilen’ [LINK]). Wanneer ouders hun kind inbakeren zonder dat instructie door een geschoold professional heeft plaatsgevonden, kan dit een verhoogd risico op DDH betekenen. In dat geval moet dit worden afgeraden en dient begeleiding aangeboden te worden. ‘Veilig inbakeren’ houdt in dat de ingebakerde baby zijn benen in opgetrokken stand moet kunnen spreiden (‘kikkerstand’) en volledig moet kunnen strekken.
10.2 Kosten voor de JGZ van toepassing van het screenings- en verwijsprotocol voor opsporing van DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud
- Wat zijn de kosten voor de JGZ van toepassing van het screenings- en verwijsprotocol voor opsporing van DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud?
De kosten van de screening bestaan uit kosten van het daadwerkelijk uitvoeren van de screening en de kosten voor aanvullende diagnostiek tot het moment dat de diagnose DDH gesteld of verworpen is. De kosten kunnen worden gespecificeerd op het niveau van het totale screeningsprogramma, de kosten per gescreend kind en de kosten per kind met de diagnose DDH.
Boere-Boonekamp [13] berekende in 1995 de kosten van screening op DDH (anamnese van risicofactoren, lichamelijk onderzoek) door de jeugdgezondheidszorg per 2000 levend geboren kinderen, op basis van financiële gegevens, verstrekt door de financiële afdeling van de JGZ-organisatie die deelnam aan de Twentse studie. De kosten die bij de berekening meegenomen zijn betreffen de geïnvesteerde tijd per gescreend kind inclusief anamnese, lichamelijk onderzoek, verwijzing (indien geïndiceerd; tot start behandeling), documentatie en registratie (prijspeil 1995). Bij 2,8% werd op basis van de screening de diagnose DDH gesteld. De kosten per gescreend kind werden geschat op €23,09 (exclusief consult huisarts) of €26,77 (inclusief consult huisarts). De kosten per kind gediagnosticeerd met DDH werden geschat op €839,52 (exclusief consult huisarts) of €973,35 (inclusief consult huisarts).
Roovers [89] voerde in 2002 een kosteneffectiviteitsanalyse over echografische screening op DDH uit om de verschillen in kosten en effecten tussen 3 screeningsstrategieën te bepalen. De scenario’s waren: algemene echografische screening, selectieve echografische screening en de huidige screening door de jeugdgezondheidszorg (anamnese van risicofactoren, lichamelijk onderzoek). De kosten die bij de berekening meegenomen zijn betreffen de screeningskosten, de kosten voor diagnostiek en behandeling, en de kosten voor ouders (prijspeil 2002). De percentages terecht opgespoorde gevallen van DDH waren respectievelijk 3,1%, 2,4% en 2,8%. De kosten per gescreend kind in de huidige screening werden in de 3 scenario’s geschat op respectievelijk €70,6, €52,1 en €82,0. De kosten per in de screening opgespoord kind met DDH bedroegen respectievelijk €2278, €2171 en €2929.
Ramwadhdoebe [90] voerde in 2006 een kosteneffectiviteitsanalyse van verscheidene implementatiescenario’s van echografische screening op DDH met behulp van een discrete event simulation (DES) model. De data waren afkomstig uit een implementatiestudie waarvoor in totaal 5266 kinderen werden uitgenodigd. Eén van de scenario’s was de huidige screening door de jeugdgezondheidszorg (anamnese van risicofactoren, lichamelijk onderzoek), waarin bij 2,8% de diagnose DDH werd gesteld. De kosten die bij de berekening meegenomen zijn betreffen de screeningskosten, de kosten voor diagnostiek en behandeling, en de kosten voor ouders (inclusief lange termijn en maatschappelijke kosten; prijspeil 2006). De kosten per gescreend kind in de huidige screening werden geschat op €88; de kosten per in de screening opgespoord kind met DDH bedroegen op €3138. Deze cijfers zijn het meest recent. Bij echografische screening bedroegen deze kosten per gescreend kind en per in de screening opgespoord kind met DDH in stedelijk en plattelandsgebied respectievelijk €188 en €5294, en €243 en €2397.
De kosten op volwassen leeftijd gerelateerd aan verder onderzoek, operatie, revalidatie, fysiotherapeutische behandelingen, blijvende klachten, ziekteverzuim kunnen niet zorgvuldig worden geschat. Uit de gegevens van de Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging (NOV) en de Landelijke Registratie Orthopedische Implantaten (LROI) [61] blijkt dat in 2014 17,0% van de mensen jonger dan 50 jaar oud, en 6,5% van de mensen jonger dan 60 jaar oud die een totale heupprothese kregen, deze heupprothese kregen vanwege dysplasie. Bij veel medische interventies worden de kosten en de effecten niet op hetzelfde moment gerealiseerd: de kost gaat voor de baat uit. Vanwege aspecten als rente en tijdspreferentie moet voor die verschillen in tijd gecorrigeerd worden. De methode waarmee dat wordt gedaan heet disconteren [119]. Kosten die op lange termijn worden gemaakt worden minder belangrijk gevonden. Als deze lange termijn kosten wel worden meegenomen in kosteneffectiviteitsstudies, dan hebben zij door de discontering die plaatsvindt maar zeer beperkte invloed.
10.3 Screeningsprotocol en verwijs- en handelingsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud
Figuur 6 toont het screeningsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud. Het protocol is gebaseerd op aanbevelingen die in de thema’s 1.2 en 1.3 zijn beschreven. Het thema 1.2 beschrijft welke risicofactoren in de (inter)nationale literatuur naar voren komen. In bijlage 1 wordt beschreven op welke manier de anamnese over risicofactoren bij voorkeur afgenomen wordt en welke definities voor risicofactoren daarbij gehanteerd worden. Het thema 1.3 bevat meer informatie over de testeigenschappen en voorspellende waardes van de verschillende onderdelen van het lichamelijk onderzoek. Naast het verzamelde bewijs is voor de vormgeving van de het screenings- en verwijsprotocol gebruik gemaakt van bestaande protocollen [120], [121], [122], [123] die waren opgenomen in de DigiBibJGZ. Voor de specifieke verwijscriteria: zie thema 1.4 en bijlage 5.
Twijfel over het lichamelijk onderzoek kan ontstaan wanneer het lichamelijk onderzoek niet goed uitgevoerd kan worden, bijvoorbeeld als het kind ziek of overstuur is. De aanbeveling is om in dat geval het lichamelijk onderzoek binnen 2 weken opnieuw uit te voeren.
Figuur 7a en 7b tonen het verwijs- en handelingsprotocolprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud. Wanneer uit de anamnese blijkt dat het onderlichaam van het kind strak wordt ingebakerd met de heupen en knieën gestrekt, is dit geen indicatie voor verwijzing, maar wel een reden om de overige onderdelen van het lichamelijk onderzoek extra alert uit te voeren. Extra alert wil zeggen dat de onderzoeker geen twijfel mag hebben over de betrouwbaarheid van het onderzoek (abductie en kniehoogte), en laagdrempelig een eventuele controle afspreekt.
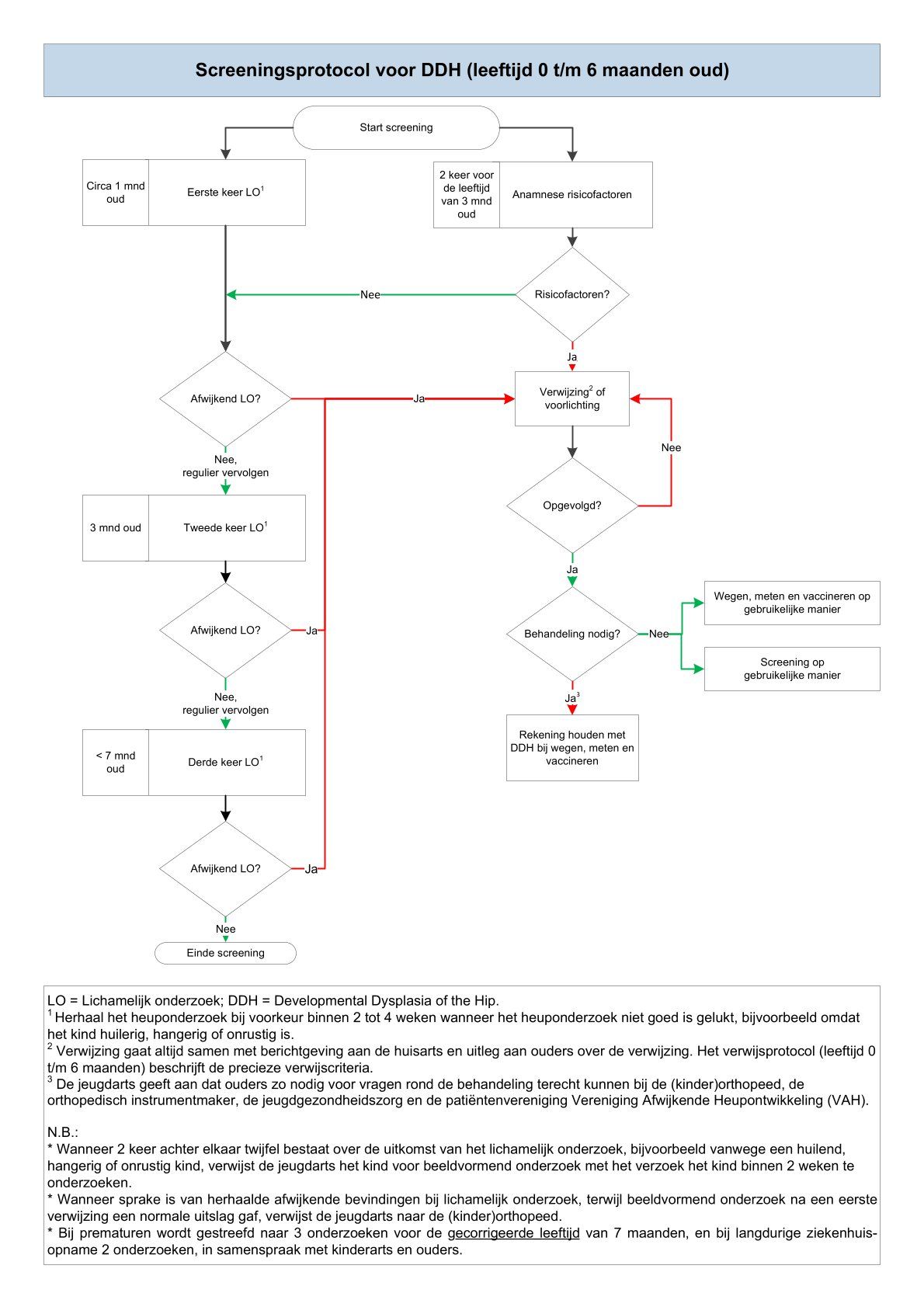
Figuur 6. Screeningsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen t/m 6 maanden oud.

Figuur 7a. Verwijs- en handelingsprotocol o.b.v. alleen risicofactoren (0-6 maanden oud).
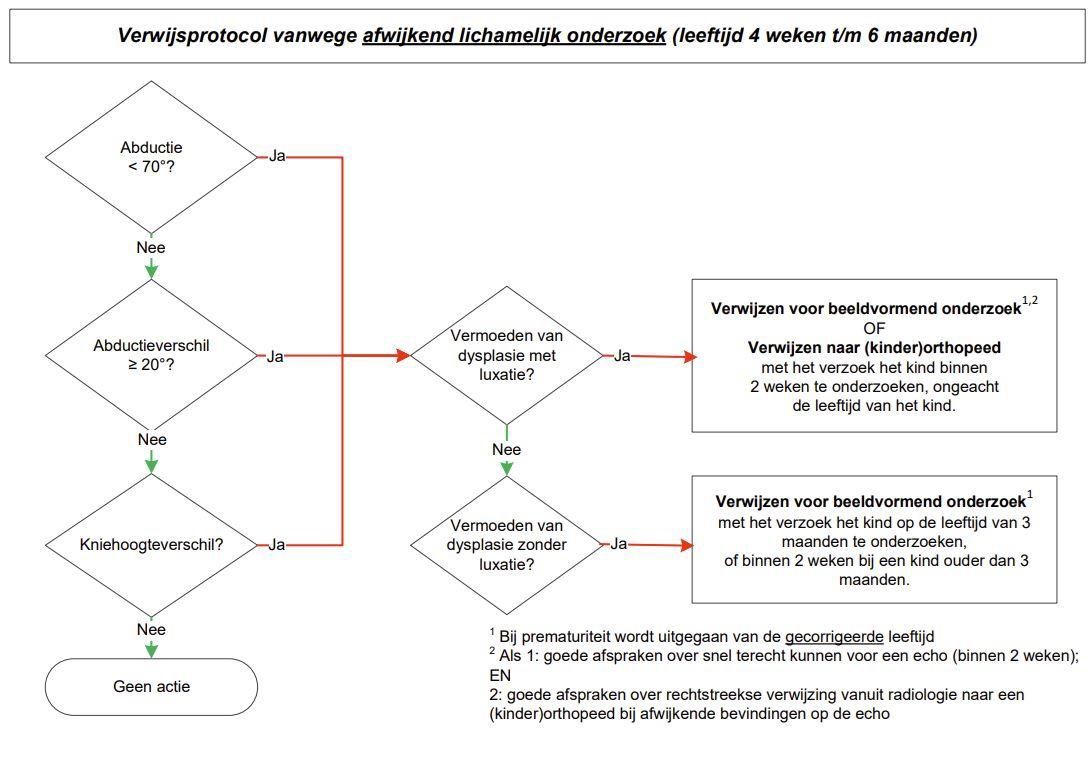
Figuur 7b. Verwijsprotocol o.b.v. afwijkend lichamelijk onderzoek (4 weken t/m 6 maanden oud).
10.4 Onderzoeks- en verwijsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen vanaf 7 maanden oud
Figuur 8a en 8b tonen het onderzoeks- en verwijsprotocol voor DDH bij kinderen vanaf 7 maanden oud.
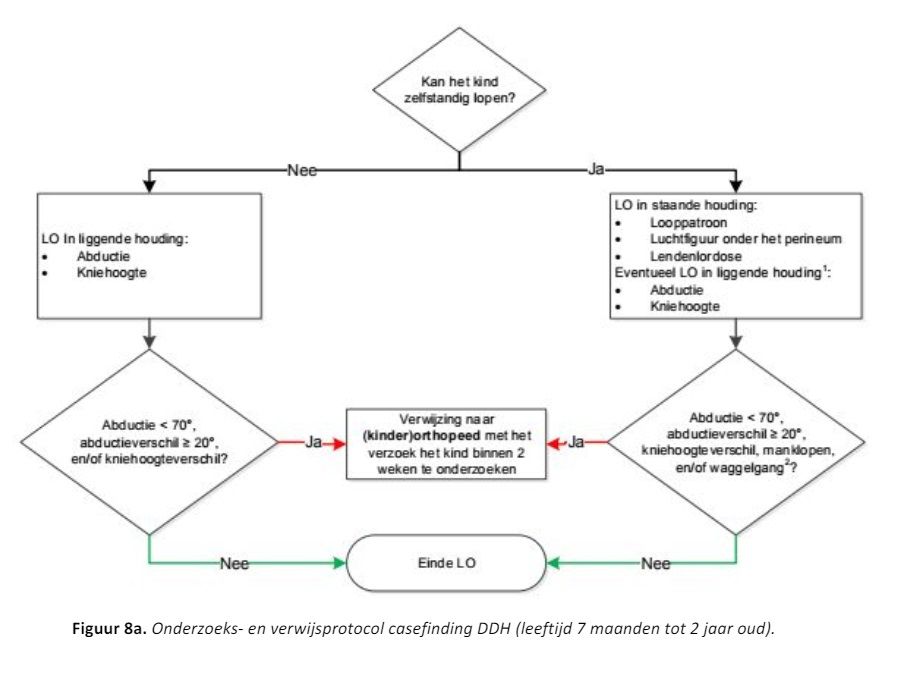
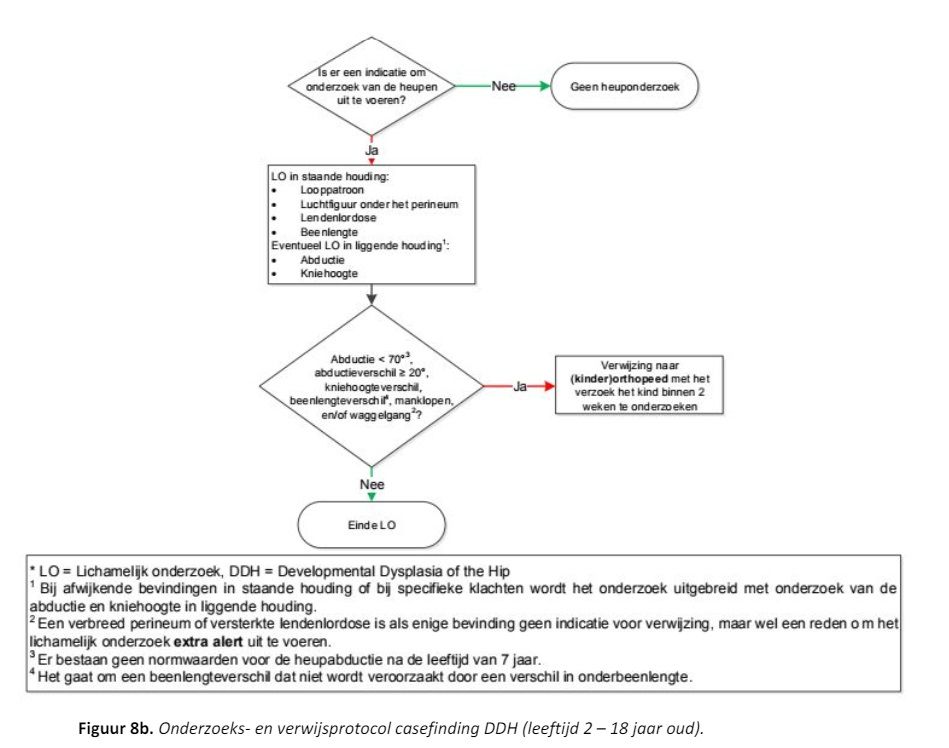
10.5 Activiteiten per contactmoment in de leeftijdsperiode 0 t/m 6 maanden
| Discipline en moment | Activiteiten |
|
Jeugdverpleegkundige of jeugdarts* 2 keer voor de leeftijd van 3 maanden oud |
Anamnese risicofactoren Familieanamnese Zijn er familieleden: ouders of zussen/broers van het kind (eerstegraad); grootouders of tantes/ooms van het kind (tweedegraad); die
Indien positief, dan andere oorzaken zoals trauma, polio, ontsteking en ziekte van Perthes, voor zover mogelijk, uitsluiten. Zwangerschap en geboorte Hoe lag het kind tijdens de controles in de zwangerschap in de baarmoeder na week 32 van de zwangerschap? In hoofdligging, stuitligging of anders? Hoe lag het kind in de baarmoeder op het moment dat u ging bevallen? In hoofdligging of stuitligging? Wanneer er sprake was van een stuitligging na week 32 van de zwangerschap ongeacht de duur en periode van de stuitligging en/of bij de bevalling, is het kind door een andere professional (b.v. de huisarts of de kinderarts) verwezen voor beeldvormend onderzoek van de heupen? Inbakeren Wordt het onderlichaam van het kind ingebakerd? Zo ja, is aan is aan de ouders uitgelegd hoe zij het kind het beste kunnen inbakeren? Zo ja, door wie? |
|
Jeugdarts Eerste bezoek JGZ Circa 1 maand oud |
Anamnese risicofactoren
Lichamelijk onderzoek Voorwaarden
Onderzoek van de abductie van de heupen
Er is sprake van een afwijkend onderzoek als de abductie van 1 of beide heupen beperkt is tot < 70 graden, of bij een abductieverschil van ≥ 20 graden. Onderzoek van de kniehoogte (proef van Galeazzi)
Normaal is er geen verschil in kniehoogte. Bij een duidelijk kniehoogteverschil kan er sprake zijn van dysplasie met of zonder luxatie. Vanzelfsprekend hoeft er bij een dubbelzijdige DDH geen verschil in kniehoogte te zijn. |
|
Jeugdarts of verpleegkundig specialist Tweede, derde en eventueel extra bezoek JGZ in de eerste 7 levensmaanden. |
Zie lichamelijk onderzoek zoals bij eerste bezoek JGZ vóór de zevende levensmaand. |
*Daar waar ‘jeugdarts’ staat, kan ook ‘verpleegkundig specialist’ worden gelezen. De verpleegkundig specialist is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied. Zij werkt op expertniveau en is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ-team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
10.6 Tekst cliëntenfolder
JGZ-organisaties kunnen gebruik maken van deze tekst om een folder in de huisstijl van de organisatie te maken. Organisaties kunnen er desgewenst voor kiezen om de afbeelding weg te laten uit de folder.
Heupdysplasie
De jeugdarts heeft u een verwijzing gegeven voor uw kind. Er is misschien een probleem met de ontwikkeling van de heupen van uw kind (heupdysplasie). In deze folder staat informatie over heupdysplasie.
Wat is heupdysplasie
Heupdysplasie (of Dysplastische Heupontwikkeling) is een probleem in de ontwikkeling van de kinderheup. Het heupgewricht bestaat uit een kop en een kom. De kop zit bovenaan het bovenbeen. De kom is een holte in het bekkenbot. Kop en kom horen mooi in elkaar te passen (plaatje A in afbeelding 1). Dan kan het gewricht soepel bewegen, bijvoorbeeld bij kruipen, lopen, fietsen en zwemmen. Bij een kind met heupdysplasie passen de kop en de kom niet goed in elkaar (plaatje B, C en D in afbeelding 1). Drie van de honderd kinderen (3%) tussen nul en een half jaar hebben een heupdysplasie.
Het is heel belangrijk om heupdysplasie op tijd te ontdekken en te behandelen. Daarmee kunnen problemen met lopen, pijnklachten en slijtage aan de heup op latere leeftijd worden voorkomen.
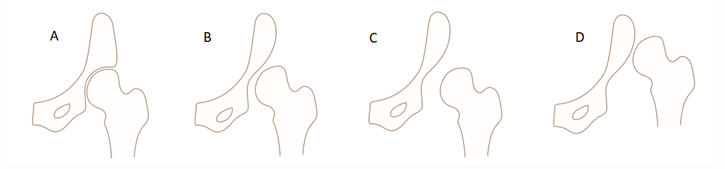
Afbeelding 1. Vereenvoudigd beeld van een normale heup (A) en heupdysplasie (B, C en D). Van links naar rechts neemt de ernst toe.
Wat is de oorzaak van heupdysplasie
Heupdysplasie kan ontstaan tijdens de zwangerschap, baby- of peutertijd. De oorzaak is niet precies bekend. Wel weten we dat de kans op heupdysplasie groter is in de volgende gevallen:
- Als een ouder, broer/zus, oom/tante of grootouder heupdysplasie heeft.
- Als een ouder, oom/tante of grootouder slijtage (‘artrose’) van de heup heeft op jonge leeftijd (voor het 50ste levensjaar)
- Als een baby in de laatste twee maanden van de zwangerschap in stuitligging lag (met de billen naar beneden in plaats van het hoofd).
- Als het onderlichaam van het kind strak wordt ingebakerd met de heupen en knieën gestrekt.
Onderzoek
De jeugdgezondheidszorg (JGZ) controleert regelmatig de heupen van uw kind.
Als u zelf iets aan de heupen van uw kind opmerkt, dan is het goed om dit te melden.
Als er een kans is dat uw kind heupdysplasie heeft, dan is verder onderzoek nodig. Dit wordt op verschillende manieren gedaan. Is uw kind jonger dan zes maanden, dan wordt de vorm van de heup met echo-onderzoek bekeken. Is uw kind ouder dan zes maanden, dan wordt meestal een röntgenfoto gemaakt. Deze onderzoeken doen geen pijn. Het kan ook zijn dat de jeugdarts uw kind rechtstreeks naar de (kinder)orthopeed verwijst. Soms wordt er daarna nog een echo of röntgenfoto gemaakt.
Hoe gaat het verder
Van de zes kinderen bij wie een echo of röntgenfoto van de heupen wordt gemaakt, wordt bij één kind een heupdysplasie gevonden. Wanneer op de echo of röntgenfoto geen heupdysplasie zichtbaar is, blijft de JGZ uw kind controleren (hetzelfde als bij alle kinderen).
Wanneer bij uw kind op de echo of röntgenfoto wel een heupdysplasie wordt gevonden, dan zal de (kinder)orthopeed uw kind verder onderzoeken en behandelen. Heupdysplasie wordt meestal behandeld door de benen van het kind te spreiden met een spreidmiddel (bijvoorbeeld een spreidbroek). Hierdoor komt de heupkop goed in de heupkom te staan en kan het gewricht zich goed ontwikkelen. Meestal duurt deze behandeling meerdere maanden. De kinderorthopeed zal u alle informatie geven over de behandeling van uw kind.
Heeft u nog vragen?
Als u na het lezen van deze informatie nog vragen heeft, dan kunt u contact opnemen met uw JGZ-team: (hier kunnen contactgegevens worden toegevoegd door organisatie)
Referenties
[1] Klisic PJ. Congenital dislocation of the hip--a misleading term: brief report. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1989;71(1):136
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2914985[2] CBO en De Argumentenfabriek, Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg. 2014
[3] Boere-Boonekamp M.M., Mostert A.K.. Dysplastische heupontwikkeling, in Basisboek Jeugdgezondheidszorg in Nederland. 2010, Elsevier Gezondheidszorg: Maarssen. p. 139-52 2010
[4] Hasegawa Y, Iwata H, Mizuno M, Genda E, Sato S, Miura T. The natural course of osteoarthritis of the hip due to subluxation or acetabular dysplasia. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery 1992;111(4):187-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1622705[5] Wedge JH, Wasylenko MJ. The natural history of congenital dislocation of the hip: a critical review. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1978
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/743823[6] Kingma M.J.. Nederlands Leerboek der orthopedie. 1977, Utrecht: Bohn, Scheltema & Holkema. 1977
[7] Boere-Boonekamp M, Ikkink A., E S, L V, Hurts M., Koornstra G., Roodbergen J., D S, Vriezen J., Wensing-Souren C.. Landelijke Eerstelijns Samenwerkings Afspraak Dysplastische HeupOntwikkeling Huisarts En Wetenschap 2010/01/01
[8] Graf R. [Hip ultrasonography. Basic principles and current aspects]. Der Orthopade 1997;26(1):14-24
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9082298[9] Graf R. Hip Sonography: Diagnosis and Management of Infant Hip Dysplasia 2006: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2006
[10] Graf R. Essentials of Infant Hip Sonography - According to Graf (manual). 2014: Stozalpe. 2014
[11] Graf R. Sonographie der Säuglingshüfte und therapeutische Konsequenzen. 2000, Stutgart: Georg Thieme Verlag. 2000
[12] Tönnis D., Brunken D.. Eine Abgrenzung normaler und pathologischer Hüftpfannendachwinkel zur Diagnose der Hüftdysplasie Archiv für orthopädische und Unfall-Chirurgie, mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Frakturenlehre und der orthopädisch-chirurgischen Technik 1968;64(3):197
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02171260 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02171260[13] Boere-Boonekamp M.M.. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip (dissertation). 1996. 1996
[14] Jackson JC, Runge MM, Nye NS. Common questions about developmental dysplasia of the hip. American family physician 2014;90(12):843-50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25591184[15] de Hundt M, Vlemmix F, Bais JMJ, Hutton EK, de Groot CJ, Mol BWJ, Kok M. Risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a meta-analysis. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology 2012;165(1):8-17
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.06.030 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22824571[16] Ortiz-Neira CL, Paolucci EO, Donnon T. A meta-analysis of common risk factors associated with the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. European journal of radiology 2012;81(3):e344-51
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.11.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22119556[17] American Academy of Pediatrics, Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: recommendation statement. Pediatrics 2006;117(3):898-902
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16510673[18] Shaw ED, Beals RK. The hip joint in Down's syndrome. A study of its structure and associated disease. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1992
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1532929[19] Broughton NS, Menelaus MB, Cole WG, Shurtleff DB. The natural history of hip deformity in myelomeningocele. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1993;75(5):760-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8376434[20] Lonstein JE, Beck K. Hip dislocation and subluxation in cerebral palsy. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1986;6(5):521-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3760161[21] Sharrard WJ, Allen JM, Heaney SH. Surgical prophylaxis of subluxation and dislocation of the hip in cerebral palsy. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1975;57(2):160-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1141282[22] Tönnis D.. Congenital Dysplasia and Dislocation of the Hip in Children and Adults. 1987
[23] Visser J.D.. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerste lijn gezondheidszorg. 2012
[24] Ziegler J, Thielemann F, Mayer-Athenstaedt C, Günther K-P. [The natural history of developmental dysplasia of the hip. A meta-analysis of the published literature]. Der Orthopade 2008;37(6):515-6, 518-24
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00132-008-1238-0 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18483804[25] Scharft A., Boere-Boonekamp M.M., Van der Kaap H.. Onderzoek naar de gezondheidsgerelateerde kwaliteit van leven bij (jong)volwassen (vrouwen) met dysplastische heupontwikkeling (bachelorscriptie). 2008
[26] Blom R.. Inbakeren brengt rust. Een handleiding voor het inbakeren van je kind. 2011
[27] Panagiotopoulou N, Bitar K, Hart WJ. The association between mode of delivery and developmental dysplasia of the hip in breech infants: a systematic review of 9 cohort studies. Acta orthopaedica Belgica 2012;78(6):697-702
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23409562[28] Blom R.. Regelmaat en inbakeren. 2010: Uitgeverij Christofoor. 2010
[29] Guner SI, Guner S, Peker E, Ceylan MF, Guler A, Turktas U, Kaki B. Are consanguineous marriage and swaddling the risk factors of developmental dysplasia of the hip? The Journal of membrane biology 2013;246(2):115-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9509-4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23080296[30] Li L.S., Zhang L., Zhao Q., Cheng X., Dang Y.. Heritability and sibling recurrent risk of developmental dysplasia of the hip in Chinese population. European journal of clinical investigation, 2013. 43(6): p. 589-594.
[31] Rühmann O, Konermann W, Lazović D, Vitek L, Bouklas P. [Ultrasound neonatal screening: the effect of anamnestic risk factors on hip dysplasia]. Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und ihre Grenzgebiete 1998;136(6):492-500
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10036736[32] Rühmann O, Lazović D, Bouklas P, Gossé F, Franke J. [Ultrasound hip joint screening in newborn infants. Correlation of anamnestic risk factors and hip dysplasia]. Klinische Padiatrie 1999;211(3):141-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10412123[33] Peterlein CD, Penner T, Schmitt J, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Fölsch C. [Sonographic screening of the newborn hip at the university hospital Marburg--a long-run analysis]. Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und Unfallchirurgie 2014;152(3):234-40
http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1368446 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24960091[34] Patterson C.C.K., Mollan R.A., Haugh P.E., Trainor B.P.. High incidence of congenital dislocation of the hip in Northern Ireland. Paediatric and perinatal epidemiology, 1995. 9(1): p. 90-97. 1995
[35] Uludag S, Seyahi A, Orak MM, Bilgili MG, Colakoglu B, Demirhan M. The effect of gestational age on sonographic screening of the hip in term infants. The bone & joint journal 2013;95-B(2):266-70
http://dx.doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.95B2.30798 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23365040[36] Partenheimer A, Scheler-Hofmann M, Lange J, Kühl R, Follak N, Ebner A, Fusch C, Stenger R, Merk H, Haas JP. [Correlation between sex, intrauterine position and familial predisposition and neonatal hip ultrasound results]. Ultraschall in der Medizin (Stuttgart, Germany : 1980) 2006;27(4):364-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16596510[37] von Deimling U, Brähler JM, Niesen M, Wagner UA, Walpert J. [Effect of birth weight on hip maturation in the newborn infant]. Klinische Padiatrie 1998;210(3):115-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9629544[38] Boere-Boonekamp M.M.. Diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. The significance of anamnestic data and findings on physical examination. Huisarts en Wetenschap, 1997. 40(6): p. 236-243. 1997
[39] Shi D, Dai J, Ikegawa S, Jiang Q. Genetic study on developmental dysplasia of the hip European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2012;42(10):1121
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2012.02682.x https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2012.02682.x[40] Ibrahim T, Riaz M, Hegazy A. The prevalence of developmental dysplasia of the hip in idiopathic clubfoot: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International orthopaedics 2015;39(7):1371-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2757-z https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25846795[41] Harcke HT, Karatas AF, Cummings S, Bowen JR. Sonographic Assessment of Hip Swaddling Techniques in Infants With and Without DDH. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2016;36(3):232-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000446 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25851676[42] Chaarani M.W., Al Mahmeid M.S., Salman A.M.. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip before and after increasing community awareness of the harmful effects of swaddling. Qatar Medical Journal, 2002. 11(1): p. 40-43.
[43] Moosa NK, Kumar PT, Mahmoodi SM. Incidence of developmental dysplasia of the hip in Dubai. Saudi medical journal 2009;30(7):952-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19618014[44] van Sleuwen BE, Engelberts AC, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Kuis W, Schulpen TWJ, L'Hoir MP. Swaddling: a systematic review. Pediatrics 2007;120(4):e1097-106
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17908730[45] Sahin F, Aktürk A, Beyazova U, Cakir B, Boyunaga O, Tezcan S, Bölükbaşi S, Kanatli U. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: results of a 7-year follow-up study. Pediatrics international : official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society 2004;46(2):162-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15056242[46] Chan A, McCaul KA, Cundy PJ, Haan EA, Byron-Scott R. Perinatal risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 1997;76(2):F94-100
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9135287[47] Burke SM, Roberts JM, Johnston C. Congenital dislocation of the hip in the American black. Clin Orthop Relat Res., 1985. 192: p. 120-3. 1985
[48] Rühmann O, Lazović D, Bouklas P, Rössig S. [Ultrasound hip joint screening in newborn infants. Is twin pregnancy a risk factor for dysplasia?]. Ultraschall in der Medizin (Stuttgart, Germany : 1980) 1998;19(2):64-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9654671[49] Orak MM, Onay T., Gümüştaş SA, Gürsoy T., Muratlí HH. Is prematurity a risk factor for developmental dysplasia The Bone & Joint Journal 2015;97-B(5):716
http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B5.34010 https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B5.34010[50] Holen KJ, Tegnander A, Terjesen T, Johansen OJ, Eik-Nes SH. Ultrasonographic evaluation of breech presentation as a risk factor for hip dysplasia. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 1996;85(2):225-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8640055[51] Quan T, Kent AL, Carlisle H. Breech preterm infants are at risk of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Journal of paediatrics and child health 2013;49(8):658-63
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jpc.12250 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23758088[52] Hill LM. Prevalence of breech presentation by gestational age. American journal of perinatology 1990;7(1):92-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2403797[53] Hickok DE, Gordon DC, Milberg JA, Williams MA, Daling JR. The frequency of breech presentation by gestational age at birth: a large population-based study. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 1992;166(3):851-2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1550152[54] Fox AJS, Chapman MG. Longitudinal ultrasound assessment of fetal presentation: a review of 1010 consecutive cases. The Australian & New Zealand journal of obstetrics & gynaecology 2006;46(4):341-4
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16866797[55] Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2000
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10796122[56] Hofmeyr GJ. Interventions to help external cephalic version for breech presentation at term. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2004
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14973948[57] Lambeek AF, De Hundt M, Vlemmix F, Akerboom BMC, Bais JMJ, Papatsonis DNM, Mol BWJ, Kok M. Risk of developmental dysplasia of the hip in breech presentation: the effect of successful external cephalic version. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2013;120(5):607-12
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12013 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23145903[58] Anderssen SIE, Soukup M., Andersen AE. Congenital hip dysplasia in Ostfold 1990-96. Tidsskrift for den Norske laegeforening : tidsskrift for praktisk medicin, ny raekke, 2000. 120(29): p. 3530-3533. 2000
[59] Chan AKA, Cundy PJ, Haan EA, Byron-Scott R.. Perinatal risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Archives of disease in childhood.Fetal and neonatal edition, 1997. 76(2): p. F94-100. 1997
[60] CBO Kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg, Evidence-based Richtlijnontwikkeling. Handleiding voor werkgroepleden. 2007
[61] Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging (NOV) and Stichting LROI, Orthopedische implantaten in beeld. 2014
[62] Nederlandse Vereniging voor Obstetrie en Gynaecologie, Richtlijn Stuitligging. 2001
[63] Walsh JJ, Morrissy RT. Torticollis and hip dislocation. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1998;18(2):219-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9531405[64] Minihane KJJ, Simmons TD, Seshadri R., Wysocki RW, Sarwark JF. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants with congenital muscular torticollis. American journal of orthopedics (Belle Mead, N.J.), 2008. 37(9): p. E155-8; discussion E158. 2008
[65] Tien YC, Su JY, Lin GT, Lin SY. Ultrasonographic study of the coexistence of muscular torticollis and dysplasia of the hip. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2001;21(3):343-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11371818[66] Cheng JC, Tang SP, Chen TM. Sternocleidomastoid pseudotumor and congenital muscular torticollis in infants: a prospective study of 510 cases. The Journal of pediatrics 1999;134(6):712-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10356139[67] Castelein RM. [Physical diagnosis--Ortolani's manoeuvre]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2002;146(23):1077-80
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12085556[68] Patel H, . Preventive health care, 2001 update: screening and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2001;164(12):1669-77
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11450209[69] Paton RW. Screening for hip abnormality in the neonate. Early human development 2005;81(10):803-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16226409[70] American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Detection and nonoperative managment of pediatric developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants up to six months of age. 2014
[71] Paton RW, Srinivasan MS, Shah B, Hollis S. Ultrasound screening for hips at risk in developmental dysplasia. Is it worth it? The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 1999;81(2):255-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10204931[72] Beentjes M, Weersma R., Koch W., Offringa A., Verduijn M, Mensink P., Wiersma T., Goudswaard L.. NHG-Standaard Zwangerschap en kraamperiode (tweede herziening) (NHG-Quality Standard Pregnancy and postnatal period (second revision)) Huisarts & Wetenschap 2012/01/01;55():1112
[73] Engelberts AC, Koerts B, Waelkens JJ, Wit JM, Burger BJ. [Measuring the length of newborn infants]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2005;149(12):632-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15813430[74] TNO, Groeidiagrammen 2010. Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen. 2010
[75] Omeroğlu H, Koparal S. The role of clinical examination and risk factors in the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a prospective study in 188 referred young infants. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery 2001;121(1-2):7-11
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11195123[76] Roposch A, Liu LQ, Hefti F, Clarke NMP, Wedge JH. Standardized diagnostic criteria for developmental dysplasia of the hip in early infancy. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 2011;469(12):3451-61
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-2066-9 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21952742[77] Stoffelen D, Urlus M, Molenaers G, Fabry G. Ultrasound, radiographs, and clinical symptoms in developmental dislocation of the hip: a study of 170 patients. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 1995;4(2):194-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7670989[78] Castelein RM, Korte J. Limited hip abduction in the infant. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2001;21(5):668-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11521039[79] Choudry Q, Goyal R, Paton RW. Is limitation of hip abduction a useful clinical sign in the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip? Archives of disease in childhood 2013;98(11):862-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2012-303121 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23946334[80] Jari S, Paton RW, Srinivasan MS. Unilateral limitation of abduction of the hip. A valuable clinical sign for DDH? The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 2002;84(1):104-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11837813[81] Senaran H, Ozdemir HM, Ogün TC, Kapicioglu MIS. Value of limited hip abduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatrics international : official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society 2004;46(4):456-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15310313[82] van Hees-van der Laan Z.J., Huttinga-Edens M.M.. Congenitale dysplasie van het heupgewricht bij zuigeligen; een onderzoek op consultatiebureaus in Groningen. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde, 1981. 125(47): p. 1913-1917. 1981
[83] Boere-Boonekamp MM, Kerkhoff TH, Schuil PB, Zielhuis GA. Early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip in The Netherlands: the validity of a standardized assessment protocol in infants. American journal of public health 1998;88(2):285-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9491024[84] Boere-Boonekamp MM, Verkerk PH. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip Seminars in Neonatology 1998;3(1):49
http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1084-2756(98)80148-6 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084275698801486[85] Donnelly KJ, Chan KW, Cosgrove AP. Delayed diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip in Northern Ireland: can we do better? The bone & joint journal 2015;97-B(11):1572-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B11.35286 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26530663[86] Mudge AJ, Bau KV, Purcell LN, Wu JC, Axt MW, Selber P, Burns J. Normative reference values for lower limb joint range, bone torsion, and alignment in children aged 4-16 years. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2014;23(1):15-25
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e328364220a https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23852035[87] Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging (NOV). Systematische screening naar dysplastische heupontwikkeling bij een primaire idiopathische klompvoet. 2014; Geraadpleegd op 9 oktober 2017 2014
http://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/primaire_idiopathische_klompvoet/klompvoet_en_dysplas%20%20tische_heupontwikkeling.html#verantwoording.%20[88] Shipman SA, Helfand M, Moyer VA, Yawn BP. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a systematic literature review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics 2006;117(3):e557-76
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16510634[89] Roovers E.A.. Post-neonatal ultrasound screening for developmental dysplasie of the hip. A study on cost-effectiveness in the Netherlands (dissertation). 2004
[90] Ramwadhdoebe S.. Screening for developmental dysplkasie of the hip in primary care. Implementation by simulation (dissertation). 2010
[91] Witting M. Towards effective implementation strategies for ultrasound hip screening in child health care Tijdschrift voor Kindergeneeskunde 2012;80(2):49
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12456-012-0013-7 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12456-012-0013-7[92] . Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: recommendation statement. American family physician 2006;73(11):1992-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16770931[93] Clinical practice guideline: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics 2000;105(4 Pt 1):896-905
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10742345[94] Rosendahl K, Dezateux C, Fosse KR, Aase H, Aukland SM, Reigstad H, Alsaker T, Moster D, Lie RT, Markestad T. Immediate treatment versus sonographic surveillance for mild hip dysplasia in newborns. Pediatrics 2010;125(1):e9-16
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0357 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20026501[95] Bache CHK, Dickens DR, Donnan L., Johnson MB, Nattrass G., O'Sullivan M., Torode IP. Ligamentum teres tenodesis in medial approach open reduction for developmental dislocation of the hip. Journal of pediatric orthopedics, 2008. 28(6): p. 607-613. 2008
[96] Danielsson L. Late-diagnosed DDH: a prospective 11-year follow-up of 71 consecutive patients (75 hips). Acta orthopaedica Scandinavica 2000;71(3):232-42
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10919293[97] Fukiage K, Futami T, Ogi Y, Harada Y, Shimozono F, Kashiwagi N, Takase T, Suzuki S. Ultrasound-guided gradual reduction using flexion and abduction continuous traction for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a new method of treatment. The bone & joint journal 2015;97-B(3):405-11
http://dx.doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B3.34287 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25737526[98] Harding MG, Harcke HT, Bowen JR, Guille JT, Glutting J. Management of dislocated hips with Pavlik harness treatment and ultrasound monitoring. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1997;17(2):189-98
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9075094[99] Inoue T, Naito M, Nomiyama H. Treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip with the Pavlik harness: factors for predicting unsuccessful reduction. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2001;10(3):186-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11497359[100] Kitoh H, Kawasumi M, Ishiguro N. Predictive factors for unsuccessful treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip by the Pavlik harness. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2009;29(6):552-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181b2f200 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19700982[101] Zamzam MM, Kremli MK, Khoshhal KI, Abak AA, Bakarman KA, Alsiddiky AMM, Alzain KO. Acetabular cartilaginous angle: a new method for predicting acetabular development in developmental dysplasia of the hip in children between 2 and 18 months of age. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2008;28(5):518-23
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31817c4e6d https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18580365[102] Eidelman M, Katzman A, Freiman S, Peled E, Bialik V. Treatment of true developmental dysplasia of the hip using Pavlik's method. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2003;12(4):253-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12821841[103] Bialik GM, Eidelman M, Katzman A, Peled E. Treatment duration of developmental dysplasia of the hip: age and sonography. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2009;18(6):308-13
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e32832f12ba https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19593215[104] Lerman JA, Emans JB, Millis MB, Share J, Zurakowski D, Kasser JR. Early failure of Pavlik harness treatment for developmental hip dysplasia: clinical and ultrasound predictors. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2001;21(3):348-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11371819[105] Westacott DJ, Mackay ND, Waton A, Webb MSL, Henman P, Cooke SJ. Staged weaning versus immediate cessation of Pavlik harness treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B 2014;23(2):103-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0000000000000025 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24322535[106] Phelan NJ, Fox C., O'Daly BJ, O'Beirne J.. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: incidence and treatment outcomes in the Southeast of Ireland. Irish journal of medical science, 2015. 184(2): p. 411-415. 2015
[107] Shipman SM, Moyer VA, Yawn BP. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a systematic literature review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics, 2006. 117(3): p. e557-76. 2006
[108] Shorter D, Hong T, Osborn DA. Screening programmes for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborn infants. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2011;2011(9):CD004595
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004595.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21901691[109] Coussement C., Meulemans B.. Betere pijnbeheersing doet ouders vaccinatiekalender respecteren JGZ Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 2016/05/25;48():
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12452-016-0061-y[110] Shendurnikar N, Thakkar PA. Communication skills to ensure patient satisfaction. Indian journal of pediatrics 2013;80(11):938-43
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12098-012-0958-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23378053[111] Barbosa CD, Balp M-M, Kulich K, Germain N, Rofail D. A literature review to explore the link between treatment satisfaction and adherence, compliance, and persistence. Patient preference and adherence 2012;6():39-48
http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S24752 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22272068[112] Berkenbosch TS, Ronde T., Konijnendijk AAJ, Boere-Boonekamp MM. Dysplastische heupontwikkeling: ervaringen van ouders met de screening door de jeugdgezondheidszorg JGZ Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 2016;48(3):57
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12452-016-0059-5 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12452-016-0059-5[113] Berkenbosch TR, Konijnendijk AAJ, Boere-Boonekamp MM. Tevredenheid van ouders met de screening op en de voorlichting en begeleiding bij dysplastische heupontwikkeling door de jeugdgezondheidszorg (bacheloropdracht). 2015
[114] Braun DD, Mansfield P.. How helping works. Towards a shared model of process. 2006, Londen: Parentline Plus. 2006
[115] Muller L.. Scholing: opvoedingsondersteuning vanuit het consultatiebureau. 2001: Centrum voor Advies en Training Luud Muller & Co. 2001
[116] Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, Boers M, Andersson N, Hamel C, Porter AC, Tugwell P, Moher D, Bouter LM. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC medical research methodology 2007;7():10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17302989[117] Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, DeBeer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of clinical epidemiology 2011;64(4):383-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21195583[118] Familie (verwanten) Wikipedia z.d. Geraadpleegd op 5 oktober 2017
https://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Familie_(verwanten)#Medisch_gebruik_van_de_familiegraden[119] van Ballegooijen M, de Kok IMCM, Habbema JDF. [Unequal discounting of health care costs and effects causes confusion]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2010;154():A1970
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20619050[120] JGZ Valent, Aangeboren heupafwijkingen. 2009
[121] Thuiszorg West-Brabant, Werkinstructie signaleren dysplastische heupontwikkeling. 2009
[122] GGD Gooi & Vechtstreek afdeling Jeugdgezondheidszorg, Protocol Dysplastische Heuptontwikkeling. 2006
[123] Thuiszorg Pantein Divisie JGZ, Protocol signaleren dysplastische heupontwikkeling. 2008
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackLET OP: print de JGZ-richtlijn in liggende afdrukstand!
Grote tabellen zijn niet volledig zichtbaar als de JGZ-richtlijn in staande afdrukstand geprint wordt. Om kleuren in de printversie goed door te laten komen, moet bij de printerinstellingen Achtergrondillustraties aangezet worden.
Disclaimer printversie JGZ-richtlijnen
De printversie van de JGZ-richtlijn bevat de algemene tekst inclusief de aanbevelingen. De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing is terug te vinden op de website, bij de aanbevelingen onder de link “Evidence”.
