Lees meer in de onderliggende hoofdstukken.
3.2 Beschrijving actief op te sporen symptomen en aandoeningen
JGZ-richtlijn Houding en bewegen
JGZ-richtlijn Houding en bewegen
Let op: deze richtlijn is momenteel in herziening.
Dit betekent niet dat de inhoud van deze richtlijn incorrect is. Tot de herziening blijft de richtlijn leidend voor de praktijk. Wel bestaat er een kans dat een deel van de informatie verouderd is.
Heb je feedback over deze JGZ-richtlijn? Stuur jouw feedback naar onze servicedesk. Zoek het tekstgedeelte waarbij je suggesties voor verbetering hebt. Via de knop ‘Geef jouw feedback’ kun je voor deze JGZ-richtlijn en het specifieke hoofdstuk jouw suggesties doorgeven.
Richtlijn inhoudsopgave
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
4 Preventie Ga naar pagina over 4 Preventie
5 Begeleiden en behandelen Ga naar pagina over 5 Begeleiden en behandelen
6 Samenwerken Ga naar pagina over 6 Samenwerken
7 Totstandkoming Ga naar pagina over 7 Totstandkoming
8 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 8 Verantwoording
9 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 9 Bijlagen
1 Inleiding Ga naar pagina over 1 Inleiding
2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen Ga naar pagina over 3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
4 Preventie Ga naar pagina over 4 Preventie
5 Begeleiden en behandelen Ga naar pagina over 5 Begeleiden en behandelen
6 Samenwerken Ga naar pagina over 6 Samenwerken
7 Totstandkoming Ga naar pagina over 7 Totstandkoming
8 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 8 Verantwoording
9 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 9 Bijlagen
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackKernaanbevelingen richtlijn Houding en bewegen
Introductiefilmpje richtlijn Houding en bewegen
Indicatoren richtlijn Houding en bewegen
BDS-registratie-protocol richtlijn Houding en bewegen
PP-presentatie voor de scholing Houding en bewegen
Rapportage praktijktest richtlijn Houding en bewegen
Randvoorwaardelijke implicaties richtlijn houding en bewegen
[1] Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg. 2017
[2] Van Empelen R, Nijhuis-van der Sanden R, Hartman A. Kinderfysiotherapie. Vierde druk. Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum. 2016
[3] Leefstijlmonitor 2018
https://www.sportenbewegenincijfers.nl/kernindicatoren/%20[4] Gezondheidsraad. Advies beweegrichtlijnen 2017. Den Haag. 2017
[5] Guidelines on Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour and Sleep for Children under 5 Years of Age 2019
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31091057[6] Bailey R, Hillman C, Arent S, Petitpas A. Physical activity: an underestimated investment in human capital? Journal of physical activity & health 2013;10(3):289-308
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23620387[7] Donnelly JE, Hillman CH, Castelli D, Etnier JL, Lee S, Tomporowski P, Lambourne K, Szabo-Reed AN. Physical Activity, Fitness, Cognitive Function, and Academic Achievement in Children: A Systematic Review. Medicine and science in sports and exercise 2016;48(6):1197-222
http://dx.doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000901 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27182986[8] Sullivan RA, Kuzel AH, Vaandering ME, Chen W. The Association of Physical Activity and Academic Behavior: A Systematic Review. The Journal of school health 2017;87(5):388-398
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/josh.12502 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28382668[9] Veldman SLC, Altenburg TM, Chin A Paw M. Literatuuronderzoek Associaties tussen Lichamelijke Activiteit en Groei en Ontwikkeling bij 0-5 jarige Kinderen Amsterdam: Amsterdam UMC, locatie VUmc. 2019
[10] Timmons BW, Leblanc AG, Carson V, Connor Gorber S, Dillman C, Janssen I, Kho ME, Spence JC, Stearns JA, Tremblay MS. Systematic review of physical activity and health in the early years (aged 0-4 years). Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme 2012;37(4):773-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/h2012-070 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22765840[11] Zeng N, Ayyub M, Sun H, Wen XU, Xiang P, Gao Z. Effects of Physical Activity on Motor Skills and Cognitive Development in Early Childhood: A Systematic Review. BioMed research international 2017;2017():2760716
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2017/2760716 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29387718[12] Hefti F. Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York. ISBN-13: 978-3-540-69963-7. 2007
[13] Van der Sluijs JA, Sakkers RJB, Bronswijk JAHM. Praktische Kindergeneeskunde: Kinderorthopedie. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten. 2009
[14] Vissers J. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. Telenga drukwerk service, Groningen. 2012
[15] Talma H, Schönbeck Y, van Dommelen P, Bakker B, van Buuren S, Hirasing RA. Trends in menarcheal age between 1955 and 2009 in the Netherlands. PloS one 2013;8(4):e60056
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060056 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23579990[16] Seregni F, Weatherby T, Beardsall K. Do all newborns with an isolated sacrococcygeal dimple require investigation for spinal dysraphism? Archives of disease in childhood 2019;104(8):816-817
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2019-317058 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31113767[17] Schönbeck Y, Hindori-Mohangoo AD, Masurel N, van der Pal-de Bruin KM. Aangeboren afwijkingen in Nederland 2001-2013: Gebaseerd op de landelijke perinatale registraties. TNO/CH 2015 R11267. TNO, Leiden. 2015
[18] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de JGZ. Koninklijke van Gorcum BV. ISBN-13: 9789023241911. 2005
[19] Touwen BCL. De neurologische ontwikkeling van de zuigeling. Utrecht/Antwerpen: Bohn Scheltema & Holkema. 1984
[20] Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, Czaprowski D, Schreiber S, de Mauroy JC, Diers H, Grivas TB, Knott P, Kotwicki T, Lebel A, Marti C, Maruyama T, O'Brien J, Price N, Parent E, Rigo M, Romano M, Stikeleather L, Wynne J, Zaina F. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis and spinal disorders 2018;13():3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13013-017-0145-8 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29435499[21] Wajchenberg M, Astur N, Kanas M, Martins DE. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: current concepts on neurological and muscular etiologies. Scoliosis and spinal disorders 2016;11():4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13013-016-0066-y https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27355084[22] Rogala EJ, Drummond DS, Gurr J. Scoliosis: incidence and natural history. A prospective epidemiological study. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1978;60(2):173-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/641080[23] Lonstein JE, Carlson JM. The prediction of curve progression in untreated idiopathic scoliosis during growth. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1984;66(7):1061-71
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6480635[24] Pehrsson K, Larsson S, Oden A, Nachemson A. Long-term follow-up of patients with untreated scoliosis. A study of mortality, causes of death, and symptoms. Spine 1992;17(9):1091-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1411763[25] Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Spratt KF, Peterson KK, Spoonamore MJ, Ponseti IV. Health and function of patients with untreated idiopathic scoliosis: a 50-year natural history study. JAMA 2003;289(5):559-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12578488[26] Lissak G. Adverse physiological and psychological effects of screen time on children and adolescents: Literature review and case study. Environmental research 2018;164():149-157
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.01.015 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29499467[27] Radesky JS, Schumacher J, Zuckerman B. Mobile and interactive media use by young children: the good, the bad, and the unknown. Pediatrics 2015;135(1):1-3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-2251 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25548323[28] Mediawijzer.net.. Iene Miene Media 2018. 2018
https://www.mediawijzer.net/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2018/04/Onderzoek-IeneMieneMedia-2018.pdf[29] NVK, AJN, V&VN,, Erasmus MC, HNN, IVO, TNO, NCJ, NJi, VUmc. Factsheet beeldschermgebruik van dichtbij. 2018
http://ajnjeugdartsen.nl/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Factsheet-beeldschermgebruik-2018-1.pdf[30] Straker L, Abbott R, Collins R, Campbell A. Evidence-based guidelines for wise use of electronic games by children. Ergonomics 2014;57(4):471-89
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2014.895856 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24665962[31] Straker L, Maslen B, Burgess-Limerick R, Johnson P, Dennerlein J. Evidence-based guidelines for the wise use of computers by children: physical development guidelines. Ergonomics 2010;53(4):458-77
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00140130903556344 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20309743[32] Potthoff T, de Bruin ED, Rosser S, Humphreys BK, Wirth B. A systematic review on quantifiable physical risk factors for non-specific adolescent low back pain. Journal of pediatric rehabilitation medicine 2018;11(2):79-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/PRM-170526 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30010152[33] Brink Y, Louw QA. A systematic review of the relationship between sitting and upper quadrant musculoskeletal pain in children and adolescents. Manual therapy 2013;18(4):281-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2012.11.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23298827[34] Huguet A, Tougas ME, Hayden J, McGrath PJ, Stinson JN, Chambers CT. Systematic review with meta-analysis of childhood and adolescent risk and prognostic factors for musculoskeletal pain. Pain 2016;157(12):2640-2656
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000685 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27525834[35] Wirth B, Potthoff T, Rosser S, Humphreys BK, de Bruin ED. Physical risk factors for adolescent neck and mid back pain: a systematic review. Chiropractic & manual therapies 2018;26():36
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12998-018-0206-y https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30258567[36] Hill JJ, Keating JL. Risk factors for the first episode of low back pain in children are infrequently validated across samples and conditions: a systematic review. Journal of physiotherapy 2010;56(4):237-44
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21091413[37] Calvo-Muñoz I, Kovacs FM, Roqué M, Gago Fernández I, Seco Calvo J. Risk Factors for Low Back Pain in Childhood and Adolescence: A Systematic Review. The Clinical journal of pain 2018;34(5):468-484
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0000000000000558 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28915154[38] Kamper SJ, Yamato TP, Williams CM. The prevalence, risk factors, prognosis and treatment for back pain in children and adolescents: An overview of systematic reviews. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology 2016;30(6):1021-1036
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2017.04.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29103547[39] Yamato TP, Maher CG, Traeger AC, Wiliams CM, Kamper SJ. Do schoolbags cause back pain in children and adolescents? A systematic review. British journal of sports medicine 2018;52(19):1241-1245
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-098927 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29720469[40] Collard DCM, Verhagen EALM, Chinapaw MJM, Knol DL, van Mechelen W. Effectiveness of a school-based physical activity injury prevention program: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2010;164(2):145-50
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2009.256 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20124143[41] Nauta J, van Mechelen W, Otten RHJ, Verhagen EALM. A systematic review on the effectiveness of school and community-based injury prevention programmes on risk behaviour and injury risk in 8-12 year old children. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2014;17(2):165-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2013.07.011 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23962868[42] MacDonald J, Stuart E, Rodenberg R. Musculoskeletal Low Back Pain in School-aged Children: A Review. JAMA pediatrics 2017;171(3):280-287
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.3334 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28135365[43] Jayanthi NA, Post EG, Laury TC, Fabricant PD. Health Consequences of Youth Sport Specialization. Journal of athletic training 2019;54(10):1040-1049
http://dx.doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-380-18 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31633420[44] Castellucci HI, Arezes PM, Molenbroek JFM, de Bruin R, Viviani C. The influence of school furniture on students' performance and physical responses: results of a systematic review. Ergonomics 2017;60(1):93-110
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2016.1170889 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27015656[45] Sandseter EB. Categorising risky play—how can we identify risk‐taking in children's play?. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal 15(2):237-252 2007
[46] Brussoni M, Gibbons R, Gray C, Ishikawa T, Sandseter EBH, Bienenstock A, Chabot G, Fuselli P, Herrington S, Janssen I, Pickett W, Power M, Stanger N, Sampson M, Tremblay MS. What is the Relationship between Risky Outdoor Play and Health in Children? A Systematic Review. International journal of environmental research and public health 2015;12(6):6423-54
http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120606423 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26062038[47] Van Wieringen JCM, Beckers M. Hoe krijgt de jeugdgezondheidszorg de jeugd in beweging? Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 47: 92–95. 2015
[48] Kenniscentrum Sport, Stichting Opvoeden.nl. Landelijk Ouderpanel; Hoe denken ouders over sport en bewegen? Resultaten van de peiling. 2019
https://opvoedinformatie.nl/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Def.-Samenvatting-peiling-ouders-over-sport-en-bewegen-2-geconverteerd.pdf[49] Van Wieringen JCM. Standpunt beweegstimulering door de jeugdgezondheidszorg. RIVM rapport 295002001. RIVM, Bilthoven. 2009
[50] Kenniscentrum Sport. Sport- en beweeginterventies. 2019
https://www.kenniscentrumsport.nl/sportinterventies-en-beweeginterventies/[51] Zwikker M, Van Dale D, Dinnink T, Willemse G, Van Rooijen S, Heeringa N, Rensen P. Erkenning van interventies. Criteria voor gezamenlijke kwaliteitsbeoordeling 2015-2018. RIVM, NJi, NISB, Trimbos instituut, Vilans, Movisie, NCJ. 2015
[52] Kriemler S, Meyer U, Martin E, van Sluijs EMF, Andersen LB, Martin BW. Effect of school-based interventions on physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents: a review of reviews and systematic update. British journal of sports medicine 2011;45(11):923-30
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2011-090186 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21836176[53] Gordon ES, Tucker P, Burke SM, Carron AV. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions for preschoolers: a meta-analysis. Research quarterly for exercise and sport 2013;84(3):287-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24261007[54] Van Empelen P, Schokker D. Factsheet: Werkzame elementen van voeding- en beweeginterventies. Slimme combinaties van gedragsveranderingstechnieken. TNO, Leiden. 2015
[55] Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, . GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2008;336(7650):924-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18436948[56] Makurthou AA, Oei L, El Saddy S, Breda SJ, Castaño-Betancourt MC, Hofman A, van Meurs JBJ, Uitterlinden AG, Rivadeneira F, Oei EHG. Scheuermann disease: evaluation of radiological criteria and population prevalence. Spine 2013;38(19):1690-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31829ee8b7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24509552[57] Wijga AH, Scholtens S, van Oeffelen AAM, Beckers M. Klachten en kwalen bij kinderen in Nederland. Omvang en gevolgen geïnventariseerd. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu (RIVM), RIVM Rapport 260136001/2010. 2010
[58] Calvo-Muñoz I, Gómez-Conesa A, Sánchez-Meca J. Prevalence of low back pain in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. BMC pediatrics 2013;13():14
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-13-14 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23351394[59] Bons SCS, Borg MAJP, Van den Donk M, Koes BW, Kuijpers T, Ostelo RWJG, Schaafstra A, Spinnewijn WEM, Verburg-Oorthuizen AFE, Verweij HA. NHG-Standaard Aspecifieke lagerugpijn (Tweede herziening). 2017
[60] Multidisciplinaire richtlijn ‘Aspecifieke klachten arm, nek en/of schouders’. Amersfoort: KNGF. 2012
[61] Kunnamo I, Kallio P, Pelkonen P. Incidence of arthritis in urban Finnish children. A prospective study. Arthritis and rheumatism 1986;29(10):1232-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3768057[62] NVK werkboek kinderinfectieziekten. 2020
https://werkboeken.nvk.nl/kinderinfectieziekten/Orgaansysteem/Botten-en-gewrichten[63] NVK. Richtlijn medicamenteuze behandeling van kinderen met juveniele idiopathische artritis 2017
[64] Hebra A. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1004953-overview (bezocht op 26-2-2019). 2018
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1004953-overview%20(bezocht%20op%2026-2-2019).[65] Ji YI, Liu W, Chen S, Xu B, Tang Y, Wang X, Yang G, Cao L. Assessment of psychosocial functioning and its risk factors in children with pectus excavatum. Health and quality of life outcomes 2011;9():28
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-9-28 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21542911[66] Obermeyer RJ, Goretsky MJ. Chest wall deformities in pediatric surgery. The Surgical clinics of North America 2012;92(3):669-84, ix
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2012.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22595715[67] Kenniscentrum Sport. Factsheet jeugd - armoede - sport 2017
https://www.kennisbanksportenbewegen.nl/?file=8235&m=1511185328&action=file.download[68] Perrone M, Orr R, Hing W, Milne N, Pope R. The Impact of Backpack Loads on School Children: A Critical Narrative Review. International journal of environmental research and public health 2018;15(11):
http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112529 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/304245171 Inleiding
Deze richtlijn is bedoeld voor JGZ-professionals (jeugdartsen, verpleegkundig specialisten1, jeugdverpleegkundigen, doktersassistenten) en beoogt een richtlijn te zijn voor het handelen in hun contacten met jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar en/of hun ouders/verzorgers. De richtlijn biedt informatie over voorlichting, (vroeg)signalering, begeleiding en verwijzing rond de onderwerpen houding en bewegen. Naast de individuele contacten kan de JGZ advies geven met betrekking tot houding en bewegen aan school en kinderopvang.
De richtlijn is gebaseerd op uitgangsvragen die zijn vastgesteld tijdens een knelpuntenanalyse onder leiding van de Argumentenfabriek [1]. Bij de knelpuntenanalyse waren diverse JGZ-professionals betrokken. De uitgangsvragen worden in de tekst beantwoord.
De JGZ kan een belangrijke rol spelen in het stimuleren van een goede houding en gezond beweeggedrag. Bij bijzonderheden kan de JGZ de bevindingen waar nodig normaliseren en/of ouders en jeugdigen informeren, adviseren of verwijzen. Met de juiste uitleg en advisering kan onnodig gebruik van de zorg worden voorkomen. Daarnaast kan worden voorkomen dat aandoeningen en klachten verergeren en/of leiden tot een afwijkende of achterblijvende motoriek, lichamelijke inactiviteit, tijdelijke of blijvende functiebeperking of standsafwijking, pijnklachten en onnodige diagnostiek en zorggebruik.
De informatie in deze richtlijn sluit aan bij de informatie in de JGZ Richtlijnen Motorische ontwikkeling, Extremiteiten, Overgewicht, Voorkeurshouding en schedelvervorming, Zindelijkheid, Huidafwijkingen en Heupdysplasie.
De informatie in deze richtlijn vervangt de ‘JGZ Standaard Methodiek Onderzoek Scoliose (2003)’, deze is in 2014 door de Richtlijnadvies- en -autorisatie Commissie (RAC) teruggetrokken. Dit besluit was gebaseerd op onderzoek door TNO, waaruit bleek dat niet aan alle voorwaarden voor een effectief screeningsprogramma werd voldaan.
Leeswijzer
De richtlijn start met een inleiding met daarin informatie over houding en bewegen.
- In sectie 2.3 wordt beschreven welke aandoeningen op het gebied van houding en bewegen actief opgespoord dienen te worden door JGZ-professionals: spina bifida, hypotonie, tremor en scoliose (op basis van een positieve familieanamnese). Daarnaast wordt beschreven op welke momenten en op welke wijze dit dient te gebeuren.
- In sectie 3 staan algemene adviezen over bewegen, houding en beeldschermgebruik beschreven. Het onderwerp beeldschermgebruik wordt alleen besproken in relatie tot houding en bewegen.
- In thema 3 worden aanbevelingen gedaan voor het gesprek met ouders over het stimuleren van een goede houding en gezond beweeggedrag.
- In thema 4 wordt beschreven welke interventies met aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit beschikbaar zijn op het gebied van houding en bewegen. De JGZ-professional kan een adviserende rol naar jeugdigen en school innemen over het bestaan en gebruik van deze interventies.
- In thema 5 worden aanbevelingen gegeven over samenwerken met andere professionals en organisaties rond het thema houding en bewegen.
1De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en hij/zij werkt op expertniveau. Hij/zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ-team, hij/zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
1.1 Afbakening
Afbakening
De JGZ Richtlijn Houding en Bewegen is ontwikkeld op basis van de knelpuntenanalyse, zoals deze is uitgevoerd door het de Argumentenfabriek [1]. Bij de knelpuntenanalyse waren diverse JGZ-professionals betrokken. De aldaar geformuleerde uitgangsvragen zijn beantwoord (zie tabel 3).
Tabel 3: De uitgangsvragen die in deze richtlijn zijn beantwoord.
| Uitgangsvragen | Beantwoording |
|
Volgen en signaleren 1. JGZ-professionals willen weten welke houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen zij bij jeugdigen moeten signaleren en hoe. Uitgangsvragen:
|
Thema 1 en Bijlage 2 |
|
2. JGZ-professionals willen weten wat de korte- en langetermijngevolgen zijn van een verkeerde houding en verkeerd bewegen bij jeugdigen van verschillende leeftijden. Uitgangsvragen:
|
Inleiding |
|
3. JGZ-professionals ervaren handelingsverlegenheid bij het adviseren van ouders en jeugdigen over het veranderen van houding en bewegen. Uitgangsvragen:
|
Thema 3 |
|
4. JGZ-professionals willen weten wat de gevolgen zijn van toenemend mediagebruik zoals tv, tablets en spelcomputers Uitgangsvragen:
|
Thema 2 |
|
Handelen 5. JGZ-professionals willen weten welke bewezen effectieve adviezen zij moeten geven rond houding en bewegen per leeftijdsgroep. Uitgangsvragen:
|
Thema 2
Thema 4 |
|
Samenwerken 6. JGZ-professionals ervaren dat ouders, voorschoolse voorzieningen en scholen hen niet weten te vinden voor advies en informatie over de gezonde ontwikkeling van houding en bewegen van jeugdigen. Uitgangsvragen:
|
Thema 5 |
2 Definities en achtergrondinformatie
Dit hoofdstuk bevat algemene kennis die nodig is als achtergrondinformatie voor de thema’s.
In deze richtlijn wordt met ‘houding’ bedoeld: de stand van het lichaam of de wijze waarop men het lichaam houdt. Met ‘bewegen’ wordt bedoeld: lichaamsbeweging of lichamelijke activiteiten.
2.1 Normale ontwikkeling van houding en beweging
Bij een normale ontwikkeling nemen de bewegingen en de mogelijkheden van kinderen om activiteiten uit te voeren voortdurend toe (in variatie en complexiteit) naarmate zij ouder worden.
De motorische vaardigheden van een kind ontwikkelen zich door de interactie van:
- Interne factoren (lichamelijke en psychologische eigenschappen van het kind),
- De mate van oefenen (mate van bewegen, vrij spelen en deelname aan sport)
- Externe factoren (gezinsgewoontes, beschikbaarheid en veiligheid van speelplekken en sportfaciliteiten).
Al deze factoren hangen nauw met elkaar samen en beïnvloeden elkaar ook onderling.
Tijdens de ontwikkeling worden mijlpalen behaald. Mijlpalen zijn herkenbare punten in de ontwikkeling van het kind. De manier en het tijdstip waarop een kind bepaalde vaardigheden ontwikkelt, vertoont echter zeer veel variatie. Deze variatie is afhankelijk van de eerder genoemde (interne, gedrags- en externe) factoren. Echter, het niet tijdig bereiken van deze mijlpalen kan een signaal zijn van een probleem op het gebied van houding en bewegen. Er kan ook sprake zijn van een terugval (bijvoorbeeld bij een kind met reuma). Belangrijke punten in de ontwikkeling van houding en bewegen worden beschreven in tabel 1. Deze tabel is gebaseerd op het schema ‘Ontwikkelingsaspecten en Omgevingsinteractie’. Daarnaast geeft het van Wiechenonderzoek ook informatie over de motorische ontwikkeling van een kind.
Tabel 1. Belangrijke punten in de ontwikkeling van houding en bewegen.
Bron: schema ‘Ontwikkelingsaspecten en Omgevingsinteractie’, NCJ
| Ontwikkelingsfase | Ontwikkeling |
| Babyfase | |
| 0-1 maand | Ontwikkeling hoofdbalans |
| 1-4 maanden | Bewust en gericht bewegen Hoofd meedraaien |
| 4-8 maanden | Omrollen en gaan zitten Grijpen voorwerpen Voorwerpen naar de mond brengen |
| 8-12 maanden | Vastpakken voorwerpen Los zitten en kruipen Optrekken om te gaan staan en lopen langs tafels |
| Peuterfase | |
| 1-2 jaar | Pincetgreep, toren bouwen, bladzijde omslaan Loslopen |
| 2-3 jaar | Tekenen (krassen), plakken Leren traplopen, rennen en springen |
| 3-4 jaar | Knippen, pen of potloodgreep Hinkelen, huppelen en fietsen (met zijwieltjes) Kleren aantrekken, knopen losmaken |
| Schoolkind | |
| 4-6 jaar | Herkenbare figuren tekenen Veters strikken Fluiten, zwemmen, ritmiciteit en timing |
| 6-12 jaar | Lichaamsbeheersing Ontwikkelen van spieren (kracht en tonus) Armen en benen in proportie |
| Puberteit | |
| 10-15 jaar | Bewegingen zijn tijdelijk ontregeld, (onhandig, slungelig) Coördinatie van langere spieren (nog) niet in evenwicht |
| Adolescent | |
| 15-18/23 jaar | Romp en ledematen in verhouding Toename spiermassa en kracht Goede lichaamsbeheersing en coördinatie |
Houding
De houding vervult een sleutelrol in de motoriek en beweging van een kind. Kort na de geboorte wordt de houdingsactiviteit van baby’s gekenmerkt door een toename in de variatie: variatie in de mate, het moment en de richting waarin de spieren worden aangespannen. Vanaf de leeftijd van 4 maanden begint het kind te leren hoe het op basis van interactie met de omgeving de houding kan aanpassen aan de omstandigheden (houdingsregulatie). De ontwikkeling naar een soepel aangepaste manier van houdingsregulatie is een continu ontwikkelingsproces en duurt tot de leeftijd van 16-18 jaar [2].
Een gezonde sta-, zit- en loophouding is een actieve houding, waarbij de buik- en rugspieren zijn aangespannen en de onderrug wat hol is. In staande houding kan dan een denkbeeldige verticale lijn getrokken worden door het oor, midden van de nek, de schouder, het midden van de onderrug, het heupgewricht, de knie en de enkel.
Bewegen
In de eerste maanden van het leven brengt een kind het grootste deel van de tijd liggend (of gesteund zittend) door. Vanaf de leeftijd dat een kind gaat rollen, kruipen en lopen zal een kind meer gaan bewegen. Kinderen van 4 t/m 11 jaar bewegen relatief veel, vanaf de leeftijd van 12 jaar wordt dit weer minder [3]
In 2017 publiceerde de Gezondheidsraad de nieuwe Beweegrichtlijnen [4]. Voor jeugdigen van 4-18 jaar zijn deze als volgt:
- Bewegen is goed, meer bewegen is beter;
- Doe minstens elke dag een uur aan matig intensieve inspanning. Langer, vaker en/of intensiever bewegen geeft extra gezondheidsvoordeel;
- Doe minstens driemaal per week spier- en botversterkende activiteiten;
- Voorkom veel stilzitten.
Voor kinderen van 0-4 jaar werden beweegrichtlijnen opgesteld door de WHO [5]. De Gezondheidsraad zal ook een beweegadvies voor jeugdigen van 0-4 jaar gaan ontwikkelen. Daarnaast is er ‘De Kleine Beweegagenda’, een initiatief van het Ministerie van VWS, Kenniscentrum Sport & Bewegen en het Mulier Instituut. Dit heeft als doel om kennis over bewegen voor 0-4 jarigen te vergroten en professionals te helpen en te stimuleren meer in te zetten op bewegen voor de allerjongsten.
Uit de Leefstijlmonitor 2018 blijkt dat kinderen (4 t/m 11 jaar) het vaakst aan de Beweegrichtlijnen (55%) voldeden, jongeren (12 t/m 17 jaar) voldeden het minst vaak aan de Beweegrichtlijnen (34%). Daarnaast bleek dat jongeren (12 t/m 17 jaar) dagelijks gemiddeld 10,1 uur zitten en kinderen (4 t/m 11 jaar) gemiddeld 7,3 uur per dag zitten [3]
Het belang van bewegen
Het ‘Advies beweegrichtlijnen’ van de Gezondheidsraad concludeert dat er bewijs is dat bewegen een positief effect heeft op (voorspellers van) chronische ziekten en indicatoren van fitheid bij kinderen en adolescenten. Volgens het advies heeft bewegen op jonge leeftijd een gunstig effect op: aerobe fitheid, spierkracht, botkwaliteit, insulinegevoeligheid, en op gewicht en vetmassa bij kinderen met overgewicht en obesitas. Bewegen bleek ook samen te hangen met een kleiner risico op depressieve symptomen [4].
Veel zitten lijkt, los van onvoldoende bewegen, ongunstig te zijn voor de gezondheid. De Gezondheidsraad concludeert echter dat de onderbouwing voor de negatieve effecten van zitten (voor zowel volwassenen als kinderen) nog beduidend minder sterk is dan voor de effecten van bewegen [4].
Behalve de voordelen die door de Gezondheidsraad zijn beschreven, heeft sporten en bewegen nog meer positieve effecten:
- Toename van zelfvertrouwen en gevoel van eigenwaarde [6];
- Beter omgaan met angst en stress, positieve invloed op emotionele stoornissen en stemmingsstoornissen [6];
- Het ontwikkelen van sociale vaardigheden [6];
- Beter cognitief functioneren [6][7][8][9];
- Motorische ontwikkeling [9][10][11].
In het Trendscenario van de Volksgezondheid Toekomst Verkenning 2018 is voorspeld dat rug- en nekklachten in 2040 de tweede meest voorkomende aandoening zal zijn. Er zijn meerdere verklaringen mogelijk voor het veel voorkomen van rug- en nekklachten. Zo kunnen (een slechte) houding en (onvoldoende) bewegen hierbij een rol spelen, maar ook ouderdom en de vergrijzing beïnvloeden het voorkomen van deze klachten.
3 Signaleren, diagnostiek en verwijzen
3.1 Symptomen en aandoeningen rond houding en beweging
Door de werkgroep is bepaald welke symptomen en aandoeningen relevant zijn voor de JGZ, en daarom behandeld dienen te worden in deze richtlijn. In dit thema worden de aandoeningen beschreven die JGZ-professionals actief op dienen te sporen. De symptomen en aandoeningen die niet actief opgespoord hoeven te worden zijn beschreven in bijlage 9.1. Sommige symptomen en aandoeningen zijn al beschreven in andere JGZ Richtlijnen, en worden daarom niet nogmaals behandeld (zie bijlage 9.2 voor een overzicht).
Onderzoek naar beenlengteverschil (bron: JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten)
Afhankelijk van de leeftijd van de jeugdige kiest de jeugdarts voor onderzoek in liggende of staande houding. Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij jeugdigen met een (mogelijk) beenlengteverschil worden de volgende punten onderzocht:
- Onderzoek in liggende houding: Bij het beoordelen van de beenlengte ligt het kind op de rug, geheel recht, het gezicht in de middenpositie. De benen zijn gestrekt en de voeten wijzen naar boven. Vervolgens wordt beoordeeld of de onderzijde van de hielen en de binnenzijde van de enkels gelijk liggen. Vervolgens worden de heupen en knieën in negentig graden flexie gebracht. In deze houding is een verschil in lengte van de bovenbenen het meest duidelijk. Een beenlengteverschil kan wijzen op aanwezigheid van een eenzijdig (sub)luxeerbare heup, zie de JGZ Richtlijn Heupdysplasie. Wanneer het kind op de buik wordt gelegd met de knieën in 90 graden zal een verschil in lengte van de onderbenen het meest duidelijk zichtbaar zijn.
- Onderzoek in staande houding: De jeugdige staat rechtop met de knieën maximaal gestrekt en de voeten naast elkaar. De onderzoeker staat achter de patiënt en plaatst beide duimen op de spinae iliacae posteriores (of anteriores) superiores. Vervolgens wordt beoordeeld of de duimen op gelijke hoogte liggen. Wanneer de beide duimen niet op gelijke hoogte staan is er waarschijnlijk sprake van een beenlengteverschil.
In staande houding wordt het beenlengteverschil bepaald met behulp van de ‘plankjesmethode’. Hierbij wordt de ruimte onder het kortste been opgevuld met een plankje van 0,5, 1 of 2 cm dik totdat de duimen op de spinae iliacae posteriores superiores even hoog staan.
Buigtest
De jeugdige buigt met gestrekte benen vanuit de heupen voorover, waarbij de armen richting de vloer hangen. Indien er sprake is van een beenlengteverschil dient dit eerst gecompenseerd te worden met behulp van een plankje (zie paragraaf onderzoek naar beenlengteverschil hierboven).
Tijdens het voorover buigen wordt de rug van achter en van opzij beoordeeld. Er wordt gelet op de af- of aanwezigheid van een gibbus en het verdwijnen of blijven bestaan van een eventuele scoliose, om onderscheid te maken tussen de houdings- en de structurele scoliose (de structurele scoliose blijft bestaan bij vooroverbuigen, sectie 3.2.4). Daarnaast wordt gelet op de aanwezigheid van een structurele kyfose of lordose (bijlage 9.1).
Als er een gibbus wordt geconstateerd, wordt deze gemeten met behulp van een scoliometer. De scoliometer wordt bij de voorovergebogen jeugdige dwars op de wervelkolom geplaatst en van het hoofd richting de onderrug verplaatst. Het verschil tussen links en rechts is in graden af te lezen. De grootste uitslag op de gradenboog wordt genoteerd en ook de plaats op de wervelkolom.
Aanbevelingen
3.2 Beschrijving actief op te sporen symptomen en aandoeningen
3.2.1 Spina bifida
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij spina bifida is er sprake van een incomplete sluiting van de neurale buis. Hierdoor zijn de wervels niet goed gesloten. Er zijn twee vormen te onderscheiden:
- Spina bifida occulta. Hierbij zijn de wervels niet goed gesloten en komen structuren buiten de wervelkolom te liggen, maar ze zijn wel overdekt met huid. Hierdoor is deze vorm van spina bifida niet altijd zichtbaar aan de buitenkant. Er kan een verkleuring van de huid, een putje (dimple), versterkte haargroei of een lipoom (onderhuidse zwelling) zichtbaar zijn ter hoogte van het defect.
- Spina bifida aperta. Spina bifida aperta wordt ook wel ‘open ruggetje’ genoemd. Hierbij worden bepaalde structuren niet meer door de huid bedekt, waardoor ze bloot komen te liggen. Als de vliezen rond het ruggenmerg blootliggen wordt dit ook wel meningocèle genoemd. Als, naast de vliezen, ook het ruggenmerg zelf naar buiten komt dan wordt dit ook wel myelomeningocèle genoemd. Deze vorm van spina bifida wordt vrijwel altijd prenataal ontdekt. Jeugdigen met spina bifida aperta zijn daarom meestal al onder behandeling van een specialist als zij de JGZ bezoeken. Spina bifida aperta gaat vaak gepaard met aanlegstoornissen aan de (kleine) hersenen (Chiari malformatie) en/of een hydrocefalus.
Uit een recente publicatie blijkt dat bij een simpele sacrale dimple (minder dan 5 mm diep, afstand minder dan 2,5 cm van de anus en geen andere sacrale afwijkingen zichtbaar aan de huid) geen aanvullend onderzoek noodzakelijk is naar spina bifida [16]. In alle andere gevallen (zoals een sacrale dimple in combinatie met andere aangeboren afwijkingen of een hemangioom) dient aanvullend onderzoek te worden verricht.
Epidemiologie
De prevalentie van spina bifida in Nederland is ongeveer 0,06% [17]. Het komt bij meisjes iets vaker voor dan bij jongens.
Gevolgen
Spina bifida leidt tot neurologische uitvalsverschijnselen. De ernst van de verschijnselen is afhankelijk van de hoogte en de uitgebreidheid van het defect. Mogelijke gevolgen van spina bifida zijn onder andere:
- Motorische stoornissen – minder spierkracht of een verstoorde besturing van de spieren;
- Gevoelsstoornissen – gedeelten van het lichaam kunnen gevoelloos zijn of minder gevoelig.
- Zindelijkheidsproblemen – de urine of ontlasting niet goed op kunnen houden.
- Orthopedische problemen – bijvoorbeeld scoliose, spitsvoet, heupluxatie.
Spina bifida is een aandoening die gepaard gaat met een grote diversiteit aan functionele beperkingen en problemen. De meeste jeugdigen met spina bifida hebben een normale intelligentie.
Behandeling
De behandeling is afhankelijk van de hoogte en de uitgebreidheid van het defect. Jeugdigen met spina bifida worden behandeld door een multidisciplinair behandelteam. Hierin kunnen bijvoorbeeld een kinderneurochirurg, kinderneuroloog, kinderorthopeed, revalidatiearts, kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut en ergotherapeut deelnemen.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren:
- JGZ-professionals dienen op de leeftijd van 2 en 4 weken actief te beoordelen of er sprake is van midline laesies (zie JGZ Richtlijn Huidafwijkingen).
- Daarnaast vindt ‘niet-actieve’ opsporing plaats op basis van signalen rond motorische ontwikkeling en zindelijkheid.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
- Op de leeftijd van 2 en 4 weken inspecteert de JGZ-professional de huid van het kind, waarbij onder andere wordt gelet op de aanwezigheid van midline laesies.
- Indien er sprake is van zindelijkheidsproblematiek dient de jeugdarts3 het lichamelijk onderzoek (onder andere) de rug en het sacrum te onderzoeken (zie JGZ Richtlijn Zindelijkheid urine en feces). Hiervoor wordt zo nodig een extra contactmoment afgesproken.
Beleid:
- Bij midline laesies dient te worden verwezen naar de kinderarts, behalve bij een simpele sacrale dimple (minder dan 5 mm diep, afstand minder dan 2,5 cm van de anus en geen andere sacrale afwijkingen zichtbaar aan de huid), lichte beharing, de mongolenvlek en een moedervlek5.
- Bij zindelijkheidsproblematiek in combinatie met afwijkingen bij het lichamelijk onderzoek dient te worden verwezen naar de kinderarts.
- Indien er op basis van andere signalen een vermoeden is van een spina bifida dient te worden verwezen naar de kinderarts.
5 Dit is een aanpassing van de originele aanbeveling in de JGZ Richtlijn Huidafwijkingen. Vanwege recente literatuur en de mogelijkheid tot rechtstreeks verwijzen is gekozen voor deze aangepaste aanbeveling.
3.2.2 Bijzonderheden tonus (hypo/hypertonie)
Beschrijving aandoening
De spierspanning verloopt van laag (hypotoon) via normaal (normotoon) naar hoog (hypertoon).
Hypotonie en hypertonie zijn uitersten in de variatie. Hypotonie en hypertonie zijn geen aandoeningen op zich. Hypotonie en hypertonie kunnen op zichzelf staan, maar kunnen ook een symptoom zijn van een onderliggend probleem in het centrale zenuwstelsel, een neuromusculaire aandoening (zoals Duchenne, spinale spieratrofie) of een syndroom (bijvoorbeeld Down, Prader Willi, Ehlers-Danlos of Marfan).
Epidemiologie
Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak hypotonie en hypertonie voorkomen, mede omdat er geen eenduidige definities of afkapwaardes zijn.
Gevolgen
Hypotonie kan (afhankelijk van de mate) onder andere leiden tot:
- Ontwikkelingsachterstand in grove en/of fijne motoriek;
- Slik- of voedingsproblemen;
- Spraakproblemen.
Hypertonie kan (afhankelijk van de mate) onder andere leiden tot:
- Problemen in grove en/of fijne motoriek;
- Slik- of voedingsproblemen;
- Vermoeidheid.
Behandeling
Indien er sprake is van hypotonie of hypertonie zonder bijkomende problemen dan is behandeling niet noodzakelijk.
Indien er sprake is van hypotonie of hypertonie in combinatie met motorische of ontwikkelingsproblemen dan kan behandeling door een eerstelijns therapeut6 zinvol zijn. Indien er slik-, voedings- of spraakproblemen zijn dan kan behandeling bij de (pre)logopedist zinvol zijn.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren:
De tonus wordt bij kinderen tot 4 jaar beoordeeld met behulp van het Van Wiechen onderzoek.
Na de leeftijd van 4 jaar is actief opsporen niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Kinderen tot 4 jaar: Voor het beoordelen van de tonus zijn onder andere de kenmerken 54 (Blijft hangen bij optillen onder de oksels) en 55 (Reacties bij optrekken tot zit) van belang. De beschrijving van de diverse kenmerken van het Van Wiechen onderzoek zijn te vinden op de website van het NCJ en in het boek ‘Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de jeugdgezondheidszorg’ [18].
Jeugdigen vanaf 4 jaar: Indien er vragen of zorgen zijn over de tonus dan onderzoekt de jeugdarts3:
- Het looppatroon. Als er sprake is van een asymmetrisch looppatroon of het kind niet in staat is tot een normaal looppatroon kan dit wijzen op een onderliggende oorzaak.
- Opstaan vanuit zittende houding op de grond. Als het kind tijdens het opstaan met de handen op de bovenbenen steunt (Gower’s teken) kan dit wijzen op de aanwezigheid van spierdystrofie of een andere spierziekte als onderliggende oorzaak.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
Indien er sprake is van bijzonderheden in de tonus dan wordt (opnieuw) nagevraagd of er bijzonderheden zijn geweest in de familieanamnese, gedurende de zwangerschap, bevalling en eerste levensdagen. Daarnaast is de JGZ-professional extra alert op eventuele bijkomende problematiek op het gebied van voeding, neuromotorische ontwikkeling en spraak.
Hypotonie bij een zich goed ontwikkelende jeugdige: de JGZ-professional geeft preventieve adviezen om de ontwikkeling te stimuleren en vervolgt de ontwikkeling door middel van lichamelijk onderzoek. Hiervoor wordt zo nodig een extra contactmoment afgesproken na 6-12 weken (bij kinderen < 1 jaar) of na 6-12 maanden (bij oudere kinderen).
Adviezen:
- 0-1 jaar: stimuleren buikligging. Stimuleer het kind om met de voeten te spelen (voetenspel), bijvoorbeeld met sokjes die geluid maken (tot 6 maanden). Van lig naar zit stimuleren, tijgeren en/of kruipen (8 maanden tot 1 jaar).
- 1-2 jaar: stimuleren kracht benen, via hurkhouding naar stand, iets van de grond oppakken en gaan staan (eventueel met steun; door de knietjes gaan) en rompkracht stimuleren (zelfstandig van lig naar zit en gaan staan).
- 2-4 jaar: in spel allerlei oefenvormen aanbieden zoals kikkersprongen, bal rollen in buiklig of klimmen op toestellen; sport- en beweegadvies (zie thema ‘Preventie’), er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor.
- 4-16 jaar: sport- en beweegadvies (zie thema ‘Preventie’). Er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor.
Bijzonderheden in de tonus in combinatie met andere problematiek (zoals slik- of voedingsproblemen of neurologische problemen): verwijzing naar de kinderarts, eventueel gecombineerd met verwijzing naar kinderfysiotherapeut of (kinder)oefentherapeut en/of (pre-)logopedist. De kinderarts stelt het behandelplan op en is het centrale aanspreekpunt voor ouder.
6Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
3.2.3 Tremor (Trillen, beven)
Beschrijving aandoening
Een tremor is een onbedoelde en oncontroleerbare ritmische beweging van een ledemaat of deel daarvan. Een tremor kan in elk deel van het lichaam en op elk moment optreden, en wordt ook wel trillen of beven genoemd. Een tremor kan geïsoleerd voorkomen of onderdeel zijn van een klinisch syndroom. Vanaf de leeftijd van 4 à 5 weken is een tremor bij spontane motoriek bij een niet-huilend kind een alarmsymptoom [19].
Er wordt onderscheid gemaakt in verschillende types tremoren:
- Rusttremor: dit is een trillende beweging die aanwezig is wanneer het lichaamsdeel in rust is;
- Actietremor (of kinetische tremor): dit is een trillende beweging die aanwezig is wanneer het lichaamsdeel in beweging is. Een actietremor is weer onder te verdelen in twee subtypes:
– Houdingstremor: de trillende beweging is aanwezig bij het volhouden van een bepaalde beweging of houding;
– Intentietremor: de trillende beweging is vooral aanwezig bij doelgerichte bewegingen.
Een tremor kan verschillende oorzaken hebben. Zo ontstaat een intentietremor vaak als gevolg van een probleem in de kleine hersenen. Een houdingstremor wordt vaak veroorzaakt door een ‘essentiële tremor’. Dit is een aandoening die vaak familiair voorkomt. Een rusttremor kan een aanwijzing zijn voor een stofwisselingsziekte.
Epidemiologie
Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak een tremor bij jeugdigen voorkomt.
Gevolgen
Een tremor kan aanleiding geven tot problemen met bijvoorbeeld eten en drinken (knoeien), tekenen en schrijven (bibberige lijnen). De tremor kan toenemen bij spanning of bij gebruik van cafeïne (cola, chocolade, thee, koffie).
Behandeling
De behandeling is afhankelijk van de aard en de oorzaak van de tremor. Vaak is het echter niet mogelijk om de oorzaak van de tremor te behandelen of weg te nemen. Soms kan dan gebruik worden gemaakt van medicatie. Ook kunnen hulpmiddelen worden ingezet zoals een verzwaarde pen of verzwaard bestek. Een ergotherapeut kan helpen bij het zo goed mogelijk uitvoeren van de dagelijkse of schoolse activiteiten en kan adviseren over het gebruik van kleine hulpmiddelen.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren:
Een tremor kan bij kinderen tot 4 jaar worden ontdekt naar aanleiding van het Van Wiechen onderzoek. Daarna is actief opsporen niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Kinderen tot 4 jaar: Voor het ontdekken van een tremor is tot de leeftijd van 52 weken onder andere kenmerk 52 (Beweegt armen goed) van belang. Op latere leeftijd kan een tremor worden gezien bij de fijne motoriek kenmerken (zoals bijvoorbeeld 11: doet blokje in/uit doos; 13/15/16: blokjes stapelen). De beschrijving van de diverse kenmerken van het Van Wiechen onderzoek zijn te vinden op de website van het NCJ en in het boek ‘Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de jeugdgezondheidszorg’ [18].
Jeugdigen vanaf 4 jaar: De jeugdarts3 observeert of er sprake is van een tremor in rust, bij bewegen en bij het uitvoeren van handelingen. Laat de jeugdige bijvoorbeeld zijn beide handen en armen uitstrekken, iets tekenen of een voorwerp pakken.
Beleid tot de leeftijd van 18 jaar (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
Indien er sprake is van een tremor bij een niet-huilend kind dat ouder is dan 5 weken dan dient te worden verwezen naar de kinderarts.
3.2.4 Scoliose
Beschrijving aandoening
Scoliose is een driedimensionale zijdelingse kromming van de wervelkolom. De mate van kromming wordt bepaald door het meten van de Cobbse hoek op een röntgenfoto van de wervelkolom. Internationaal wordt van een scoliose gesproken als de Cobbse hoek ≥ 10˚ is [20]. Scoliose kan structureel zijn, of optreden als compensatie voor (bijvoorbeeld) een beenlengteverschil (niet-structurele scoliose). Een structurele scoliose is in 80% van de gevallen idiopathisch (de oorzaak is onbekend). Bij een idiopathische scoliose kan de volgende indeling worden aangehouden op basis van de leeftijd:
- Infantiele idiopathische scoliose: ontstaat bij kinderen van 0 tot ongeveer 3 jaar;
- Juveniele idiopathische scoliose: ontstaat bij kinderen van 3 tot ongeveer 10 jaar;
- Adolescente idiopathische scoliose (AIS): ontstaat bij jongeren van 10-18 jaar. Dit is de meest voorkomende vorm, met een prevalentie van ongeveer 2-3% [20]. Het is waarschijnlijk een multifactorieel veroorzaakte aandoening, waarbij onder andere erfelijkheid een rol speelt.
Epidemiologie
De prevalentie van AIS is ongeveer 2-3% [20]. Patiënten met AIS hebben vaak een of meerdere familieleden met AIS [21].
AIS wordt meer bij meisjes gezien dan bij jongens. De ernst van de scoliose kan toenemen, stabiel blijven of spontaan verbeteren [22][23]. Indien er sprake is van een toename, dan ontstaat deze vooral tijdens de groeispurt aan het begin van de puberteit.
Gevolgen
Als er bij een volgroeid skelet sprake is van een matige tot ernstige curve (Cobbse hoek ≥ 40˚) is er een toegenomen risico op problemen zoals een verminderde kwaliteit van leven, pijnklachten, functionele beperkingen en ademhalingsproblemen [24][25].
Behandeling
Behandeling van scoliose kan bestaan uit kinderfysiotherapie of (kinder)oefentherapie, bracebehandeling of operatieve correctie.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren:
Actief opsporen op basis van positieve familieanamnese.
Bij jeugdigen met een positieve familieanamnese (één of meerdere eerste of tweedegraads familieleden met scoliose) kunnen extra contactmomenten vanaf de leeftijd van circa 10 jaar (voor de start van de groeispurt) worden aangeboden om de rug te controleren.
Het wordt aanbevolen om de familieanamnese voor scoliose na te vragen in de leeftijdsperiode 9-11 jaar. Dit kan in een persoonlijk contact of via een vragenlijst worden nagevraagd.
Lichamelijk onderzoek (op indicatie, zoals positieve familieanamnese):
De jeugdarts3 beoordeelt de houding van de jeugdige in staande positie, waarbij ten minste het bovenlichaam ontbloot is (BH mag desgewenst aanblijven) en de schoenen uit zijn. Hierbij wordt gelet op de symmetrie van de schouderhoogte, de hoogte van het schouderblad, de taille driehoek, en de hoogte van de spinae iliacae posteriores superiores. Belangrijk hierbij is dat het kind het gewicht over beide benen gelijk verdeelt.
Eerst wordt onderzocht of er sprake is van een beenlengteverschil.
Vervolgens wordt de rug beoordeeld door middel van de buigtest.
Indien er bij de buigtest een afwijking aan de wervelkolom wordt vastgesteld, wordt tevens (aan de hand van de groeicurve en het puberteitsstadium volgens Tanner) bepaald of de groei van de jeugdige vrijwel voltooid is. Dit is van belang voor het bepalen van het vervolgbeleid.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
De familieanamnese voor scoliose wordt nagevraagd in de leeftijdsperiode 9-11 jaar. Er is sprake van een positieve familieanamnese als er sprake is van gediagnosticeerde of behandelde (fysiotherapie, oefentherapie, brace, operatie) scoliose bij één of meerdere familieleden in de eerste graad (ouders, zussen, broers) of tweede graad (grootouders, tantes, ooms).
Vraag bijvoorbeeld: ‘Zijn er familieleden die een scoliose (ook bekend als een S-bocht of zijdelingse kromming in de rug) hebben gehad?’. Bij een positief antwoord kan worden doorgevraagd naar welk familielid het betrof en eventuele behandeling.
Bij een positieve familieanamnese worden extra contactmomenten vanaf de leeftijd van circa 10 jaar (voor de start van de groeispurt) aangeboden om de rug te controleren. De voorgestelde leeftijden voor deze contactmomenten zijn:
- Rond de leeftijd van 10 jaar (voor de start van de puberteit)
- Daarna 1x per 6-12 maanden, afhankelijk van de lengtegroei en de puberteitsontwikkeling (hoe sneller de groei, des te frequenter de controle).
- De controles worden afgerond bij een (vrijwel) voltooide groeispurt7.
7Dit is een professionele beoordeling op basis van de groeicurve en de puberteitskenmerken.
De JGZ Richtlijn Lengtegroei vermeld: De groeispurt treedt bij meisjes op vanaf het begin van de puberteit en is maximaal bij M3-4. De menarche treedt gemiddeld op bij 13,05 jaar [15], de groeispurt is dan voorbij het maximum. De groeispurt bij jongens begint 1 à 2 jaar na het begin van de puberteit, in puberteitsstadium G3-4, wanneer de testis ongeveer 10 ml inhoud heeft. De groeisnelheid is maximaal wanneer de testis ongeveer 15-17 ml inhoud heeft (G4-5).
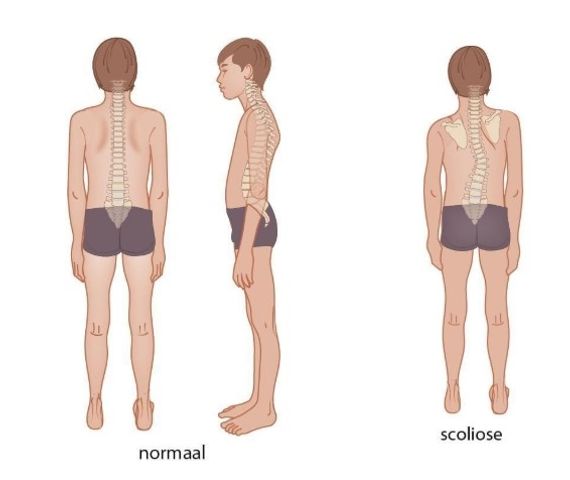
Figuur 1: Normale houding en scoliose
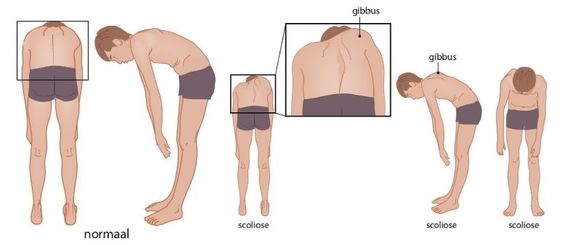
Figuur 2: Buigtest bij normale anatomie
Niet-structurele scoliose
Op basis van houding: eventueel houding- of sportadvies (zie sectie 3 ‘Preventie’), er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor. Er is geen controle nodig.
Op basis van beenlengteverschil (bron: JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten):
- Bij kinderen jonger dan 10 jaar:
Bij een beenlengteverschil < 1 cm dient het beenlengteverschil na 6-12 maanden te worden gecontroleerd (hoe jonger het kind, hoe korter de controletermijn).
Bij een beenlengteverschil ≥ 1 cm dient te worden verwezen naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
- Bij kinderen ouder dan 10 jaar:
Bij een beenlengteverschil < 2 cm: verwijzing is niet nodig. Zo nodig kan na 6-12 maanden nogmaals het beenlengteverschil gemeten worden. Wanneer dit verschil constant blijft is het zeer onwaarschijnlijk dat er nog een toename in het beenlengteverschil zal zijn.
Bij een beenlengteverschil ≥ 2 cm dient te worden verwezen naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
Structurele scoliose
– Hoek < 7˚ en onvoltooide groei: controle na 6 maanden.
- Indien bij controle ≥ 2˚ progressie is opgetreden dan moet verwezen worden naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
- Is na zes maanden <2˚ progressie opgetreden, dan volgt opnieuw controle binnen zes maanden. Is dan weer <2˚ progressie opgetreden, dan volgt jaarlijkse controle tot het einde van de groeispurt.
– Hoek <7˚ en (vrijwel) voltooide groeispurt: geen verdere controle nodig.
– Hoek ≥ 7˚: verwijzing naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
4 Preventie
JGZ-professionals kunnen jeugdigen en hun ouders adviseren over een goede houding en gezond bewegen. In dit thema staan algemene adviezen ter preventie van houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen. Het onderwerp beeldschermgebruik wordt alleen besproken in relatie tot houding en bewegen. In sectie 3.5 worden aanbevelingen gedaan over hoe JGZ-professionals deze adviezen het beste kunnen overbrengen op jeugdigen en hun ouders.
4.1 Algemene adviezen over beweging, houding en beeldschermgebruik
Aanbevelingen
4.2 Preventieve adviezen houding
4.2.1 Baby’s van 0-1 jaar
Aanbevelingen
4.2.2 Kinderen van 1-18 jaar
Voor ouders en leerkrachten is het niet altijd praktisch haalbaar om voor jeugdigen van alle leeftijden een ergonomische zitplek te creëren. Daarom blijft het afwisselen van de houding het belangrijkste advies. In dit instructiefilmpje kunnen ouders vanaf minuut 1.21 zien hoe zij de zithouding van een kind kunnen optimaliseren.
Een goede houding is op de volgende manier uit te leggen aan ouders en jeugdigen:
Ga zitten of staan alsof er een touwtje vanaf beneden door je heen loopt en vanaf je hoofd recht omhoog wordt getrokken. Houd de schouders ontspannen en naar achteren. Trek je buik in. Je voeten staan op heupbreedte. Verdeel je gewicht evenredig over beide voeten. Probeer je hoofd rechtop te houden. Houd je benen recht, maar ontspan je knieën. Van de zijkant gezien zijn de oren, schouders en heup in één lijn. Een lichte holling in de nek, een lichte bolling in de bovenrug en een lichte holling in de onderrug zijn normaal. Voor meer informatie: klik hier.
Aanbevelingen
4.3 Preventieve adviezen bewegen
Aanbevelingen
4.4 Preventieve adviezen beeldschermgebruik
Beeldschermgebruik
Jeugdigen gebruiken steeds meer soorten beeldschermen (bijv. tablet, laptop, vaste computer, smartphone, etc.) en zij besteden steeds meer tijd aan beeldschermen [27]. Jeugdigen gebruiken deze beeldschermen voor ontspannende activiteiten, bijv. het kijken van filmpjes, het spelen van spelletjes en sociaal mediagebruik. Daarnaast gebruiken zij beeldschermen voor leerzame activiteiten, zowel op school als bij het maken van huiswerk [28].
Het gebruiken van beeldschermen kan allerlei voordelen met zich meebrengen, zoals een efficiënter leerproces en op het individu afgestemd onderwijs. Er zijn ook nadelen van beeldschermgebruik. Deze nadelen zijn er op het gebied van houding en bewegen en (ongezond) beeldschermgebruik kan leiden tot o.a. oogproblemen en slaapproblemen [29]. In deze richtlijn is de focus alleen op beeldschermgebruik in relatie tot houding en bewegen.
Straker en collega’s ontwikkelden een richtlijn voor het verstandig gebruik van elektronisch gamen door kinderen en een richtlijn voor verstandig gebruik van computers voor de fysieke ontwikkeling van kinderen [30][31]. Zij stellen dat er weinig wetenschappelijk bewijs is voor veel onderdelen van beide richtlijnen. Een deel van deze richtlijnen zijn vertaald en opgenomen in de Toolbox Mediaopvoeding: ‘Media? Gewoon opvoeden!’ van het NJI. Hierin zijn factsheets voor professionals en leerkrachten en tipsheets voor ouders opgenomen. De fact- en tipsheets zijn ingedeeld in verschillende leeftijdsgroepen.
Zie onderbouwing Evidence 3.2
4.4.1 Kinderen van 0-4 jaar
Aanbevelingen
4.4.2 Kinderen van 4-18 jaar
Aanbevelingen
4.5 Handvatten voor het gesprek met de jeugdigen en hun ouders
JGZ-professionals kunnen een goede houding en gezond bewegen bij ouders en jeugdigen stimuleren. Dit thema bevat aanbevelingen voor het gesprek met ouders over het stimuleren van een goede houding en gezond beweeggedrag en het voorkomen van houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen in de JGZ.
Strategieën om preventieve adviezen over te brengen op kinderen en hun ouders:
Aanbevelingen
5 Begeleiden en behandelen
In 2009 is het standpunt ‘Beweegstimulering door de jeugdgezondheidszorg’ opgesteld [49]. Hierin wordt aangegeven dat de JGZ een beleidsadviserende rol naar gemeenten kan vervullen voor de mogelijkheden om het beweeggedrag van de jeugd te stimuleren. Daarnaast kan de JGZ een actieve, adviserende rol spelen naar scholen, sportsector en andere beweegaanbieders om hun kennis over groei en ontwikkeling van jeugdige en de gevolgen hiervan voor sport en bewegen te verspreiden [49]. De JGZ-professional kan bij de meeste interventies een adviserende rol naar jeugdigen en school innemen over het bestaan en gebruik van de aanbevolen interventies die vermeld worden in bijlage 9.4. De interventies benoemd in de bijlage worden (meestal) niet door JGZ-professionals uitgevoerd.
Aanbevelingen
6 Samenwerken
Dit thema bevat aanbevelingen over samenwerken met andere professionals en organisaties rond het thema houding en bewegen.
Goede samenwerking en afstemming tussen de verschillende disciplines die in de eerste en tweede lijn betrokken zijn bij de signalering, verwijzing, diagnostisering, behandeling en nazorg van jeugdigen met houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen en sport- en beweegprofessionals zoals vakleerkrachten in het bewegingsonderwijs is essentieel. Een goede samenwerking en afstemming garandeert de continuïteit in de zorg voor jeugdigen en ouders. Daarnaast komen goede samenwerking en afstemming ten goede aan de kwaliteit, toegankelijkheid en betaalbaarheid van de zorg. Ook kunnen problemen met houding en beweging samenhangen met andere problematiek. In dat kader kan samenwerking met bijvoorbeeld integrale vroeghulp van belang zijn.
Kenmerkend voor de JGZ-professional is de integrale visie, dat wil zeggen: de JGZ-professional kijkt niet alleen naar lichamelijke, psychische en sociale aspecten van de jeugdige, maar ook naar het sociale en fysieke leefmilieu van de jeugdige. In deze integrale werkwijze werkt de JGZ-professional samen met andere professionals die betrokken zijn bij de jeugdige en/of zijn leefomgeving, bijvoorbeeld het onderwijs en wijk- en buurtteams.
Samenwerking met andere betrokken (para)medici en hulpverleners
De volgende partijen kunnen betrokken zijn bij de signalering, verwijzing, diagnostisering en behandeling van kinderen met houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen:
Medische zorg:
- Het JGZ-team (jeugdarts, verpleegkundig specialist, jeugdverpleegkundige, doktersassistente): speelt een signalerende rol bij houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen, normaliseert waar mogelijk de bevindingen en adviseert ouders/jeugdigen; jeugdarts bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is;
- De huisarts: speelt een signalerende rol bij houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen, normaliseert waar mogelijk de bevindingen en adviseert ouders/jeugdigen; bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is;
- De (kinder)orthopeed: normaliseert waar mogelijk de bevindingen en adviseert ouders/jeugdigen bij houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen; bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is; bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is;
- De kinderarts: normaliseert waar mogelijk de bevindingen en adviseert ouders/jeugdigen houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen; bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is;
- De sportarts: helpt (sport) blessures te voorkomen en behandelt (sport)blessures. De sportarts kijkt daarbij naar de verhouding tussen belasting en belastbaarheid;
Paramedische zorg:
- De kinderfysiotherapeut: heeft specialistische kennis en vaardigheden met betrekking tot aandoeningen/ problemen in het houdings- en bewegingsapparaat en onderzoekt/behandelt/adviseert waarbij de hulpvraag op het gebied van bewegen in het dagelijkse leven, op school bij sport en spel centraal staat;
- De (kinder)oefentherapeut: behandelt aandoeningen op het gebied van houding en beweging, waarbij de kinderoefentherapeut Cesar/Mensendieck gespecialiseerd is in de behandeling van jeugdigen met motorische problemen die een negatieve invloed hebben op het dagelijks functioneren;
- De kinderergotherapeut: behandelt, adviseert en begeleidt jeugdigen, ouders en leerkrachten bij het mogelijk maken van dagelijkse activiteiten die belangrijk zijn voor de jeugdige, zodat hij/zij kan blijven meedoen bij activiteiten thuis, op school en in de vrije tijd. De kinderergotherapeut denkt mee over de keuze het (aangepaste) meubilair en over de afwisseling van activiteiten over de dag, preventief, bij hulpvragen en bij houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen.
In deze richtlijn worden deze paramedici ook omschreven als ‘eerstelijns therapeuten’.
Overige professionals
Naast bovenstaande professionals kunnen ook de volgende personen mogelijke (risicofactoren voor) houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen signaleren, hoewel zij daartoe op dit moment niet altijd worden opgeleid:
- Vakleerkrachten Lichamelijke Opvoeding en andere leerkrachten op school.
- Pedagogisch medewerkers
- Sporttrainers en (buurtsport)coaches
Kosten (para)medische zorg
Soms brengt (para)medische zorg kosten voor ouders met zich mee. Bezoeken aan de huisarts en het ziekenhuis vallen onder de basisverzekering, voor kinderen geldt geen eigen risico. Soms dient er wel een eigen bijdrage betaald te worden. Daarnaast kan er sprake zijn van indirecte kosten zoals het opnemen van vrije uren en parkeerkosten.
Ten tijde van het schrijven van deze richtlijn (2020) geldt voor fysio- en oefentherapie dat de basisverzekering de eerste negen behandelingen voor jeugdigen vergoed, op indicatie worden de volgende negen behandelingen ook vergoed. Voor ergotherapie dekt de basisverzekering de kosten voor tien behandeluren ergotherapie per kalenderjaar. Het Zorginstituut Nederland biedt actuele informatie over de inhoud van het basispakket van de zorgverzekering. Indien er sprake is van een chronische aandoening of motorische ontwikkelingsachterstand worden alle behandelingen in het basispakket vergoed.
Programma’s gericht op samenwerking
Gezonde School
De aanpak van de Gezonde School werkt aan gezondheidsbevordering van jeugdigen in het primair onderwijs, voortgezet onderwijs en het middelbaar beroepsonderwijs. Eén van de gezondheidsthema’s van de Gezonde School aanpak is het thema ‘’Werken aan Bewegen en sport’’. De JGZ-professional kan samenwerken met de Gezonde School aan verschillende projecten om o.a. de beweging bij jeugdigen te stimuleren zoals met de projecten ‘’Fitheid en motoriek goed peilen’’, ‘’Zit met Pit!’’, ‘’Een gezondheidsprofiel van de 15-16 jarigen op uw school’’ of ‘’Ouders erbij betrekken: wat werkt?’’. Lees hier meer informatie over de Gezonde School aanpak.
GGD Gelderland-Zuid heeft in het kader van de Gezonde School een toolkit ‘’Verantwoord beeldschermgebruik’’ ontwikkeld. Deze toolkit biedt scholen handvatten om verantwoord beeldschermgebruik op scholen te bevorderen en is geschikt voor landelijk gebruik.
Gezonde Kinderopvang
De Gezonde Kinderopvang werkt aan een gezonde leefstijl van jonge kinderen (0-12 jaar). De Gezonde Kinderopvang heeft als doel de gezondheid van kinderen in de kinderopvang te bevorderen. Om dit te bereiken worden coaches Gezonde Kinderopvang opgeleid, die als taak hebben om binnen hun organisatie aan de slag te gaan met Gezonde Kinderopvang door systematisch o.a. het beleid aan te passen, een plan van aanpak te maken en scholing te geven aan pedagogisch medewerkers.
VeiligheidNL ontwikkelde samen met de Gezonde Kinderopvang materialen voor pedagogisch medewerkers en ouders om uitdagend spelen te stimuleren. Onderdeel van de materialen is een video over uitdagend spelen voor ouders. JGZ-professionals kunnen deze video delen met ouders om hen te stimuleren om hun kind uitdagend te laten spelen.
JOGG en ketenaanpak
Jongeren Op Gezond Gewicht (JOGG) legt de focus op het creëren van een gezonde leefomgeving voor jeugdigen, gericht op voeding en beweging.
Zorg voor een goede ketenaanpak. Bijvoorbeeld volgens de werkwijze Kind naar Gezonder Gewicht.
Buurtsportcoaches, sportservicebureaus, trainers, coaches, zwemdocenten
Buurtsportcoaches richten zich op het organiseren van een sport- en beweegaanbod in de buurt en het maken van een verbinding tussen sport- en beweegaanbieders en andere sectoren zoals zorg, welzijn, jeugdzorg en kinderopvang en onderwijs. De JGZ kan samenwerken met buurtsportcoaches om gebruik te maken van kansen in de wijk. Door samen te werken met andere partners in de wijk worden beweegkansen meer zichtbaar voor gezinnen. Het is belangrijk om een sociale beweegkaart te hebben waarin staat waar gezinnen wie kunnen bereiken en waarvoor. Ook belangrijk: vertel met dezelfde boodschap in de wijk. JGZ-organisaties kunnen informeren bij sportservicebureaus of er een sociale beweegkaart bestaat, of dat er één opgesteld kan worden [47].
Resultaten focusgroepen cliëntparticipatie
In de focusgroepen met kinderen en jongeren valt op dat kinderen de invloed van leerkrachten, het meubilair, aandacht voor houding en bewegen veelal in verband brengen met school. Daar zit mogelijk wel een bias in, omdat de focusgroepen op school zijn gehouden. Jongeren en kinderen benoemen dat zij de adviezen over een goede houding en voldoende bewegen nu vooral via school krijgen, namelijk door docenten die hier op letten of hier echt les over geven, en via ouders. Daarnaast gaven jongeren op het MBO aan hier online video’s over te hebben gekeken. Op school zitten kinderen en jongeren daarnaast in een specifieke routine en is weinig aandacht voor extra bewegen (met name op MBO). Schoolmeubilair is bijvoorbeeld niet verstelbaar en voor grote/kleine kinderen/adolescenten niet altijd goed voor hun houding.
Aanbevelingen
7 Totstandkoming
Werkwijze
Voor de start van het project is een werkgroep samengesteld, deze werkgroep is bij alle fasen van de ontwikkeling van de richtlijn intensief betrokken geweest. Bij de formatie van de werkgroep is gelet op een goede balans tussen wetenschappers, inhoudelijke experts en uitvoerende JGZ-professionals. Zie voor de leden van de werkgroep tabel 4. Met de werkgroepleden zijn afspraken gemaakt over taken en rollen in het project.
Tijdens de eerste werkgroepvergadering (november 2018) zijn de uitgangsvragen besproken en zo nodig nader gespecificeerd. Hierna is een systematisch literatuuronderzoek verricht op de uitgangsvragen. TNO heeft de literatuur bestudeerd en samengevat in een eerste conceptversie. Deze conceptversie 1 is besproken tijdens de werkgroepvergadering in januari 2019. In maart 2019 heeft een schriftelijke feedbackronde plaatsgevonden met de werkgroep. Deze resultaten zijn verwerkt voor een versie van de richtlijn voor de praktijktest en de landelijke commentaarronde. De feedback die werd verzameld tijdens de praktijktest en landelijke commentaarronde werd voorgelegd aan de werkgroep tijdens de bijeenkomst in maart 2020.
Tevens is een klankbordgroep samengesteld. Zie voor de deelnemers aan de klankbordgroep tabel 5. De klankbordgroep was verantwoordelijk voor het becommentariëren en aanvullen van conceptteksten vanuit ieders eigen ervaring en expertise. De klankbordgroep is bijeengekomen in november 2018. In maart 2019 heeft een schriftelijke feedbackronde plaatsgevonden met de klankbordgroep. Deze resultaten zijn verwerkt voor een versie van de richtlijn voor de praktijktest en de landelijke commentaarronde. Nadat de opmerkingen van de werkgroep begin maart 2020 zijn verwerkt is deze versie van de richtlijn aan de klankbordgroep voorgelegd.
In september 2019 is gestart met de praktijktest. De conceptrichtlijn is in deze periode ook verspreid voor de landelijke commentaarronde. In december 2019 werden conceptindicatoren ontwikkeld en voorgelegd aan de indicatorenwerkgroep. In januari 2020 werd een conceptrapport voor de indicatoren opgesteld. Na het verwerken van de resultaten van de praktijktest en de landelijke commentaarronde is de richtlijn in mei 2020 opnieuw voorgelegd aan de RAC van het NCJ en ZonMw. In maart 2020 werd het BDS-protocol aangepast en voorgelegd aan de BDS redactieraad van het NCJ. De conceptversie werd opgesteld en voorgelegd aan de RAC van het NCJ en ZonMw ter autorisatie in juni 2020.
Werkgroep
| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| Mw. E. van Hoorn | Arts Maatschappij & Gezondheid, profiel jeugdarts | AJN |
| Mw. G. Sinnema | Jeugdarts KNMG | AJN |
| Mw. M. Basten | Verpleegkundig specialist | V&VN, vakgroep jeugdverpleegkundigen |
| Mw. L. Graat | Jeugdverpleegkundige | V&VN, mw. Graat leest mee |
| Mw. M.E.J. Wegdam | Kinderarts | NVK |
| Mw. M. van Hartingsveldt | (Kinder)ergotherapeut | Ergotherapie Nederland |
| Mw. M. L. van den Berg | Sportarts | Vereniging voor Sportgeneeskunde |
| Mw. I. van Bommel | (Kinder)fysiotherapeut | Ned. Ver. voor Kinderfysiotherapie |
| Mw. A. Overvelde | (Kinder)fysiotherapeut | Ned. Ver. voor Kinderfysiotherapie |
| Mw. A. Zeegers | Orthopedisch chirurg | Ned. Orthopaedische Vereniging |
| Mw. Y. van Hoorn | Zelfstandig gevestigd oefentherapeut | Vereniging van Oefentherapeuten Cesar en Mensendieck (VvOCM) |
| Mw. S. de Vries | Lector Gezonde leefstijl in een stimulerende omgeving | Haagse Hogeschool |
| Dhr. J. Hoeboer | Docent en onderzoeke | Haagse Hogeschool |
| Dhr. P. Coenen | Post-doc onderzoeker bij EMGO/VUMC | VUMC |
| Mw. M. Gianotten | Ouder | Ouders en onderwijs |
| Mw. J. Verburg | Arts Maatschappij & Gezondheid, profiel jeugdarts | AJN |
| Mw. R. Beck | Specialist bewegen bij kinderen | Kenniscentrum Sport & Bewegen |
| Mw. F. van Brussel | Specialist bewegen bij kinderen | Kenniscentrum Sport & Bewegen |
| Mw. A. Cornelissen | Jeugdverpleegkundige | V&VN, vakgroep jeugdverpleegkundigen |
Klankbordgroep
| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| Mw. H. Heineman | Huisarts | NHG |
| Mw. M. van Zoonen | Ouder | |
| Dhr. P. Legters | Programmamanager Gezonde Schoolomgeving | JOGG |
| Mw. J. van Wieringen | Expert op het gebied van bewegen en diversiteit | Pharos |
| Mw. M. Cotterink | Onderzoeker | Veiligheid NL |
| Dhr. M. Jansen | Ontwikkelaar kindermeubilair | Presikhaaf schoolmeubelen |
| Mw. N. Könemann-van der Krogt | Vakleerkracht gymnastiek en fysiotherapeut | |
| Mw. V. Kruitwagen | Projectleider Aanpak Gezonde School / Adviseur Gezonde Kinderopvang | RIVM |
| Mw. H. de Kraker | Ergonoom | TNO |
| Dhr. L. van Delden | Onderzoekt zit-sta meubels op Leidse school | Leyden Academy |
| Dhr. R. Alberts | Voorzitter RSI-vereniging en fysiotherapeut | RSI-vereniging |
| Dhr. P. van Loon8 | Orthopeed | Houdingsnetwerk Nederland |
| Mw. D. Collard | Beweegexpert, onderzoeker | Mulier instituut |
8 De orthopedisch chirurg Piet van Loon heeft vanuit Houding Netwerk Nederland geconstateerd, dat de aanvankelijk door hem geleverde orthopedische en biomechanische input in de klankbordgroep niet of onvoldoende in de richtlijn tot uitdrukking is gekomen. De urgentie van het kunnen leveren van preventieve geneeskunde door de jeugdartsen aan de jeugd met hun intensieve sedentaire leefstijl is hiermee vanuit de visie van Houding Netwerk Nederland onvoldoende geborgd.
Belangenverstrengeling
Alle deelnemers aan de projectgroep en werkgroep hebben een belangenverklaring ingevuld.
J. Hoeboer geeft aan in de laatste drie jaar (tot op heden) wel een relatie of bemoeienis te hebben gehad met de volgende bedrijven of organisaties: (1) ASM B.V (consultatie/advisering en (na)scholing) en (2) MQ scan (verkoper motorische test). Y. van Hoorn geeft aan in de laatste drie jaar (tot op heden) wel een relatie of bemoeienis te hebben gehad met de volgende bedrijven of organisaties: (1) Zit met Pit (eigen bedrijf).
De overige werkgroepleden hebben verklaard geen relatie of bemoeienis te hebben gehad met bedrijven of organisaties, zoals sponsors, farmaceutische industrie, belangenvereniging, of werkzaamheden te ontplooien vanuit een eigen bedrijf of (mede) methoden, instrumenten ed., waardoor een belangenconflict zou kunnen ontstaan met de werkzaamheden in de richtlijnwerkgroep.
7.1 Cliëntparticipatie
Cliëntenparticipatie
De cliëntenparticipatie bij de ontwikkeling van de JGZ Richtlijn is vormgegeven door deelname van een ouder namens oudervereniging Ouders & Onderwijs aan alle werkgroep vergaderingen. Daarnaast was er een ouder vertegenwoordigd in de klankbordgroep.
Deze richtlijn maakte deel uit van het project “Kinderen, jongeren en ouders op betekenisvolle wijze betrekken bij JGZ Richtlijnen: de co-creatie van een inspirerende Roadmap”, in opdracht van ZonMw. Uitvoerders van het project zijn het Athena Instituut van de Vrij Universiteit Amsterdam, in
samenwerking met Stichting Kind & Ziekenhuis, Stichting Ouders & Onderwijs, NCJ en TNO.
Het project had een tweeledig doel: ten eerste het ontwerpen van een zogenaamde ‘roadmap’ die betrokkenen bij (JGZ-)richtlijnontwikkeling ondersteund in het vormgeven en uitvoeren van kind- en ouderparticipatie. In het kader van onder andere de richtlijn “Houding en bewegen” zijn verschillende participatie activiteiten uitgevoerd:
- Meerdere basisscholen zijn benaderd voor deelname aan creatieve focusgroepen.
- In zes focusgroepen op verschillende basisscholen in Nederland is aandacht besteed aan de perceptie die kinderen hebben van de jeugdarts, en de communicatie met de jeugdarts.
- Daarnaast is tijdens vier van deze focusgroepen aandacht geweest voor hoe kinderen kijken naar de gevolgen van een goede of slechte houding. De manieren waarop zij dagelijks bewegen dan wel stilzitten en de invloed van hun omgeving hierop zijn besproken. Tot slot is inzicht verkregen in hun perceptie van adviezen over houding en bewegen.
- Daarnaast is er in drie focusgroepen met studenten van 16-18 jaar op het MBO gesproken over hun kijk op adviezen over gezond leven in het algemeen. In het bijzonder is gesproken over de (on)mogelijkheden van het opvolgen van adviezen over houding en bewegen op school en thuis.
De uitkomsten van het onderzoek zijn in de richtlijn verwerkt.
Daarnaast zijn er online focusgroepen gehouden met ouders en jongeren over deze richtlijn. Er is aan hen gevraagd of zij zich zorgen maken over de onderwerpen houding, bewegen en beeldschermgebruik en bij wie zij dan eventuele hulp zoeken. Daarnaast is naar hun mening gevraagd over het concept van de tips. Onderstaand worden de resultaten weergegeven.
Daarnaast zijn er online focusgroepen gehouden met ouders en jongeren over deze richtlijn. Er is aan hen gevraagd of zij zich zorgen maken over de onderwerpen houding, bewegen en beeldschermgebruik en bij wie zij dan eventuele hulp zoeken. Daarnaast is naar hun mening gevraagd over het concept van de tips. Onderstaand worden de resultaten weergegeven.
Online focusgroep met ouders
Via sociale media zijn tien ouders geworven voor de online focusgroep, waarvan er uiteindelijk acht hebben deelgenomen. Van de acht deelnemers hadden twee ouders een MBO opleiding en zes ouders een HBO/universitaire opleiding afgerond. Van de deelnemende ouders hadden zes ouders twee kinderen en twee ouders één kind. De leeftijd van hun kinderen varieerden van één tot 15 jaar. Onderstaand worden de belangrijkste resultaten beschreven.
Zorgen over houding, bewegen en beeldschermgebruik
Aan de ouders is voorgelegd of zij zich zorgen maken over de houding, bewegen en beeldschermgebruik van hun kind(eren). Van de ouders gaven vijf ouders aan zich weleens zorgen te maken over de houding van hun kind(eren), vijf ouders maakten zich weleens zorgen over de beweging en vijf ouders maakten zich weleens zorgen over het beeldschermgebruik. Ook gaven zij aan hier zelf een voorbeeldrol te hebben, voornamelijk bij beeldschermgebruik.
Alle ouders gaven aan hun zorgen met hun sociale omgeving te bespreken. Daarnaast gaven zes ouders aan op internet te zoeken bij zorgen. De JGZ werd niet in eerste instantie niet als optie benoemd om hun zorgen mee te bespreken. Aan een aantal ouders is gevraagd of zij wel weten hoe zij contact kunnen opnemen met de jeugdarts en jeugdverpleegkundige. De meeste ouders gaven aan dat zij dat wel weten: ‘’Ja, ik weet de wegen, maar ik probeer het vaak eerst zelf op te lossen. Soms is sneller hulp vragen wel fijn. Om samen met je kind het zetje te geven tot opletten. Maar ik ben niet iemand die snel hulp vraagt eerlijk gezegd’’. Één ouder gaf juist aan niet te weten hoe je in contact komt met de jeugdarts of jeugdverpleegkundige: ‘’Niet zo snel. Ik weet niet precies hoe ik met de jeugdverpleegkundige op school in contact kan komen. Staat wat te ver van me af’’.
Tips over houding, bewegen en beeldschermgebruik
Aan de ouders is voorgelegd wat zij van de conceptversie van de tips vonden. Ouders gaven hier voornamelijk aan dat zij de vertaling van de adviezen naar de praktijk soms lastig vinden: ‘’Tips van deskundigen komen altijd van pas. Een online overzicht helpt daarbij. De Factsheet is heel uitgebreid. Er is veel informatie die nuttig kan zijn. De kunst is vooral hoe maak je het bespreekbaar en hoe pas je dingen toe’’. Ook hun rol als voorbeeldfunctie werd benoemd.
Online focusgroep met jongeren
Via sociale media zijn tien jongeren geworven voor de online focusgroep, waarvan er uiteindelijk zes hebben deelgenomen. Vijf van deze jongeren deden HAVO/VWO en één jongere deed VMBO theoretische leerweg. Gemiddeld waren de jongeren 16 jaar. Onderstaand worden de belangrijkste resultaten beschreven.
Zorgen over houding, bewegen en beeldschermgebruik
De meeste jongeren gaven aan zich weleens zorgen te maken over hun houding, de hoeveelheid beweging en het beeldschermgebruik. Bij het onderwerp houding gaven vijf jongeren aan zich weleens zorgen te maken, voor het onderwerp beeldschermgebruik waren dit vier jongeren en voor bewegen waren dit twee jongeren. Een jongere gaf bijvoorbeeld aan over de vraag of hij/zij zich weleens zorgen maakt over de houding: ‘’Ja vooral met het zitten op school’’. Een andere jongere gaf aan zich geen zorgen te maken, maar dat de sociale omgeving wel een rol speelt: ‘’Niet echt en als dit wel is het meer een soort sociale druk qua uiterlijk dat ik me er zorgen om maak’’, waarop een andere jongere reageert: ‘’Ik herken dat van die sociale druk heel erg, maar bij mij motiveert het me ook wel om meer te sporten. Is dat bij jou ook zo?’’.
Als jongeren zich zorgen maken zoeken zij op internet of vragen het aan hun omgeving. Op de vraag of zij hun zorgen delen met de jeugdarts of jeugdverpleegkundige gaven zij aan dit meestal niet te doen.
Tips over houding, bewegen en beeldschermgebruik
Het concept van de tips is ook voorgelegd aan de jongeren. Een jongere gaf hierover aan:
‘’De tips zijn standaard maar spreken voor zich. Ik vind ze helemaal goed’’. Verbeterpunten
die de jongeren voornamelijk hadden waren om de lay-out van de tips te verbeteren en ook
gaven zij aan het lastig te vinden om te informatie te vertalen naar de praktijk.
8 Verantwoording
Wetenschappelijke bewijsvoering
Als eerste stap bij de ontwikkeling van de richtlijn werd gestart met een systematisch literatuuronderzoek. Gevonden artikelen werden door twee medewerkers van TNO beoordeeld op relevantie. Bij verschil van mening tussen de twee beoordelaars werd in onderling overleg consensus bereikt. Relevante artikelen werden gewaardeerd aan de hand van drie aspecten, namelijk methodologische kwaliteit, toepasbaarheid in de praktijk en toepasbaarheid binnen de Nederlandse gezondheidszorg. Voor het beoordelen van de methodologische kwaliteit werd gebruik gemaakt van GRADE. Bij onderwerpen waarbij studies waarin verschillende instrumenten met elkaar werden vergeleken ontbraken werd afgezien van een gradering van de kwaliteit van bewijs. De studies zijn wel volgens de GRADE-systematiek beoordeeld.
De kwaliteit van bewijs – ook wel aangeduid als de mate van zekerheid van de effectgrootte – werd beoordeeld met behulp van GRADE [55]. GRADE is een methode die per uitkomstmaat van een interventie een gradering aan de kwaliteit van bewijs toekent op basis van de mate van vertrouwen in de schatting van de effectgrootte (tabel 6). Een belangrijk verschil tussen GRADE en andere beoordelingssystemen (bijvoorbeeld het niveau I-IV systeem of A1-D systeem) is dat GRADE niet alleen kijkt naar het studie design maar ook andere factoren overweegt die de kwaliteit van bewijs bepalen (tabel 7).
Tabel 6: Indeling van de kwaliteit van bewijs of mate van zekerheid ten aanzien van de effectgrootte voor een uitkomstmaat volgens GRADE.
| Mate van zekerheid effectgrootte | Omschrijving |
| Groot | Het werkelijke effect ligt dicht in de buurt van de schatting van het effect. |
| Matig | Het werkelijke effect ligt waarschijnlijk dicht bij de schatting van het effect, maar er is een mogelijkheid dat het hier substantieel van afwijkt. |
| Laag | Het werkelijke effect kan substantieel verschillend zijn van de schatting van het effect. |
| Zeer laag | Het werkelijke effect wijkt waarschijnlijk substantieel af van de schatting van het effect. |
Tabel 7: De kwaliteit van bewijs of mate van zekerheid ten aanzien van de effectgrootte wordt bepaald op basis van de volgende criteria.
|
Type bewijs |
RCT start in de categorie ‘hoog’.Observationele studie start in de categorie ‘laag’.Alle overige studietypen starten in de categorie ‘zeer laag’. | |
| Afwaarderen | ‘Risk of bias’ | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
| Inconsistentie | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
|
| Indirect bewijs | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
|
| Onnauwkeurigheid | − 1 Ernstig − 2 Zeer ernstig |
|
| Publicatiebias | − 1 Waarschijnlijk − 2 Zeer waarschijnlijk |
|
| Opwaarderen | Groot effect | + 1 Groot + 2 Zeer groot |
| Dosis response relatie | + 1 Bewijs voor gradiënt | |
| Alle plausibele confounding | + 1 zou een effect kunnen reduceren + 1 zou een tegengesteld effect kunnen suggereren terwijl de resultaten geen effect laten zien |
|
Aanbevelingen in deze richtlijn zijn daar waar mogelijk gebaseerd op wetenschappelijk bewijs, aangevuld met kennis, ervaring en mening van de werkgroep leden. Voor het formuleren van aanbevelingen zijn daarnaast andere aspecten van belang, bijvoorbeeld: voorkeuren van jongeren en ouders, kosten, beschikbaarheid, randvoorwaarden of organisatorische aspecten.
In de verschillende fasen van de richtlijnontwikkeling is geprobeerd rekening te houden met de implementatie van de richtlijn en de daadwerkelijke uitvoerbaarheid van de aanbevelingen. Daarbij is expliciet gelet op factoren die de invoering van de richtlijn in de praktijk kunnen bevorderen of belemmeren.
Zoekstrategie
Artikelen werden gezocht door het verrichten van systematische zoekacties in relevante database zoals Pubmed en Web of Science. Om de uitgangsvragen op een gestructureerde manier uit te werken zijn deze eerst omgevormd tot PICO uitgangsvragen. Hierbij wordt achtereenvolgens het volgende expliciet gemaakt: P = patient, I = intervention, C = comparison, O = outcome. De volgende PICO-uitgangsvragen zijn gehanteerd als basis voor het literatuuronderzoek:
Tabel 8: PICO uitgangsvragen.
PICO 1
| Beschrijf de vraag volgens de PICO-systematiek |
Met welke instrumenten kunnen JGZ-professionals houdings- en bewegingsafwijkingen en verkeerde gewoontes signaleren bij jeugdigen van verschillende leeftijden? P: Jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar |
| Wat is het domein van het probleem? | Diagnose |
| Welke typen onderzoek zijn geschikt voor deze vraagstelling? |
Observationeel onderzoek
Systematische review |
| Formuleer de inclusiecriteria voor studies | Leeftijd: 0-18 jaar Taal: Nederlands, Engels Publicatie jaar: vanaf 2008 (en aanvullende studies includeren via sneeuwbaleffect |
| Formuleer de exclusiecriteria | Geen |
| Formuleer de zoektermen om de PICO-vraag te beantwoorden | Zie tabel 9 |
| Welke databestanden worden geraadpleegd? | Pubmed Web Of Science |
PICO 2
| Beschrijf de vraag volgens de PICO-systematiek |
Wat zijn bewezen korte- en langetermijngevolgen van een verkeerde houding bij jeugdigen? P: Jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar I: Jeugdigen met ‘verkeerde houding’ (nader te definiëren) C: Jeugdigen zonder ‘verkeerde houding’ (nader te definiëren) O: Gezondheidsproblemen (afwijkingen skelet, spieren, overgewicht, conditie, kwaliteit van leven) |
| Wat is het domein van het probleem? | Diagnose |
| Welke typen onderzoek zijn geschikt voor deze vraagstelling? |
Observationeel onderzoek
Systematische review |
| Formuleer de inclusiecriteria voor studies | Leeftijd: 0-18 jaar Taal: Nederlands, Engels Publicatie jaar: vanaf 2008 (en aanvullende studies includeren via sneeuwbaleffect) |
| Formuleer de exclusiecriteria | Geen |
| Formuleer de zoektermen om de PICO-vraag te beantwoorden | Zie tabel 9 |
| Welke databestanden worden geraadpleegd? | Pubmed Web Of Science |
PICO 3
| Beschrijf de vraag volgens de PICO-systematiek |
Wat zijn bewezen korte- en langetermijngevolgen van verkeerd bewegen bij jeugdigen? P: Jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar I: Jeugdigen die ‘verkeerd bewegen’ (nader te definiëren?) C: Jeugdigen die ‘verkeerd bewegen’ (nader te definiëren?) O: Gezondheidsproblemen (afwijkingen skelet, spieren, overgewicht, conditie, kwaliteit van leven) |
| Wat is het domein van het probleem? | Diagnose |
| Welke typen onderzoek zijn geschikt voor deze vraagstelling? |
Observationeel onderzoek
Systematische review |
| Formuleer de inclusiecriteria voor studies | Leeftijd: 0-18 jaar Taal: Nederlands, Engels Publicatie jaar: vanaf 2008 (en aanvullende studies includeren via sneeuwbaleffect) |
| Formuleer de exclusiecriteria | Geen |
| Formuleer de zoektermen om de PICO-vraag te beantwoorden | Zie tabel 9 |
| Welke databestanden worden geraadpleegd? | Pubmed Web Of Science |
PICO 4
| Beschrijf de vraag volgens de PICO-systematiek |
Welke actuele en specifieke strategieën zijn effectief om ouders en jeugdigen te ondersteunen bij het veranderen van houding en bewegen? P: Jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar I: Toepassing van C: Geen toepassing van O: Verandering in houding en bewegen |
| Wat is het domein van het probleem? | Interventie |
| Welke typen onderzoek zijn geschikt voor deze vraagstelling? |
Randomised Controlled Trial
Systematische review |
| Formuleer de inclusiecriteria voor studies | Leeftijd: 0-18 jaar Taal: Nederlands, Engels Publicatie jaar: vanaf 2008 (en aanvullende studies includeren via sneeuwbaleffect) |
| Formuleer de exclusiecriteria | Geen |
| Formuleer de zoektermen om de PICO-vraag te beantwoorden | Zie tabel 9 |
| Welke databestanden worden geraadpleegd? | Pubmed Web Of Science |
PICO 5
| Beschrijf de vraag volgens de PICO-systematiek |
Wat zijn bewezen gevolgen van langdurig mediagebruik voor ontwikkeling van houding en bewegen bij jeugdigen? P: Jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar I: Jeugdigen met ‘langdurig mediagebruik’ (nader te definiëren?) C: Jeugdigen zonder ‘langdurig mediagebruik’ (nader te definiëren?) O: Gezondheidsproblemen (afwijkingen skelet, spieren, overgewicht, conditie, kwaliteit van leven) |
| Wat is het domein van het probleem? | Diagnose |
| Welke typen onderzoek zijn geschikt voor deze vraagstelling? |
Observationeel onderzoek
Systematische review |
| Formuleer de inclusiecriteria voor studies | Leeftijd: 0-18 jaar Taal: Nederlands, Engels Publicatie jaar: vanaf 2008 (en aanvullende studies includeren via sneeuwbaleffect) |
| Formuleer de exclusiecriteria | Geen |
| Formuleer de zoektermen om de PICO-vraag te beantwoorden | Zie tabel 9 |
| Welke databestanden worden geraadpleegd? | Pubmed Web Of Science |
Tabel 9: Gehanteerde zoekstrategieën.
| Gehanteerde zoekstrategieën | Aantal artikelen (na verwijderen duplicaten) | Geselecteerd op basis van titel en abstract | Daadwerkelijk geïncludeerd in richtlijn |
|
PUBMED “Back Pain/analysis”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/anatomy and histology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/classification”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/complications”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/diagnosis”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/economics”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/epidemiology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/ethnology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/etiology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/history”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/injuries”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/nursing”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/organization and administration”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/pathology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/physiopathology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/prevention and control”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/psychology”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/rehabilitation”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/statistics and numerical data”[Mesh] OR “Back Pain/therapy”[Mesh] OR “Spine/abnormalities”[Mesh] OR “Spine/complications”[Mesh] OR “Spine/diagnosis”[Mesh] OR “Spine/etiology”[Mesh] OR “Spine/growth and development”[Mesh] OR “Spine/pathology”[Mesh] OR “Spine/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Spine/physiopathology”[Mesh] OR “Gait”[Mesh] OR “Posture/abnormalities”[Mesh] OR “Posture/adverse effects”[Mesh] OR “Posture/analysis”[Mesh] OR “Posture/classification”[Mesh] OR “Posture/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/analysis”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/anatomy and histology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/classification”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/complications”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/diagnosis”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/economics”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/epidemiology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/ethnology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/etiology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/nursing”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/organization and administration”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/pathology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/physiopathology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/prevention and control”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/psychology”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/rehabilitation”[Mesh] OR “Neck Pain/statistics and numerical data”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/analysis”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/anatomy and histology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/classification”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/diagnosis”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/economics”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/epidemiology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/ethnology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/etiology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/nursing”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/organization and administration”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/pathology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/physiopathology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/prevention and control”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/psychology”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/rehabilitation”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/statistics and numerical data”[Mesh] OR “Shoulder Pain/therapy”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/analysis”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/anatomy and histology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/classification”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/diagnosis”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/economics”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/epidemiology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/ethnology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/etiology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/nursing”[Mesh] “Musculoskeletal Pain/organization and administration”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/pathology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/physiopathology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/prevention and control”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/psychology”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/rehabilitation”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/statistics and numerical data”[Mesh] OR “Musculoskeletal Pain/therapy”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/adverse effects”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/analysis”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/anatomy and histology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/classification”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/economics”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/education”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/epidemiology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/etiology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/instrumentation”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/organization and administration”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/pathology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/pharmacology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/physiopathology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/psychology”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/standards”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/statistics and numerical data”[Mesh] OR “Motor Activity/trends”[Mesh] OR “Sedentary Lifestyle/epidemiology”[Mesh] “Sedentary Lifestyle/statistics and numerical data”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/abnormalities”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/analysis”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/diagnosis”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/epidemiology”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/growth and development”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/instrumentation”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/pathology”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/physiology”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/physiopathology”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/prevention and control”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/statistics and numerical data”[Mesh] OR “Lower Extremity/therapy”[Mesh] OR “Scoliosis”[Mesh] OR “Cumulative Trauma Disorders”[Mesh] OR “Torticollis”[Mesh] OR “Muscle Hypotonia”[Mesh] OR “Kyphosis”[Mesh] OR “Scheuermann Disease”[Mesh] OR “Postural Balance”[Mesh] OR “Contracture”[Mesh] OR “Muscle Contraction”[Mesh] OR “Spinal Dysraphism”[Mesh] OR “Meningomyelocele”[Mesh] OR “Meningocele”[Mesh] OR “Tremor”[Mesh] OR “Pectus Carinatum”[Mesh] OR “Funnel Chest”[Mesh] OR “Lordosis”[Mesh] OR “Rheumatic Diseases”[Mesh] OR “Hypokinesia”[Mesh] OR “Spasm”[Mesh] OR “Muscle Hypertonia”[Mesh] OR “Muscle Cramp”[Mesh] OR “Tendinopathy”[Mesh] OR “Hernia”[Mesh] “Adolescent”[Mesh] OR “Child”[Mesh] OR “Infant”[Mesh] WEB OF SCIENCE child OR children OR child*s OR infant* OR adolescen* OR preschooler* OR toddler* OR newborn* OR teens OR youth* AND (Spine) OR (back) OR (gait) OR (posture) OR (Neck) OR (Shoulder) OR (musculoskeletal) OR (“Physical fitness” OR exercise OR “physical activity” OR “motor Skills” OR “physical literacy” OR “Motor activity” OR “fundamental movement skill”) OR (inactivity OR “sedentary behaviour”) OR (Lower extremities) AND
(“Cumulative Trauma Disorder*”) OR (“overuse” OR overtraining) OR (Torticollis) OR (“muscle tone” OR hypotonia OR “muscle flaccidity” ) OR (kyphosis) OR (scoliosis) OR (Scheuermann) OR ((asymmetry OR asymmetric) AND (body OR posture)) OR (“Muscle contracture*” OR “muscle shortening”) OR (“spina bifida aperta” OR “spina bifida occulta”) OR (Meningocele OR Myelomeningocele OR “Spinal Dysraphism”) OR (Tremor*) OR (“Pectus carinatum”) OR (“Pectus excavatum”) OR (“Repetitive strain injury” OR “RSI” ) OR (lordosis) OR (rheumatism OR “rheumatic disorder” OR “Rheumatic Diseases” OR “joint complaints” OR “joint diseases”) OR (Hypokinesia) OR (Spasm* OR muscle spasticity OR “muscle rigidity” OR hypertonia) OR (“muscle cramp”) OR (“healthy posture” OR “Physical fitness” ) OR (“Achilles tendonitis”) OR (“medial epicondylitis”) OR (“Little league elbow” OR “overuse of the medial epicondyle apophysis”) OR (“Little league shoulder” OR “overuse of the proximal humeral physis”) OR (Tendonitis) OR (“lateral epicondylitis”) OR (“lumbar disc herniation”) AND NOT “cerebral palsy” English-NL |
2207
|
263
|
43
|
Naast de literatuur uit de search zijn er bij een aantal vragen ook publicaties meegenomen uit de archieven van de werkgroepleden, mits zij aan de inclusiecriteria voldeden. De in de PICO-vragenstelling voorgestelde zoektermen werden tijdens het literatuuronderzoek gevalideerd, en daar waar nodig bijgesteld. Hieronder worden de definitief gehanteerde zoek strategieën en de bijbehorende resultaten kort weergegeven.
Voor geen van de uitgangsvragen werd een GRADE-rapport opgesteld. De reden hiervan is beschreven onder het kopje “methoden” van elk thema.
Kennislacunes
Door werkgroepleden wordt benoemd dat JGZ-professionals in hun opleiding meer kennis zouden moeten opdoen over anatomische, fysiologische en ontwikkelingsprocessen.
Het is nog onbekend wat het effect gaat zijn van de nieuwe aanbeveling over het aanbieden van extra contactmomenten op basis van een familieanamnese. Nader onderzoek is gewenst naar het aantal jeugdigen met scoliose dat op deze wijze wordt opgespoord en wat de gezondheidswinst is van deze aanbeveling.
9 Bijlagen
9.1 Bijlage 1: niet actief op te sporen symptomen en aandoeningen
Rug
Versterkte kyfose of hyperkyfose
Beschrijving aandoening
De wervelkolom heeft van nature een ‘bolling’ ter hoogte van de thorax (borstkas). Bij hyperkyfose of versterkte kyfose is er sprake van een versterkte bolling van de wervelkolom. Deze gaat vaak gepaard met voorover hangende schouders. Een versterkte kyfose kan structureel (de ziekte van Scheuermann, of aangeboren wervelafwijkingen) of niet-structureel zijn (verkeerde (zit)houding en/of slappe rugspieren).
Figuur 4: Normale houding en hyperkyfose
Epidemiologie
De versterkte kyfose als gevolg van de houding ontstaat vaak in de loop van de basisschoolleeftijd [13]. Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak versterkte kyfose bij jeugdigen voorkomt.
Gevolgen
Een milde versterkte kyfose geeft over het algemeen geen klachten [12]. Pas bij een ernstige versterkte kyfose kunnen stijfheid van de rug en pijnklachten voorkomen.
Behandeling
De behandeling van versterkte kyfose hangt af van de ernst en de oorzaak. De ernstig versterkte kyfose als gevolg van de houding kan worden behandeld met kinderfysiotherapie of (kinder)oefentherapie. Bij versterkte kyfose als gevolg van de ziekte van Scheuermann: zie behandeling van ziekte van Scheuermann. Versterkte kyfose als gevolg van aangeboren wervelafwijkingen wordt vaak al op jonge leeftijd operatief gecorrigeerd.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Bij verdenking op een versterkte kyfose beoordeelt de jeugdarts9 de houding van de jeugdige in staande positie, waarbij ten minste het bovenlichaam ontbloot is (BH mag desgewenst aanblijven) en de schoenen uit zijn.
Vervolgens wordt de rug beoordeeld door middel van de buigtest. Bij een structurele kyfose is dan van opzij gezien een knik in de bovenrug te zien in plaats van een egale kromming (zie figuur 5).
Indien er sprake lijkt te zijn van een versterkte kyfose, wordt onderzocht of de jeugdige de kyfose actief kan corrigeren door de schouders naar achter te bewegen en de kin op te tillen. Als alternatief kan worden onderzocht of de kyfose corrigeert als de jeugdige op de rug gaat liggen. De mate van kyfose wordt bepaald op basis van de normale anatomie en de professionele inschatting van de jeugdarts.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
|
verwijzing naar (kinder)orthopeed. | |
|
|
|
|
|
9 Daar waar ‘jeugdarts’ staat, kan ook ‘verpleegkundig specialist’ worden gelezen. De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en hij/zij werkt op expertniveau. Hij/zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ-team, hij/zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
Figuur 5: Buigtest bij normale anatomie en structurele kyfose.
Ziekte van Scheuermann
Beschrijving aandoening
De ziekte van Scheuermann is een groeistoornis, waarbij de wervels in het bovenste deel van de rug vergroeid zijn. Onregelmatige groei aan de voorkant van de wervellichamen zorgt ervoor dat deze aan de voorzijde uiteindelijk platter (wigvormig) zijn, dan aan de achterzijde. Hierdoor kan “wigvorming” ontstaan die een versterkte kyfose (bolle bovenrug) veroorzaakt. De versterkte kyfose gaat vaak gepaard met voorover hangende schouders.
Epidemiologie
De ziekte manifesteert zich vaak tussen het 13e en 17e jaar, en komt vaker voor bij jongens dan bij meisjes [12]. De gerapporteerde prevalentie van de ziekte van Scheuermann is wisselend, van ongeveer 0,2%-3% [13, 56].
Gevolgen
Om toch rechtop te staan hebben veel mensen met de ziekte van Scheuermann juist een versterkte lordose (extra holle onderrug). Naast de zichtbare versterkte kyfose (bolling) van de rug kan er in ernstigere gevallen sprake zijn van pijnklachten. Ook spierpijn en vermoeidheid in de rug komen voor, vooral aan het einde van de dag.
Behandeling
Oefentherapie doet de afwijking niet verminderen maar kan wel helpen de houding te verbeteren [13]. Soms kan behandeling met een korset verbetering geven. In zeer ernstige gevallen kan een operatieve correctie overwogen worden.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek: Zie bij ‘kyfose’.
Beleid: Zie bij ‘kyfose’.
Versterkte lordose of hyperlordose
Beschrijving aandoening
De wervelkolom heeft van nature een ‘holling’ (lordose) ter hoogte van de taille. Bij hyperlordose of versterkte lordose is er een versterkte holling van de wervelkolom onder in de rug. Men spreekt ook wel van een ‘holle rug’. Een versterkte lordose kan verschillende oorzaken hebben, zoals slappe buik- en rugspieren, spondylolisthesis (afschuiving van een wervel ten opzichte van een onderliggende wervel), of compensatie van een versterkte kyfose. Bij kinderen ontstaat soms tijdens de groei tijdelijk een versterkte lordose. Deze te holle rug verdwijnt meestal ook weer spontaan.
Epidemiologie
Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak versterkte lordose bij jeugdigen voorkomt.
Gevolgen
Een mild versterkte lordose geeft over het algemeen geen klachten. Pas bij een ernstig versterkte lordose of spondylolisthesis kunnen stijfheid van de rug en pijnklachten voorkomen.
Behandeling
De behandeling van versterkte lordose hangt af van de oorzaak. De versterkte lordose als gevolg van slappe spieren kan worden behandeld met kinderfysiotherapie of (kinder)oefentherapie. De behandeling van spondylolisthesis is afhankelijk van de mate van afglijding, en kan bestaan uit oefeningen of operatieve behandeling.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Bij verdenking op een versterkte lordose beoordeelt de jeugdarts9 de houding van de jeugdige in staande positie, waarbij ten minste het bovenlichaam ontbloot is (BH mag desgewenst aanblijven) en de schoenen uit zijn. Indien er sprake lijkt te zijn van een versterkte lordose, wordt onderzocht of de jeugdige de lordose actief kan corrigeren door de buikspieren aan te spannen, de knieën ‘van slot’ te halen en de billen naar voren te duwen (het bekken achterover te kantelen). Soms lukt dit in stand niet maar wel in rugligging.
Vervolgens wordt de rug beoordeeld door middel van de buigtest. Bij een niet-structurele lordose is dan een egale kromming zichtbaar (de lordose verdwijnt). De mate van lordose wordt bepaald wordt bepaald op basis van de normale anatomie en de professionele inschatting van de jeugdarts.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
- Structurele lordose (lordose niet actief te corrigeren en verdwijnt niet bij voorover buigen): verwijzing naar (kinder)orthopeed.
- Niet-structurele lordose (lordose actief te corrigeren en verdwijnt bij vooroverbuigen):
- Milde lordose: de JGZ-professional geeft sport- en beweegadvies (zie thema 2). Er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor. Eventueel wordt een controle na 6-12 maanden afgesproken (afhankelijk van de leeftijd van de jeugdige).
- Matige tot ernstige lordose: verwijzing naar kinderfysiotherapeut of (kinder)oefentherapeut.
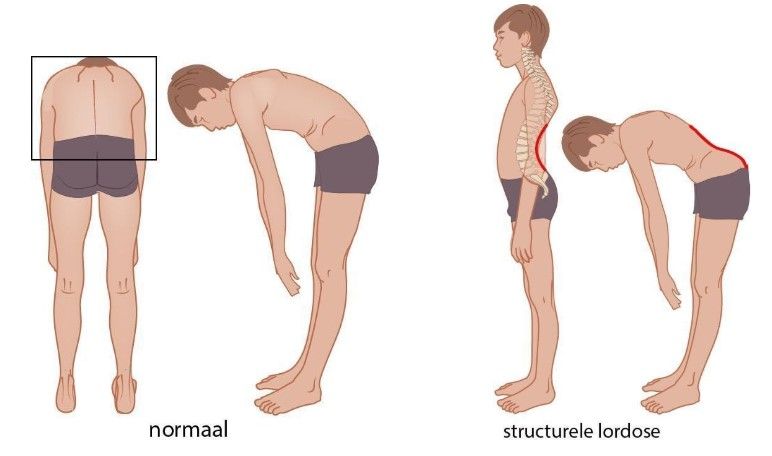
Figuur 6: Buigtest bij normale anatomie en structurele lordose.
Rugklachten
Beschrijving aandoening
Rugklachten kunnen zich op verschillende manieren uiten. Vaak is er sprake van pijnklachten, vooral laag in de rug. Lage rugpijn is vaak een zeurende pijn die kan toenemen bij bepaalde houdingen of bewegingen. Naast rugpijn kunnen jeugdigen bijvoorbeeld ook last hebben van spanning, stijfheid, een beperking van de beweeglijkheid of een vermoeid gevoel in de rug. Rugklachten kunnen ook veroorzaakt worden door aandoeningen buiten de rug, zoals bij bekkenproblematiek of menstruatieklachten.
Epidemiologie
Uit Nederlands onderzoek blijkt dat per jaar 3% van de jongeren (12-18 jaar) vanwege rugklachten bij de huisarts komt, de prevalenties van zelf gerapporteerde rugklachten liggen tussen de 9% en 16% [57]. In een internationale meta-analyse werd een prevalentie van lage rugpijn van 12% gevonden bij jeugdigen jonger dan 18 jaar [58]. Lage rugpijn is vaak een terugkerende klacht, na oorspronkelijk herstel komen de klachten vaak (na korte of lange tijd) weer terug. Lage rugpijn komt vaker voor bij meisjes dan bij jongens en komt vaker voor naarmate jeugdigen ouder worden [58].
Gevolgen
Rugklachten kunnen leiden tot beperkingen in het dagelijks functioneren, schoolverzuim en het verminderen of stoppen van sportactiviteiten.
Behandeling
Lage rugpijn gaat vaak vanzelf weer over. Het is belangrijk dat men, ondanks de klachten, zoveel mogelijk in beweging blijft [59]. Daarnaast kan het gebruik van pijnstillers overwogen worden, alhoewel de werkzaamheid van pijnstillers ten aanzien van pijn en functionaliteit bij aspecifieke lage rugpijn waarschijnlijk beperkt is [59].
Bij aanhoudende lage rugpijn (langer dan 4 weken) kan een eerstelijns therapeut10 helpen bij het opbouwen van activiteiten en het aanleren van de juiste gewoontes ter voorkoming van herhaling [59]. Het is hierbij belangrijk om naar de oorzaak van de klachten te zoeken zodat deze bij de bron aangepakt kunnen worden. Denk hierbij aan het analyseren van de houding van de rug op school, tijdens computergebruik, gamen of hobby’s en de menstruatiecyclus bij meisjes (indien van toepassing).
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
De jeugdarts9 beoordeelt de houding van de jeugdige in staande positie, waarbij ten minste het bovenlichaam ontbloot is (BH mag desgewenst aanblijven) en de schoenen uit zijn.
Beleid [59]:
- De JGZ-professional geeft uitleg over de aandoening en mogelijke oorzaken (de precieze oorzaak is vaak onbekend, het gaat meestal binnen een aantal weken vanzelf over).
- De JGZ-professional overweegt samen met de jeugdige en ouders mogelijke oorzaken zoals niet neutrale houding tijdens computeren, gamen, in de klas, hobby’s.
- De JGZ-professional geeft sport- en beweegadvies (zie sectie 3.3). Het advies is om in beweging te blijven en door te gaan met de normale dagelijkse activiteiten. Bedrust is niet zinvol. Bij ernstige klachten kan eventueel worden geadviseerd om enkele dagen zo nu en dan enkele uren rust te nemen en daarna geleidelijk de normale activiteiten weer op te pakken, zelfs als de pijn nog steeds hevig is.
- De JGZ-professional bespreekt de mogelijkheid van tijdelijke pijnstilling ter ondersteuning van het activerende beleid. Spreek af hoelang en hoe vaak de pijnstilling gebruikt mag worden. Paracetamol kan zowel op vaste tijden als naar behoefte worden voorgeschreven; er is geen verschil in effectiviteit. NSAID’s zijn waarschijnlijk niet effectiever dan paracetamol bij lage rugpijn.
- Indien de klachten hiermee onvoldoende verbeteren dan dient te worden verwezen naar een eerstelijns therapeut11.
- Indien er sprake is van nachtelijke pijn, neurologische uitvalsverschijnselen, uitstralende pijn naar de benen, algehele malaise of gewichtsverlies dan dient binnen 24 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts.
10 Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
11 Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
Hernia
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij een hernia is er sprake van een uitstulping van een tussenwervelschijf, deze kan druk uitoefenen op een zenuw en kan pijnklachten geven. Een hernia komt vaker voor bij jeugdigen met een positieve familieanamnese voor hernia, na een trauma van de rug of spondylolisthesis (afschuiving van een wervel ten opzichte van een onderliggende wervel).
Epidemiologie
Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak een hernia bij jeugdigen voorkomt.
Gevolgen
Er is sprake van pijn in de heup of onderrug, die uitstraalt naar de bil of het been. Tevens kan sprake zijn van neurologische verschijnselen: verminderde kracht en/of een slapend/doof/branderig gevoel in het been. Bij jeugdigen komen uitstralende pijn en neurologische verschijnselen bij een hernia minder vaak voor dan bij volwassenen met een hernia.
Behandeling
Een hernia bij jeugdigen wordt conservatief behandeld met pijnstilling en houdings- en beweegadviezen. Het is belangrijk dat de jeugdige, ondanks de klachten, zoveel mogelijk in beweging blijft. Operatieve behandeling is zelden nodig.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Bij verdenking op een hernia onderzoekt de jeugdarts9 in hoeverre de jeugdige (in liggende houding) het been gestrekt kan optillen. Bij een hernia is er een links-rechts verschil ten nadele van de aangedane zijde. Tevens wordt de kniepeesreflex en het gevoel in de benen onderzocht.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
- De JGZ-professional geeft sport- en beweegadvies (zie sectie 3.3). Het advies is om in beweging te blijven en door te gaan met de normale dagelijkse activiteiten. Bedrust is niet zinvol. Bij ernstige klachten kan eventueel worden geadviseerd om enkele dagen zo nu en dan enkele uren rust te nemen en daarna geleidelijk de normale activiteiten weer op te pakken, zelfs als de pijn nog steeds hevig is.
- Zo nodig kan de jeugdige worden verwezen naar een eerstelijns therapeut12 voor verdere begeleiding bij het in beweging blijven.
- Indien er sprake is van neurologische (uitvals)verschijnselen of uitstralende pijn naar de benen dan dient binnen 48 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts.
12Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
Neuromusculaire problemen
Spierverkortingen (contracturen)
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij een spierverkorting is de lengte van de spier afgenomen, waardoor er een bewegingsbeperking ontstaat. Als een spier te weinig gebruikt wordt, verkort het (bind-)weefsel. De verkorting van dit bindweefsel beperkt de bewegingsmogelijkheid van een spier. Deze bewegingsbeperking heet een (myogene) contractuur. Vooral de buigspieren zijn gevoelig voor contracturen.
Een spierverkorting kan onder andere ontstaan als gevolg van spasticiteit, musculaire disbalans en inactiviteit. Daarnaast kan een spierverkorting het gevolg zijn van tenenloop (zie JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten).
Epidemiologie
Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak een contractuur bij jeugdigen voorkomt. Bij jeugdigen is een spierverkorting het meest frequent aanwezig in de hamstrings en de kuiten.
Gevolgen
Een spierverkorting leidt tot bewegingsbeperking en functiebeperking. Daarnaast kan het leiden tot pijnklachten.
Behandeling
Een spierverkorting kan worden behandeld door de kinderfysiotherapeut of (kinder)oefentherapeut.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Indien er een verdenking is op een spierverkorting dan onderzoekt de jeugdarts9 de (passieve en actieve) beweeglijkheid van het betreffende lichaamsdeel. Op basis van de kennis van de normale anatomie wordt bepaald of er sprake is van een spierverkorting.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
- Advies gericht op de juiste houding, gecombineerd met sport- en beweegadvies (zie sectie 3 Preventie). Er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor. Regelmatig van houding wisselen en bewegen is belangrijk om (verergering) van een spierverkorting te voorkomen.
- Indien er sprake is van een bewegingsbeperking of pijnklachten dient te worden verwezen naar de kinderfysiotherapeut of (kinder)oefentherapeut. Bespreek met ouders dat zij bij onvoldoende verbetering terugkomen voor een hernieuwde beoordeling, en vraag dit in de verwijsbrief ook aan de kinderfysiotherapeut of (kinder)oefentherapeut. Bij onvoldoende verbetering dient te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed, (kinder)revalidatiearts of kinderarts.
Overige problemen
Fysieke over- en onderbelasting
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij fysieke overbelasting beweegt de jeugdige te veel ten opzichte van zijn/haar belastbaarheid. Fysieke overbelasting kan ontstaan door repeterende bewegingen (bijvoorbeeld frequent buigen of draaien van de romp, frequente bewegingen met de armen/ polsen) of het langdurig aanhouden van een ongunstige houding (voorovergebogen staan, opgetrokken schouders). Ook te frequent of intensief sporten kan leiden tot klachten van fysieke overbelasting.
Bij fysieke onderbelasting beweegt de jeugdige onvoldoende. De oorzaken hiervoor kunnen heel divers zijn.
Epidemiologie
Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak fysieke over- of onderbelasting bij jeugdigen voorkomt.
Gevolgen
Fysieke overbelasting kan leiden tot klachten aan het bewegingsapparaat. Zo kunnen repeterende bewegingen en langdurig aangehouden statische houdingen leiden tot klachten aan rug, schouders en armen (zie onderwerp KANS (Klachten Arm, Nek en/of Schouder). Bij fysieke onderbelasting gaat de conditie achteruit en bestaat het risico op overgewicht.
Behandeling
De behandeling bestaat uit adviezen over de juiste vorm en mate van bewegen (sportadvies, houdingsadvies, afwisselen van houding en activiteiten). Daarnaast kan behandeling door een eerstelijns therapeut13 zinvol zijn voor het herkennen en realiseren van juiste balans in belasting en belastbaarheid en het aanleren van de juiste bewegingspatronen.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Afhankelijk van de aard en lokalisatie van de klachten bepaalt de jeugdarts9 het lichamelijk onderzoek.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
- Advies gericht op de juiste houding, gecombineerd met sport- en beweegadvies (zie sectie 3 Preventie). Er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor. Na 6-12 weken kan een extra contactmoment worden afgesproken om de klachten te vervolgen.
- Bij aanhoudende klachten kan worden verwezen naar een eerstelijns therapeut14.
13 Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
14 Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
KANS (Klachten Arm, Nek en/of Schouder) en RSI-klachten (Repetitive Strain Injury)
Beschrijving aandoening
KANS is een verzamelnaam voor klachten aan de arm, nek en/of schouders waaraan geen acuut trauma of een systemische aandoening ten grondslag ligt. Het is geen diagnose maar een beschrijvende term. Er kan sprake zijn van pijn, stijfheid, krachtsverlies en/of tintelingen.
Andere termen of diagnoses die onder de verzamelnaam ‘KANS’ vallen zijn: RSI (Repetitive Strain Injury), Cumulative Trauma Disorder (CTD), whatsapp-duim, muisarm, en tablet-nek.
KANS kan worden ingedeeld in specifieke en aspecifieke KANS [60]. Voorbeelden van specifieke KANS zijn de epicondylitis (tenniselleboog), carpaal tunnelsyndroom of een peesontsteking. Indien er geen duidelijke diagnose te stellen is dan wordt gesproken van aspecifieke KANS.
De klachten worden vaak veroorzaakt door repeterende bewegingen, een langdurige statische houding of een combinatie van beide. Zie ook ‘fysieke over- en onderbelasting’.
Epidemiologie
Het is op dit moment niet bekend hoe vaak KANS bij jeugdigen voorkomt.
Gevolgen
De gevolgen kunnen variëren van tijdelijke milde klachten tot schoolverzuim.
Behandeling
Voor de juiste behandeling is het belangrijk dat er een onderscheid gemaakt wordt tussen specifieke KANS (waarbij de behandeling gericht is op de specifieke diagnose) of aspecifieke KANS. Voor de behandeling van aspecifieke KANS (bij volwassenen) is in 2012 een multidisciplinaire richtlijn ontwikkeld [60]. Het is hierbij belangrijk om naar de oorzaak van de klachten te zoeken zodat deze bij de bron aangepakt kunnen worden. Denk hierbij aan het analyseren van de houding en bewegingen tijdens computergebruik.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Afhankelijk van de aard en lokalisatie van de klachten bepaalt de jeugdarts9 het lichamelijk onderzoek.
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
- Navragen mogelijke oorzaken, advies gericht op de juiste houding, gecombineerd met sport- en beweegadvies (zie sectie 3 Preventie). Er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor. Na 6-12 weken kan een extra contactmoment worden afgesproken om de klachten te vervolgen.
- Bij aanhoudende klachten kan worden verwezen naar een eerstelijns therapeut15.
- Bij aanhoudende klachten wordt binnen een week verwezen naar de huisarts, ter uitsluiting van specifieke KANS/diagnoses.
15 Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
Gewrichtsklachten (algemeen)
Beschrijving aandoening
Gewrichtsklachten kunnen door een groot aantal aandoeningen worden veroorzaakt. In deze paragraaf zal vooral worden ingegaan op pijnklachten aan de gewrichten.
De belangrijkste oorzaken van pijnklachten aan de gewrichten bij jeugdigen zijn:
- Een gewrichtsontsteking (bacteriële artritis). Hierbij is het gewricht rood, warm en zeer pijnlijk. Tevens kan de jeugdige koorts hebben en een zieke indruk maken;
- Een reactieve artritis als gevolg van een virusinfectie. Bijvoorbeeld coxitis fugax (zie JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten);
- Reumatische aandoeningen, zoals Juveniele Idiopathische Artritis (JIA), zie paragraaf Jeugdreuma;
- Ziekte van Henoch-Schönlein. Hierbij is er sprake van paars-rode niet wegdrukbare vlekken op de huid van de benen en billen. Soms is er ook sprake van pijnklachten van de grote gewrichten zoals knie, elleboog of pols. Daarnaast kan er sprake zijn van nierafwijkingen en buikpijn;
- Ziekte van Osgood-Schlatter (zie JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten;
- Traumata, zoals het verzwikken van de enkel.
Voor een nadere diagnose is het belangrijk om te weten hoe lang de (pijn)klachten bestaan, waar de (pijn)klachten zitten en of het kind verkouden is geweest of koorts heeft (gehad).
Epidemiologie
De verschillende oorzaken van gewrichtsklachten verschillen onderling in de mate van voorkomen.
- De prevalentie van acute en chronische artritis bij kinderen is respectievelijk 2-8 en 0,1-0,5 per 10.000 [61].
- De ziekte van Henoch-Schönlein komt jaarlijks bij 1:7000 jeugdigen voor, in 90% van de gevallen voor het tiende levensjaar. Het komt vaker voor bij jongens dan bij meisjes.
- De incidentie van bacteriële artritis varieert van 5 tot 37 gevallen per 100.000 kinderen [62].
Gevolgen
De gevolgen zijn afhankelijk van de onderliggende oorzaak. Zo zal na een trauma vrijwel altijd een volledig herstel optreden, terwijl een bacteriële artritis kan leiden tot een onomkeerbare beschadiging van het gewricht.
Behandeling
De behandeling is afhankelijk van de onderliggende oorzaak.
- (Bacteriële) artritis: intraveneuze antibiotica;
- Reactieve artritis: enkele dagen rust, gevolgd door opbouw belasting aan de hand van de klachten (zie JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten);
- Ziekte van Henoch-Schönlein: zo nodig pijnstilling, urinecontrole (op aanwezigheid bloed en eiwit);
- Traumata: over het algemeen behandeling door middel van rust, gevolgd door het opbouwen van de activiteiten aan de hand van de klachten. Zo nodig kan hierbij begeleiding geboden worden door een eerstelijns therapeut16.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
NB: zie hiervoor ook de JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten, thema 3 (pijnklachten).
Bij lichamelijk onderzoek wordt gelet op de algemene indruk van de jeugdige (koorts, ziek zijn). Bij klachten aan heupen of benen onderzoekt de jeugdarts9 het looppatroon. Het gewricht wordt onderzocht op zwelling, afwijkende vorm of stand, pijn of gevoeligheid en warmte. De beweeglijkheid van het betreffende gewricht en naastgelegen gewrichten wordt onderzocht.
Beleid:
NB: zie hiervoor ook de JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten, thema 3 (pijnklachten).
- Alle mank lopende kinderen dienen binnen 24 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts voor aanvullend onderzoek.
- Indien er sprake is van hoge koorts of ernstig ziek zijn dient de jeugdige met spoed (dezelfde dag) verwezen te worden naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
16 Dit kan een kinderfysiotherapeut, (kinder)oefentherapeut of kinderergotherapeut zijn.
Jeugdreuma (Juveniele Idiopathische Artritis (JIA))
Beschrijving aandoening
Juveniele Idiopathische Artritis (JIA) is de meest voorkomende vorm van jeugdreuma. Men spreekt van JIA wanneer er een chronische artritis is die gedurende tenminste drie maanden in één of meer gewrichten aanwezig is bij een jeugdige jonger dan 16 jaar.
De ziekte is onderverdeeld in meerdere klinische verschillende types: onder andere gebaseerd op het voorkomen van systemische ziektekenmerken, en het aantal betrokken gewrichten. Iedere subgroep is anders wat betreft complicaties, prognose en tot op zekere hoogte wat betreft de behandeling.
Epidemiologie
Jeugdreuma komt voor bij ongeveer 1 op de 1.000 kinderen. In Nederland hebben tussen de 2.000 en 3.000 jeugdigen jeugdreuma.
Gevolgen
JIA kan leiden tot gewrichtsschade met als gevolg chronische pijn en verlies van gewrichtsfunctie. Daarnaast zijn vermoeidheid, pijn, schoolverzuim en moeite met slapen klachten die bij veel JIA-patiënten voorkomen en de kwaliteit van leven beïnvloeden, ongeacht de activiteit van de ziekte [63].
Behandeling
De behandeling van JIA is multidisciplinair, en is gericht op het volledig onderdrukken van ziekteactiviteit en het stimuleren van normale groei en ontwikkeling zodat jeugdigen kunnen deelnemen aan de normale dagelijkse activiteiten zoals spelen, onderwijs, sport en sociale contacten.
Voor de behandeling van jeugdigen met JIA met anti reumatische medicatie heeft de Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde een richtlijn opgesteld [63].
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Bij lichamelijk onderzoek wordt gelet op de algemene indruk van de jeugdige (koorts, ziek zijn). Bij klachten aan heupen of benen onderzoekt de jeugdarts9 het looppatroon. Het gewricht wordt onderzocht op zwelling, afwijkende vorm, pijn of gevoeligheid en warmte. De beweeglijkheid van het betreffende gewricht en naastgelegen gewrichten wordt onderzocht.
Bij jeugdigen met JIA zijn een of meerdere gewrichten warm, pijnlijk, gezwollen en stijf (vooral ’s morgens of na lang zitten of staan).
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
Bij verdenking op JIA dient de jeugdige binnen een week te worden verwezen naar de huisarts.
Afwijkend herstel na trauma
Het kan voorkomen dat een jeugdige na een trauma of letsel (zoals een fractuur of enkelcontusie) klachten blijft houden, JGZ-professionals zullen dit echter weinig tegenkomen tijdens hun contactmomenten. Bij twijfels over het herstel na trauma of letsel (bijvoorbeeld in verband met een afwijkende stand of groei) wordt de jeugdige naar de huisarts of kinderorthopeed verwezen voor verdere beoordeling.
Pectus excavatum
Beschrijving aandoening
Pectus excavatum of ‘trechterborst’/’schoenmakersborst’ is een aandoening waarbij er een kuil aan de voorzijde van de thorax zichtbaar is, het sternum ligt dieper dan de voorzijde van de ribben. Het wordt veroorzaakt door te snelle groei van het ribkraakbeen naast het sternum, waardoor het borstbeen naar achteren geduwd wordt. De oorzaak van de te snelle groei is niet bekend. De diepte van de pectus is zeer variabel. De aandoening is vaak al op jonge leeftijd zichtbaar (2-jarige leeftijd), en verergert vaak tijdens de groeispurt in de puberteit.
Jeugdigen met een pectus excavatum hebben vaak een ‘ineengedoken’ houding met een versterkte kyfose en afhangende schouders. Pectus excavatum kan voorkomen in combinatie met een scoliose, een prolaps van de mitralisklep, een bindweefselaandoening (zoals Marfan-syndroom) of de ziekte van Scheuermann.
Figuur 7: Pectus excavatum
Epidemiologie
Ongeveer 1 op de 300 à 400 jeugdigen heeft een pectus excavatum, de aandoening komt vaker voor bij jongens dan bij meisjes [64].
Gevolgen
De afwijkende vorm van de borstkas kan leiden tot psychosociale problemen (schaamte, negatief zelfbeeld, pesten) [65]. Een pectus excavatum leidt niet vaak tot lichamelijke problemen [64]. In ernstige gevallen kunnen er cardiale of pulmonale problemen optreden, dit is vooral het geval als de voor-achterwaartse diameter van de thorax meer dan de helft is afgenomen [12].
Behandeling
Behandeling van pectus excavatum is vaak niet nodig, alleen als er sprake is van duidelijke cosmetische of lichamelijke klachten kan behandeling wenselijk zijn. Pectus excavatum kan alleen operatief worden behandeld.
Indien er sprake is van houdingsproblemen in combinatie met een pectus excavatum dan kunnen houdings- en sportadviezen worden gegeven.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Indien er geen klachten zijn is nader lichamelijk onderzoek niet nodig. Zo nodig beoordeelt de jeugdarts9 de vorm van de thorax en ausculteert het hart (waarbij wordt gelet op de aanwezigheid van een eventuele souffle).
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
- Uitleg aan ouders en jeugdige dat de aandoening in principe geen kwaad kan, en alleen in zeer ernstige gevallen lichamelijke klachten veroorzaakt. Leg uit dat operatieve correctie eventueel tot de mogelijkheden behoort als er sprake is van duidelijke cosmetische of lichamelijke klachten.
- Advies gericht op de juiste houding, gecombineerd met sport- en beweegadvies (zie sectie 3 Preventie). Er zijn geen specifieke sporten aan- of af te raden, het plezier in sport is een belangrijke factor.
- Indien ouders of jeugdige een operatieve correctie overwegen dan dient (ongeacht de leeftijd) te worden verwezen naar de kinderchirurg, kinderorthopeed of thoraxchirurg.
Pectus carinatum
Beschrijving aandoening
Pectus carinatum of ‘kippenborst’ is een aandoening waarbij het sternum naar voren uitsteekt. Het wordt veroorzaakt door te snelle groei van het ribkraakbeen naast het sternum, waardoor het borstbeen naar voren geduwd wordt. De exacte oorzaak hiervan is onbekend. De ernst van de pectus is zeer variabel. De aandoening is vaak al op jonge leeftijd zichtbaar (2-jarige leeftijd), en verergert vaak tijdens de groeispurt in de puberteit. Pectus carinatum komt soms voor in combinatie met een scoliose, hartafwijkingen (zoals afwijkingen aan de mitralisklep) of een syndroom (zoals Marfan- of Poland syndroom).
Figuur 8: Pectus carinatum.
Epidemiologie
Pectus carinatum komt minder vaak voor dan pectus excavatum, de geschatte prevalentie is 1 op de 1500-1700 mensen [66].
Gevolgen
De afwijkende vorm van de borstkas kan leiden tot psychosociale problemen (schaamte, negatief zelfbeeld, pesten). Door een afname van de flexibiliteit van de thorax kunnen er pijnklachten optreden bij het borstbeen, kortademigheid bij inspanning, vermoeidheid en een verminderd uithoudingsvermogen.
Behandeling
Behandeling van pectus carinatum is in principe niet nodig, alleen als er sprake is van duidelijke cosmetische of lichamelijke klachten kan behandeling wenselijk zijn. Pectus carinatum kan met een brace of een operatie worden behandeld door de kinderchirurg, kinderorthopeed of thoraxchirurg.
Taken JGZ
Wijze van signaleren: Actief opsporen is niet nodig.
Lichamelijk onderzoek:
Indien er geen klachten zijn is nader lichamelijk onderzoek niet nodig. Zo nodig beoordeelt de jeugdarts9 de vorm van de thorax en ausculteert het hart (waarbij wordt gelet op de aanwezigheid van een eventuele souffle).
Beleid (op basis van consensus werkgroep):
- Uitleg aan ouders en jeugdige dat de aandoening in principe geen kwaad kan, en alleen in zeer ernstige gevallen lichamelijk klachten veroorzaakt. Leg uit dat een brace of operatieve correctie eventueel tot de mogelijkheden behoort als er sprake is van duidelijke cosmetische of lichamelijke klachten.
- Advies gericht op de juiste houding, gecombineerd met sport- en beweegadvies (zie sectie 3).
- Indien ouders of jeugdige een brace of een operatieve correctie overwegen dan dient (ongeacht de leeftijd) te worden verwezen naar de kinderchirurg, kinderorthopeed of thoraxchirurg.
9.2 Bijlage 2: symptomen en aandoenigen rond het onderwerp houding en beweging
Per onderwerp staat beschreven in welke JGZ Richtlijn informatie over het onderwerp te vinden is.
| Onderwerp | |
| Aangeboren afwijkingen (bijv. standsafwijkingen zoals dwerggroei/syndromen) | In diverse richtlijnen, aspecifiek onderwerp |
| Afwijkend herstel na trauma | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Beenlengteverschil | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Camptodactylie | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Cerebrale parese | JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling |
| Cumulative Trauma Disorders, zie KANS (Klachten Arm, Nek en/of Schouder) | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) |
JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling Richtlijn DCD (Federatie Medisch Specialisten) |
| Fysieke over- en onderbelasting | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Gewrichtsklachten (bijv. reuma) | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Hakvoet | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Hernia | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Heupdysplasie | JGZ Richtlijn Heupdysplasie |
| Hyperlaxiteit/hypermobiliteit | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Hypotonie en hypertonie | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| KANS (Klachten Arm, Nek en/of Schouder) | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Klompvoet | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Krulteen | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Kyfose | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Lengte | JGZ Richtlijn Lengtegroei |
| Lordose | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Metatarsus adductus | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Metatarsus primus varus | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Nekklachten door houding hoofd, zie KANS (Klachten Arm, Nek en/of Schouder) | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| O-benen | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Ondergewicht | JGZ Richtlijn Ondergewicht |
| Osgood Schlatter | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Overgewicht | JGZ Richtlijn Overgewicht |
| Pectus carinatum/excavatum | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Platvoeten | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Polydactylie | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| RSI (Repetitive strain injury), zie KANS (Klachten Arm, Nek en/of Schouder) | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Rugklachten | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Schedelasymmetrie | JGZ Richtlijn Voorkeurshouding en schedelvervorming |
| Scheuermann | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Schrijfproblemen | JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling |
| Scoliose | Let op, de JGZ Richtlijn Scoliose is niet meer geldig. In de richtlijn Houding en Bewegen wordt Scoliose wel benoemd |
| Somatisch Onvoldoende Verklaarde Klachten (SOLK) | Richtlijn SOLK (Federatie Medisch Specialisten) |
| Spierverkortingen | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Spierziekten | JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling |
| Spina bifida | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Statische of eenzijdige houding | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Struikelen | JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling |
| Syndactylie | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Tenenloop | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Toeing in JGZ | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Torticollis | JGZ Richtlijn Voorkeurshouding en schedelvervorming |
| Tremoren | JGZ Richtlijn Houding en bewegen |
| Triggerfinger/duim | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Voorkeurshoudingen | JGZ Richtlijn Voorkeurshouding en schedelvervorming |
| X-benen | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
| Ziekte van Perthes | JGZ Richtlijn Extremiteiten |
9.3 Bijlage 3: adviezen bewegen
Voor alle leeftijden
Zie de JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling voor adviezen rond bewegen en de motorische ontwikkeling.
Buitenspelen: Elke dag buitenspelen is gezond, ook als het regent. Via Playadvisor en Volksgezondheidenzorg zijn buitenspeelplekken in de buurt te vinden.
Binnenspelen: Ook bij binnenspelen kunnen kinderen actief bewegen. Bijvoorbeeld dansen, verstoppertje spelen, een klauterparcours maken over banken, tafels en stoelen, etc. Voor meer voorbeelden, kijk op Huisvoorbeweging en Dutchgymnastics. Daarnaast zijn er ook allerlei elektronische beweeggames waarbij jeugdigen gestimuleerd worden te bewegen.
Gezond bewegen in het dagelijks leven: Stimuleer ouders bijvoorbeeld om hun kinderen van- en naar school te laten lopen of fietsen, dan bewegen zij meer dan als zij gebracht en gehaald worden met de auto.
Georganiseerde beweegactiviteiten en sporten:
- Vanaf welke leeftijd. Al vanaf jonge leeftijd kunnen kinderen (en hun ouders) meedoen met georganiseerde beweegactiviteiten. Kijk voor meer informatie op de website Alles-over-sport.
- Armoede en sport. Er zijn allerlei mogelijkheden om aan sport deel te nemen, ook al hebben ouders daar geen geld voor. Juist voor kinderen die opgroeien in armoede kan bewegen extra betekenis hebben, zoals voor vriendschappen, structuur, normen en waarden, etc. [67]. Veel gemeenten zijn aangesloten bij het Jeugdfonds Sport & Cultuur. Zij betalen zo nodig de contributie van de sportvereniging. De spelregels voor deelname zijn voor iedere gemeente anders. Kijk op de website Jeugdfondssportencultuur voor meer informatie. Ouders kunnen zelf geen aanvraag doen, maar een intermediair wel (bijv. de JGZ-professional, leerkracht, buurtsportcoach, cultuurcoach, schuldhulpverlener, jeugdhulpverlener, vrijwilliger van de Stichting Leergeld of het sociaal wijkteam). Er kan om een inkomensbewijs van de ouders worden gevraagd. Ook Leergeld kan de contributie van de sportclub of bijv. de sportuitrusting van kinderen die in armoede opgroeien betalen. Kijk op de website Leergeld voor meer informatie.
- Kinderen met een beperking. Via Sport.nl kun je via de Sportwijzer een sport zoeken die past bij de mogelijkheden van het kind.
- Buurtsportcoaches. Buurtsportcoaches werken in de wijk of buurt samen met diverse organisaties om meer mensen te laten sporten en bewegen. Bijna alle gemeenten hebben een buurtsportcoach. Buurtsportcoaches zijn lokaal actief in uiteenlopende settings en voor diverse doelgroepen. In sommige gemeenten heeft de buurtsportcoach een andere naam, bijvoorbeeld combinatiefunctionaris, beweegconsulent, leefstijlmakelaar of talentcoach. Kijk op Alles-over-sport voor meer informatie.
- Welke sport? Het is belangrijk een sport te kiezen die bij het kind past. Via Sportwijzer kun je nagaan welke sport het beste bij het kind past.
Risicovol spelen. Bij risicovol spelen gaan kinderen aan de slag met spannende, uitdagende en avontuurlijke activiteiten, waarbij een risico bestaat op een (kleine) verwonding. Risicovol spelen heeft niet alleen een positieve invloed op fysieke gezondheid, het vergroot ook het zelfvertrouwen, zelfredzaamheid, doorzettingsvermogen en sociale vaardigheden van kinderen. Meer informatie is te vinden op de website van VeiligheidNL.
Voorkomen van sportblessures. Het gradueel opbouwen in intensiteit, frequentie en variatie van fysieke activiteiten, bijvoorbeeld een paar weken voordat de sport (weer) begint, kan sportblessures voorkomen. Zie voor meer informatie Veiligheid.nl
Baby’s van 0-1 jaar
- Gedurende de dag bewegen op verschillende momenten en op verschillende manieren. Meer bewegen is beter.
- Zie de JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling voor adviezen rond buikligging onder toezicht en het voorkomen van langdurig in een zittende houding doorbrengen bij baby’s.
Kinderen van 1-3 jaar:
- Minstens 180 minuten per dag bewegen op verschillende manieren, verspreid over de dag. Meer bewegen is beter.
Kinderen van 3-4 jaar:
- Minstens 180 minuten per dag bewegen op verschillende manieren, waarvan minstens 60 minuten matig- tot intensief actief bewegen, verspreid over de dag. Meer bewegen is beter.
Kinderen van 4-18 jaar [4]:
- Bewegen is goed, meer bewegen is beter.
- Doe minstens elke dag een uur aan matig intensieve inspanning. Bij matig intensief bewegen gaat het om het krijgen van een hogere hartslag en een versnelde ademhaling. Dat gebeurt bijvoorbeeld bij fietsen, trampolinespringen, zwemmen, voetballen, tennis, op straat spelen of paardrijden.
- Langer, vaker en/of intensiever bewegen geeft extra gezondheidsvoordeel.
- Doe minstens driemaal per week spier- en botversterkende activiteiten. Botversterkende activiteiten zijn activiteiten waarbij je lichaam met je eigen gewicht wordt belast, zoals springen, traplopen, hardlopen en dansen. Spierversterkende activiteiten zijn activiteiten die kracht en uithoudingsvermogen van de spieren verbeteren (zie Alles-over-sport).
- En: voorkom veel stilzitten.
9.4 Bijlage 4: voorbeelden overzicht beweeginterventies met aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit
Beweeginterventies
| Beweeginterventies | Primaire doelgroep | Inhoud | Beoordeling/erkenning | Rol JGZ |
| B-Fit | Kinderen van 2 t/m 15 jaar. | Voorkomen en stabiliseren van de groei van overgewicht. | Eerste aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit. | Deze interventie wordt op de school uitgevoerd, door een B-Fit coach. De JGZ heeft een actieve, adviserende rol spelen naar scholen over het bestaan en gebruik van deze interventie. |
| Vallen is ook een sport | Kinderen van 4 t/m 12 jaar. | Gericht op veilig vallen. | Eerste aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit | De interventie vindt plaats op de basisschool, tijdens de lessen bewegingsonderwijs. De JGZ heeft een actieve, adviserende rol spelen naar scholen over het bestaan en gebruik van deze interventie. |
| PLAYgrounds | Kinderen van 6 t/m 12 jaar. | Stimuleren van lichamelijke activiteit door inrichting schoolplein | Goede aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit. | De school (evt. in samenwerking met de gemeente) voert deze interventie uit. De JGZ heeft een actieve, adviserende rol naar scholen over het bestaan en gebruik van deze interventie. |
| Lekker Fit! Basisonderwijs. | Kinderen van 6 t/m 12 jaar. | Stimuleren van een gezonder voedingspatroon en kwalitatief en beter bewegen. | Eerste aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit. | De uitvoerders van deze interventie zijn vakleerkracht Lichamelijke Opvoeding, een schooldiëtist en sportdocenten van een (school)sportvereniging. De JGZ heeft een actieve, adviserende rol spelen naar scholen over het bestaan en gebruik van deze interventie. |
| LEFF | Kinderen van 7 t/m 12 jaar met overgewicht of obesitas. | Stimuleren van een gezonder voedings- en beweegpatroon. | Eerste aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit. | LEFF wordt op landelijk niveau gecoördineerd. Lokale coördinatie gebeurt door gemeente of o.a. welzijnsorganisaties, sportorganisatie en GGD-en. De JGZ kan een rol spelen bij de toeleiding en werving naar LEFF voor jeugdigen (Kenniscentrum Sport & Bewegen). |
| Realfit | Jongeren tussen 13 en 18 jaar. | Afname of stabilisatie van overgewicht. | Goede aanwijzingen voor effectiviteit. | De uitvoering vindt plaats door een fitnesscentrum. De JGZ heeft een actieve, adviserende rol naar jeugdigen over bestaan van deze interventie. |
Houdingsinterventies
| Houdingsinterventie | Primaire doelgroep | Inhoud | Beoordeling/erkenning | Rol JGZ | Link |
| Zit met Pit! | Groep 5 of 6 | Het aanleren van een goede houding en gezond gedrag rondom zitten, bewegen en computergebruik | Goed beschreven. | Een actieve, adviserende rol spelen naar scholen over het bestaan en gebruik van deze interventie. | Meer informatie |
Referenties
[1] Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg. 2017
[2] Van Empelen R, Nijhuis-van der Sanden R, Hartman A. Kinderfysiotherapie. Vierde druk. Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum. 2016
[3] Leefstijlmonitor 2018
https://www.sportenbewegenincijfers.nl/kernindicatoren/%20[4] Gezondheidsraad. Advies beweegrichtlijnen 2017. Den Haag. 2017
[5] Guidelines on Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour and Sleep for Children under 5 Years of Age 2019
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31091057[6] Bailey R, Hillman C, Arent S, Petitpas A. Physical activity: an underestimated investment in human capital? Journal of physical activity & health 2013;10(3):289-308
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23620387[7] Donnelly JE, Hillman CH, Castelli D, Etnier JL, Lee S, Tomporowski P, Lambourne K, Szabo-Reed AN. Physical Activity, Fitness, Cognitive Function, and Academic Achievement in Children: A Systematic Review. Medicine and science in sports and exercise 2016;48(6):1197-222
http://dx.doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000901 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27182986[8] Sullivan RA, Kuzel AH, Vaandering ME, Chen W. The Association of Physical Activity and Academic Behavior: A Systematic Review. The Journal of school health 2017;87(5):388-398
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/josh.12502 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28382668[9] Veldman SLC, Altenburg TM, Chin A Paw M. Literatuuronderzoek Associaties tussen Lichamelijke Activiteit en Groei en Ontwikkeling bij 0-5 jarige Kinderen Amsterdam: Amsterdam UMC, locatie VUmc. 2019
[10] Timmons BW, Leblanc AG, Carson V, Connor Gorber S, Dillman C, Janssen I, Kho ME, Spence JC, Stearns JA, Tremblay MS. Systematic review of physical activity and health in the early years (aged 0-4 years). Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme 2012;37(4):773-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/h2012-070 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22765840[11] Zeng N, Ayyub M, Sun H, Wen XU, Xiang P, Gao Z. Effects of Physical Activity on Motor Skills and Cognitive Development in Early Childhood: A Systematic Review. BioMed research international 2017;2017():2760716
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2017/2760716 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29387718[12] Hefti F. Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York. ISBN-13: 978-3-540-69963-7. 2007
[13] Van der Sluijs JA, Sakkers RJB, Bronswijk JAHM. Praktische Kindergeneeskunde: Kinderorthopedie. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten. 2009
[14] Vissers J. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. Telenga drukwerk service, Groningen. 2012
[15] Talma H, Schönbeck Y, van Dommelen P, Bakker B, van Buuren S, Hirasing RA. Trends in menarcheal age between 1955 and 2009 in the Netherlands. PloS one 2013;8(4):e60056
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060056 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23579990[16] Seregni F, Weatherby T, Beardsall K. Do all newborns with an isolated sacrococcygeal dimple require investigation for spinal dysraphism? Archives of disease in childhood 2019;104(8):816-817
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2019-317058 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31113767[17] Schönbeck Y, Hindori-Mohangoo AD, Masurel N, van der Pal-de Bruin KM. Aangeboren afwijkingen in Nederland 2001-2013: Gebaseerd op de landelijke perinatale registraties. TNO/CH 2015 R11267. TNO, Leiden. 2015
[18] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de JGZ. Koninklijke van Gorcum BV. ISBN-13: 9789023241911. 2005
[19] Touwen BCL. De neurologische ontwikkeling van de zuigeling. Utrecht/Antwerpen: Bohn Scheltema & Holkema. 1984
[20] Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, Czaprowski D, Schreiber S, de Mauroy JC, Diers H, Grivas TB, Knott P, Kotwicki T, Lebel A, Marti C, Maruyama T, O'Brien J, Price N, Parent E, Rigo M, Romano M, Stikeleather L, Wynne J, Zaina F. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis and spinal disorders 2018;13():3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13013-017-0145-8 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29435499[21] Wajchenberg M, Astur N, Kanas M, Martins DE. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: current concepts on neurological and muscular etiologies. Scoliosis and spinal disorders 2016;11():4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13013-016-0066-y https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27355084[22] Rogala EJ, Drummond DS, Gurr J. Scoliosis: incidence and natural history. A prospective epidemiological study. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1978;60(2):173-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/641080[23] Lonstein JE, Carlson JM. The prediction of curve progression in untreated idiopathic scoliosis during growth. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1984;66(7):1061-71
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6480635[24] Pehrsson K, Larsson S, Oden A, Nachemson A. Long-term follow-up of patients with untreated scoliosis. A study of mortality, causes of death, and symptoms. Spine 1992;17(9):1091-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1411763[25] Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Spratt KF, Peterson KK, Spoonamore MJ, Ponseti IV. Health and function of patients with untreated idiopathic scoliosis: a 50-year natural history study. JAMA 2003;289(5):559-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12578488[26] Lissak G. Adverse physiological and psychological effects of screen time on children and adolescents: Literature review and case study. Environmental research 2018;164():149-157
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.01.015 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29499467[27] Radesky JS, Schumacher J, Zuckerman B. Mobile and interactive media use by young children: the good, the bad, and the unknown. Pediatrics 2015;135(1):1-3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-2251 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25548323[28] Mediawijzer.net.. Iene Miene Media 2018. 2018
https://www.mediawijzer.net/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2018/04/Onderzoek-IeneMieneMedia-2018.pdf[29] NVK, AJN, V&VN,, Erasmus MC, HNN, IVO, TNO, NCJ, NJi, VUmc. Factsheet beeldschermgebruik van dichtbij. 2018
http://ajnjeugdartsen.nl/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Factsheet-beeldschermgebruik-2018-1.pdf[30] Straker L, Abbott R, Collins R, Campbell A. Evidence-based guidelines for wise use of electronic games by children. Ergonomics 2014;57(4):471-89
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2014.895856 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24665962[31] Straker L, Maslen B, Burgess-Limerick R, Johnson P, Dennerlein J. Evidence-based guidelines for the wise use of computers by children: physical development guidelines. Ergonomics 2010;53(4):458-77
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00140130903556344 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20309743[32] Potthoff T, de Bruin ED, Rosser S, Humphreys BK, Wirth B. A systematic review on quantifiable physical risk factors for non-specific adolescent low back pain. Journal of pediatric rehabilitation medicine 2018;11(2):79-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/PRM-170526 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30010152[33] Brink Y, Louw QA. A systematic review of the relationship between sitting and upper quadrant musculoskeletal pain in children and adolescents. Manual therapy 2013;18(4):281-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2012.11.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23298827[34] Huguet A, Tougas ME, Hayden J, McGrath PJ, Stinson JN, Chambers CT. Systematic review with meta-analysis of childhood and adolescent risk and prognostic factors for musculoskeletal pain. Pain 2016;157(12):2640-2656
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000685 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27525834[35] Wirth B, Potthoff T, Rosser S, Humphreys BK, de Bruin ED. Physical risk factors for adolescent neck and mid back pain: a systematic review. Chiropractic & manual therapies 2018;26():36
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12998-018-0206-y https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30258567[36] Hill JJ, Keating JL. Risk factors for the first episode of low back pain in children are infrequently validated across samples and conditions: a systematic review. Journal of physiotherapy 2010;56(4):237-44
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21091413[37] Calvo-Muñoz I, Kovacs FM, Roqué M, Gago Fernández I, Seco Calvo J. Risk Factors for Low Back Pain in Childhood and Adolescence: A Systematic Review. The Clinical journal of pain 2018;34(5):468-484
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0000000000000558 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28915154[38] Kamper SJ, Yamato TP, Williams CM. The prevalence, risk factors, prognosis and treatment for back pain in children and adolescents: An overview of systematic reviews. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology 2016;30(6):1021-1036
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2017.04.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29103547[39] Yamato TP, Maher CG, Traeger AC, Wiliams CM, Kamper SJ. Do schoolbags cause back pain in children and adolescents? A systematic review. British journal of sports medicine 2018;52(19):1241-1245
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-098927 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29720469[40] Collard DCM, Verhagen EALM, Chinapaw MJM, Knol DL, van Mechelen W. Effectiveness of a school-based physical activity injury prevention program: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2010;164(2):145-50
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2009.256 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20124143[41] Nauta J, van Mechelen W, Otten RHJ, Verhagen EALM. A systematic review on the effectiveness of school and community-based injury prevention programmes on risk behaviour and injury risk in 8-12 year old children. Journal of science and medicine in sport 2014;17(2):165-72
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2013.07.011 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23962868[42] MacDonald J, Stuart E, Rodenberg R. Musculoskeletal Low Back Pain in School-aged Children: A Review. JAMA pediatrics 2017;171(3):280-287
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.3334 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28135365[43] Jayanthi NA, Post EG, Laury TC, Fabricant PD. Health Consequences of Youth Sport Specialization. Journal of athletic training 2019;54(10):1040-1049
http://dx.doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-380-18 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31633420[44] Castellucci HI, Arezes PM, Molenbroek JFM, de Bruin R, Viviani C. The influence of school furniture on students' performance and physical responses: results of a systematic review. Ergonomics 2017;60(1):93-110
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2016.1170889 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27015656[45] Sandseter EB. Categorising risky play—how can we identify risk‐taking in children's play?. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal 15(2):237-252 2007
[46] Brussoni M, Gibbons R, Gray C, Ishikawa T, Sandseter EBH, Bienenstock A, Chabot G, Fuselli P, Herrington S, Janssen I, Pickett W, Power M, Stanger N, Sampson M, Tremblay MS. What is the Relationship between Risky Outdoor Play and Health in Children? A Systematic Review. International journal of environmental research and public health 2015;12(6):6423-54
http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120606423 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26062038[47] Van Wieringen JCM, Beckers M. Hoe krijgt de jeugdgezondheidszorg de jeugd in beweging? Tijdschrift voor jeugdgezondheidszorg 47: 92–95. 2015
[48] Kenniscentrum Sport, Stichting Opvoeden.nl. Landelijk Ouderpanel; Hoe denken ouders over sport en bewegen? Resultaten van de peiling. 2019
https://opvoedinformatie.nl/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Def.-Samenvatting-peiling-ouders-over-sport-en-bewegen-2-geconverteerd.pdf[49] Van Wieringen JCM. Standpunt beweegstimulering door de jeugdgezondheidszorg. RIVM rapport 295002001. RIVM, Bilthoven. 2009
[50] Kenniscentrum Sport. Sport- en beweeginterventies. 2019
https://www.kenniscentrumsport.nl/sportinterventies-en-beweeginterventies/[51] Zwikker M, Van Dale D, Dinnink T, Willemse G, Van Rooijen S, Heeringa N, Rensen P. Erkenning van interventies. Criteria voor gezamenlijke kwaliteitsbeoordeling 2015-2018. RIVM, NJi, NISB, Trimbos instituut, Vilans, Movisie, NCJ. 2015
[52] Kriemler S, Meyer U, Martin E, van Sluijs EMF, Andersen LB, Martin BW. Effect of school-based interventions on physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents: a review of reviews and systematic update. British journal of sports medicine 2011;45(11):923-30
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2011-090186 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21836176[53] Gordon ES, Tucker P, Burke SM, Carron AV. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions for preschoolers: a meta-analysis. Research quarterly for exercise and sport 2013;84(3):287-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24261007[54] Van Empelen P, Schokker D. Factsheet: Werkzame elementen van voeding- en beweeginterventies. Slimme combinaties van gedragsveranderingstechnieken. TNO, Leiden. 2015
[55] Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, . GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2008;336(7650):924-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18436948[56] Makurthou AA, Oei L, El Saddy S, Breda SJ, Castaño-Betancourt MC, Hofman A, van Meurs JBJ, Uitterlinden AG, Rivadeneira F, Oei EHG. Scheuermann disease: evaluation of radiological criteria and population prevalence. Spine 2013;38(19):1690-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31829ee8b7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24509552[57] Wijga AH, Scholtens S, van Oeffelen AAM, Beckers M. Klachten en kwalen bij kinderen in Nederland. Omvang en gevolgen geïnventariseerd. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu (RIVM), RIVM Rapport 260136001/2010. 2010
[58] Calvo-Muñoz I, Gómez-Conesa A, Sánchez-Meca J. Prevalence of low back pain in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. BMC pediatrics 2013;13():14
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-13-14 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23351394[59] Bons SCS, Borg MAJP, Van den Donk M, Koes BW, Kuijpers T, Ostelo RWJG, Schaafstra A, Spinnewijn WEM, Verburg-Oorthuizen AFE, Verweij HA. NHG-Standaard Aspecifieke lagerugpijn (Tweede herziening). 2017
[60] Multidisciplinaire richtlijn ‘Aspecifieke klachten arm, nek en/of schouders’. Amersfoort: KNGF. 2012
[61] Kunnamo I, Kallio P, Pelkonen P. Incidence of arthritis in urban Finnish children. A prospective study. Arthritis and rheumatism 1986;29(10):1232-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3768057[62] NVK werkboek kinderinfectieziekten. 2020
https://werkboeken.nvk.nl/kinderinfectieziekten/Orgaansysteem/Botten-en-gewrichten[63] NVK. Richtlijn medicamenteuze behandeling van kinderen met juveniele idiopathische artritis 2017
[64] Hebra A. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1004953-overview (bezocht op 26-2-2019). 2018
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1004953-overview%20(bezocht%20op%2026-2-2019).[65] Ji YI, Liu W, Chen S, Xu B, Tang Y, Wang X, Yang G, Cao L. Assessment of psychosocial functioning and its risk factors in children with pectus excavatum. Health and quality of life outcomes 2011;9():28
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-9-28 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21542911[66] Obermeyer RJ, Goretsky MJ. Chest wall deformities in pediatric surgery. The Surgical clinics of North America 2012;92(3):669-84, ix
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2012.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22595715[67] Kenniscentrum Sport. Factsheet jeugd - armoede - sport 2017
https://www.kennisbanksportenbewegen.nl/?file=8235&m=1511185328&action=file.download[68] Perrone M, Orr R, Hing W, Milne N, Pope R. The Impact of Backpack Loads on School Children: A Critical Narrative Review. International journal of environmental research and public health 2018;15(11):
http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112529 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30424517Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackLET OP: print de JGZ-richtlijn in liggende afdrukstand!
Grote tabellen zijn niet volledig zichtbaar als de JGZ-richtlijn in staande afdrukstand geprint wordt. Om kleuren in de printversie goed door te laten komen, moet bij de printerinstellingen Achtergrondillustraties aangezet worden.
Disclaimer printversie JGZ-richtlijnen
De printversie van de JGZ-richtlijn bevat de algemene tekst inclusief de aanbevelingen. De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing is terug te vinden op de website, bij de aanbevelingen onder de link “Evidence”.
