Het gebruik van oxytocine neusspray (Syntocinon) lijkt tijdelijk de toeschietreflex te bevorderen. Een betere lediging van de borst door een goede toeschietreflex bevordert de productie en in die zin kan de neusspray bijdragen aan een goed verlopende lactatie. Maar in een onderzoek bij moeders van premature baby’s naar gebruik van oxytocine neusspray ter bevordering van de toeschietreflex, in combinatie met een elektrische kolf ter bevordering van de melkproductie, bleek er geen verschil in de hoeveelheid moedermelk die gedurende de eerste vijf dagen postpartum was gekolfd[21]. De gevolgen van gebruik gedurende een langere periode zijn niet onderzocht.
1.2.5 Oxytocine neusspray
Richtlijn Borstvoeding (JGZ, multidisciplinair)
Richtlijn Borstvoeding (JGZ, multidisciplinair)
Let op: deze richtlijn is momenteel in herziening.
Dit betekent niet dat de inhoud van deze richtlijn incorrect is. Tot de herziening blijft de richtlijn leidend voor de praktijk. Wel bestaat er een kans dat een deel van de informatie verouderd is.
Heb je feedback over deze JGZ-richtlijn? Stuur jouw feedback naar onze servicedesk. Zoek het tekstgedeelte waarbij je suggesties voor verbetering hebt. Via de knop ‘Geef jouw feedback’ kun je voor deze JGZ-richtlijn en het specifieke hoofdstuk jouw suggesties doorgeven.
Richtlijn inhoudsopgave
1 Definitie en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 1 Definitie en achtergrond informatie
2 Preventie en begeleiden Ga naar pagina over 2 Preventie en begeleiden
3 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 3 Totstandkoming richtlijn
4 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 4 Verantwoording
1 Definitie en achtergrond informatie Ga naar pagina over 1 Definitie en achtergrond informatie
2 Preventie en begeleiden Ga naar pagina over 2 Preventie en begeleiden
3 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 3 Totstandkoming richtlijn
4 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 4 Verantwoording
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackRandvoorwaardelijke implicaties richtlijn Borstvoeding
Rapportage praktijktest richtlijn Borstvoeding
PP-presentatie voor de scholing Borstvoeding
[1] Riordan J., Wambach K.. Anatomy and Physiology of Lactation. 2010
[2] Kent JC, Mitoulas LR, Cregan MD, Ramsay DT, Doherty DA, Hartmann PE. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics 2006;117(3):e387-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16510619[3] Cadwell K. Latching-on and suckling of the healthy term neonate: breastfeeding assessment. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):638-42
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17984002[4] Inch S, Fisher C. Breastfeeding: early problems. The practising midwife 2000;3(1):12-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11029947[5] Inch S. Breastfeeding problems: prevention and management. Community practitioner : the journal of the Community Practitioners' & Health Visitors' Association 2006;79(5):165-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16724483[6] Mulder PJ. A concept analysis of effective breastfeeding. Journal of obstetric, gynecologic, and neonatal nursing : JOGNN 2006;35(3):332-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16700682[7] Walker M. Breast-feeding: good starts, good outcomes. The Journal of perinatal & neonatal nursing 2007;21(3):191-7; quiz 198-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17700094[8] Henderson A, Stamp G, Pincombe J. Postpartum positioning and attachment education for increasing breastfeeding: a randomized trial. Birth (Berkeley, Calif.) 2001;28(4):236-42
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11903211[9] Kronborg H, Vaeth M, Olsen J, Iversen L, Harder I. Effect of early postnatal breastfeeding support: a cluster-randomized community based trial. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(7):1064-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17524018[10] Wallace LM, Dunn OM, Alder EM, Inch S, Hills RK, Law SM. A randomised-controlled trial in England of a postnatal midwifery intervention on breast-feeding duration. Midwifery 2006;22(3):262-73
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16380197[11] Reede-Dunselman de A.. Begeleiding bij borstvoeding. 2010
[12] Colson SD, Meek JH, Hawdon JM. Optimal positions for the release of primitive neonatal reflexes stimulating breastfeeding. Early human development 2008;84(7):441-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2007.12.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18243594[13] Hale T.W., Hartmann P.E.. Textbook of human lactation. 2007
[14] Ramsay DT, Kent JC, Owens RA, Hartmann PE. Ultrasound imaging of milk ejection in the breast of lactating women. Pediatrics 2004;113(2):361-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14754950[15] Geddes DT. Inside the lactating breast: the latest anatomy research. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):556-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983992[16] Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.. Breastfeeding: a guide for the medical profession. 2005
[17] Jordan S, Emery S, Watkins A, Evans JD, Storey M, Morgan G. Associations of drugs routinely given in labour with breastfeeding at 48 hours: analysis of the Cardiff Births Survey. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2009;116(12):1622-9; discussion 1630-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02256.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19735379[18] Becker GE, McCormick FM, Renfrew MJ. Methods of milk expression for lactating women. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2008
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006170.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18843707[19] Biancuzzo M. Selecting pumps for breastfeeding mothers. Journal of obstetric, gynecologic, and neonatal nursing : JOGNN 1999;28(4):417-26
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10438087[20] Jones E, Dimmock PW, Spencer SA. A randomised controlled trial to compare methods of milk expression after preterm delivery. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2001;85(2):F91-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11517200[21] Fewtrell MS, Loh KL, Blake A, Ridout DA, Hawdon J. Randomised, double blind trial of oxytocin nasal spray in mothers expressing breast milk for preterm infants. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2006;91(3):F169-74
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16223754[22] Van der Wijden C, Kleijnen J, Van den Berk T. Lactational amenorrhea for family planning. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2003
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14583931[23] Lanting C.I., Heerdink-Obenhuijsen N., Schuit-van Raamsdonk H.L.L., Hofman-van den Hoogen E.M.M., Leeuwenburg-Grijseels E.H., Broerse A.. JGZ-Richtlijn Voeding en Eetgedrag. 2013
https://www.jgzrichtlijnen.nl/alle-richtlijnen/richtlijn/voeding-en-eetgedrag[24] Gezondheidsraad. Vitamine K-suppletie bij zuigelingen. 2010;11():
https://www.gezondheidsraad.nl/binaries/gezondheidsraad/documenten/adviezen/2010/06/29/vitamine-k-suppletie-bij-zuigelingen/dossier-briefadvies-over-vitamine-k-suppletie-bij-zuigelingen.pdf[25] Gezondheidsraad. Evaluatie van de voedingsnormen voor vitamine D 2012;15():
https://www.gezondheidsraad.nl/binaries/gezondheidsraad/documenten/adviezen/2012/09/26/evaluatie-van-de-voedingsnormen-voor-vitamine-d/201215evaluatievoedingsnormenvitamineD.pdf[26] Kazi A, Kennedy KI, Visness CM, Khan T. Effectiveness of the lactational amenorrhea method in Pakistan. Fertility and sterility 1995;64(4):717-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7672141[27] Pérez A, Labbok MH, Queenan JT. Clinical study of the lactational amenorrhoea method for family planning. Lancet (London, England) 1992;339(8799):968-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1348806[28] Ramos R, Kennedy KI, Visness CM. Effectiveness of lactational amenorrhoea in prevention of pregnancy in Manila, the Philippines: non-comparative prospective trail. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 1996;313(7062):909-12
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8876092[29] van Wouwe JP, Lanting CI, van Dommelen P, Treffers PE, van Buuren S. Breastfeeding duration related to practised contraception in the Netherlands. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2009;98(1):86-90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2008.01019.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18771482[30] Kremer JA, Schellekens LA, Rolland R. [Contraception following pregnancy]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1994;138(38):1898-900
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7935934[31] Neville M.C., Walsh C.T.. Effects of drugs on milk secretion and composition. 1996
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044481981-9/50021-7[32] Truitt ST, Fraser AB, Grimes DA, Gallo MF, Schulz KF. Hormonal contraception during lactation. systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Contraception 2003;68(4):233-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14572885[33] Kapp N, Curtis KM. Combined oral contraceptive use among breastfeeding women: a systematic review. Contraception 2010;82(1):10-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2010.02.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20682139[34] Kapp N, Curtis K, Nanda K. Progestogen-only contraceptive use among breastfeeding women: a systematic review. Contraception 2010;82(1):17-37
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2010.02.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20682140[35] Hale T.W.. Medications and Mothers’ Milk: A Manual of Lactational Pharmacology 2010
[36] Anticonceptiepleister en hormoonbelasting. Geneesmiddelenbulletin 2008
https://www.ge-bu.nl/artikel/anticonceptiepleisters-en-hormoonbelasting[37] Grimes DA, Lopez LM, Van Vliet HAAM, Stanwood NL. Immediate post-partum insertion of intrauterine devices. 2010
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD003036.pub2/abstract[38] Brand A, Bruinsma A, van Groeningen K, Kalmijn S, Kardolus I, Peerden M, Smeenk R, de Swart S, Kurver M, Goudswaard L. NHG-Standaard Anticonceptie Huisarts en Wetenschap 2011;54(12)():652
https://www.henw.org/files/2018-07/H%26W%2012_LR%20incl%20omslag.pdf[39] Trussell J. Contraceptive failure in the United States. Contraception 2011;83(5):397-404
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2011.01.021 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21477680[40] Möhner S, Heinemann K, Westhoff C, Grimes A. Intrauterine Devices and the Risk of Uterine Perforations: Final Results From the EURAS-IUD Study Obstetrics and Gynecology 2014;123 (1)():
http://dx.doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000000209 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261921403_Intrauterine_Devices_and_the_Risk_of_Uterine_Perforations_Final_Results_from_the_EURAS-IUD_Study[41] Frank-Herrmann P, Heil J, Gnoth C, Toledo E, Baur S, Pyper C, Jenetzky E, Strowitzki T, Freundl G. The effectiveness of a fertility awareness based method to avoid pregnancy in relation to a couple's sexual behaviour during the fertile time: a prospective longitudinal study. Human reproduction (Oxford, England) 2007;22(5):1310-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17314078[42] Jahanfar S, Ng CJ, Teng CL. Antibiotics for mastitis in breastfeeding women. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2013
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005458.pub3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23450563[43] Betzold CM. An update on the recognition and management of lactational breast inflammation. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):595-605
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983997[44] Beentjes MM, Weersma RLS, Koch W, Offringa AK, Verduijn MM, Mensink PAJS, Wiersma TJ, Goudswaard AN, van Asselt KM. NHG-Standaard Zwangerschap en kraamperiode (Tweede herziening). Huisarts en Wetenschap 2012;55(3)():112
https://www.nhg.org/standaarden/volledig/nhg-standaard-zwangerschap-en-kraamperiode[45] Michie C, Lockie F, Lynn W. The challenge of mastitis. Archives of disease in childhood 2003;88(9):818-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12937109[46] Schaefer C, Peters P, Miller RK. Drugs during pregnancy and lactation: handbook of prescription drugs and comparative risk assessment. 2007
[47] Walker M. Conquering common breast-feeding problems. The Journal of perinatal & neonatal nursing 2008;22(4):267-74
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.JPN.0000341356.45446.23 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19011490[48] Prachniak GK. Common breastfeeding problems. Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America 2002;29(1):77-88, vi
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11892875[49] Yoshida M, Shinohara H, Sugiyama T, Kumagai M, Muto H, Kodama H. Taste of milk from inflamed breasts of breastfeeding mothers with mastitis evaluated using a taste sensor. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2014;9(2):92-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2013.0084 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24350703[50] Eekhof JAH, Verduijn MM. Pijnlijke borsten: stuwing, mastitis en tepelkloven bij borstvoeding en candida-infectie van de borst. 2011
[51] Kamphuis M. JGZ Richtlijn Huidafwijkingen 2012
https://www.jgzrichtlijnen.nl/alle-richtlijnen/richtlijn/huidafwijkingen[52] de Vries TW, Wewerinke ME, de Langen JJ. [Near asphyxiation of a neonate due to miconazole oral gel]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2004;148(32):1598-600
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15382562[53] Hoppe JE. Treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis and candidal diaper dermatitis in neonates and infants: review and reappraisal. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 1997;16(9):885-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9306485[54] Gloor M, Wolnicki D. Anti-irritative effect of methylrosaniline chloride (Gentian violet). Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland) 2001;203(4):325-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11752822[55] Heinig MJ, Francis J, Pappagianis D. Mammary candidosis in lactating women. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 1999;15(4):281-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10776178[56] Mulder-Wildemors LGM, Verduijn MM. Candidiasis bij borstvoeding Pharma Selecte 2004;20():49
https://www.pharmaselecta.nl/site/index.php/hoofdartikelen-archief/2004/533-64[57] Hoppe JE, Hahn H. Randomized comparison of two nystatin oral gels with miconazole oral gel for treatment of oral thrush in infants. Antimycotics Study Group. Infection 1996;24(2):136-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8740106[58] Hoppe JEM. Comparison of miconazole gel with nystatin hydroxyethylcellulose gel in the treatment of oral thrush in infants. Monatsschrift fur Kinderheilkunde 1994;142():285
[59] Hoppe JE. Treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis in immunocompetent infants: a randomized multicenter study of miconazole gel vs. nystatin suspension. The Antifungals Study Group. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 1997;16(3):288-93
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9076817[60] Schaad UB, Bachmann D. [Prospective comparison of miconazole gel and nystatin suspension in the treatment of oral candidiasis]. Schweizerische medizinische Wochenschrift 1983;113(38):1356-62
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6356343[61] Goins RA, Ascher D, Waecker N, Arnold J, Moorefield E. Comparison of fluconazole and nystatin oral suspensions for treatment of oral candidiasis in infants. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 2002;21(12):1165-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12506950[62] Swart EL, van der Waal I. [Use of methylrosaniline (gentian violet) to treat candidiasis]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2004;148(14):688
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15106322[63] Weijerman ME, van Furth AM, Vonk Noordegraaf A, van Wouwe JP, Broers CJM, Gemke RJBJ. Prevalence, neonatal characteristics, and first-year mortality of Down syndrome: a national study. The Journal of pediatrics 2008;152(1):15-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18154890[64] Pisacane A, Toscano E, Pirri I, Continisio P, Andria G, Zoli B, Strisciuglio P, Concolino D, Piccione M, Lo Giudice C, Vicari S. Down syndrome and breastfeeding. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2003;92(12):1479-81
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14971802[65] Anten EJ, Oudesluys HM, Semmekort BA, van Wouwe JP. Een professionele kijk op borstvoeding. 2010
[66] Aumonier ME, Cunningham CC. Breast feeding in infants with Down's syndrome. Child: care, health and development 1983;9(5):247-55
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6227426[67] Cooper-Brown L, Copeland S, Dailey S, Downey D, Petersen MC, Stimson C, Van Dyke DC. Feeding and swallowing dysfunction in genetic syndromes. Developmental disabilities research reviews 2008;14(2):147-57
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ddrr.19 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18646013[68] Neifert M, Lawrence R, Seacat J. Nipple confusion: toward a formal definition. The Journal of pediatrics 1995;126(6):S125-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7776072[69] Nowak AJ, Smith WL, Erenberg A. Imaging evaluation of breast-feeding and bottle-feeding systems. The Journal of pediatrics 1995;126(6):S130-4
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7776073[70] Smith WL, Erenberg A, Nowak A, Franken EA. Physiology of sucking in the normal term infant using real-time US. Radiology 1985;156(2):379-81
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3892576[71] Smith WL, Erenberg A, Nowak A. Imaging evaluation of the human nipple during breast-feeding. American journal of diseases of children (1960) 1988;142(1):76-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3277390[72] Woolridge MW. The 'anatomy' of infant sucking. Midwifery 1986;2(4):164-71
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3643397[73] Aarts C, Hörnell A, Kylberg E, Hofvander Y, Gebre-Medhin M. Breastfeeding patterns in relation to thumb sucking and pacifier use. Pediatrics 1999;104(4):e50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10506275[74] Binns CW, Scott JA. Using pacifiers: what are breastfeeding mothers doing? Breastfeeding review : professional publication of the Nursing Mothers' Association of Australia 2002;10(2):21-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12227560[75] Howard CR, Howard FM, Lanphear B, deBlieck EA, Eberly S, Lawrence RA. The effects of early pacifier use on breastfeeding duration. Pediatrics 1999;103(3):E33
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10049989[76] Kronborg H, Vaeth M. How are effective breastfeeding technique and pacifier use related to breastfeeding problems and breastfeeding duration? Birth (Berkeley, Calif.) 2009;36(1):34-42
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-536X.2008.00293.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19278381[77] Victora CG, Behague DP, Barros FC, Olinto MT, Weiderpass E. Pacifier use and short breastfeeding duration: cause, consequence, or coincidence? Pediatrics 1997;99(3):445-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9041303[78] Hauck FR, Omojokun OO, Siadaty MS. Do pacifiers reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome? A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2005;116(5):e716-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16216900[79] O'Connor NR, Tanabe KO, Siadaty MS, Hauck FR. Pacifiers and breastfeeding: a systematic review. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2009;163(4):378-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2008.578 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19349568[80] Kramer MS, Barr RG, Dagenais S, Yang H, Jones P, Ciofani L, Jané F. Pacifier use, early weaning, and cry/fuss behavior: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001;286(3):322-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11466098[81] Jenik AG, Vain NE, Gorestein AN, Jacobi NE, . Does the recommendation to use a pacifier influence the prevalence of breastfeeding? The Journal of pediatrics 2009;155(3):350-4.e1
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.03.038 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19464025[82] Schubiger G, Schwarz U, Tönz O. UNICEF/WHO baby-friendly hospital initiative: does the use of bottles and pacifiers in the neonatal nursery prevent successful breastfeeding? Neonatal Study Group. European journal of pediatrics 1997;156(11):874-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9392404[83] Howard CR, Howard FM, Lanphear B, Eberly S, deBlieck EA, Oakes D, Lawrence RA. Randomized clinical trial of pacifier use and bottle-feeding or cupfeeding and their effect on breastfeeding. Pediatrics 2003;111(3):511-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12612229[84] . The changing concept of sudden infant death syndrome: diagnostic coding shifts, controversies regarding the sleeping environment, and new variables to consider in reducing risk. Pediatrics 2005;116(5):1245-55
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16216901[85] Collins CT, Ryan P, Crowther CA, McPhee AJ, Paterson S, Hiller JE. Effect of bottles, cups, and dummies on breast feeding in preterm infants: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2004;329(7459):193-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15208209[86] Vennemann MM, Bajanowski T, Brinkmann B, Jorch G, Yücesan K, Sauerland C, Mitchell EA, . Does breastfeeding reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome? Pediatrics 2009;123(3):e406-10
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2145 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19254976[87] Jaafar SH, Jahanfar S, Angolkar M, Ho JJ. Effect of restricted pacifier use in breastfeeding term infants for increasing duration of breastfeeding. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2012
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007202.pub3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22786506[88] Stuebe A, Lee K. The pacifier debate. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1848-9; author reply 1850-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651349[89] Buzzetti R, D'Amico R. The pacifier debate. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1850; author reply 1850-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651351[90] Mitchell EA, Blair PS, L'Hoir MP. Should pacifiers be recommended to prevent sudden infant death syndrome? Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1755-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651334[91] De Cock KM, Fowler MG, Mercier E, de Vincenzi I, Saba J, Hoff E, Alnwick DJ, Rogers M, Shaffer N. Prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in resource-poor countries: translating research into policy and practice. JAMA 2000;283(9):1175-82
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10703780[92] Boer K, Nellen JF, Kreyenbroek ME, Godfried MH. [Treatment of HIV-infected pregnant women: prevention of virus transmission and adverse effects in mother and child]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2009;153():B410
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19785876[93] op de Coul ELM, van Weert JWMY, Oomen PJ, Smit C, van der Ploeg CPBK, Hahné SJM, Notermans DW, van der Sande MAB. [Antenatal screening in the Netherlands for HIV, hepatitis B and syphilis is effective]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2010;154():A2175
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21176248[94] Kuhn L, Reitz C, Abrams EJ. Breastfeeding and AIDS in the developing world. Current opinion in pediatrics 2009;21(1):83-93
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0b013e328320d894 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19242244[95] Kuhn L, Aldrovandi GM, Sinkala M, Kankasa C, Semrau K, Mwiya M, Kasonde P, Scott N, Vwalika C, Walter J, Bulterys M, Tsai W-Y, Thea DM, . Effects of early, abrupt weaning on HIV-free survival of children in Zambia. The New England journal of medicine 2008;359(2):130-41
http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa073788 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18525036[96] Coutsoudis A, Pillay K, Spooner E, Kuhn L, Coovadia HM. Influence of infant-feeding patterns on early mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Durban, South Africa: a prospective cohort study. South African Vitamin A Study Group. Lancet (London, England) 1999;354(9177):471-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10465172[97] Horvath T, Madi BC, Iuppa IM, Kennedy GE, Rutherford G, Read JS. Interventions for preventing late postnatal mother-to-child transmission of HIV. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2009;2009(1):CD006734
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006734.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19160297[98] Boer K, Nellen JF, Patel D, Timmermans S, Tempelman C, Wibaut M, Sluman MA, van der Ende ME, Godfried MH. The AmRo study: pregnancy outcome in HIV-1-infected women under effective highly active antiretroviral therapy and a policy of vaginal delivery. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2007;114(2):148-55
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17305888[99] Shapiro RL, Hughes MD, Ogwu A, Kitch D, Lockman S, Moffat C, Makhema J, Moyo S, Thior I, McIntosh K, van Widenfelt E, Leidner J, Powis K, Asmelash A, Tumbare E, Zwerski S, Sharma U, Handelsman E, Mburu K, Jayeoba O, Moko E, Souda S, Lubega E, Akhtar M, Wester C, Tuomola R, Snowden W, Martinez-Tristani M, Mazhani L, Essex M. Antiretroviral regimens in pregnancy and breast-feeding in Botswana. The New England journal of medicine 2010;362(24):2282-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0907736 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20554983[100] Moore ER, Anderson GC, Bergman N. Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2007
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17636727[101] Mackie RI, Sghir A, Gaskins HR. Developmental microbial ecology of the neonatal gastrointestinal tract. The American journal of clinical nutrition 1999;69(5):1035S-1045S
http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/69.5.1035s https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10232646[102] Bramson L, Lee JW, Moore E, Montgomery S, Neish C, Bahjri K, Melcher CL. Effect of early skin-to-skin mother--infant contact during the first 3 hours following birth on exclusive breastfeeding during the maternity hospital stay. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 2010;26(2):130-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0890334409355779 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20110561[103] Rozance PJ, Hay WW. Hypoglycemia in newborn infants: Features associated with adverse outcomes. Biology of the neonate 2006;90(2):74-86
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16534190[104] Boluyt N, van Kempen A, Offringa M. Neurodevelopment after neonatal hypoglycemia: a systematic review and design of an optimal future study. Pediatrics 2006;117(6):2231-43
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16740869[105] Hawdon JM, Ward Platt MP, Aynsley-Green A. Patterns of metabolic adaptation for preterm and term infants in the first neonatal week. Archives of disease in childhood 1992;67(4 Spec No):357-65
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1586171[106] Voeten M, Gerrits GPJM, Voorhoeve PG. [Treatment of neonatal hypoglycaemia: more frequent latching onto the breast versus supplementary feeding with formula; retrospective study of patient files]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2008;152(31):1732-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18727605[107] Wight N, Marinelli KA, . ABM clinical protocol #1: guidelines for blood glucose monitoring and treatment of hypoglycemia in term and late-preterm neonates, revised 2014. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2014;9(4):173-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2014.9986 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24823918[108] Cornblath M, Hawdon JM, Williams AF, Aynsley-Green A, Ward-Platt MP, Schwartz R, Kalhan SC. Controversies regarding definition of neonatal hypoglycemia: suggested operational thresholds. Pediatrics 2000;105(5):1141-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10790476[109] Alexander JM, Grant AM, Campbell MJ. Randomised controlled trial of breast shells and Hoffman's exercises for inverted and non-protractile nipples. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 1992;304(6833):1030-2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1586788[110] Dewey KG, Nommsen-Rivers LA, Heinig MJ, Cohen RJ. Risk factors for suboptimal infant breastfeeding behavior, delayed onset of lactation, and excess neonatal weight loss. Pediatrics 2003;112(3 Pt 1):607-19
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12949292[111] Preparing for breast feeding: treatment of inverted and non-protractile nipples in pregnancy. The MAIN Trial Collaborative Group. Midwifery 1994;10(4):200-14
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7837987[112] McKechnie AC, Eglash A. Nipple shields: a review of the literature. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2010;5(6):309-14
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2010.0003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20807104[113] Webb AN, Hao W, Hong P. The effect of tongue-tie division on breastfeeding and speech articulation: a systematic review. International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology 2013;77(5):635-46
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.03.008 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23537928[114] Post EDM, Rupert AWMS, Schulpen TWJ. [Problematic breastfeeding due to a short frenulum]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2010;154():A918
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20170571[115] Ballard JL, Auer CE, Khoury JC. Ankyloglossia: assessment, incidence, and effect of frenuloplasty on the breastfeeding dyad. Pediatrics 2002;110(5):e63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12415069[116] Mettias B, O'Brien R, Abo Khatwa MM, Nasrallah L, Doddi M. Division of tongue tie as an outpatient procedure. Technique, efficacy and safety. International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology 2013;77(4):550-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.01.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23411135[117] Hogan M, Westcott C, Griffiths M. Randomized, controlled trial of division of tongue-tie in infants with feeding problems. Journal of paediatrics and child health 2005;41(5-6):246-50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15953322[118] Geddes DT, Langton DB, Gollow I, Jacobs LA, Hartmann PE, Simmer K. Frenulotomy for breastfeeding infants with ankyloglossia: effect on milk removal and sucking mechanism as imaged by ultrasound. Pediatrics 2008;122(1):e188-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2007-2553 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18573859[119] Emond A, Ingram J, Johnson D, Blair P, Whitelaw A, Copeland M, Sutcliffe A. Randomised controlled trial of early frenotomy in breastfed infants with mild-moderate tongue-tie. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2014;99(3):F189-95
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2013-305031 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24249695[120] Buryk M, Bloom D, Shope T. Efficacy of neonatal release of ankyloglossia: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 2011;128(2):280-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-0077 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21768318[121] Dollberg S, Botzer E, Grunis E, Mimouni FB. Immediate nipple pain relief after frenotomy in breast-fed infants with ankyloglossia: a randomized, prospective study. Journal of pediatric surgery 2006;41(9):1598-600
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16952598[122] Algar V. Question 2. Should an infant who is breastfeeding poorly and has a tongue tie undergo a tongue tie division? Archives of disease in childhood 2009;94(11):911-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.2009.163428 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19847004[123] O'Callahan C, Macary S, Clemente S. The effects of office-based frenotomy for anterior and posterior ankyloglossia on breastfeeding. International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology 2013;77(5):827-32
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.02.022 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23523198[124] Cho A, Kelsberg G, Safranek S. Clinical inquiries. When should you treat tongue-tie in a newborn? The Journal of family practice 2010;59(12):712a-b
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21135930[125] Begg EJ, Duffull SB, Hackett LP, Ilett KF. Studying drugs in human milk: time to unify the approach. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 2002;18(4):323-32
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12449047[126] Weibert RT, Townsend RJ, Kaiser DG, Naylor AJ. Lack of ibuprofen secretion into human milk. Clinical pharmacy 1982;1(5):457-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7184678[127] Townsend RJ, Benedetti TJ, Erickson SH, Cengiz C, Gillespie WR, Gschwend J, Albert KS. Excretion of ibuprofen into breast milk. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 1984;149(2):184-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6720796[128] Walter K, Dilger C. Ibuprofen in human milk. British journal of clinical pharmacology 1997;44(2):211-2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9278216[129] Fowler PD. Diclofenac sodium (Voltarol): drug interactions and special studies. Rheumatology and rehabilitation 1979;Suppl 2():60-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/394276[130] Flidel-Rimon O, Shinwell ES. Breast feeding twins and high multiples. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2006;91(5):F377-80
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16923939[131] Friedman S, Flidel-Rimon O, Lavie E, Shinwell ES. The effect of prenatal consultation with a neonatologist on human milk feeding in preterm infants. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2004;93(6):775-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15244226[132] Neifert MR. Prevention of breastfeeding tragedies. Pediatric clinics of North America 2001;48(2):273-97
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11339153[133] Hurst NM. Recognizing and treating delayed or failed lactogenesis II. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):588-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983996[134] Amir LH. Breastfeeding--managing 'supply' difficulties. Australian family physician 2006;35(9):686-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16969436[135] Gatti L. Maternal perceptions of insufficient milk supply in breastfeeding. Journal of nursing scholarship : an official publication of Sigma Theta Tau International Honor Society of Nursing 2008;40(4):355-63
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2008.00234.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19094151[136] Powers NG. How to assess slow growth in the breastfed infant. Birth to 3 months. Pediatric clinics of North America 2001;48(2):345-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11339156[137] Zembo CT. Breastfeeding. Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America 2002;29(1):51-76
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11892874[138] Centuori S, Burmaz T, Ronfani L, Fragiacomo M, Quintero S, Pavan C, Davanzo R, Cattaneo A. Nipple care, sore nipples, and breastfeeding: a randomized trial. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 1999;15(2):125-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10578788[139] Tait P. Nipple pain in breastfeeding women: causes, treatment, and prevention strategies. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2000;45(3):212-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10907330[140] Mass S. Breast pain: engorgement, nipple pain and mastitis. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology 2004;47(3):676-82
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15326430[141] Blair PS, Fleming PJ, Smith IJ, Platt MW, Young J, Nadin P, Berry PJ, Golding J. Babies sleeping with parents: case-control study of factors influencing the risk of the sudden infant death syndrome. CESDI SUDI research group. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 1999;319(7223):1457-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10582925[142] Carpenter RG, Irgens LM, Blair PS, England PD, Fleming P, Huber J, Jorch G, Schreuder P. Sudden unexplained infant death in 20 regions in Europe: case control study. Lancet (London, England) 2004;363(9404):185-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14738790[143] Horsley T, Clifford T, Barrowman N, Bennett S, Yazdi F, Sampson M, Moher D, Dingwall O, Schachter H, Côté A. Benefits and harms associated with the practice of bed sharing: a systematic review. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2007;161(3):237-45
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17339504[144] Ruys JH, de Jonge GA, Brand R, Engelberts AC, Semmekrot BA. Bed-sharing in the first four months of life: a risk factor for sudden infant death. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(10):1399-403
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17714547[145] McKenna JJ, Mosko SS, Richard CA. Bedsharing promotes breastfeeding. Pediatrics 1997;100(2 Pt 1):214-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9240802[146] McKenna JJ, McDade T. Why babies should never sleep alone: a review of the co-sleeping controversy in relation to SIDS, bedsharing and breast feeding. Paediatric respiratory reviews 2005;6(2):134-52
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15911459[147] Vogel A, Hutchison BL, Mitchell EA. Factors associated with the duration of breastfeeding. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 1999;88(12):1320-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10626515[148] Scragg RK, Mitchell EA, Stewart AW, Ford RP, Taylor BJ, Hassall IB, Williams SM, Thompson JM. Infant room-sharing and prone sleep position in sudden infant death syndrome. New Zealand Cot Death Study Group. Lancet (London, England) 1996;347(8993):7-12
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8531589[149] Mitchell EA. Recommendations for sudden infant death syndrome prevention: a discussion document. Archives of disease in childhood 2007;92(2):155-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17264285[150] Horne RSC, Parslow PM, Ferens D, Watts A-M, Adamson TM. Comparison of evoked arousability in breast and formula fed infants. Archives of disease in childhood 2004;89(1):22-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14709496[151] Mosko S, Richard C, McKenna J. Infant arousals during mother-infant bed sharing: implications for infant sleep and sudden infant death syndrome research. Pediatrics 1997;100(5):841-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9346985[152] Baddock SA, Galland BC, Bolton DPG, Williams SM, Taylor BJ. Differences in infant and parent behaviors during routine bed sharing compared with cot sleeping in the home setting. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1599-607
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651313[153] Blair PS, Sidebotham P, Berry PJ, Evans M, Fleming PJ. Major epidemiological changes in sudden infant death syndrome: a 20-year population-based study in the UK. Lancet (London, England) 2006;367(9507):314-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16443038[154] Blair PS, Ball HL. The prevalence and characteristics associated with parent-infant bed-sharing in England. Archives of disease in childhood 2004;89(12):1106-10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15557042[155] Brenner RA, Simons-Morton BG, Bhaskar B, Revenis M, Das A, Clemens JD. Infant-parent bed sharing in an inner-city population. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2003;157(1):33-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12517192[156] McGarvey C, McDonnell M, Chong A, O'Regan M, Matthews T. Factors relating to the infant's last sleep environment in sudden infant death syndrome in the Republic of Ireland. Archives of disease in childhood 2003;88(12):1058-64
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14670769[157] Breuning-Boers JM, van Dommelen P, van Wouwe JP, Verkerk PH. [Weight loss, serum sodium concentration and residual symptoms in patients with hypernatremic dehydration caused by insufficient breastfeeding]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2006;150(16):904-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16686091[158] van Dommelen P, Boer S, Unal S, van Wouwe JP. Charts for weight loss to detect hypernatremic dehydration and prevent formula supplementing. Birth (Berkeley, Calif.) 2014;41(2):153-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/birt.12105 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24698284[159] Pelleboer RA, Bontemps STH, Verkerk PH, Van Dommelen P, Pereira RR, Van Wouwe JP. A nationwide study on hospital admissions due to dehydration in exclusively breastfed infants in the Netherlands: its incidence, clinical characteristics, treatment and outcome. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2009;98(5):807-11
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2009.01230.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19245535[160] Taveras EM, Scanlon KS, Birch L, Rifas-Shiman SL, Rich-Edwards JW, Gillman MW. Association of breastfeeding with maternal control of infant feeding at age 1 year. Pediatrics 2004;114(5):e577-83
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15492358[161] Wiklund I, Norman M, Uvnäs-Moberg K, Ransjö-Arvidson A-B, Andolf E. Epidural analgesia: breast-feeding success and related factors. Midwifery 2009;25(2):e31-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17980469[162] Kools EJ, Thijs C, de Vries H. The behavioral determinants of breast-feeding in The Netherlands: predictors for the initiation of breast-feeding. Health education & behavior : the official publication of the Society for Public Health Education 2005;32(6):809-24
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16267150[163] Scott JA, Binns CW. Factors associated with the initiation and duration of breastfeeding: a review of the literature. Breastfeeding review : professional publication of the Nursing Mothers' Association of Australia 1999;7(1):5-16
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10197366[164] Chung M, Raman G, Trikalinos T, Lau J, Ip S. Interventions in primary care to promote breastfeeding: an evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Annals of internal medicine 2008;149(8):565-82
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18936504[165] Spiby H, McCormick F, Wallace L, Renfrew MJ, D'Souza L, Dyson L. A systematic review of education and evidence-based practice interventions with health professionals and breast feeding counsellors on duration of breast feeding. Midwifery 2009;25(1):50-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17418464[166] Hannula L, Kaunonen M, Tarkka M-T. A systematic review of professional support interventions for breastfeeding. Journal of clinical nursing 2008;17(9):1132-43
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2007.02239.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18416790[167] Howard C, Howard F, Lawrence R, Andresen E, DeBlieck E, Weitzman M. Office prenatal formula advertising and its effect on breast-feeding patterns. Obstetrics and gynecology 2000;95(2):296-303
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10674597[168] Lutsiv O, Pullenayegum E, Foster G, Vera C, Giglia L, Chapman B, Fusch C, McDonald SD. Women's intentions to breastfeed: a population-based cohort study. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2013;120(12):1490-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12376 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859024[169] Sachs M, Dykes F, Carter B. Weight monitoring of breastfed babies in the UK - centile charts, scales and weighing frequency. Maternal & child nutrition 2005;1(2):63-76
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16881882[170] Sachs M, Dykes F, Carter B. Weight monitoring of breastfed babies in the United Kingdom--interpreting, explaining and intervening. Maternal & child nutrition 2006;2(1):3-18
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16881910[171] Hill PD, Johnson TS. Assessment of breastfeeding and infant growth. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):571-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983994[172] Peñacoba C, Catala P. Associations Between Breastfeeding and Mother-Infant Relationships: A Systematic Review. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2019;14(9):616-629
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2019.0106 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31424264[173] de Cock ESA, Henrichs J, Vreeswijk CMJM, Maas AJBM, Rijk CHAM, van Bakel HJA. Continuous feelings of love? The parental bond from pregnancy to toddlerhood. Journal of family psychology : JFP : journal of the Division of Family Psychology of the American Psychological Association (Division 43) 2016;30(1):125-34
http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/fam0000138 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26280095[174] Seefat-van Teeffelen A, Nieuwenhuijze M, Korstjens I. Women want proactive psychosocial support from midwives during transition to motherhood: a qualitative study. Midwifery 2011;27(1):e122-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2009.09.006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19931954[175] Pinquart M, Silbereisen RK. Changes in adolescents' and mothers' autonomy and connectedness in conflict discussions: an observation study. Journal of adolescence 2002;25(5):509-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12234557[176] Bijsluiter miconazol
https://db.cbg-meb.nl/bijsluiters/h15382.pdf[177] Lareb-Nederlands Bijwerkingen Centrum
http://www.lareb.nl[178] Geneesmiddelen, zwangerschap en borstvoeding. 2011
[179] van Rossum CTM, Buchner FL, Hoekstra J. Quantification of health effects of breastfeeding - Review of the literature and model simulation (Kwantificering van de gezondheidseffecten van borstvoeding - Literatuuroverzicht en modelsimulatie). 2005
https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/350040001.html[180] van Bakel AM. Wat zijn de mogelijke gezondheidseffecten van borstvoeding? 2013
http://www.nationaalkompas.nl/gezondheidsdeterminanten/leefstijl/borstvoeding/wat-zijn-de-mogelijke-gezondheidsgevolgen-van-borstvoeding[181] WHO. HIV and infant feeding; Revised principles and recommendations Rapid Advice 2009
https://www.aidsdatahub.org/sites/default/files/resource/hiv-infant-feeding-revised-principles-recommendations-rapid-advice.pdf[182] Landelijk Coördinatiecentrum Infectieziektebestrijding
http://www.rivm.nl/[183] UNHCR. Guidance on infant feeding and HIV in the context of refugees and displaced populations.
https://www.ennonline.net/attachments/1512/unhcr-guide-2009.pdf[184] WHO, Unicef. HIV and infant feeding counselling tools: reference guide’ van Unicef/WHOUSAID. 2005
[185] Ruys JH, Engelberst AC, van Velzen-Mol HWM. JGZ-richtlijn Preventie wiegendood. 2009
https://www.jgzrichtlijnen.nl/alle-richtlijnen/richtlijn/preventie-wiegendood[186] Gerrits GJPM, de Hosson MP, Semmekrot BA. Afname complicaties door family-centered care: minder hypo's in de kraamsuite. Medisch Contact 2009;64():498
https://www.medischcontact.nl/actueel/laatste-nieuws/artikel/minder-hypos-in-de-kraamsuite[187] van Kempen A, van Toledo-Eppinga L. Glucose, uit: Werkboek Enterale en parenterale voeding bij pasgeboren, 2012
[188] Mohrbacher N, Stock J. Handboek lactatiebegeleiding van La Leche League International. 2002
[189] Walker M. Breastfeeding Management for the Clinician: Using the Evidence. 2006
[190] Stichting Health Base. Commentaren Medicatiebewaking 2014-2015. 2014
[191] Landsmeer M, Nauta M, Te Winkel B. Vormen medicatie en borstvoeding een veilige combinatie? Farmacotherapie bij kinderen 2009;2():35
[192] College voor Zorgverzekeringen. Farmacotherapeutisch Kompas 2010
[193] Nauta M, Landsmeer M, De Wildt SN. Zijn NSAID’s veilig tijdens de lactatie? Farmacotherapie bij kinderen 2010;1():28
[194] Hale TW, Row HE. Medications and Mothers’ Milk. 2014
[195] Post EDM, Verduijn MM. Medicatie en borstvoeding, mag dat? Bijblijven 2012;4():20
[196] Briggs GG, Freeman RK. Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation: A Reference Guide to Fetal and Neonatal Risk. 2014
[197] Lanting CI, van Wouwe JP. Redenen en motieven om te starten en te stoppen met borstvoeding. 2007
https://www.tno.nl/media/1350/kvl-pz-borstvoeding-redenen-stoppen.pdf[198] Oskamp G. Handleiding voor de Zorgverlener. Borstvoedingorganisatie La Leche League. 2014
[199] de Reede-Dunselman A. Begeleiding bij borstvoeding. 8e herz.dr. 2009
[200] Ball HL, Hooker E, Kelly PJ. Where will the baby sleep? Attitudes and practices of new and experienced parents regarding co-sleeping with their newborn infants. American Anthropologist 1999;101():143
[201] McKenna JJ. Samen slapen met je baby – het handboek voor ouders over coslapen. 2011
[202] Pelleboer RAA. Voorkómen van uitdroging en ondervoeding. In 'Een professionele kijk op borstvoeding ' 2010
[203] Derksen-Lubsen G, Moll HA, Oudesluys-Murphy AJ. Compendium Kindergeneeskunde. 4e druk 2012
[204] WHO. Evidence for the ten steps to succesfull breastfeeding 1998
https://www.tensteps.org/pdf/evidence-for-the-ten-steps-to-successful-breastfeeding-eng.pdf[205] WHO. International code of marketing of breast-milk substitutes. 1981
https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/40382/9241541601_dut.pdf[206] Van Eijsden M, Berkenpas ME, van der Wal MF. Borstvoeding in een multi-etnische populatie: de rol van de (aanstaande) vader en grootmoeder. Tijdschrift voor Sociale geneeskunde 2009;87():100
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF03082193[207] World Health Organization. Proposed global targets for maternal, infant and young child nutrition. 2012
https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/nutritionlibrary/events/consultation-on-proposed-global-targets-on-maternal-infant-and-young-child-nutrition/2012-proposed-globaltargets-backgroundpaper-en.pdf?sfvrsn=6a1c2738_14[208] Vogel I, van Rossem L, Raat H. Redenen en motieven van vrouwen om gedeeltelijk of geheel te stoppen in de eerste zes maanden. In 'Een professionele kijk op borstvoeding.'' 2011
[209] EU-richtlijn 2006/141, inzake volledige zuigelingenvoeding en opvolgzuigelingenvoeding.
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:2006L0141:20081028:NL:PDF[210] CBS. Tabel: Bevalling, lengte en gewicht bij geboorte, borstvoeding. 2014
https://opendata.cbs.nl/statline/#/CBS/nl/dataset/37302/table[211] Verduijn MM. Anticonceptiepleister en hormoonbelasting. Geneesmiddelenbulletin 2008;42:42():
[212] Lemmens E, Leveau C. Frenotomie, een geknipt idee! Tijdschrift voor verloskundigen 2005
[213] Goudswaard AN, In 't Veld CJ, Kramer WLM. Handboek verrichtingen in de huisartsenpraktijk. 2009
[214] Kerkhoff Z, Martijn R, van der Horst M. Een verkennend onderzoek naar de relatie tussen borstvoedingsduur en tevredenheid. 2008
[215] van Everdingen JJE, Dreesens DHH, Burgers JS, Swinkels JA, van Barneveld TA, van der Weijden T. Handboek evidence-based richtlijnontwikkeling: een leidraad voor de praktijk, 2e druk 2014
[216] Lanting C, van Wouwe JP. Borstvoeding in Nederland, een nadere beschouwing: achtergrondkenmerken, redenen en motieven, en het effect van BFHI. 2005
1 Definitie en achtergrond informatie
De richtlijn Borstvoeding ondersteunt bij het informeren, stimuleren en adviseren van ouders van gezonde zuigelingen. Het uitgangspunt van deze richtlijn is het WHO-standpunt dat moedermelk de optimale voeding is voor zuigelingen en jonge kinderen.
1.1 Anatomie en fysiologie
Anatomie en fysiologie
Ontwikkeling van de borst
De borsten ontwikkelen zich op de ‘primitieve melklijsten’ rond de 16e week na de bevruchting. Deze melklijsten bevinden zich tussen de oksel en de lies van de foetus. In deze regio kunnen zich ook extra melkklierweefsel en tepels ontwikkelen. Tot de puberteit groeien de borsten niet. Bij meisjes groeien de borsten in de puberteit onder invloed van geslachtshormonen en ontstaan er melkkanaaltjes met aan het eind daarvan knoppen. Onder invloed van de menstruatiecyclus raken deze knoppen telkens gestimuleerd. Nieuwe knoppen blijven ontstaan tot de leeftijd van ongeveer 35 jaar.
Structuur van de borst
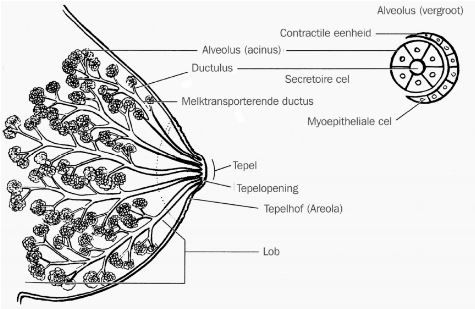
De volwassen borst bestaat uit klier- en vetweefsel, ondersteund door de ‘ligamenten van Cooper’. De hoeveelheid vet bepaalt de grootte van de borst. Het is normaal dat beide borsten niet even groot zijn. Het klierweefsel is verdeeld over 15 tot 20 lobben (lobi). Tussen deze lobben ligt bindweefsel en vet. De lobben zijn weer onderverdeeld in kleine ‘lobuli’ met daarin de ‘alveoli’. In de alveolus wordt de melk geproduceerd en opgeslagen. De lobi monden uit in 15 tot 25 melkgangen. Een aantal melkgangen voegt zich vlak achter de tepel samen en gemiddeld heeft de tepel dan ongeveer negen openingen. Om de tepel heen bevindt zich de tepelhof (areola). Op de tepelhof bevinden zich de ‘kliertjes van Montgomery’. Die scheiden een wat vettige substantie af. Het melkklierweefsel en de melkkanalen liggen dicht onder de oppervlakte van de borst.
Figuur 1: Structuur van de borst (met toestemming van de uitgever overgenomen uit J. Riordan, Breastfeeding and Human Lactation, 2005)[1].
Fysiologie van de melkproductie
Als een vrouw zwanger is, ontwikkelt de functie van de borst zich verder. De borst wordt ± 150 tot ± 500 gram zwaarder (dat verschilt per vrouw). De cellen van het klierweefsel vermeerderen en rekken op. Meestal zijn de borsten bij 22 weken zwangerschap tot melkproductie in staat. Het verband tussen de hoeveelheid klierweefsel en de productie- en opslagcapaciteit van de borst ligt genuanceerd. Bij sommige vrouwen treedt pas aanzienlijke groei van de borsten op in de periode na de bevalling (post partum). Afhankelijk van het gevoerde borstvoedingsbeleid (zoals wel of niet starten met borstvoeding, maar ook frequentie van aanleggen) zal het aanwezige klierweefsel meer of minder effectief worden gestimuleerd en tot een al dan niet toereikende productie worden aangezet. Bij optimaal beleid zijn de meeste moeders in staat meer melk te produceren dan hun baby nodig heeft. Een geringere opslagcapaciteit leidt niet per definitie tot een geringere dagproductie; wel moet de borst wellicht vaker worden geleegd om in de behoefte van de baby te voorzien. Er zijn situaties waarin een vrouw te weinig klierweefsel heeft om volledig aan haar baby’s vraag tegemoet te komen. Dat neemt echter de waarde van wat zij wél kan produceren, niet weg.
Tijdens de zwangerschap neemt de bloedtoevoer naar de borsten sterk toe. Deze blijft gedurende de lactatie hoog. Vanaf de tweede helft van de zwangerschap is al colostrum aanwezig in de alveoli. Tijdens de zwangerschap worden de tepels onder invloed van prolactine groter en donkerder van kleur. Een aantal weken na de bevalling worden de borsten soepeler dan ze in het kraambed waren. Dit is geen signaal voor afnemende melkproductie.
Melkproductie, een natuurlijk proces
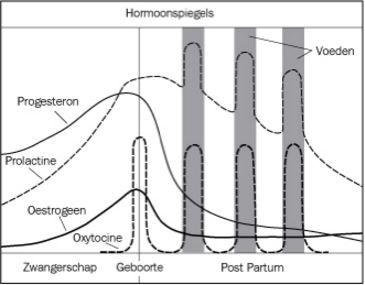
Het op gang komen van de melkproductie is een natuurlijk proces. Goed en vaak (overdag en ’s nachts) aanleggen van de baby of afkolven is noodzakelijk voor het onderhouden van de melkproductie. Het hormoon progesteron, gevormd door de placenta, remt de werking van prolactine. Progesteron daalt sterk bij de geboorte van de placenta. De aanwezige prolactine kan de melkproductie vervolgens volop op gang brengen. Wordt er geen borstvoeding gegeven, dan daalt de prolactinespiegel geleidelijk tot ‘normale’ waarden in ongeveer zeven dagen na de bevalling. Blijft de moeder borstvoeding geven, dan blijft de spiegel verhoogd, met pieken na de voedingen en een verhoogde baseline. Het afscheiden van prolactine wordt geremd als de alveoli overvol raken. Frequent legen van de borst is daarom belangrijk voor het in stand houden van de melkproductie. Nachtvoedingen zijn vooral belangrijk om te zorgen dat de baby voldoende melk binnen krijgt[2]. In de loop van weken daalt de prolactinespiegel geleidelijk tot een licht verhoogde spiegel tussen de voedingen in. De concentratie prolactine varieert gedurende 24 uur, met ’s nachts hogere spiegels dan overdag.
Toeschietreflex
Het hormoon oxytocine stijgt bij iedere voeding door stimulans van tepel en tepelhof, door lichamelijk contact en oogcontact tussen moeder en kind en door geluidjes en geur van de baby. Dit zorgt voor het samentrekken van het spierweefsel in de alveoli. Hierdoor wordt de melk de melkgangen ingeperst. Dit noemen we de ‘toeschietreflex’. De gedachte aan de baby of aan het voeden kan de melk al spontaan doen toeschieten. Zonder een effectieve toeschietreflex zal de baby onvoldoende of geen voeding binnenkrijgen en dus de borst onvoldoende legen. Hierdoor zal de melkproductie afnemen. De intensiteit waarmee vrouwen de toeschietreflex voelen, verschilt. Sommige vrouwen voelen niets, anderen ervaren tintelingen tot een sterke pijnprikkel. Factoren als stress en angst, waardoor adrenaline in de circulatie van de moeder komt, kunnen de toeschietreflex tijdelijk belemmeren. Het vrijkomen van oxytocine geeft ook aanleiding tot samentrekken van de baarmoeder. In de eerste dagen tot een week na de bevalling geeft dit soms naweeën, die ervoor zorgen dat de baarmoeder sneller involueert. Het kan een aantal minuten duren voordat de toeschietreflex optreedt en er kunnen meerdere toeschietreflexen zijn tijdens de voeding. Aan het einde van de voeding blijft de melk niet in de kanalen, maar loopt deze terug naar de alveoli. Oxytocine is een hormoon met een stressverlagende werking. De moeder is rustiger en positiever gestemd. Dit bevordert een sensitieve interactie met haar kind.
Vaak aanleggen, borst goed leeg laten drinken
Op het moment van geboorte is er colostrum aanwezig. In de eerste 24 uur drinkt de baby gemiddeld 5-12 ml moedermelk per voeding, 8 tot 12 keer per 24 uur. Het colostrum verandert in de eerste dagen na de bevalling geleidelijk van samenstelling. In de eerste dagen zijn hoge concentraties lactoferrine en secretoir IgA aanwezig. Na enkele dagen nemen de concentraties van deze stoffen af. De concentraties vet en lactose nemen geleidelijk toe. Hoe leger de borst, hoe hoger de vetconcentratie in de melk is. En hoe langer het interval tussen de voedingen, hoe voller de borsten en hoe lager het vetgehalte in de melk. De optimale voeding wordt verkregen door frequent aanleggen, de eerste borst goed ‘leeg’ laten drinken voordat de tweede borst wordt aangeboden, en voedingen afwisselend met de linker en rechter borst te beginnen.
Figuur 2: Verloop van de hormoonspiegels (met toestemming van de uitgever overgenomen uit J. Riordan, Breastfeeding and Human Lactation, 2005)[1]
.
1.2 Starten met borstvoeding
Het op gang komen van de lactatie is een natuurlijk proces, dat start tijdens de zwangerschap. Na de geboorte van de placenta komt de melkproductie volop op gang. De zorgverlener is op de hoogte van en geeft uitleg over de basisprincipes van borstvoeding: voeden op verzoek (geen beperking in duur en frequentie) en goed aanleggen. Bij voeden op verzoek voedt de moeder haar kind wanneer de baby voedingssignalen geeft.
Borstvoedingsproblemen zijn vaak gerelateerd aan niet goed, niet vaak genoeg of niet lang genoeg aanleggen [3];[4];[5];[6];[7]. De zorgverlener moedigt moeder en kind aan om tijdens het huid-op-huidcontact direct na de geboorte de borstvoedingsrelatie op gang te brengen. Wanneer dit moment om medische redenen moet worden uitgesteld, dient het zo spoedig mogelijk te worden ingehaald. Een goede start bevordert de duur van de borstvoedingsperiode en de frequentie van het aantal voedingen per etmaal. Een doeltreffende houding van moeder en kind bevordert vervolgens het juiste ‘aanhappen’ aan de borst, waardoor de baby in staat is om goed te zuigen, de toeschietreflex uit te lokken en voldoende melk binnen te krijgen [6].
Aanbevelingen
1.2.1 Aanleggen
Instructie over aanleggen
Onderzoeksresultaten suggereren dat een eenmalige instructie over aanleggen niet voldoende is voor een blijvend positief effect op de duur van de borstvoedingsperiode [8];[9];[10]. Bovendien is een standaardinstructie niet het juiste middel; een individuele benadering is noodzakelijk. Huisbezoeken door de jeugdgezondheidszorg-professional en uitleg van de kraamverzorgende blijken effectief[9]. Verondersteld mag worden dat dit ook geldt voor begeleiding door verloskundigen, lactatiekundigen en verpleegkundigen.
Hieronder volgen de belangrijkste aspecten in de voorlichting over starten met borstvoeding.
Voedingshouding
Wanneer de moeder zich comfortabel en goed gesteund voelt, is er sprake van een goede houding. De moeder kiest de houding die zij op dat moment het prettigst vindt. Hierna volgt een aantal veel gebruikte houdingen.
- De madonnahouding: de moeder zit rechtop, buik aan buik met haar kind. Het kind ligt op zijn zij, het hoofdje rust op de onderarm van de moeder.
- De aangepaste madonnahouding: de moeder zit rechtop, buik aan buik met haar kind. Het kind ligt op zijn zij. De baby ligt op de rechterarm van de moeder. Ze steunt het hoofdje met haar rechterhand, terwijl met ze met haar linkerhand de linkerborst aanbiedt. Dit geldt vice versa voor de rechterborst.
- De bakerhouding: de moeder zit rechtop en het kind ligt naast de moeder op een groot kussen met het lichaam naar de moeder toe gedraaid. Het hoofdje ligt in de hand van de moeder, de voetjes wijzen naar achteren. De baby ligt zodanig dat hij niet ‘om een hoekje’ de borst hoeft aan te happen. Het hoofdje ligt iets achterover gekanteld.
- Liggend op de zij: de moeder ligt op haar zij met een kussen onder haar hoofd. Haar schouder ligt op het matras. Het kind ligt op zijn zij met het hele lichaampje naar haar toegedraaid.
- Liggend op de rug: het kind ligt op zijn buikje, hetzij op de moeder, hetzij (deels) op een kussen naast haar. Ze steunt het voorhoofdje met haar hand, zodat hij niet voorover in de borst zakt en met de kin goed tegen de borst van de moeder aan ligt9.Biological nurturing’: Suzanne Colson, gepromoveerd verloskundig onderzoeker, beschrijft de neonatale reflexen om de borst te zoeken en de beste houdingen om deze reflexen uit te lokken. Haar onderzoek heeft aangetoond dat de baby, op zijn buik liggend en met zijn hele lijfje in contact met de moeder, zelf de borst kan pakken. De moeder leunt hierbij goed gesteund achterover[12].
Aanhappen
Het kind ligt tijdens het voeden met zijn hoofdje en lijfje in een rechte lijn met de buik naar de moeder toe gedraaid. Er is ruimte om het hoofd naar achteren te bewegen en het mondje ligt net iets lager dan de tepel. De moeder strijkt met de tepel over het mondje van het kind. Op het moment dat de baby het mondje wijd opendoet, beweegt de moeder hem rustig en stevig naar zich toe, waardoor hij kan aanhappen. Wanneer de baby op deze manier aanhapt (hoofdje iets achterover), ligt het neusje van de baby na het aanhappen vanzelf vrij. Het kind heeft gedurende de hele voeding het mondje wijd open, waarbij de lipjes naar buiten zijn gekruld en de tong over de onderkaak ligt. Een gedeelte van de tepelhof ligt in het mondje, waarbij de baby aan de onderkant een groter deel aanhapt dan aan de bovenkant. De kin ligt tegen de moederborst aan en het neusje kan de borst raken. De wangetjes blijven bol[3];[7]. De moeder kan haar borst met haar hand ondersteunen, waarbij zij er op moet letten dat zij niet te veel druk uitoefent op het borstweefsel: de melkkanalen mogen niet worden dichtgedrukt[6];[13];[14]. Bovendien kan hierdoor de borst uit het mondje glijden. Om de borst dan toch in de mond te houden, klemt de baby soms de kaken op elkaar en dat kan pijnlijke tepels tot gevolg hebben. Als het nodig is om meer ruimte te creëren voor het neusje, kan de moeder de billen van de baby naar zich toe bewegen.
Melkinname door de baby
In eerste instantie zal het kind een zuigritme aanhouden van ‘een paar keer zuigen, één keer slikken’. Na het toeschieten van de melk verandert het zuigritme meestal naar één keer zuigen, één keer slikken [3];[5]. Men spreekt van ‘voedend zuigen’. Het slikken is hoorbaar, zeker als de melkproductie goed op gang is. Uit echoscopisch onderzoek is gebleken dat de melk het mondje van de baby instroomt op het moment dat de tong naar beneden beweegt [15]. Het vacuüm dat de baby met zijn mondje maakt, is dus een belangrijke component bij de melkoverdracht. De moeder voelt het zuigen als een stevige sensatie. Indien het voeden na het eerste aanzuigen pijnlijk blijft, moet het vacuüm worden verbroken en moet de baby opnieuw worden aangelegd. Naarmate de voeding vordert, raakt de baby meer verzadigd en zal hij meestal vanzelf de borst loslaten[4];[5];[7];[14];[16]. De duur van een voeding is niet altijd gerelateerd aan de hoeveelheid melk die de baby binnenkrijgt[14] .
Aanbevelingen
1.2.2 Stuwing
Als de baby twee tot vier dagen oud is, nemen de vocht- en bloedtoevoer naar de borsten toe en de melkproductie komt verder op gang. Hierdoor raken de borsten vol. Het is belangrijk hierbij onderscheid te maken tussen ‘volle borsten’ en pathologische stuwing. Bij pathologische stuwing staan de borsten strak en gespannen, is er sprake van oedeem in de tepelhof en/of de hele borst en ervaart de moeder pijn. Doordat de tepelhof gespannen is, kan de baby niet goed aanhappen. Hierdoor kan de moeder pijnlijke tepels krijgen en krijgt de baby onvoldoende melk binnen. Doordat de alveoli overvol zijn en continu onder spanning staan, daalt de prolactinespiegel en kunnen melkvormende cellen worden beschadigd. Door de obstructie die de stuwing veroorzaakt, wordt de toeschietreflex vertraagd. Een verminderde productie en een niet goed groeiende baby zijn het logische gevolg van extreme stuwing.
Stuwing kan worden voorkomen door de borsten goed leeg te laten drinken en dus vroeg, frequent en lang genoeg aan te leggen. Als toch pathologische stuwing optreedt, is het wenselijk dat er snel lactatiekundige zorg wordt ingeschakeld. Warmte op de borst, in combinatie met voorzichtige massage en kolven met de hand of met een kolfapparaat kunnen behulpzaam zijn. Bij ernstige pathologische stuwing is het belangrijk dat de moeder eerst haar borsten kolft totdat ze zachter aanvoelen. Daarna kan de baby weer goed worden aangelegd. Eventueel kan pijnmedicatie nodig zijn (paracetamol of ibuprofen in normale dosering).
Aanbevelingen
1.2.3 Problemen bij het aan de borst gaan
Het komt voor dat een baby in de periode direct na de bevalling niet aan de borst kan drinken. Er is weinig onderzoek gedaan naar de oorzaken hiervan. Als mogelijke verklaringen worden geopperd: intramusculair opiatengebruik [17], epidurale anaesthesie [17], kunstverlossing, geboortetrauma of anatomische afwijkingen bij het kind. Voorbeelden van routines die het borstvoedingsproces verstoren zijn: verstoring van het eerste contact, scheiding van moeder en kind, het aanbieden van een fopspeen of het geven van bijvoeding zonder medische indicatie. Oplossingen zijn gericht op het herstellen van het contact tussen moeder en kind en het op gang brengen van de melkproductie: ‘rooming-in’, inhalen van huid-op-huidcontact, hulp bij het aanleggen en eventueel kolven.
Het gebruik van een tepelhoedje als oplossing bij de bovengenoemde verstoringen in de vroege periode postpartum wordt in principe afgeraden. Tepelhoedjes kunnen een negatief effect hebben op de moedermelkproductie en op de melkoverdracht. Desondanks kunnen ze voor sommige baby’s tijdelijk een nuttig hulpmiddel zijn om goed te leren drinken aan de borst (zie ook het hoofdstuk ‘Ingetrokken of vlakke tepels’). Gebruik gaat altijd in overleg met een zorgverlener.
1.2.4 Kolven
Bij moeder en/of kind kunnen zich omstandigheden voordoen waardoor de baby niet rechtstreeks uit de borst kan drinken. In Tabel 1 staan voorbeelden van redenen om te kolven. Hierbij bestaat een onderscheid tussen kolven voor het opbouwen van de melkproductie en voor het op peil houden van de productie. Als de borsten onvoldoende zijn geleegd, kan de moeder nakolven.
|
Tabel 1: Redenen om te kolven |
| Moeder en kind zijn van elkaar gescheiden (bijvoorbeeld door ziekenhuisopname of activiteiten buitenshuis zoals werk). |
| De baby is tijdelijk niet of onvoldoende in staat om zelf volledig aan de borst te drinken. |
| Er wordt getracht de tepels wat meer naar voren te laten komen (bijvoorbeeld bij ingetrokken tepels). |
| Er is sprake van pathologische stuwing. |
| De moeder gebruikt medicijnen waarbij borstvoeding wordt afgeraden. |
| De baby heeft al een aantal keren niet goed aan de borst gedronken en de borst moet worden geleegd. |
| De moeder wil incidenteel een voeding overslaan. |
| De moeder wil haar melkproductie verhogen. |
| De moeder wil melk doneren aan de moedermelkbank. |
Een moeder kan veel stress ervaren als zij de melkproductie op gang moet brengen door middel van kolven. De emotionele respons van de moeder op haar baby ontbreekt, waardoor de melk minder makkelijk toeschiet. Het heeft daarom de voorkeur om, als het enigszins mogelijk is, te kolven naast de baby. De uiteindelijke productie zal afhangen van veel factoren, zoals de duur, frequentie en techniek van het kolven. Het is belangrijk dat een moeder goed passend materiaal gebruikt om beschadiging van de tepel te voorkomen. Daarnaast is goede hygiëne essentieel: handen wassen voor het kolven en bewaarflessen en kolfapparaat reinigen volgens instructie.
Opbouwen van de melkproductie
Als het regelmatig aanleggen van de baby vanaf de geboorte niet mogelijk is, kan een moeder de melkproductie opbouwen door te starten met kolven. Hiermee wordt gestart zodra haar conditie dit toe laat, maar bij voorkeur binnen zes uur na de bevalling[16];[18];[19];[20]. De moeder kolft dan ongeveer even vaak als de baby aan de borst zou drinken: in de eerste weken minimaal acht keer per 24 uur, waarvan een keer ’s nachts. Het principe van vraag- en aanbod regelt ook nu de melkproductie. Een effectieve methode om de melk te laten toeschieten, is zachte tactiele stimulatie van de borsten (borstmassage) vlak voor de afkolfsessie[16];[18];[19];[20]. Hierdoor neemt het oxytocinegehalte in het bloed toe[20]. Prettige omstandigheden maken het toeschieten en kolven gemakkelijker. Denk bij prettige omstandigheden aan een rustige omgeving, ontspannende muziek en kijken of luisteren naar de baby. Kijken naar beelden van de baby en het ruiken van de geur van de baby kunnen ook stimulerend werken. De moeder kan één of twee borsten tegelijkertijd kolven. Dubbelzijdig kolven vermindert de kolftijd en verhoogt de melkproductie[16];[18];[19];[20]. Door een hogere opbrengst bij het kolven, neemt de melkproductie gemakkelijker toe[16];[18];[19];[20].
Op peil houden van de melkproductie
Als de borstvoeding goed op gang is gekomen, kan een moeder haar melk kolven als ze incidenteel niet bij haar baby kan zijn. Zo kan ze de productie op peil houden, zodat haar baby geen kunstmatige zuigelingenvoeding hoeft te krijgen[16];[18];[19]. De moeder kan dan iedere ‘gemiste’ voeding kolven. Welke methode zij kiest, zal afhangen van haar persoonlijke omstandigheden[16];[18];[19]. Hieronder worden de verschillende kolfmethoden besproken.
Kolfmethoden
Kolven met de hand (zonder hulpmiddelen)
Kolven met de hand is de meest natuurlijke manier van kolven. Door het contact van de handen met de borst raakt een moeder vertrouwd met de voedende functie van haar lichaam. Ze kan in de eerste dagen kostbare druppels colostrum op een lepeltje kolven en die rechtstreeks aan haar baby geven, zodat er niks verloren gaat. Een moeder kan veel profijt hebben van deze methode en het is belangrijk dat de zorgverlener haar deze methode kan uitleggen. Kolven met de hand kan de spanning verminderen, waardoor de baby gemakkelijker kan happen. Wanneer de baby niet aan de borst kan drinken, kan de borst met de hand worden leeg gekolfd. De melk kan vervolgens op een andere manier aan de baby worden gegeven.
Er zijn verschillende methodes om met de hand te kolven:
- Kolven met de hand: Eerst de toeschietreflex opwekken d.m.v. zachte massage van de borsten. Wanneer de melk toeschiet: zet duim en wijsvinger van een hand tegenover elkaar op de rand van de tepelhof. Beweeg de hand nu in de richting van de borstkas, zonder de vingers over de huid te laten glijden. Duw de duim en wijsvinger vervolgens naar elkaar toe en dan weer in de richting van de tepel. Ook hierbij mogen de vingers niet over de huid bewegen of wrijven. Herhaal deze beweging met de duim en wijsvinger na een paar keer op een andere plaats rond de tepelhof.
- Kolven met twee handen: De hierboven beschreven methode wordt met beide handen op beide borsten tegelijk toegepast.
- Kolven met een elektrische kolf: Deze methode wordt veel gebruikt door moeders die gedurende langere tijd kolven, bijvoorbeeld door een buitenshuis werkende moeder die haar kind moedermelk wil geven door op het werk te kolven.
Er zijn verschillende methodes om elektrisch te kolven:
- Enkelzijdig: Eerst wordt de ene borst leeg gekolfd en vervolgens de andere. De kolfsessie duurt inclusief voorbereiding en opruimen gewoonlijk ongeveer 30 tot 60 minuten.
- Dubbelzijdig: Beide borsten worden tegelijkertijd gekolfd. De kolfsessie duurt inclusief voorbereiding en opruimen gewoonlijk ongeveer 20 tot 45 minuten.
Kolven met een handkolf
Handkolven kunnen worden gebruikt als de borstvoeding goed op gang is gekomen.
De zorgverlener legt de moeder uit hoe ze zich op het kolven kan voorbereiden en de toeschietreflex kan opwekken. Tevens wordt uitleg gegeven over hoe de moeder de zuiger of de hendel van de kolf zodanig kan bedienen dat ze de zuigkracht en de zuigfrequentie goed kan reguleren.
Vrouwen horen tijdens de zwangerschap voorlichting te krijgen over kolven (onder andere uitleg over verschillende kolfmethoden). De volgende aspecten komen dan ook ter sprake:
- De eerste keren worden er geen of slechts enkele druppels melk gekolfd.
- De hoeveelheid en kleur van de gekolfde moedermelk kan per kolfsessie variëren.
- Er kan een spoortje bloed in de melk aanwezig zijn; dit is geen probleem voor de baby. Wel is het van belang uit te zoeken waar het bloed vandaan komt. In geval van kloven is het zaak de kolftechniek en/of de aanlegtechniek te verbeteren.
- De hoeveelheid afgekolfde melk is vaak minder is dan dat wat een kind uit de borst drinkt. Er kan daarom op basis van de hoeveelheid afgekolfde melk geen uitspraak worden gedaan over de werkelijke melkproductie.
1.2.5 Oxytocine neusspray
Het gebruik van oxytocine neusspray (Syntocinon) lijkt tijdelijk de toeschietreflex te bevorderen. Een betere lediging van de borst door een goede toeschietreflex bevordert de productie en in die zin kan de neusspray bijdragen aan een goed verlopende lactatie. Maar in een onderzoek bij moeders van premature baby’s naar gebruik van oxytocine neusspray ter bevordering van de toeschietreflex, in combinatie met een elektrische kolf ter bevordering van de melkproductie, bleek er geen verschil in de hoeveelheid moedermelk die gedurende de eerste vijf dagen postpartum was gekolfd[21]. De gevolgen van gebruik gedurende een langere periode zijn niet onderzocht.
1.2.6 Vitaminesuppletie
Moedermelk bevat te weinig vitamine K en vitamine D om aan de vitamine K-behoefte van het kind te voldoen in de eerste weken na de geboorte. Baby’s die borstvoeding krijgen, hebben de eerste 12 weken 150 microgram aan vitamine K-druppels nodig [23];[24]. Geadviseerd wordt om alle kinderen van 0-4 jaar, ongeacht het type voeding, dagelijks 10 microgram vitamine D-suppletie te geven [23];[25].
Aanbevelingen
1.3 Voeden op verzoek
Inleiding
Het is belangrijk dat zowel ouders als zorgverleners de betekenis en het belang van voeden op verzoek begrijpen en daarnaar handelen. Goede begeleiding draagt eraan bij dat ouders leren vertrouwen op de signalen die het kind geeft, zodat het borstvoedingsproces, een systeem van vraag en aanbod, optimaal verloopt.
Aanbevelingen
1.4 Slapen met de baby
Inleiding
Zorgverleners dienen ouders te informeren over de voor- en nadelen van samen slapen. In deze richtlijntekst wordt onderscheid gemaakt tussen twee vormen van samen slapen, te weten 1) rooming- in: baby en ouder(s) slapen in dezelfde kamer, en 2) bedding-in: baby en ouder(s) slapen in hetzelfde bed. Rooming-in en bedding-in hebben mogelijk een positief effect op de borstvoedingsduur. Bedding-in bij kinderen jonger dan vier maanden (jonger dan zes maanden bij rokende ouders) geeft een verhoogde kans op zuigelingensterfte, doordat de slaapomstandigheden vaak onveilig zijn.
Aanbevelingen
1.5 Gezondheidseffecten van borstvoeding
Inleiding
Wetenschappelijk onderzoek laat zien dat borstvoeding op korte en lange termijn de gezondheid van zowel de moeder als haar kind optimaal ondersteunt. Dit komt naar voren uit meerdere systematische reviews en meta-analyses. Het geven van borstvoeding dient daarom zoveel mogelijk te worden gestimuleerd en ondersteund.
Toelichting
Uit studies waarin borstvoeding en kunstmatige zuigelingenvoeding worden vergeleken blijkt dat borstvoeding de optimale ontwikkeling geeft zowel voor de moeder als voor het kind. Hoe langer er borstvoeding wordt gegeven, hoe groter de verschillen zijn[179]. In deze richtlijn gaan we er dan ook vanuit dat borstvoeding de norm is. Voor conclusies per thema kan het Nationaal Kompas van het RIVM geraadpleegd worden[180]. De eindconclusie van alle studies is dat borstvoeding zowel de gezondheid van moeder als kind optimaal ondersteunt. Het geven van borstvoeding dient daarom zoveel mogelijk te worden gestimuleerd en ondersteund.
1.6 Gevolgen
1.6.1 Borstontsteking
Inleiding
Bij een borstontsteking (mastitis) streeft de zorgverlener naar een vlot herstel door een doeltreffende behandeling, zodat de continuïteit van de borstvoeding niet in gevaar komt.
Advisering
- Beoordeel samen met de moeder de aanlegtechniek, de duur en de frequentie van het voeden en geef adviezen om melkstase (stilstand van de melk) te voorkomen. Overweeg consultatie van een lactatiekundige.
- Leg uit dat het continueren van de borstvoeding belangrijk is voor het herstel van de borst. Stoppen met borstvoeding tijdens een borstontsteking werkt abcedering juist in de hand. Leg eveneens uit dat het drinken aan een aangedane borst onschadelijk is voor moeder en kind.
- Adviseer warmtecompressen voorafgaand aan voeding ter bevordering van dilatatie van melkgangen en daarmee ontlediging van borst[44].
- Overweeg pijnstilling met behulp van ijskompressen na de voeding en paracetamol of ibuprofen.
- Laat de baby de borsten zo goed mogelijk leegdrinken. Leg uit dat het kind de borst kan weigeren, doordat moedermelk uit een ontstoken borst anders kan smaken. De moeder kan eventueel nakolven om haar borsten nog verder te legen.
- Leg de moeder uit dat zij stuwing kan voorkomen door haar kind eerst aan de aangedane borst aan te leggen. Het is belangrijk daarbij te voorkomen dat de andere borst overvol raakt.
- Adviseer de moeder om haar baby bij voorkeur minstens iedere twee uur aan te leggen of te kolven als de baby niet wil drinken.
- Raad de moeder aan om rustig aan te doen, omdat daardoor haar welbevinden en herstel bevorderd worden. Er is onvoldoende bewijs voor het nut van bedrust.
- Bij geen vermindering van klachten na 24 uur of bij een acuut begin van klachten met algemeen ziek zijn of koorts in aanwezigheid van tepelkloven of bij abces wordt gestart met antibiotica of verwijs naar de huisarts[44].
- Zie ook de NHG standaard ‘Zwangerschap en kraamperiode’ uit 2012.[44]
Aanbevelingen
1.6.2 Candida-infectie bij borstvoeding
Inleiding
Candida albicans kan bij de baby spruw veroorzaken*. Candida albicans kan ook de borst/tepel van de moeder infecteren. Spruw, candidiasis en candida (albicans) infectie zijn verschillende benamingen voor een infectie met candida albicans. Wanneer er geen klachten zijn bij de moeder of bij het kind is geen behandeling nodig en kan het natuurlijk beloop worden afgewacht. Bij klachten door een candida infectie (spruw en frequent loslaten van de tepel en huilen bij de baby, al dan niet in combinatie met pijn tijdens en na voeden bij de moeder) streeft men naar een snelle en optimale behandeling van kind én moeder, waardoor de pijn zo snel mogelijk verdwijnt en de continuïteit van de borstvoeding niet in gevaar komt. (Stekende) pijn tijdens het voeden zonder spruw bij de baby is op zichzelf geen indicatie voor behandeling met schimmeldodende middelen[50]
*Candida albicans kan bij de baby ook luieruitslag veroorzaken. Zie daarvoor de JGZ-richtlijn Huidafwijkingen [51]
Aanbevelingen
1.6.3 Uitdroging en ondervoeding
Inleiding
Uitdroging (dehydratie) en ondervoeding bij de baby kunnen ongemerkt voorkomen, zorgverleners hebben een rol bij de herkenning, om ernstige complicaties en mogelijk overlijden te voorkomen.
Figuur 1: Groeicurve voor gewichtsverlies bij borstgevoede kinderen (beschikbaar via www.tno.nl/rwc)
Overige overwegingen bij de advisering
Bij het vermoeden van stille ondervoeding aan de borst in de eerste levensweken is het raadzaam om in de klinische setting naast het glucose- en bilirubinegehalte ook het natriumgehalte te bepalen. Urine moet ook onderzocht worden op natrium- en kaliumgehalte en de osmolaliteit, omdat bij een zouttekort het serum-natrium volledig normaal kan zijn.
Voor het signaleren van ondervoeding in de eerste levensmaanden zijn geen duidelijke afkappunten voor het gewicht gesteld. Een afbuigend gewicht (in korte tijd of in grote mate) en het klinisch ‘niet goed gedijen’ van de baby vormen samen een indicatie voor mogelijke ondervoeding.
|
Tabel 1: Kenmerken en symptomen die reden zijn voor opname[159] • Onvoldoende melkinname; |
Aanbevelingen
1.6.4 Pijnlijke tepels
Aanbevelingen
1.7 Anticonceptie
Inleiding
Zorgverleners moeten (aanstaande) ouders kunnen informeren over de vruchtbaarheid en het gebruik van anticonceptiemethoden tijdens de borstvoedingsperiode. Op grond van deze informatie kunnen ouders vervolgens een weloverwogen beslissing nemen.
Uitgebreide informatie over anticonceptiemethoden, voor zowel zorgverleners als ouders, is te vinden op onderstaande sites:
- NHG-Standaard Anticonceptie
- NVOG-voorlichtingsfolder Anticonceptie
- Informatie voor cliënten
- Thuisarts.nl Anticonceptie
- De verloskundige.nl Net bevallen
- Keuzehulp Anticonceptie
- Overzicht voor cliënten van alle methoden
Lees verder voor de onderbouwing Evidence 1.7.1.
Aanbevelingen
1.8 Risico- en beschermende factoren
1.8.1 Moeder: (Mogelijk) onvoldoende melkproductie
Inleiding
Zorgverleners dienen objectief te kunnen vaststellen of er sprake is van onvoldoende melkproductie en hun beleid daarop aan te passen, om vroegtijdig stoppen van het geven van borstvoeding te voorkomen.
|
Tabel 1: Signalen die een indicatie kunnen zijn voor onvoldoende melkproductie en -inname[136],[44]
|
Aanbevelingen
1.8.2 Moeder: Ingetrokken of vlakke tepel
Inleiding
Diepliggende, ingetrokken tepels en vlakke tepels kunnen het aanhappen en drinken aan de borst bemoeilijken. Zorgverleners dienen moeders met ingetrokken of vlakke tepels te informeren en begeleiden bij het geven van borstvoeding. Met ingetrokken of vlakke tepels kan een moeder borstvoeding geven.
Overige overwegingen bij de advisering
- Indien een pasgeborene binnen zes uur ook met een tepelhoedje niet effectief aan de borst heeft gedronken, is het voor het op gang komen van de melkproductie belangrijk dat de moeder start met kolven. Het afgekolfde colostrum wordt niet met een fles, maar op een andere wijze aan de baby gegeven, zoals met een spuitje of cupje. De baby heeft tijd nodig om de borst te leren kennen en het gebruik van de fles kan mogelijk dat proces verstoren. Gebruik de fles alleen als er onvoldoende motivatie is voor voeden met een spuitje of cupje.
- Veel jonge baby’s hebben behoefte aan stevige prikkeling van het gehemelte voor het opwekken van de zuigreflex. Een tepelhoedje kan daarbij in de beginfase behulpzaam zijn. Naarmate moeder en baby samen vaardiger worden, zal de baby steeds beter in staat zijn de borst goed aan te happen en effectief te drinken, ook als de tepel niet ver naar voren komt. Door de borst bij het aanleggen goed te vormen, wordt de tepel beter gepresenteerd.
- Het is belangrijk om het vertrouwen van de moeder in haar mogelijkheden om borstvoeding te geven, te stimuleren. Te veel aandacht van de zorgverlener voor tepelproblemen kan ontmoedigend werken en moet dus worden voorkomen.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.3 Moeder: pijn bij borstvoeding
Inleiding
Zorgverleners dienen de oorzaak van pijn bij het geven van borstvoeding op te sporen en te behandelen om voortijdige beëindiging van de borstvoeding te voorkomen.
- Zie voor veelvoorkomende klachten de sectie 1.8.4 thema ‘Pijnlijke tepels’.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.4 Moeder: pijnlijke tepels
Inleiding
De eerste week na de bevalling ervaren bijna alle vrouwen (96%) die borstvoeding geven tijdelijk pijnlijke tepels. Pijn die na deze week aanhoudt vergt nader onderzoek. Pijnlijke tepels zijn dan meestal een signaal van een niet-optimale borstvoedingstechniek. Zorgverleners dienen samen met de moeder de oorzaak van de pijnklachten te achterhalen. Hoe oe eerder de oorzaak wordt achterhaalt, hoe sneller een effectief beleid kan worden ingezet. Dit zal leiden tot een vermindering van de problemen en uiteindelijk tot het verdwijnen van de klachten. Daarmee kunnen vervolgproblemen worden voorkomen en komt het de duur van de borstvoeding ten goede.
Overige overwegingen bij de advisering
- Adviseer eerst om het voeden te beginnen met de niet-pijnlijke borst, zodat pas als de melk is toegeschoten de baby aan de pijnlijke zijde kan drinken. Voorwaarde is wel dat er wordt gekeken naar de oorzaken van de pijn. Anders zullen de klachten bij de hervatting van het voeden aan de borst vermoedelijk terugkeren. Bij ondragelijke pijn is het soms noodzakelijk dat de moeder een aantal etmalen kolft.
- Het doorslikken van bloed van beschadigde tepels is onschadelijk voor de baby. De baby kan er mogelijk misselijk van worden of van gaan spugen. Het is geen reden om de borstvoeding te stoppen.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.5 Moeder: medicatie en borstvoeding
Inleiding
Veel medicijnen komen in de moedermelk terecht. Sommige geneesmiddelen kunnen een (al dan niet nadelig) effect hebben op het kind dat borstvoeding krijgt. Andere kunnen een nadelig effect hebben op de melkproductie. In verreweg de meeste situaties gaat geneesmiddelengebruik door de moeder echter goed samen met het geven van borstvoeding. Voorwaarde is dat de zorgverlener voor het juiste geneesmiddel kiest.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.6 Moeder: HIV
Inleiding
Een vrouw die geïnfecteerd is met HIV kan haar kind met het virus besmetten door het borstvoeding te geven.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.7 Kind: Huid-op-huidcontact
Inleiding
Het kort na de geboorte tot stand brengen van huid-op-huidcontact tussen moeder en kind bevordert een langere duur van de borstvoedingsperiode en de frequentie van voedingen per etmaal.
Toelichting
Onder ‘vroeg huid-op-huidcontact’ verstaan we dat de baby kort na de geboorte naakt en toegedekt op de blote huid van de moeder ligt en daar tenminste één uur ongestoord blijft liggen. Deze periode is een ‘gevoelige periode’ voor het programmeren van toekomstig gedrag van moeder en kind.
Tot enkele decennia geleden werden baby’s na de geboorte vaak van hun moeder gescheiden of aangekleed voordat ze aan de moeder teruggegeven werden, onder meer uit angst voor onderkoeling van de pasgeborene. Inmiddels weten we dat scheiding van moeder en kind schadelijk is omdat het de vroege interacties onmogelijk maakt. Bij vroeg huid-op-huidcontact zal de baby, als hij niet wordt gestoord, uit zichzelf naar de borst ‘kruipen’ en aanhappen[3];[16] Dit stimuleert het vrijkomen van het hormoon oxytocine, de uitdrijving van de placenta en het op gang komen van het borstvoedingsproces. Tevens betekent het huid-op-huidcontact dat de flora van de moeder de steriele darmen van de pasgeborene koloniseert[101]. Dit is essentieel voor een gezonde darmflora in de baby en daarmee voor de opbouw van zijn immuniteit. Het voorkomt in belangrijke mate dat de baby wordt blootgesteld aan bacteriën die voor de moeder lichaamsvreemd zijn. Wanneer hij wordt gekoloniseerd met de flora van zijn moeder, krijgt hij via de borstvoeding een daarbij passend aanbod aan antistoffen die hem tegen infecties beschermen.
Aantoonbaar belang voor borstvoeding
Een aantal wetenschappers[100]onderzocht welk effect vroeg huid-op-huidcontact heeft op de borstvoeding, het gedrag van moeder en kind en de fysiologie van de pasgeborene. Ze analyseerden de uitkomsten van dertig studies, uit verschillende westerse en niet-westerse landen.
Hieruit bleek dat vroeg huid-op-huidcontact een positief effect heeft op het geven van borstvoeding, gedurende één tot vier maanden na de geboorte. Zuigelingen die bloot op de blote borst van de moeder liggen, blijven bovendien beter warm en hun bloedsuikerspiegel, hartslag en ademhaling zijn stabieler. Er zijn aanwijzingen dat baby’s zonder vroeg huid-op-huidcontact later een hoger risico hebben op overmatig huilen en zich minder goed hechten. Ook de moeder hecht zich minder snel aan de baby (als gevolg van een tekort aan oxytocine). Negatieve effecten van het huid-op-huidcontact zijn niet beschreven. Wel komt uit de praktijk naar voren dat het op de buik liggen van de pasgeborene als onveilige houding dient te worden gezien (verhoogd risico op Apparent Life Threatening Event (ALTE, schijnbaar levensbedreigende gebeurtenis/bijna-wiegendood), luchtwegblokkering)1;5. Alerte supervisie door ouders/zorgverlener is daarom nodig (zie ook het thema ‘Slapen met de baby’).
Duur van het contact
Onderzoekers[102] ontdekten dat het van belang is hoe lang een baby op de huid van de moeder ligt. Uit een studie onder 21.842 moeders bleek dat als het huid-op-huidcontact postpartum minimaal een uur duurt de kans op een succesvolle start van de borstvoeding het grootst is. In vergelijking met kinderen die van hun moeder werden gescheiden had deze groep een drie maal zo grote kans om uitsluitend borstvoeding te krijgen.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.8 Kind: Hyperbilirubinemie (geelzien)
Inleiding
De meeste zuigelingen maken een periode van ‘icterus neonatorum’ (geelzien) door. Het tijdig herkennen en erkennen van ernstige hyperbilirubinemie is zowel klinisch als in de thuissituatie een aandachtspunt. De combinatie van icterus en borstvoeding kan op een achterblijvende moedermelkproductie of –inname wijzen.
Advisering
Zie voor advisering over hyperbilirubinemie (geelzien) de richtlijn ‘Preventie, diagnostiek en behandeling van hyperbilirubinemie bij de pasgeborene, geboren na een zwangerschapsduur van meer dan 35 weken’.
De nieuwe richtlijn is tot stand gekomen door samenwerking van alle beroepsorganisaties van zorgverleners die betrokken zijn bij de zorg voor pasgeborenen. Deze nieuwe richtlijn vervangt de richtlijn uit 2008 opgesteld door de Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde (NVK) in samenwerking met het Kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg CBO.
Twee specifieke aanbevelingen voor de preventie van hyperbilirubinemie uit de richtlijn luiden als volgt:
Aanbevelingen
1.8.9 Kind: Hypoglykemie
Inleiding
Voor de preventie en behandeling van hypoglykemie bij pasgeborenen is een goed (borstvoedings)beleid belangrijk.
Tabel 1. Symptomen die bij neonatale hypoglykemie kunnen optreden
Algemene bevindingen
- Abnormaal huilen (hoog of zwak);
- Niet willen drinken;
- Aanhoudende onderkoeling (persisterende hypothermie);
- Transpireren.
Neurologische tekenen
- Fladderen (tremoren);
- Slapheid (hypotonie);
- Overprikkelbaarheid;
- (Extreme) lusteloosheid (apathie/lethargie);
- Stuipen (convulsies).
Cardiorespiratoire tekenen
- Blauw zien (cyanose);
- Bleekheid;
- Verhoogde hartslag (tachycardie);
- Versnelde ademhaling (tachypnoe);
- Lage zuurstofsaturatie;
- Ademhalingsstop (apneu);
- Hartstilstand.
Tabel 2 Belangrijke factoren die geassocieerd worden met een verhoogd risico op hypoglykemie
Maternale condities
- Maternale diabetes
- Alcohol- en/of drugsgebruik;
- Behandeling met medicamenten (ß-sympathicomimetica of ß-blokkers, corticosteroïden, orale glucoseverlagende middelen);
- Intraveneuze toediening van glucose vlak voor of tijdens de bevalling.
Neonatale condities
- Small for gestational age (SGA, ook wel dysmatuur genoemd) (groeiachterstand: ≤ 10e percentiel voor gewicht naar zwangerschapsduur of bij uiterlijke aspecten van dysmaturitas) (conform GROW-methode);
- Macrosoom (≥ 90e percentiel voor gewicht naar zwangerschapsduur);
- Prematuur (zwangerschap < 37 weken);
- Perinatale asfyxie/foetale nood (Apgar-score na 5 min < 7; navelstreng pH < 7,20);
- Hypothermie (< 35 °C);
- Congenitale afwijkingen;
- Zieke neonaat (onder andere verdenking van infectie, sepsis, respiratoire distress, endocriene of metabole stoornis).
Aanbevelingen
1.8.10 Kind: Korte tongriem
Inleiding
Een korte tongriem bij de pasgeborene kan de oorzaak zijn van borstvoedingsproblemen[114]. Dit is vaak eenvoudig te verhelpen door middel van het doorknippen van de tongriem. Bij voorkeur wordt dit (in geval van borstvoedingsproblemen) zo snel mogelijk na de geboorte gedaan, maar in ieder geval vóór de leeftijd van drie maanden. Daarna wordt de ingreep bij voorkeur onder algehele narcose uitgevoerd.
Symptomen korte tongriem
Korte tongriem en drinken door de zuigeling
Bij zuigelingen kan een korte tongriem zowel het drinken aan de borst als het drinken uit een fles bemoeilijken.
Symptomen die bij de zuigeling kunnen optreden zijn:
- Luidruchtig drinken met een klakkend geluid;
- Frequent loslaten van de borst of de fles, doordat de baby geen vacuüm kan houden;
- Niet kunnen pakken van de borst met als gevolg onvoldoende inname en continu willen drinken;
- ‘Failure to thrive’ (slecht groeien en gedijen);
- Reflux.
Symptomen die bij de moeder kunnen optreden zijn[115];[212]:
- Tepelpijn en/of tepelkloven;
- Stase of stuwing of juist onvoldoende melkproductie;
- Mastitis.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.11 Kind: Fopspeengebruik
Inleiding
Ouders gebruiken vaak een fopspeen om hun kind tot rust te brengen, te troosten of in slaap te laten vallen. Zorgverleners dienen ouders te informeren over de mogelijke effecten van fopspeengebruik op het borstvoedingsproces.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.12 Kind: Downsyndroom
Inleiding
Ook voor kinderen met Downsyndroom is het omwille van hun gezondheid en ontwikkeling aan te raden dat zij gedurende geruime tijd borstvoeding krijgen. Kinderen met Downsyndroom hebben echter een zwakkere lichamelijke conditie dan andere kinderen en hun moeders zijn emotioneel zwaarder belast. Daarom is het wenselijk dat moeder en kind extra aandacht en begeleid worden bij het geven en krijgen van borstvoeding.
Aanbevelingen
1.8.13 Kind: Meerlingen
Inleiding
De verzorging van een meerling betekent een extra belasting in vergelijking met de verzorging van één kind. Daarom is extra aandacht nodig voor goede begeleiding bij borstvoeding.
Aanbevelingen
2 Preventie en begeleiden
2.1 Voorlichting over borstvoeding en kunstmatige zuigelingenvoeding
Inleiding
Het doel is dat zorgverleners vrouwen consistent en objectief (en niet door commercie gekleurd) informeren over borstvoeding en kunstmatige zuigelingenvoeding. Op grond van deze informatie worden ouders in de gelegenheid gesteld een weloverwogen beslissing te nemen.
Aanbevelingen
2.2 Weegbeleid
Inleiding
Wegen is een instrument om te bepalen of een baby voldoende voeding krijgt. Door te wegen kan onnodig bijvoeden worden voorkomen en stille ondervoeding/uitdroging aan de borst tijdig worden opgespoord.
Figuur 1: Groeicurve voor gewichtsverlies bij borstgevoede kinderen (beschikbaar via www.tno.nl)

Aanbevelingen
3 Totstandkoming richtlijn
Knelpuntanalyse en uitgangsvragen
De inhoud van de richtlijn moet aansluiten bij vragen de professionals hebben. Daarom werd voorafgaande aan de ontwikkeling een knelpuntanalyse uitgevoerd (literatuuronderzoek, landelijke inventarisatie en beoordeling van protocollen aangaande borstvoeding (ZonMw project 8400.0004), raadplegen van digitale discussiefora, raadplegen experts, et cetera). Hieruit kwamen de factoren naar voren die bevorderend of belemmerend werken voor het geven van borstvoeding. Vervolgens bepaalde de werkgroep welke onderwerpen nader dienden te worden bestudeerd met systematisch literatuuronderzoek.
Voor het ontwikkelen van de richtlijn zijn knelpunten geoperationaliseerd tot de volgende uitgangsvragen die als uitgangspunt werden genomen voor de richtlijn. Om aan te sluiten bij de werkwijze van professionals is een onderverdeling gemaakt in een algemeen deel en vragen met betrekking tot signalering, diagnostiek en interventie bij borstvoedingsproblemen. Zie Verantwoording voor een overzicht van de uitgangsvragen.
Werkgroep
Voor het ontwikkelen van de richtlijn is in Fase 1 een werkgroep met experts opgericht. Deze werkgroep was multidisciplinair, met vertegenwoordigers van beroepsverenigingen die een rol hebben in de zorg rondom borstvoeding, en vertegenwoordigers van borstvoedingsorganisaties. De werkgroepleden zijn gemandateerde vertegenwoordigers van de partij die zij vertegenwoordigen. Zie bijlage 2 voor de deelnemers aan deze werkgroep. Tijdens de eerste plenaire werkgroepvergadering werden de leden gevraagd naar conflicterende belangen. Er werden geen belangen gemeld die het schrijven van een onafhankelijke richtlijn voor de preventie en aanpak van borstvoedingsproblemen in de weg zouden staan. Er werden verder afspraken gemaakt om conflicterende belangen die gedurende het ontwikkelproces ontstaan rechtstreeks te melden (geen gemeld).
TNO begeleidde het proces en de methodiek van evidence-based richtlijnontwikkeling. Twee adviseurs van TNO (richtlijnmethodoloog/ arts-epidemioloog en kinderarts-onderzoeker) zijn continu betrokken bij het proces van richtlijnontwikkeling. Er is daarnaast een informatiespecialist van TNO betrokken om het systematisch zoeken van literatuur uit te voeren (zie onderdeel wetenschappelijke onderbouwing). De epidemioloog van TNO adviseerde tevens over het samenvatten van en de waardering van gevonden literatuur.
De plenaire werkgroep werd op basis van knelpunten en uitgangsvragen ingedeeld in subgroepen van elk drie personen van verschillende disciplines. Deze drie experts beschreven de literatuur behorende bij de aan hen toegewezen uitgangsvra(a)g(en) in termen van resultaten van onderzoek en zo mogelijk ook met vermelding van de grootte en relevantie van verschillen (uitgedrukt in bijv. odds ratio). in samenspraak met de adviseurs van TNO. Door een kleine kernredactie werd vervolgens een extra redactionele slag gemaakt. Deze beschrijvingen zijn in de richtlijn te vinden onder het kopje ‘toelichting’. Het belangrijkste wetenschappelijk bewijs uit de beschrijvingen is vermeld onder het kopje ‘conclusies uit de literatuur’. De studies waarop de conclusie is gebaseerd staan bij de conclusie vermeld, inclusief de kwaliteit van het bewijs.
Voor het formuleren van adviezen zijn naast het wetenschappelijk bewijs vaak nog andere aspecten van belang, zoals voorkeuren van moeders en professionals, kosten, beschikbaarheid of organisatorische aspecten. Deze aspecten worden, voor zover niet wetenschappelijk onderzocht, vermeld onder het kopje ‘overwegingen bij de advisering’. In de overwegingen spelen dus de ervaring en de mening van werkgroepleden een belangrijke rol. Tijdens plenaire werkgroepvergaderingen werd de advisering zoals die uit de conceptteksten naar voren kwam besproken. Daarnaast werden kennislacunes vastgesteld (vermeld onder het kopje ‘Kennislacune(s)’). Bij verschillende inzichten (wetenschappelijk of beroepsmatig) werden de werkgroepleden door de voorzitter en adviseurs gestimuleerd om tot consensus te komen. De ‘advisering’ is het resultaat van de integratie van het beschikbare bewijs met de overige overwegingen.
Na een raadpleging van hun achterban is door de werkgroepleden een vaste indeling voor de richtlijnteksten vastgesteld. Op verzoek van de werkgroep zijn er geen afzonderlijke secties voor de verschillende beroepsgroepen, daarvoor is de overlap tussen de onderwerpen te groot.
Nadat alle conceptteksten vastgesteld waren, werden als praktijktest alle werkgroepleden gevraagd de advisering in de concepttekst per thema te beoordelen op belangrijkheid, juistheid en formulering. Bij het ‘scoren’ van de items raadpleegden zij een aantal collega’s. Op basis daarvan werden als onbelangrijk aangemerkte adviezen verwijderd, andere adviezen zijn aangepast. Deze teksten vormen samen de conceptrichtlijn.
Tijdens de eerste fase van de ontwikkeling van deze richtlijn (2007-2009) waren de volgende partijen betrokken:
Kerngroep:
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde, Sectie Sociale en Psychosociale Kindergeneeskunde
- Stichting Zorg voor Borstvoeding
- TNO
- Voedingscentrum
Werkgroep:
- Artsen Jeugdgezondheid Nederland
- Beroepsvereniging V&VN VOG (voortplanting, obstetrie en gynaecologie)
- Borstvoedingsorganisatie LLL
- Eerstelijnsverpleegkundigen V&VN
- Koninklijke Nederlandse Organisatie van Verloskundigen
- Nederlands Huisartsen Genootschap
- Nederlandse Beroepsvereniging van Kraamverzorgenden
- Nederlandse Vereniging van Dietisten
- Nederlandse Vereniging van Lactatiekundigen
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Obstetrie en Gynaecologie
- Sectie Sociale en Psychosociale Kindergeneeskunde
- Stichting Baby-Voeding
- Stichting Ecobaby
- Vereniging Borstvoeding Natuurlijk
Adviseurs:
- Actiz
- Centrum Jeugdgezondheidszorg
- Ministerie van VWS
Tijdens de eerste herziening (2013-2014) waren de volgende partijen en personen betrokken:
Werkgroep:
- Artsen Jeugdgezondheidszorg Nederland, drs. R. van Tuyll
- Borstvoedingorganisatie La Leche League, M. Roomer-van Zalinge
- Nederlands Huisartsen Genootschap, drs. M.M. Verduijn
- Nederlandse Beroepsvereniging van Kraamverzorgenden, S. de Rijke
- Nederlandse Vereniging van Diëtisten, J.M.T. Badart-Smook
- Nederlandse Vereniging van Lactatiekundigen, ing. K.E. Tiktak
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde, sectie Sociale en Psychosociale Kindergeneeskunde, prof.dr. H.M. Oudesluys-Murphy
- Stichting Babyvoeding, mr. I.C. Kruger, IBCLC
- Stichting Voedingscentrum Nederland, K.I. van Drongelen en dr. ir. A. Stafleu
- Stichting Zorg voor Borstvoeding, M. Steen
- TNO Child Health, dr. M. Kamphuis en drs. Y. Schönbeck (projectleider)
- Vereniging Borstvoeding Natuurlijk, D. Hays
- Verpleegkundigen en Verzorgenden Nederland, afdeling Voortplanting, Obstetrie en Gynaecologie, G. Wessels-Vlieger
- Prof.dr. S.P. Verloove-Vanhorick (werkgroepvoorzitter)
Meelezende werkgroepleden:
- Koninklijke Nederlandse Organisatie van Verloskundigen, A. de Roon-Immerzeel, MS (werkgroeplid fase 1: K.C. Zeeman)
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde, commissie Voeding, prof.dr. J.B. van Goudoever
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde, sectie Neonatologie, drs. A.P.G.F. Maingay-Visser
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde, sectie Neonatologie, drs. J.P.F. van der Sluijs-Bens
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Obstetrie en Gynaecologie, Werkgroep klinische verloskunde NVOG en drs. C.L. van der Wijden, gynaecoloog
- Verpleegkundigen en Verzorgenden Nederland, afdeling Jeugdgezondheidszorg, K. Bischoff, MANP
4 Verantwoording
Doel en doelgroep
De Haamstede-definitie van richtlijnen luidt als volgt:
‘Een richtlijn is een document met aanbevelingen, adviezen en handelingsinstructies ter ondersteuning van de besluitvorming van professionals in de zorg en patiënten, berustend op resultaten van wetenschappelijk onderzoek met daarop gebaseerde discussie en aansluitende meningsvorming, gericht op het expliciteren van doeltreffend en doelmatig medisch handelen’[215].
Het doel van deze multidisciplinaire richtlijn is het ondersteunen van zorgverleners bij het informeren, stimuleren en adviseren van ouders die borstvoeding (willen) geven aan gezonde zuigelingen. Hiermee wordt ingezet op een optimaal verloop van het borstvoedingsproces. Het uitgangspunt van deze richtlijn is het WHO standpunt dat moedermelk de optimale voeding is voor zuigelingen en jonge kinderen. Bij het opstellen van de richtlijn is het geven van borstvoeding (en niet kunstmatige zuigelingenvoeding) als uitgangspunt gehanteerd.
Ouders dienen consistent en objectief (en niet door commercie gekleurd) geïnformeerd te worden over het geven van borstvoeding. Ook dient het borstvoedingsproces professioneel te worden begeleidϒ. Professionele begeleiding houdt ook in dat moeders die, hoe graag ze ook willen, niet in staat blijken om (volledige) borstvoeding te geven, en moeders die ervoor kiezen om geen (volledige) borstvoeding te geven, zonder oordeel worden begeleid.
Deze richtlijn is ontwikkeld voor zorgverleners die te maken hebben met moeders van gezonde zuigelingen die borstvoeding (willen) geven. Bij begeleiding en ondersteuning bij borstvoeding zijn veel verschillende zorgaanbieders betrokken. De borstvoedingsketen begint bij de ouders zelf en loopt via de verloskundige, via zorgaanbieders in ziekenhuizen(kinderartsen, neonatologen, gynaecologen, O&G-verpleegkundigen, kinderverpleegkundigen), de kraamzorg en huisartsen tot en met de jeugdgezondheidszorg, met daarbij verschillende samenwerkingspartners (zoals lactatiekundigen, borstvoedingsorganisaties, diëtisten, kinderdagverblijven, apothekers, (dokters-/apothekers)assistenten). In specifieke gevallen kan deze richtlijn ook aan andere disciplines waardevolle informatie bieden, zoals voor medewerkers van kinderdagverblijven, in geval van HIV voor internisten en HIV-behandelaren, en bij een korte tongriem voor (kaak)chirurgen, KNO-artsen en logopedisten. Gebleken is dat zorgverleners tegenstrijdige informatie en ondersteuning bieden. Dit leidt tot verwarring die het zelfvertrouwen aantast en tot verschillen in succespercentages en belevingen van moeders[214];[216]. Deze richtlijn biedt uniforme informatie voor al deze zorgverleners. De afbakening van de taken van deze zorgverleners ligt soms voor de hand, maar dient daarnaast lokaal te worden afgestemd.
Totstandkoming
Deze richtlijn is tot stand gekomen in twee fasen. In fase 1 (2007 – 2009) is gestart met het opstellen van de knelpuntanalyse en de uitgangsvragen. In 2009 werd de eerste versie van de richtlijn voorgelegd aan diverse beroepsgroepen en betrokken partijen. Er kon echter niet tot accordering van alle partijen gekomen worden. Om die reden heeft het traject een doorstart gekregen in de vorm van een eerste herziening. Deze fase is gestart in 2013. In december 2014 is de herziene richtlijn ter accordering aangeboden.
Wetenschappelijke onderbouwing
Voor de beschrijving van de anatomie en fysiologie van borstvoeding zijn verschillende leerboeken gebruikt. De overige delen van de richtlijn zijn zo veel mogelijk gebaseerd op bewijs verkregen uit systematisch literatuuronderzoek. Er is door de informatiespecialist gezocht naar artikelen in het Nederlands en Engels in de databases van PubMed, Cochrane en MIDIRS, gepubliceerd vanaf 1998. Indien dit geen of weinig relevante literatuur opleverde, werd de zoekopdracht uitgebreid naar eerdere jaren. In tweede instantie zijn artikelen uit referentielijsten van opgevraagde literatuur gehaald (‘sneeuwbalmethode’). Als laatste werd door de werkgroepleden literatuur ingebracht. De aldus verzamelde artikelen zijn door de redactieleden, in samenspraak met de TNO-epidemioloog, beoordeeld op relevantie en kwaliteit. Voor de beoordeling van de methodologische kwaliteit van individuele studies en het graderen van de kwaliteit van het bewijs is gebruik gemaakt worden van de EBRO-systematiek ontwikkeld door het CBO (zie bijlage 2).
Eerste herziening
De onderhavige versie betreft een eerste herziening van de versie uit 2009. Primaire doelstelling van dit traject was om tot consensus te komen met alle betrokken partijen, uitgaande van de tekst uit 2009 en de daarbij geleverde commentaren van de niet accorderende partijen. Uitbreiding en nieuwe intensieve literatuursearches behoorden niet tot het doel van deze eerste herziening.
Alle partijen uit de eerste fase zijn opnieuw, met grotendeels dezelfde vertegenwoordigers, bijeen gekomen tijdens twee werkgroepsessies. Er is met name practice-based gekeken en daar waar nodig is recente literatuur gezocht of door experts uit de werkgroep aangedragen, en toegevoegd. In december 2014 is de richtlijn opnieuw ter accordering aangeboden aan alle partijen.
Toekomstige Herziening
Volgens de methode van Evidence Based Richtlijnontwikkeling (EBRO) verdient het aanbeveling om na uiterlijk vijf jaar te bepalen of de richtlijn nog actueel is. Bij belangrijke nieuwe ontwikkelingen binnen deze termijn kan de richtlijn eerder worden geactualiseerd. Niet-inhoudelijke wijzigingen kunnen tussentijds worden doorgevoerd.
4.1 Uitgangsvragen Multidisciplinaire richtlijn borstvoeding
Algemeen
Hoe is de fysiologie?
- Aanleggen
- Voeden op verzoek / huid-op-huid contact
- Stuwing
- Ingetrokken of vlakke tepels
- Effect van fopspeen
- Effect van kolven
Wat zijn de gezondheidseffecten van borstvoeding?
Bij het kind:
- Optimale groei en ontwikkeling
- Moeder-kindbinding
- Preventie van infecties
- Preventie van chronische aandoeningen
Bij de moeder:
- Moeder-kindbinding
- Herstel na de bevalling
- Preventie van chronische aandoeningen en kanker
Signalering en diagnostiek
Wat is de bijdrage van verschillende factoren die een rol spelen bij de beslissing om niet te starten/vroegtijdig te stoppen met borstvoeding?
Wat zijn mogelijke contra-indicaties voor het geven van borstvoeding?
- Medicatie
- Milieuverontreinigingen
- HIV/AIDS
Wat is de rol van signalering en diagnostiek bij (mogelijk) onvoldoende melkproductie?
Welke criteria moeten worden gehanteerd bij onvoldoende groei?
Interventies
Wat is de bijdrage van elk van de mogelijke vormen van begeleiding?
Welke stappen moeten worden gezet in de volgende situaties?
- Pijn bij borstvoeding
- Te kort tongriempje
- Pijnlijke tepels en tepelkloven
- Een (dreigende) borstontsteking
- Candida-infectie
- (Mogelijk) onvoldoende melkproductie
- Hyperbilirubinemie
- Hypoglycaemie
Welke criteria moeten worden gehanteerd in de volgende situaties?
- Bijvoeding
- Verwijzing
- Samen slapen
Welk (poli)klinisch behandelprotocol moet worden gevolgd bij dehydratie?
Welke specifieke aandachtspunten zijn er in de volgende situaties?
- Meerling
- Downsyndroom
Hoe kan ondersteuning worden geboden in de volgende situaties?
- Borstvoeding en anticonceptie
4.2 Tabellen EBRO-systematiek
Voor de mate van bewijskracht en het niveau van bewijs van de conclusie is de volgende indeling gebruikt (Tabel 1 en Tabel 2).
Tabel 1: Indeling van methodologische kwaliteit van individuele studies (bron: CBO)
| Interventie | Signalering | Etiologie, prognose* | |
| A1 | Systematische review van tenminste twee onafhankelijk van elkaar uitgevoerde onderzoeken van A2-niveau | ||
| A2 | Gerandomiseerd dubbelblind vergelijkend klinisch onderzoek van goede kwaliteit van voldoende omvang | Onderzoek ten opzichte van een referentietest (een ‘gouden standaard’) met tevoren gedefinieerde afkapwaarden en onafhankelijke beoordeling van de resultaten van test en gouden standaard, betreffende een voldoende grote serie van opeenvolgende patiënten die allen de index- en referentietest hebben gehad | Prospectief cohortonderzoek van voldoende omvang en follow-up, waarbij adequaat gecontroleerd is voor ‘confounding’ en selectieve follow-up voldoende is uitgesloten. |
| B | Vergelijkend onderzoek, maar niet met alle kenmerken als genoemd onder A2 (hieronder valt ook patiënt-controleonderzoek, cohortonderzoek) | Onderzoek ten opzichte van een referentietest, maar niet met alle kenmerken die onder A2 zijn genoemd | Prospectief cohortonderzoek, maar niet met alle kenmerken als genoemd onder A2 of retrospectief cohortonderzoek of patiënt-controleonderzoek |
| C | Niet-vergelijkend onderzoek | ||
| D | Mening van deskundigen | ||
* Deze classificatie is alleen van toepassing in situaties waarin om ethische of andere redenen gecontroleerde trials niet mogelijk zijn. Zijn die wel mogelijk, dan geldt de classificatie voor interventies.
Tabel 2: Niveau van bewijs van conclusies
| 1 | Gebaseerd op één systematische review (A1) of ten minste twee onafhankelijk van elkaar uitgevoerde onderzoeken van niveau A1 of A2 |
| 2 | Gebaseerd op ten minste twee onafhankelijk van elkaar uitgevoerde onderzoeken van niveau B |
| 3 | Gebaseerd op één onderzoek van niveau A2 of B of onderzoek(en) van niveau C |
| 4 | Gebaseerd op mening van deskundigen, bijvoorbeeld de werkgroepleden |
4.3 Kennislacunes
- Er is geen eenduidig bewijs voor invloed van hormonale anticonceptie op de melkproductie en op de gezondheid van baby’s die borstvoeding krijgen.
- De effectiviteit van antibiotica bij borstontsteking is onvoldoende duidelijk. Randomized controlled trials hiernaar zijn wenselijk.
- Meer duidelijkheid over diagnostische criteria voor candidiasis mammae is wenselijk. Laboratoriumonderzoek naar (mogelijke) candida infecties van de borst/tepels bij lacterende vrouwen in Nederland is wenselijk.
- De effectiviteit van behandeling van candidiasis (in het bijzonder met gentiaan violet) is onduidelijk. Randmised controlled trials hiernaar zijn wenselijk.
- Prospectief onderzoek naar een (causale) relatie tussen fopspeengebruik en de duur van de borstvoedingsperiode is gewenst.
- Prospectief onderzoek naar een (causale) relatie tussen fopspeengebruik en borstvoedingsproblemen (tepelproblemen, pijn bij borstvoeding) is gewenst.
- Wetenschappelijke publicaties worden niet geformuleerd met borstvoeding als norm. Meer publicaties over de effecten van borstvoeding waarin zowel in de titel als in de weergave van de resultaten borstvoeding als norm wordt genomen, zijn wenselijk.
- Er is meer onderzoek nodig naar de invloed van factoren als optimale kamertemperatuur voor huid-op-huidcontact, en optimale duur en timing van het huid-op-huidcontact.
- In de literatuur is geen eenduidige informatie aanwezig voor het vaststellen van een grens in bloedglucoseconcentratie waaronder onomkeerbare hypoglycaemische schade aan het centraal zenuwstelsel ontstaat.
- Er is onduidelijkheid over welke zorgverleners verantwoordelijk zijn voor het uitvoeren van frenulotomie.
- Over het effect van pijnbestrijding bij bevalling op de melkproductie, zowel op korte als op lange termijn, is nog weinig bekend.
- We zouden meer willen weten over de risicogroepen voor een (verondersteld) tekort aan melkproductie.
- Wanneer vrouwen tepelklachten hebben en de huid is aangedaan, is er vaak behoefte om iets op de tepels aan te brengen (crème, zalf, kompres). De literatuur geeft geen eenduidige resultaten voor de effectiviteit van verschillende middelen.
- De precieze interactie tussen borstvoeding, wiegendood en samen slapen is nog onbekend.
- In de literatuur is niet onderbouwd wat de optimale behandeling van dehydratie bij volledig borstgevoede baby’s inhoudt. Daarnaast is het gebruik van ORS (Oral Rehydration Solutions) als behandeling niet onderzocht.
- Er is nog onvoldoende bekend over het mogelijk onterecht constateren van gewichtsverlies door vochttoediening durante partu of vochtretentie (diabetes).
- Er is nog te weinig informatie over de hongersignalen bij oudere baby’s en kinderen.
- Overproductie bij de moeder en risico op blijvend overgewicht van het kind.
- Het is nog onvoldoende duidelijk welke begeleiding bij de voorbereiding op de borstvoedingsperiode het best werkt, omdat in de praktijk vaak een combinatie van strategieën wordt toegepast.
- Op basis van de literatuur is geen conclusie te trekken over wat de beste weegmethode en -frequentie is voor een gezonde pasgeborene.
- Er is geen duidelijkheid over indicaties voor het frequenter wegen van baby’s dan aangegeven in de richtlijn.
Referenties
[1] Riordan J., Wambach K.. Anatomy and Physiology of Lactation. 2010
[2] Kent JC, Mitoulas LR, Cregan MD, Ramsay DT, Doherty DA, Hartmann PE. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics 2006;117(3):e387-95
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16510619[3] Cadwell K. Latching-on and suckling of the healthy term neonate: breastfeeding assessment. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):638-42
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17984002[4] Inch S, Fisher C. Breastfeeding: early problems. The practising midwife 2000;3(1):12-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11029947[5] Inch S. Breastfeeding problems: prevention and management. Community practitioner : the journal of the Community Practitioners' & Health Visitors' Association 2006;79(5):165-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16724483[6] Mulder PJ. A concept analysis of effective breastfeeding. Journal of obstetric, gynecologic, and neonatal nursing : JOGNN 2006;35(3):332-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16700682[7] Walker M. Breast-feeding: good starts, good outcomes. The Journal of perinatal & neonatal nursing 2007;21(3):191-7; quiz 198-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17700094[8] Henderson A, Stamp G, Pincombe J. Postpartum positioning and attachment education for increasing breastfeeding: a randomized trial. Birth (Berkeley, Calif.) 2001;28(4):236-42
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11903211[9] Kronborg H, Vaeth M, Olsen J, Iversen L, Harder I. Effect of early postnatal breastfeeding support: a cluster-randomized community based trial. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(7):1064-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17524018[10] Wallace LM, Dunn OM, Alder EM, Inch S, Hills RK, Law SM. A randomised-controlled trial in England of a postnatal midwifery intervention on breast-feeding duration. Midwifery 2006;22(3):262-73
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16380197[11] Reede-Dunselman de A.. Begeleiding bij borstvoeding. 2010
[12] Colson SD, Meek JH, Hawdon JM. Optimal positions for the release of primitive neonatal reflexes stimulating breastfeeding. Early human development 2008;84(7):441-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2007.12.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18243594[13] Hale T.W., Hartmann P.E.. Textbook of human lactation. 2007
[14] Ramsay DT, Kent JC, Owens RA, Hartmann PE. Ultrasound imaging of milk ejection in the breast of lactating women. Pediatrics 2004;113(2):361-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14754950[15] Geddes DT. Inside the lactating breast: the latest anatomy research. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):556-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983992[16] Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.. Breastfeeding: a guide for the medical profession. 2005
[17] Jordan S, Emery S, Watkins A, Evans JD, Storey M, Morgan G. Associations of drugs routinely given in labour with breastfeeding at 48 hours: analysis of the Cardiff Births Survey. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2009;116(12):1622-9; discussion 1630-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02256.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19735379[18] Becker GE, McCormick FM, Renfrew MJ. Methods of milk expression for lactating women. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2008
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006170.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18843707[19] Biancuzzo M. Selecting pumps for breastfeeding mothers. Journal of obstetric, gynecologic, and neonatal nursing : JOGNN 1999;28(4):417-26
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10438087[20] Jones E, Dimmock PW, Spencer SA. A randomised controlled trial to compare methods of milk expression after preterm delivery. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2001;85(2):F91-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11517200[21] Fewtrell MS, Loh KL, Blake A, Ridout DA, Hawdon J. Randomised, double blind trial of oxytocin nasal spray in mothers expressing breast milk for preterm infants. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2006;91(3):F169-74
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16223754[22] Van der Wijden C, Kleijnen J, Van den Berk T. Lactational amenorrhea for family planning. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2003
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14583931[23] Lanting C.I., Heerdink-Obenhuijsen N., Schuit-van Raamsdonk H.L.L., Hofman-van den Hoogen E.M.M., Leeuwenburg-Grijseels E.H., Broerse A.. JGZ-Richtlijn Voeding en Eetgedrag. 2013
https://www.jgzrichtlijnen.nl/alle-richtlijnen/richtlijn/voeding-en-eetgedrag[24] Gezondheidsraad. Vitamine K-suppletie bij zuigelingen. 2010;11():
https://www.gezondheidsraad.nl/binaries/gezondheidsraad/documenten/adviezen/2010/06/29/vitamine-k-suppletie-bij-zuigelingen/dossier-briefadvies-over-vitamine-k-suppletie-bij-zuigelingen.pdf[25] Gezondheidsraad. Evaluatie van de voedingsnormen voor vitamine D 2012;15():
https://www.gezondheidsraad.nl/binaries/gezondheidsraad/documenten/adviezen/2012/09/26/evaluatie-van-de-voedingsnormen-voor-vitamine-d/201215evaluatievoedingsnormenvitamineD.pdf[26] Kazi A, Kennedy KI, Visness CM, Khan T. Effectiveness of the lactational amenorrhea method in Pakistan. Fertility and sterility 1995;64(4):717-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7672141[27] Pérez A, Labbok MH, Queenan JT. Clinical study of the lactational amenorrhoea method for family planning. Lancet (London, England) 1992;339(8799):968-70
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1348806[28] Ramos R, Kennedy KI, Visness CM. Effectiveness of lactational amenorrhoea in prevention of pregnancy in Manila, the Philippines: non-comparative prospective trail. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 1996;313(7062):909-12
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8876092[29] van Wouwe JP, Lanting CI, van Dommelen P, Treffers PE, van Buuren S. Breastfeeding duration related to practised contraception in the Netherlands. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2009;98(1):86-90
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2008.01019.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18771482[30] Kremer JA, Schellekens LA, Rolland R. [Contraception following pregnancy]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 1994;138(38):1898-900
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7935934[31] Neville M.C., Walsh C.T.. Effects of drugs on milk secretion and composition. 1996
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044481981-9/50021-7[32] Truitt ST, Fraser AB, Grimes DA, Gallo MF, Schulz KF. Hormonal contraception during lactation. systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Contraception 2003;68(4):233-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14572885[33] Kapp N, Curtis KM. Combined oral contraceptive use among breastfeeding women: a systematic review. Contraception 2010;82(1):10-6
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2010.02.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20682139[34] Kapp N, Curtis K, Nanda K. Progestogen-only contraceptive use among breastfeeding women: a systematic review. Contraception 2010;82(1):17-37
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2010.02.002 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20682140[35] Hale T.W.. Medications and Mothers’ Milk: A Manual of Lactational Pharmacology 2010
[36] Anticonceptiepleister en hormoonbelasting. Geneesmiddelenbulletin 2008
https://www.ge-bu.nl/artikel/anticonceptiepleisters-en-hormoonbelasting[37] Grimes DA, Lopez LM, Van Vliet HAAM, Stanwood NL. Immediate post-partum insertion of intrauterine devices. 2010
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD003036.pub2/abstract[38] Brand A, Bruinsma A, van Groeningen K, Kalmijn S, Kardolus I, Peerden M, Smeenk R, de Swart S, Kurver M, Goudswaard L. NHG-Standaard Anticonceptie Huisarts en Wetenschap 2011;54(12)():652
https://www.henw.org/files/2018-07/H%26W%2012_LR%20incl%20omslag.pdf[39] Trussell J. Contraceptive failure in the United States. Contraception 2011;83(5):397-404
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2011.01.021 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21477680[40] Möhner S, Heinemann K, Westhoff C, Grimes A. Intrauterine Devices and the Risk of Uterine Perforations: Final Results From the EURAS-IUD Study Obstetrics and Gynecology 2014;123 (1)():
http://dx.doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000000209 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261921403_Intrauterine_Devices_and_the_Risk_of_Uterine_Perforations_Final_Results_from_the_EURAS-IUD_Study[41] Frank-Herrmann P, Heil J, Gnoth C, Toledo E, Baur S, Pyper C, Jenetzky E, Strowitzki T, Freundl G. The effectiveness of a fertility awareness based method to avoid pregnancy in relation to a couple's sexual behaviour during the fertile time: a prospective longitudinal study. Human reproduction (Oxford, England) 2007;22(5):1310-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17314078[42] Jahanfar S, Ng CJ, Teng CL. Antibiotics for mastitis in breastfeeding women. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2013
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005458.pub3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23450563[43] Betzold CM. An update on the recognition and management of lactational breast inflammation. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):595-605
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983997[44] Beentjes MM, Weersma RLS, Koch W, Offringa AK, Verduijn MM, Mensink PAJS, Wiersma TJ, Goudswaard AN, van Asselt KM. NHG-Standaard Zwangerschap en kraamperiode (Tweede herziening). Huisarts en Wetenschap 2012;55(3)():112
https://www.nhg.org/standaarden/volledig/nhg-standaard-zwangerschap-en-kraamperiode[45] Michie C, Lockie F, Lynn W. The challenge of mastitis. Archives of disease in childhood 2003;88(9):818-21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12937109[46] Schaefer C, Peters P, Miller RK. Drugs during pregnancy and lactation: handbook of prescription drugs and comparative risk assessment. 2007
[47] Walker M. Conquering common breast-feeding problems. The Journal of perinatal & neonatal nursing 2008;22(4):267-74
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.JPN.0000341356.45446.23 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19011490[48] Prachniak GK. Common breastfeeding problems. Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America 2002;29(1):77-88, vi
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11892875[49] Yoshida M, Shinohara H, Sugiyama T, Kumagai M, Muto H, Kodama H. Taste of milk from inflamed breasts of breastfeeding mothers with mastitis evaluated using a taste sensor. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2014;9(2):92-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2013.0084 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24350703[50] Eekhof JAH, Verduijn MM. Pijnlijke borsten: stuwing, mastitis en tepelkloven bij borstvoeding en candida-infectie van de borst. 2011
[51] Kamphuis M. JGZ Richtlijn Huidafwijkingen 2012
https://www.jgzrichtlijnen.nl/alle-richtlijnen/richtlijn/huidafwijkingen[52] de Vries TW, Wewerinke ME, de Langen JJ. [Near asphyxiation of a neonate due to miconazole oral gel]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2004;148(32):1598-600
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15382562[53] Hoppe JE. Treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis and candidal diaper dermatitis in neonates and infants: review and reappraisal. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 1997;16(9):885-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9306485[54] Gloor M, Wolnicki D. Anti-irritative effect of methylrosaniline chloride (Gentian violet). Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland) 2001;203(4):325-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11752822[55] Heinig MJ, Francis J, Pappagianis D. Mammary candidosis in lactating women. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 1999;15(4):281-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10776178[56] Mulder-Wildemors LGM, Verduijn MM. Candidiasis bij borstvoeding Pharma Selecte 2004;20():49
https://www.pharmaselecta.nl/site/index.php/hoofdartikelen-archief/2004/533-64[57] Hoppe JE, Hahn H. Randomized comparison of two nystatin oral gels with miconazole oral gel for treatment of oral thrush in infants. Antimycotics Study Group. Infection 1996;24(2):136-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8740106[58] Hoppe JEM. Comparison of miconazole gel with nystatin hydroxyethylcellulose gel in the treatment of oral thrush in infants. Monatsschrift fur Kinderheilkunde 1994;142():285
[59] Hoppe JE. Treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis in immunocompetent infants: a randomized multicenter study of miconazole gel vs. nystatin suspension. The Antifungals Study Group. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 1997;16(3):288-93
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9076817[60] Schaad UB, Bachmann D. [Prospective comparison of miconazole gel and nystatin suspension in the treatment of oral candidiasis]. Schweizerische medizinische Wochenschrift 1983;113(38):1356-62
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6356343[61] Goins RA, Ascher D, Waecker N, Arnold J, Moorefield E. Comparison of fluconazole and nystatin oral suspensions for treatment of oral candidiasis in infants. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 2002;21(12):1165-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12506950[62] Swart EL, van der Waal I. [Use of methylrosaniline (gentian violet) to treat candidiasis]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2004;148(14):688
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15106322[63] Weijerman ME, van Furth AM, Vonk Noordegraaf A, van Wouwe JP, Broers CJM, Gemke RJBJ. Prevalence, neonatal characteristics, and first-year mortality of Down syndrome: a national study. The Journal of pediatrics 2008;152(1):15-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18154890[64] Pisacane A, Toscano E, Pirri I, Continisio P, Andria G, Zoli B, Strisciuglio P, Concolino D, Piccione M, Lo Giudice C, Vicari S. Down syndrome and breastfeeding. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2003;92(12):1479-81
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14971802[65] Anten EJ, Oudesluys HM, Semmekort BA, van Wouwe JP. Een professionele kijk op borstvoeding. 2010
[66] Aumonier ME, Cunningham CC. Breast feeding in infants with Down's syndrome. Child: care, health and development 1983;9(5):247-55
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6227426[67] Cooper-Brown L, Copeland S, Dailey S, Downey D, Petersen MC, Stimson C, Van Dyke DC. Feeding and swallowing dysfunction in genetic syndromes. Developmental disabilities research reviews 2008;14(2):147-57
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ddrr.19 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18646013[68] Neifert M, Lawrence R, Seacat J. Nipple confusion: toward a formal definition. The Journal of pediatrics 1995;126(6):S125-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7776072[69] Nowak AJ, Smith WL, Erenberg A. Imaging evaluation of breast-feeding and bottle-feeding systems. The Journal of pediatrics 1995;126(6):S130-4
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7776073[70] Smith WL, Erenberg A, Nowak A, Franken EA. Physiology of sucking in the normal term infant using real-time US. Radiology 1985;156(2):379-81
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3892576[71] Smith WL, Erenberg A, Nowak A. Imaging evaluation of the human nipple during breast-feeding. American journal of diseases of children (1960) 1988;142(1):76-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3277390[72] Woolridge MW. The 'anatomy' of infant sucking. Midwifery 1986;2(4):164-71
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3643397[73] Aarts C, Hörnell A, Kylberg E, Hofvander Y, Gebre-Medhin M. Breastfeeding patterns in relation to thumb sucking and pacifier use. Pediatrics 1999;104(4):e50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10506275[74] Binns CW, Scott JA. Using pacifiers: what are breastfeeding mothers doing? Breastfeeding review : professional publication of the Nursing Mothers' Association of Australia 2002;10(2):21-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12227560[75] Howard CR, Howard FM, Lanphear B, deBlieck EA, Eberly S, Lawrence RA. The effects of early pacifier use on breastfeeding duration. Pediatrics 1999;103(3):E33
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10049989[76] Kronborg H, Vaeth M. How are effective breastfeeding technique and pacifier use related to breastfeeding problems and breastfeeding duration? Birth (Berkeley, Calif.) 2009;36(1):34-42
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-536X.2008.00293.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19278381[77] Victora CG, Behague DP, Barros FC, Olinto MT, Weiderpass E. Pacifier use and short breastfeeding duration: cause, consequence, or coincidence? Pediatrics 1997;99(3):445-53
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9041303[78] Hauck FR, Omojokun OO, Siadaty MS. Do pacifiers reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome? A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2005;116(5):e716-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16216900[79] O'Connor NR, Tanabe KO, Siadaty MS, Hauck FR. Pacifiers and breastfeeding: a systematic review. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2009;163(4):378-82
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2008.578 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19349568[80] Kramer MS, Barr RG, Dagenais S, Yang H, Jones P, Ciofani L, Jané F. Pacifier use, early weaning, and cry/fuss behavior: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001;286(3):322-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11466098[81] Jenik AG, Vain NE, Gorestein AN, Jacobi NE, . Does the recommendation to use a pacifier influence the prevalence of breastfeeding? The Journal of pediatrics 2009;155(3):350-4.e1
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.03.038 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19464025[82] Schubiger G, Schwarz U, Tönz O. UNICEF/WHO baby-friendly hospital initiative: does the use of bottles and pacifiers in the neonatal nursery prevent successful breastfeeding? Neonatal Study Group. European journal of pediatrics 1997;156(11):874-7
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9392404[83] Howard CR, Howard FM, Lanphear B, Eberly S, deBlieck EA, Oakes D, Lawrence RA. Randomized clinical trial of pacifier use and bottle-feeding or cupfeeding and their effect on breastfeeding. Pediatrics 2003;111(3):511-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12612229[84] . The changing concept of sudden infant death syndrome: diagnostic coding shifts, controversies regarding the sleeping environment, and new variables to consider in reducing risk. Pediatrics 2005;116(5):1245-55
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16216901[85] Collins CT, Ryan P, Crowther CA, McPhee AJ, Paterson S, Hiller JE. Effect of bottles, cups, and dummies on breast feeding in preterm infants: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2004;329(7459):193-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15208209[86] Vennemann MM, Bajanowski T, Brinkmann B, Jorch G, Yücesan K, Sauerland C, Mitchell EA, . Does breastfeeding reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome? Pediatrics 2009;123(3):e406-10
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2145 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19254976[87] Jaafar SH, Jahanfar S, Angolkar M, Ho JJ. Effect of restricted pacifier use in breastfeeding term infants for increasing duration of breastfeeding. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2012
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007202.pub3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22786506[88] Stuebe A, Lee K. The pacifier debate. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1848-9; author reply 1850-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651349[89] Buzzetti R, D'Amico R. The pacifier debate. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1850; author reply 1850-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651351[90] Mitchell EA, Blair PS, L'Hoir MP. Should pacifiers be recommended to prevent sudden infant death syndrome? Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1755-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651334[91] De Cock KM, Fowler MG, Mercier E, de Vincenzi I, Saba J, Hoff E, Alnwick DJ, Rogers M, Shaffer N. Prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in resource-poor countries: translating research into policy and practice. JAMA 2000;283(9):1175-82
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10703780[92] Boer K, Nellen JF, Kreyenbroek ME, Godfried MH. [Treatment of HIV-infected pregnant women: prevention of virus transmission and adverse effects in mother and child]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2009;153():B410
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19785876[93] op de Coul ELM, van Weert JWMY, Oomen PJ, Smit C, van der Ploeg CPBK, Hahné SJM, Notermans DW, van der Sande MAB. [Antenatal screening in the Netherlands for HIV, hepatitis B and syphilis is effective]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2010;154():A2175
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21176248[94] Kuhn L, Reitz C, Abrams EJ. Breastfeeding and AIDS in the developing world. Current opinion in pediatrics 2009;21(1):83-93
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0b013e328320d894 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19242244[95] Kuhn L, Aldrovandi GM, Sinkala M, Kankasa C, Semrau K, Mwiya M, Kasonde P, Scott N, Vwalika C, Walter J, Bulterys M, Tsai W-Y, Thea DM, . Effects of early, abrupt weaning on HIV-free survival of children in Zambia. The New England journal of medicine 2008;359(2):130-41
http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa073788 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18525036[96] Coutsoudis A, Pillay K, Spooner E, Kuhn L, Coovadia HM. Influence of infant-feeding patterns on early mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Durban, South Africa: a prospective cohort study. South African Vitamin A Study Group. Lancet (London, England) 1999;354(9177):471-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10465172[97] Horvath T, Madi BC, Iuppa IM, Kennedy GE, Rutherford G, Read JS. Interventions for preventing late postnatal mother-to-child transmission of HIV. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2009;2009(1):CD006734
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006734.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19160297[98] Boer K, Nellen JF, Patel D, Timmermans S, Tempelman C, Wibaut M, Sluman MA, van der Ende ME, Godfried MH. The AmRo study: pregnancy outcome in HIV-1-infected women under effective highly active antiretroviral therapy and a policy of vaginal delivery. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2007;114(2):148-55
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17305888[99] Shapiro RL, Hughes MD, Ogwu A, Kitch D, Lockman S, Moffat C, Makhema J, Moyo S, Thior I, McIntosh K, van Widenfelt E, Leidner J, Powis K, Asmelash A, Tumbare E, Zwerski S, Sharma U, Handelsman E, Mburu K, Jayeoba O, Moko E, Souda S, Lubega E, Akhtar M, Wester C, Tuomola R, Snowden W, Martinez-Tristani M, Mazhani L, Essex M. Antiretroviral regimens in pregnancy and breast-feeding in Botswana. The New England journal of medicine 2010;362(24):2282-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0907736 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20554983[100] Moore ER, Anderson GC, Bergman N. Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2007
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17636727[101] Mackie RI, Sghir A, Gaskins HR. Developmental microbial ecology of the neonatal gastrointestinal tract. The American journal of clinical nutrition 1999;69(5):1035S-1045S
http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/69.5.1035s https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10232646[102] Bramson L, Lee JW, Moore E, Montgomery S, Neish C, Bahjri K, Melcher CL. Effect of early skin-to-skin mother--infant contact during the first 3 hours following birth on exclusive breastfeeding during the maternity hospital stay. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 2010;26(2):130-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0890334409355779 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20110561[103] Rozance PJ, Hay WW. Hypoglycemia in newborn infants: Features associated with adverse outcomes. Biology of the neonate 2006;90(2):74-86
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16534190[104] Boluyt N, van Kempen A, Offringa M. Neurodevelopment after neonatal hypoglycemia: a systematic review and design of an optimal future study. Pediatrics 2006;117(6):2231-43
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16740869[105] Hawdon JM, Ward Platt MP, Aynsley-Green A. Patterns of metabolic adaptation for preterm and term infants in the first neonatal week. Archives of disease in childhood 1992;67(4 Spec No):357-65
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1586171[106] Voeten M, Gerrits GPJM, Voorhoeve PG. [Treatment of neonatal hypoglycaemia: more frequent latching onto the breast versus supplementary feeding with formula; retrospective study of patient files]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2008;152(31):1732-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18727605[107] Wight N, Marinelli KA, . ABM clinical protocol #1: guidelines for blood glucose monitoring and treatment of hypoglycemia in term and late-preterm neonates, revised 2014. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2014;9(4):173-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2014.9986 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24823918[108] Cornblath M, Hawdon JM, Williams AF, Aynsley-Green A, Ward-Platt MP, Schwartz R, Kalhan SC. Controversies regarding definition of neonatal hypoglycemia: suggested operational thresholds. Pediatrics 2000;105(5):1141-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10790476[109] Alexander JM, Grant AM, Campbell MJ. Randomised controlled trial of breast shells and Hoffman's exercises for inverted and non-protractile nipples. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 1992;304(6833):1030-2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1586788[110] Dewey KG, Nommsen-Rivers LA, Heinig MJ, Cohen RJ. Risk factors for suboptimal infant breastfeeding behavior, delayed onset of lactation, and excess neonatal weight loss. Pediatrics 2003;112(3 Pt 1):607-19
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12949292[111] Preparing for breast feeding: treatment of inverted and non-protractile nipples in pregnancy. The MAIN Trial Collaborative Group. Midwifery 1994;10(4):200-14
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7837987[112] McKechnie AC, Eglash A. Nipple shields: a review of the literature. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2010;5(6):309-14
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2010.0003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20807104[113] Webb AN, Hao W, Hong P. The effect of tongue-tie division on breastfeeding and speech articulation: a systematic review. International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology 2013;77(5):635-46
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.03.008 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23537928[114] Post EDM, Rupert AWMS, Schulpen TWJ. [Problematic breastfeeding due to a short frenulum]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2010;154():A918
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20170571[115] Ballard JL, Auer CE, Khoury JC. Ankyloglossia: assessment, incidence, and effect of frenuloplasty on the breastfeeding dyad. Pediatrics 2002;110(5):e63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12415069[116] Mettias B, O'Brien R, Abo Khatwa MM, Nasrallah L, Doddi M. Division of tongue tie as an outpatient procedure. Technique, efficacy and safety. International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology 2013;77(4):550-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.01.003 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23411135[117] Hogan M, Westcott C, Griffiths M. Randomized, controlled trial of division of tongue-tie in infants with feeding problems. Journal of paediatrics and child health 2005;41(5-6):246-50
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15953322[118] Geddes DT, Langton DB, Gollow I, Jacobs LA, Hartmann PE, Simmer K. Frenulotomy for breastfeeding infants with ankyloglossia: effect on milk removal and sucking mechanism as imaged by ultrasound. Pediatrics 2008;122(1):e188-94
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2007-2553 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18573859[119] Emond A, Ingram J, Johnson D, Blair P, Whitelaw A, Copeland M, Sutcliffe A. Randomised controlled trial of early frenotomy in breastfed infants with mild-moderate tongue-tie. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2014;99(3):F189-95
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2013-305031 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24249695[120] Buryk M, Bloom D, Shope T. Efficacy of neonatal release of ankyloglossia: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 2011;128(2):280-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-0077 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21768318[121] Dollberg S, Botzer E, Grunis E, Mimouni FB. Immediate nipple pain relief after frenotomy in breast-fed infants with ankyloglossia: a randomized, prospective study. Journal of pediatric surgery 2006;41(9):1598-600
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16952598[122] Algar V. Question 2. Should an infant who is breastfeeding poorly and has a tongue tie undergo a tongue tie division? Archives of disease in childhood 2009;94(11):911-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.2009.163428 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19847004[123] O'Callahan C, Macary S, Clemente S. The effects of office-based frenotomy for anterior and posterior ankyloglossia on breastfeeding. International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology 2013;77(5):827-32
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.02.022 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23523198[124] Cho A, Kelsberg G, Safranek S. Clinical inquiries. When should you treat tongue-tie in a newborn? The Journal of family practice 2010;59(12):712a-b
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21135930[125] Begg EJ, Duffull SB, Hackett LP, Ilett KF. Studying drugs in human milk: time to unify the approach. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 2002;18(4):323-32
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12449047[126] Weibert RT, Townsend RJ, Kaiser DG, Naylor AJ. Lack of ibuprofen secretion into human milk. Clinical pharmacy 1982;1(5):457-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7184678[127] Townsend RJ, Benedetti TJ, Erickson SH, Cengiz C, Gillespie WR, Gschwend J, Albert KS. Excretion of ibuprofen into breast milk. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 1984;149(2):184-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6720796[128] Walter K, Dilger C. Ibuprofen in human milk. British journal of clinical pharmacology 1997;44(2):211-2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9278216[129] Fowler PD. Diclofenac sodium (Voltarol): drug interactions and special studies. Rheumatology and rehabilitation 1979;Suppl 2():60-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/394276[130] Flidel-Rimon O, Shinwell ES. Breast feeding twins and high multiples. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition 2006;91(5):F377-80
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16923939[131] Friedman S, Flidel-Rimon O, Lavie E, Shinwell ES. The effect of prenatal consultation with a neonatologist on human milk feeding in preterm infants. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2004;93(6):775-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15244226[132] Neifert MR. Prevention of breastfeeding tragedies. Pediatric clinics of North America 2001;48(2):273-97
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11339153[133] Hurst NM. Recognizing and treating delayed or failed lactogenesis II. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):588-94
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983996[134] Amir LH. Breastfeeding--managing 'supply' difficulties. Australian family physician 2006;35(9):686-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16969436[135] Gatti L. Maternal perceptions of insufficient milk supply in breastfeeding. Journal of nursing scholarship : an official publication of Sigma Theta Tau International Honor Society of Nursing 2008;40(4):355-63
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2008.00234.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19094151[136] Powers NG. How to assess slow growth in the breastfed infant. Birth to 3 months. Pediatric clinics of North America 2001;48(2):345-63
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11339156[137] Zembo CT. Breastfeeding. Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America 2002;29(1):51-76
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11892874[138] Centuori S, Burmaz T, Ronfani L, Fragiacomo M, Quintero S, Pavan C, Davanzo R, Cattaneo A. Nipple care, sore nipples, and breastfeeding: a randomized trial. Journal of human lactation : official journal of International Lactation Consultant Association 1999;15(2):125-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10578788[139] Tait P. Nipple pain in breastfeeding women: causes, treatment, and prevention strategies. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2000;45(3):212-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10907330[140] Mass S. Breast pain: engorgement, nipple pain and mastitis. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology 2004;47(3):676-82
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15326430[141] Blair PS, Fleming PJ, Smith IJ, Platt MW, Young J, Nadin P, Berry PJ, Golding J. Babies sleeping with parents: case-control study of factors influencing the risk of the sudden infant death syndrome. CESDI SUDI research group. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 1999;319(7223):1457-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10582925[142] Carpenter RG, Irgens LM, Blair PS, England PD, Fleming P, Huber J, Jorch G, Schreuder P. Sudden unexplained infant death in 20 regions in Europe: case control study. Lancet (London, England) 2004;363(9404):185-91
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14738790[143] Horsley T, Clifford T, Barrowman N, Bennett S, Yazdi F, Sampson M, Moher D, Dingwall O, Schachter H, Côté A. Benefits and harms associated with the practice of bed sharing: a systematic review. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2007;161(3):237-45
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17339504[144] Ruys JH, de Jonge GA, Brand R, Engelberts AC, Semmekrot BA. Bed-sharing in the first four months of life: a risk factor for sudden infant death. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2007;96(10):1399-403
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17714547[145] McKenna JJ, Mosko SS, Richard CA. Bedsharing promotes breastfeeding. Pediatrics 1997;100(2 Pt 1):214-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9240802[146] McKenna JJ, McDade T. Why babies should never sleep alone: a review of the co-sleeping controversy in relation to SIDS, bedsharing and breast feeding. Paediatric respiratory reviews 2005;6(2):134-52
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15911459[147] Vogel A, Hutchison BL, Mitchell EA. Factors associated with the duration of breastfeeding. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 1999;88(12):1320-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10626515[148] Scragg RK, Mitchell EA, Stewart AW, Ford RP, Taylor BJ, Hassall IB, Williams SM, Thompson JM. Infant room-sharing and prone sleep position in sudden infant death syndrome. New Zealand Cot Death Study Group. Lancet (London, England) 1996;347(8993):7-12
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8531589[149] Mitchell EA. Recommendations for sudden infant death syndrome prevention: a discussion document. Archives of disease in childhood 2007;92(2):155-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17264285[150] Horne RSC, Parslow PM, Ferens D, Watts A-M, Adamson TM. Comparison of evoked arousability in breast and formula fed infants. Archives of disease in childhood 2004;89(1):22-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14709496[151] Mosko S, Richard C, McKenna J. Infant arousals during mother-infant bed sharing: implications for infant sleep and sudden infant death syndrome research. Pediatrics 1997;100(5):841-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9346985[152] Baddock SA, Galland BC, Bolton DPG, Williams SM, Taylor BJ. Differences in infant and parent behaviors during routine bed sharing compared with cot sleeping in the home setting. Pediatrics 2006;117(5):1599-607
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16651313[153] Blair PS, Sidebotham P, Berry PJ, Evans M, Fleming PJ. Major epidemiological changes in sudden infant death syndrome: a 20-year population-based study in the UK. Lancet (London, England) 2006;367(9507):314-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16443038[154] Blair PS, Ball HL. The prevalence and characteristics associated with parent-infant bed-sharing in England. Archives of disease in childhood 2004;89(12):1106-10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15557042[155] Brenner RA, Simons-Morton BG, Bhaskar B, Revenis M, Das A, Clemens JD. Infant-parent bed sharing in an inner-city population. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2003;157(1):33-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12517192[156] McGarvey C, McDonnell M, Chong A, O'Regan M, Matthews T. Factors relating to the infant's last sleep environment in sudden infant death syndrome in the Republic of Ireland. Archives of disease in childhood 2003;88(12):1058-64
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14670769[157] Breuning-Boers JM, van Dommelen P, van Wouwe JP, Verkerk PH. [Weight loss, serum sodium concentration and residual symptoms in patients with hypernatremic dehydration caused by insufficient breastfeeding]. Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2006;150(16):904-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16686091[158] van Dommelen P, Boer S, Unal S, van Wouwe JP. Charts for weight loss to detect hypernatremic dehydration and prevent formula supplementing. Birth (Berkeley, Calif.) 2014;41(2):153-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/birt.12105 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24698284[159] Pelleboer RA, Bontemps STH, Verkerk PH, Van Dommelen P, Pereira RR, Van Wouwe JP. A nationwide study on hospital admissions due to dehydration in exclusively breastfed infants in the Netherlands: its incidence, clinical characteristics, treatment and outcome. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992) 2009;98(5):807-11
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2009.01230.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19245535[160] Taveras EM, Scanlon KS, Birch L, Rifas-Shiman SL, Rich-Edwards JW, Gillman MW. Association of breastfeeding with maternal control of infant feeding at age 1 year. Pediatrics 2004;114(5):e577-83
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15492358[161] Wiklund I, Norman M, Uvnäs-Moberg K, Ransjö-Arvidson A-B, Andolf E. Epidural analgesia: breast-feeding success and related factors. Midwifery 2009;25(2):e31-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17980469[162] Kools EJ, Thijs C, de Vries H. The behavioral determinants of breast-feeding in The Netherlands: predictors for the initiation of breast-feeding. Health education & behavior : the official publication of the Society for Public Health Education 2005;32(6):809-24
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16267150[163] Scott JA, Binns CW. Factors associated with the initiation and duration of breastfeeding: a review of the literature. Breastfeeding review : professional publication of the Nursing Mothers' Association of Australia 1999;7(1):5-16
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10197366[164] Chung M, Raman G, Trikalinos T, Lau J, Ip S. Interventions in primary care to promote breastfeeding: an evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Annals of internal medicine 2008;149(8):565-82
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18936504[165] Spiby H, McCormick F, Wallace L, Renfrew MJ, D'Souza L, Dyson L. A systematic review of education and evidence-based practice interventions with health professionals and breast feeding counsellors on duration of breast feeding. Midwifery 2009;25(1):50-61
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17418464[166] Hannula L, Kaunonen M, Tarkka M-T. A systematic review of professional support interventions for breastfeeding. Journal of clinical nursing 2008;17(9):1132-43
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2007.02239.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18416790[167] Howard C, Howard F, Lawrence R, Andresen E, DeBlieck E, Weitzman M. Office prenatal formula advertising and its effect on breast-feeding patterns. Obstetrics and gynecology 2000;95(2):296-303
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10674597[168] Lutsiv O, Pullenayegum E, Foster G, Vera C, Giglia L, Chapman B, Fusch C, McDonald SD. Women's intentions to breastfeed: a population-based cohort study. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2013;120(12):1490-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12376 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859024[169] Sachs M, Dykes F, Carter B. Weight monitoring of breastfed babies in the UK - centile charts, scales and weighing frequency. Maternal & child nutrition 2005;1(2):63-76
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16881882[170] Sachs M, Dykes F, Carter B. Weight monitoring of breastfed babies in the United Kingdom--interpreting, explaining and intervening. Maternal & child nutrition 2006;2(1):3-18
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16881910[171] Hill PD, Johnson TS. Assessment of breastfeeding and infant growth. Journal of midwifery & women's health 2007;52(6):571-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17983994[172] Peñacoba C, Catala P. Associations Between Breastfeeding and Mother-Infant Relationships: A Systematic Review. Breastfeeding medicine : the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2019;14(9):616-629
http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2019.0106 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31424264[173] de Cock ESA, Henrichs J, Vreeswijk CMJM, Maas AJBM, Rijk CHAM, van Bakel HJA. Continuous feelings of love? The parental bond from pregnancy to toddlerhood. Journal of family psychology : JFP : journal of the Division of Family Psychology of the American Psychological Association (Division 43) 2016;30(1):125-34
http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/fam0000138 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26280095[174] Seefat-van Teeffelen A, Nieuwenhuijze M, Korstjens I. Women want proactive psychosocial support from midwives during transition to motherhood: a qualitative study. Midwifery 2011;27(1):e122-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2009.09.006 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19931954[175] Pinquart M, Silbereisen RK. Changes in adolescents' and mothers' autonomy and connectedness in conflict discussions: an observation study. Journal of adolescence 2002;25(5):509-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12234557[176] Bijsluiter miconazol
https://db.cbg-meb.nl/bijsluiters/h15382.pdf[177] Lareb-Nederlands Bijwerkingen Centrum
http://www.lareb.nl[178] Geneesmiddelen, zwangerschap en borstvoeding. 2011
[179] van Rossum CTM, Buchner FL, Hoekstra J. Quantification of health effects of breastfeeding - Review of the literature and model simulation (Kwantificering van de gezondheidseffecten van borstvoeding - Literatuuroverzicht en modelsimulatie). 2005
https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/350040001.html[180] van Bakel AM. Wat zijn de mogelijke gezondheidseffecten van borstvoeding? 2013
http://www.nationaalkompas.nl/gezondheidsdeterminanten/leefstijl/borstvoeding/wat-zijn-de-mogelijke-gezondheidsgevolgen-van-borstvoeding[181] WHO. HIV and infant feeding; Revised principles and recommendations Rapid Advice 2009
https://www.aidsdatahub.org/sites/default/files/resource/hiv-infant-feeding-revised-principles-recommendations-rapid-advice.pdf[182] Landelijk Coördinatiecentrum Infectieziektebestrijding
http://www.rivm.nl/[183] UNHCR. Guidance on infant feeding and HIV in the context of refugees and displaced populations.
https://www.ennonline.net/attachments/1512/unhcr-guide-2009.pdf[184] WHO, Unicef. HIV and infant feeding counselling tools: reference guide’ van Unicef/WHOUSAID. 2005
[185] Ruys JH, Engelberst AC, van Velzen-Mol HWM. JGZ-richtlijn Preventie wiegendood. 2009
https://www.jgzrichtlijnen.nl/alle-richtlijnen/richtlijn/preventie-wiegendood[186] Gerrits GJPM, de Hosson MP, Semmekrot BA. Afname complicaties door family-centered care: minder hypo's in de kraamsuite. Medisch Contact 2009;64():498
https://www.medischcontact.nl/actueel/laatste-nieuws/artikel/minder-hypos-in-de-kraamsuite[187] van Kempen A, van Toledo-Eppinga L. Glucose, uit: Werkboek Enterale en parenterale voeding bij pasgeboren, 2012
[188] Mohrbacher N, Stock J. Handboek lactatiebegeleiding van La Leche League International. 2002
[189] Walker M. Breastfeeding Management for the Clinician: Using the Evidence. 2006
[190] Stichting Health Base. Commentaren Medicatiebewaking 2014-2015. 2014
[191] Landsmeer M, Nauta M, Te Winkel B. Vormen medicatie en borstvoeding een veilige combinatie? Farmacotherapie bij kinderen 2009;2():35
[192] College voor Zorgverzekeringen. Farmacotherapeutisch Kompas 2010
[193] Nauta M, Landsmeer M, De Wildt SN. Zijn NSAID’s veilig tijdens de lactatie? Farmacotherapie bij kinderen 2010;1():28
[194] Hale TW, Row HE. Medications and Mothers’ Milk. 2014
[195] Post EDM, Verduijn MM. Medicatie en borstvoeding, mag dat? Bijblijven 2012;4():20
[196] Briggs GG, Freeman RK. Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation: A Reference Guide to Fetal and Neonatal Risk. 2014
[197] Lanting CI, van Wouwe JP. Redenen en motieven om te starten en te stoppen met borstvoeding. 2007
https://www.tno.nl/media/1350/kvl-pz-borstvoeding-redenen-stoppen.pdf[198] Oskamp G. Handleiding voor de Zorgverlener. Borstvoedingorganisatie La Leche League. 2014
[199] de Reede-Dunselman A. Begeleiding bij borstvoeding. 8e herz.dr. 2009
[200] Ball HL, Hooker E, Kelly PJ. Where will the baby sleep? Attitudes and practices of new and experienced parents regarding co-sleeping with their newborn infants. American Anthropologist 1999;101():143
[201] McKenna JJ. Samen slapen met je baby – het handboek voor ouders over coslapen. 2011
[202] Pelleboer RAA. Voorkómen van uitdroging en ondervoeding. In 'Een professionele kijk op borstvoeding ' 2010
[203] Derksen-Lubsen G, Moll HA, Oudesluys-Murphy AJ. Compendium Kindergeneeskunde. 4e druk 2012
[204] WHO. Evidence for the ten steps to succesfull breastfeeding 1998
https://www.tensteps.org/pdf/evidence-for-the-ten-steps-to-successful-breastfeeding-eng.pdf[205] WHO. International code of marketing of breast-milk substitutes. 1981
https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/40382/9241541601_dut.pdf[206] Van Eijsden M, Berkenpas ME, van der Wal MF. Borstvoeding in een multi-etnische populatie: de rol van de (aanstaande) vader en grootmoeder. Tijdschrift voor Sociale geneeskunde 2009;87():100
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF03082193[207] World Health Organization. Proposed global targets for maternal, infant and young child nutrition. 2012
https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/nutritionlibrary/events/consultation-on-proposed-global-targets-on-maternal-infant-and-young-child-nutrition/2012-proposed-globaltargets-backgroundpaper-en.pdf?sfvrsn=6a1c2738_14[208] Vogel I, van Rossem L, Raat H. Redenen en motieven van vrouwen om gedeeltelijk of geheel te stoppen in de eerste zes maanden. In 'Een professionele kijk op borstvoeding.'' 2011
[209] EU-richtlijn 2006/141, inzake volledige zuigelingenvoeding en opvolgzuigelingenvoeding.
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:2006L0141:20081028:NL:PDF[210] CBS. Tabel: Bevalling, lengte en gewicht bij geboorte, borstvoeding. 2014
https://opendata.cbs.nl/statline/#/CBS/nl/dataset/37302/table[211] Verduijn MM. Anticonceptiepleister en hormoonbelasting. Geneesmiddelenbulletin 2008;42:42():
[212] Lemmens E, Leveau C. Frenotomie, een geknipt idee! Tijdschrift voor verloskundigen 2005
[213] Goudswaard AN, In 't Veld CJ, Kramer WLM. Handboek verrichtingen in de huisartsenpraktijk. 2009
[214] Kerkhoff Z, Martijn R, van der Horst M. Een verkennend onderzoek naar de relatie tussen borstvoedingsduur en tevredenheid. 2008
[215] van Everdingen JJE, Dreesens DHH, Burgers JS, Swinkels JA, van Barneveld TA, van der Weijden T. Handboek evidence-based richtlijnontwikkeling: een leidraad voor de praktijk, 2e druk 2014
[216] Lanting C, van Wouwe JP. Borstvoeding in Nederland, een nadere beschouwing: achtergrondkenmerken, redenen en motieven, en het effect van BFHI. 2005
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackLET OP: print de JGZ-richtlijn in liggende afdrukstand!
Grote tabellen zijn niet volledig zichtbaar als de JGZ-richtlijn in staande afdrukstand geprint wordt. Om kleuren in de printversie goed door te laten komen, moet bij de printerinstellingen Achtergrondillustraties aangezet worden.
Disclaimer printversie JGZ-richtlijnen
De printversie van de JGZ-richtlijn bevat de algemene tekst inclusief de aanbevelingen. De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing is terug te vinden op de website, bij de aanbevelingen onder de link “Evidence”.
