Lees meer in de onderliggende hoofdstukken.
2.3 Standsafwijkingen
JGZ-richtlijn Extremiteiten
JGZ-richtlijn Extremiteiten
Let op: deze richtlijn is momenteel in herziening.
Dit betekent niet dat de inhoud van deze richtlijn incorrect is. Tot de herziening blijft de richtlijn leidend voor de praktijk. Wel bestaat er een kans dat een deel van de informatie verouderd is.
Heb je feedback over deze JGZ-richtlijn? Stuur jouw feedback naar onze servicedesk. Zoek het tekstgedeelte waarbij je suggesties voor verbetering hebt. Via de knop ‘Geef jouw feedback’ kun je voor deze JGZ-richtlijn en het specifieke hoofdstuk jouw suggesties doorgeven.
Richtlijn inhoudsopgave
1 Introductie Ga naar pagina over 1 Introductie
2 Kennismodule achtergrondinformatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Kennismodule achtergrondinformatie
3 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 3 Totstandkoming richtlijn
4 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 4 Verantwoording
5 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 5 Bijlagen
1 Introductie Ga naar pagina over 1 Introductie
2 Kennismodule achtergrondinformatie Ga naar pagina over 2 Kennismodule achtergrondinformatie
3 Totstandkoming richtlijn Ga naar pagina over 3 Totstandkoming richtlijn
4 Verantwoording Ga naar pagina over 4 Verantwoording
5 Bijlagen Ga naar pagina over 5 Bijlagen
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackSamenvattingskaart richtlijn Extremiteiten
Beslisschema Tenenloop richtlijn Extremiteiten
Introductiefilmpje richtlijn Extremiteiten
PP-presentatie voor de scholing Extremiteiten
Rapportage praktijktest richtlijn Extremiteiten
BDS-registratieprotocol richtlijn Extremiteiten
Beslisschema Platvoeten richtlijn Extremiteiten
[1] Pin T, Eldridge B, Galea MP. A review of the effects of sleep position, play position, and equipment use on motor development in infants. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):858-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979866[1] Pin T, Eldridge B, Galea MP. A review of the effects of sleep position, play position, and equipment use on motor development in infants. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):858-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979866[2] Engström P, Tedroff K. The prevalence and course of idiopathic toe-walking in 5-year-old children. Pediatrics 2012;130(2):279-84
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-0225 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22826572[2] Engström P, Tedroff K. The prevalence and course of idiopathic toe-walking in 5-year-old children. Pediatrics 2012;130(2):279-84
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-0225 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22826572[3] Engström P, Van't Hooft I, Tedroff K. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and problems among children with idiopathic toe-walking. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):848-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31826bec08 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147630[3] Engström P, Van't Hooft I, Tedroff K. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and problems among children with idiopathic toe-walking. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):848-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31826bec08 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147630[4] Oetgen ME, Peden S. Idiopathic toe walking. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2012;20(5):292-300
http://dx.doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-20-05-292 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22553101[4] Oetgen ME, Peden S. Idiopathic toe walking. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2012;20(5):292-300
http://dx.doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-20-05-292 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22553101[5] Sass P, Hassan G. Lower extremity abnormalities in children. American family physician 2003;68(3):461-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12924829[5] Sass P, Hassan G. Lower extremity abnormalities in children. American family physician 2003;68(3):461-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12924829[6] McCluskey G, O'Kane E, Hann D, Weekes J, Rooney M. Hypermobility and musculoskeletal pain in children: a systematic review. Scandinavian journal of rheumatology 2012;41(5):329-38
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/03009742.2012.676064 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22639794[6] McCluskey G, O'Kane E, Hann D, Weekes J, Rooney M. Hypermobility and musculoskeletal pain in children: a systematic review. Scandinavian journal of rheumatology 2012;41(5):329-38
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/03009742.2012.676064 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22639794[7] Rikken-Bultman DG, Wellink L, van Dongen PW. Hypermobility in two Dutch school populations. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology 1997;73(2):189-92
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9228503[7] Rikken-Bultman DG, Wellink L, van Dongen PW. Hypermobility in two Dutch school populations. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology 1997;73(2):189-92
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9228503[8] van der Giessen LJ, Liekens D, Rutgers KJ, Hartman A, Mulder PG, Oranje AP. Validation of beighton score and prevalence of connective tissue signs in 773 Dutch children. The Journal of rheumatology 2001;28(12):2726-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11764224[8] van der Giessen LJ, Liekens D, Rutgers KJ, Hartman A, Mulder PG, Oranje AP. Validation of beighton score and prevalence of connective tissue signs in 773 Dutch children. The Journal of rheumatology 2001;28(12):2726-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11764224[9] Cheng JC, Chan PS, Hui PW. Joint laxity in children. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1991;11(6):752-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1960200[9] Cheng JC, Chan PS, Hui PW. Joint laxity in children. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1991;11(6):752-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1960200[10] Remvig L, Jensen DV, Ward RC. Epidemiology of general joint hypermobility and basis for the proposed criteria for benign joint hypermobility syndrome: review of the literature. The Journal of rheumatology 2007;34(4):804-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17407233[10] Remvig L, Jensen DV, Ward RC. Epidemiology of general joint hypermobility and basis for the proposed criteria for benign joint hypermobility syndrome: review of the literature. The Journal of rheumatology 2007;34(4):804-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17407233[11] Murray KJ. Hypermobility disorders in children and adolescents. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology 2006;20(2):329-51
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16546060[11] Murray KJ. Hypermobility disorders in children and adolescents. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology 2006;20(2):329-51
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16546060[12] Armon K. Musculoskeletal pain and hypermobility in children and young people: is it benign joint hypermobility syndrome? Archives of disease in childhood 2015;100(1):2-3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-306556 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25336435[12] Armon K. Musculoskeletal pain and hypermobility in children and young people: is it benign joint hypermobility syndrome? Archives of disease in childhood 2015;100(1):2-3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-306556 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25336435[13] Bauer AS, Bae DS. Pediatric Trigger Digits. The Journal of hand surgery 2015;40(11):2304-9; quiz 2309
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.04.041 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26440744[13] Bauer AS, Bae DS. Pediatric Trigger Digits. The Journal of hand surgery 2015;40(11):2304-9; quiz 2309
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.04.041 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26440744[14] Lincoln TL, Suen PW. Common rotational variations in children. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2003;11(5):312-20
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14565753[14] Lincoln TL, Suen PW. Common rotational variations in children. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2003;11(5):312-20
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14565753[15] Nurzynska D, Di Meglio F, Castaldo C, Latino F, Romano V, Miraglia R, Guerra G, Brunese L, Montagnani S. Flatfoot in children: anatomy of decision making. Italian journal of anatomy and embryology = Archivio italiano di anatomia ed embriologia 2012;117(2):98-106
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23420997[15] Nurzynska D, Di Meglio F, Castaldo C, Latino F, Romano V, Miraglia R, Guerra G, Brunese L, Montagnani S. Flatfoot in children: anatomy of decision making. Italian journal of anatomy and embryology = Archivio italiano di anatomia ed embriologia 2012;117(2):98-106
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23420997[16] Carr JB, Yang S, Lather LA. Pediatric Pes Planus: A State-of-the-Art Review. Pediatrics 2016;137(3):e20151230
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-1230 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26908688[16] Carr JB, Yang S, Lather LA. Pediatric Pes Planus: A State-of-the-Art Review. Pediatrics 2016;137(3):e20151230
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-1230 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26908688[17] Stolzman S, Irby MB, Callahan AB, Skelton JA. Pes planus and paediatric obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Clinical obesity 2015;5(2):52-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cob.12091 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25808780[17] Stolzman S, Irby MB, Callahan AB, Skelton JA. Pes planus and paediatric obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Clinical obesity 2015;5(2):52-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cob.12091 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25808780[18] Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M. The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1987;69(3):426-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3818704[18] Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M. The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1987;69(3):426-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3818704[19] Pfeiffer M, Kotz R, Ledl T, Hauser G, Sluga M. Prevalence of flat foot in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics 2006;118(2):634-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16882817[19] Pfeiffer M, Kotz R, Ledl T, Hauser G, Sluga M. Prevalence of flat foot in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics 2006;118(2):634-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16882817[20] Tudor A, Ruzic L, Sestan B, Sirola L, Prpic T. Flat-footedness is not a disadvantage for athletic performance in children aged 11 to 15 years. Pediatrics 2009;123(3):e386-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2262 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19254974[20] Tudor A, Ruzic L, Sestan B, Sirola L, Prpic T. Flat-footedness is not a disadvantage for athletic performance in children aged 11 to 15 years. Pediatrics 2009;123(3):e386-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2262 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19254974[21] Jane MacKenzie A, Rome K, Evans AM. The efficacy of nonsurgical interventions for pediatric flexible flat foot: a critical review. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):830-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182648c95 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147627[21] Jane MacKenzie A, Rome K, Evans AM. The efficacy of nonsurgical interventions for pediatric flexible flat foot: a critical review. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):830-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182648c95 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147627[22] Wenger DR, Mauldin D, Speck G, Morgan D, Lieber RL. Corrective shoes and inserts as treatment for flexible flatfoot in infants and children. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1989;71(6):800-10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2663868[22] Wenger DR, Mauldin D, Speck G, Morgan D, Lieber RL. Corrective shoes and inserts as treatment for flexible flatfoot in infants and children. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1989;71(6):800-10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2663868[23] Whitford D, Esterman A. A randomized controlled trial of two types of in-shoe orthoses in children with flexible excess pronation of the feet. Foot & ankle international 2007;28(6):715-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17592702[23] Whitford D, Esterman A. A randomized controlled trial of two types of in-shoe orthoses in children with flexible excess pronation of the feet. Foot & ankle international 2007;28(6):715-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17592702[24] Rome K, Ashford RL, Evans A. Non-surgical interventions for paediatric pes planus. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2010
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006311.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20614443[24] Rome K, Ashford RL, Evans A. Non-surgical interventions for paediatric pes planus. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2010
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006311.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20614443[25] Calmbach WL, Hutchens M. Evaluation of patients presenting with knee pain: Part II. Differential diagnosis. American family physician 2003;68(5):917-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13678140[25] Calmbach WL, Hutchens M. Evaluation of patients presenting with knee pain: Part II. Differential diagnosis. American family physician 2003;68(5):917-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13678140[26] Wiegerinck JI, Yntema C, Brouwer HJ, Struijs PAA. Incidence of calcaneal apophysitis in the general population. European journal of pediatrics 2014;173(5):677-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2219-9 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24297670[26] Wiegerinck JI, Yntema C, Brouwer HJ, Struijs PAA. Incidence of calcaneal apophysitis in the general population. European journal of pediatrics 2014;173(5):677-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2219-9 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24297670[27] Perhamre S, Janson S, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury: treatment with insoles provides effective pain relief. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):819-23
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01051.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20492591[27] Perhamre S, Janson S, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury: treatment with insoles provides effective pain relief. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):819-23
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01051.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20492591[28] Perhamre S, Lundin F, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury; treat it with a heel cup: a randomized, crossover study with two insole alternatives. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):e42-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01140.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20673253[28] Perhamre S, Lundin F, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury; treat it with a heel cup: a randomized, crossover study with two insole alternatives. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):e42-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01140.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20673253[29] Wiegerinck JI, Zwiers R, Sierevelt IN, van Weert HCPM, van Dijk CN, Struijs PAA. Treatment of Calcaneal Apophysitis: Wait and See Versus Orthotic Device Versus Physical Therapy: A Pragmatic Therapeutic Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2016;36(2):152-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000417 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25985369[29] Wiegerinck JI, Zwiers R, Sierevelt IN, van Weert HCPM, van Dijk CN, Struijs PAA. Treatment of Calcaneal Apophysitis: Wait and See Versus Orthotic Device Versus Physical Therapy: A Pragmatic Therapeutic Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2016;36(2):152-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000417 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25985369[30] Cassas KJ, Cassettari-Wayhs A. Childhood and adolescent sports-related overuse injuries. American family physician 2006;73(6):1014-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16570735[30] Cassas KJ, Cassettari-Wayhs A. Childhood and adolescent sports-related overuse injuries. American family physician 2006;73(6):1014-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16570735[31] Chiodo WA, Cook KD. Pediatric heel pain. Clinics in podiatric medicine and surgery 2010;27(3):355-67
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2010.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20691369[31] Chiodo WA, Cook KD. Pediatric heel pain. Clinics in podiatric medicine and surgery 2010;27(3):355-67
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2010.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20691369[32] Mohanta MP. Growing pains: practitioners' dilemma. Indian pediatrics 2014;51(5):379-83
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24953579[32] Mohanta MP. Growing pains: practitioners' dilemma. Indian pediatrics 2014;51(5):379-83
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24953579[33] Lowe RM, Hashkes PJ. Growing pains: a noninflammatory pain syndrome of early childhood. Nature clinical practice. Rheumatology 2008;4(10):542-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0903 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18762787[33] Lowe RM, Hashkes PJ. Growing pains: a noninflammatory pain syndrome of early childhood. Nature clinical practice. Rheumatology 2008;4(10):542-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0903 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18762787[34] Pavone V, Lionetti E, Gargano V, Evola FR, Costarella L, Sessa G. Growing pains: a study of 30 cases and a review of the literature. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2011;31(5):606-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318220ba5e https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21654473[34] Pavone V, Lionetti E, Gargano V, Evola FR, Costarella L, Sessa G. Growing pains: a study of 30 cases and a review of the literature. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2011;31(5):606-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318220ba5e https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21654473[35] Baxter MP, Dulberg C. "Growing pains" in childhood--a proposal for treatment. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1988;8(4):402-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3292578[35] Baxter MP, Dulberg C. "Growing pains" in childhood--a proposal for treatment. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1988;8(4):402-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3292578[36] Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg CBO & Argumentenfabriek 2015
[36] Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg CBO & Argumentenfabriek 2015
[37] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de JGZ. Koninklijke van Gorcum BV 2005;ISBN-13: 9789023241911():
[37] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de JGZ. Koninklijke van Gorcum BV 2005;ISBN-13: 9789023241911():
[38] Eekhof JAH, Knuistingh Neven A, Opstelten W. Kleine kwalen bij kinderen. Elsevier Gezondheidszorg 2009
[38] Eekhof JAH, Knuistingh Neven A, Opstelten W. Kleine kwalen bij kinderen. Elsevier Gezondheidszorg 2009
[39] Le Cras S, Bouck J, Brausch S, Taylor-Haas A. Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center: Evidence-based clinical care guideline for Management of Idiopathic Toe Walking 2011;Guideline 040():1
http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/service/j/anderson-center/evidence-based-care/occupational-therapy-physical-therapy/[39] Le Cras S, Bouck J, Brausch S, Taylor-Haas A. Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center: Evidence-based clinical care guideline for Management of Idiopathic Toe Walking 2011;Guideline 040():1
http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/service/j/anderson-center/evidence-based-care/occupational-therapy-physical-therapy/[40] Staheli LT.. Fundamentals of pediatric orthopedics Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 2014;ISBN-13: 978-0781774970():
[40] Staheli LT.. Fundamentals of pediatric orthopedics Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 2014;ISBN-13: 978-0781774970():
[41] Thackeray C, Beeson P. In-toeing gait in children. A review of the literature. The foot 1996;6():1
[41] Thackeray C, Beeson P. In-toeing gait in children. A review of the literature. The foot 1996;6():1
[42] Visser J. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. Groningen Telengg drukwerk service 2012
[42] Visser J. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. Groningen Telengg drukwerk service 2012
[43] Hefti F. Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York 2007; ISBN-13: 978-3-540-69963-7():
[43] Hefti F. Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York 2007; ISBN-13: 978-3-540-69963-7():
[44] Neligan PC. Plastic Surgery, volume 6: Hand and upper extremity. Elsevier 2017;6(ISBN-13: 978-0323356305.):
[44] Neligan PC. Plastic Surgery, volume 6: Hand and upper extremity. Elsevier 2017;6(ISBN-13: 978-0323356305.):
[45] EUROCAT Website Database
http://www.eurocat-network.eu/ACCESSPREVALENCEDATA/PrevalenceTables%20(data%20uploaded%2008/02/2017)[45] EUROCAT Website Database
http://www.eurocat-network.eu/ACCESSPREVALENCEDATA/PrevalenceTables%20(data%20uploaded%2008/02/2017)[46] Dijkman RR. Radial polydactyly: double or nothing? Proefschrift, Rotterdam 2016
http://www.publicatie-online.nl/uploaded/flipbook/13797-r-dijkman/index.html#8[46] Dijkman RR. Radial polydactyly: double or nothing? Proefschrift, Rotterdam 2016
http://www.publicatie-online.nl/uploaded/flipbook/13797-r-dijkman/index.html#8[47] Meer IM. Vitamine D tekort in een multi-etnische populatie; determinanten, prevalentie en consequenties. Samenvatting proefschrift. Epidemiologisch bulletin 2010;45():3
[47] Meer IM. Vitamine D tekort in een multi-etnische populatie; determinanten, prevalentie en consequenties. Samenvatting proefschrift. Epidemiologisch bulletin 2010;45():3
[48] Richtlijn Primaire Idiopathische Klompvoet Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging 2013
[48] Richtlijn Primaire Idiopathische Klompvoet Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging 2013
[49] Sluijs JA, Sakkers RJB, Bronswijk JAHM. Praktische Kindergeneeskunde: Kinderorthopedie. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten 2009
[49] Sluijs JA, Sakkers RJB, Bronswijk JAHM. Praktische Kindergeneeskunde: Kinderorthopedie. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten 2009
[50] Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen. TNO: Groeidiagrammen. 2010
[50] Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen. TNO: Groeidiagrammen. 2010
[51] RIVM: Richtlijn Uitvoering RVP 2017
http://rivm.nl/[51] RIVM: Richtlijn Uitvoering RVP 2017
http://rivm.nl/[52] NHG-Standaard Niet-traumatische knieklachten 2016
[52] NHG-Standaard Niet-traumatische knieklachten 2016
[53] Wiegerinck JI, Struijs PA, Oudhof B, van Weert HCPM. Hielpijn bij kinderen. Huisarts en Wetenschap 2012;55(6):260
[53] Wiegerinck JI, Struijs PA, Oudhof B, van Weert HCPM. Hielpijn bij kinderen. Huisarts en Wetenschap 2012;55(6):260
[54] Stakenborg J, Hobma S. Kinderen met hielpijn Huisarts en Wetenschap 2015;58(5):274
[54] Stakenborg J, Hobma S. Kinderen met hielpijn Huisarts en Wetenschap 2015;58(5):274
[55] Hilbink M, Ouwens M, Kool T. De HARING-tools. Dertien instrumenten voor ondersteuning bij het opstellen, herzien, implementeren en evalueren van richtlijnen. Scientific Institute for Quality of Healthcare (IQ healthcare), Nijmegen 2013
[55] Hilbink M, Ouwens M, Kool T. De HARING-tools. Dertien instrumenten voor ondersteuning bij het opstellen, herzien, implementeren en evalueren van richtlijnen. Scientific Institute for Quality of Healthcare (IQ healthcare), Nijmegen 2013
1 Introductie
Deze richtlijn is bedoeld voor JGZ-professionals (jeugdartsen, verpleegkundig specialisten*, jeugdverpleegkundigen, doktersassistenten) en beoogt een richtlijn te zijn voor het handelen in hun contacten met jeugdigen van 0-18 jaar en/of hun ouders/verzorgers. De richtlijn geeft zicht op voorlichting, (vroeg)signalering, begeleiding en verwijzing voor diverse aandoeningen aan de extremiteiten.
De onderwerpen die in deze richtlijn aan de orde komen zijn onderverdeeld in drie thema’s: algemene aandoeningen van de extremiteiten, standsafwijkingen en pijnklachten. De richtlijn is gebaseerd op uitgangsvragen die zijn vastgesteld tijdens een knelpuntenanalyse onder leiding van de Argumentenfabriek [36]. Bij de knelpuntenanalyse waren diverse JGZ-professionals betrokken. De uitgangsvragen worden in de tekst per onderwerp beantwoord. Uit praktische overwegingen zijn de aanbevelingen per onderwerp niet gebaseerd op de uitgangsvragen, maar op de handelingsadviezen voor de JGZ-professional.
De JGZ kan bij veel waarneembare kenmerken en vragen over de extremiteiten een belangrijke rol spelen in het normaliseren van de bevindingen en het adviseren van de ouders/jeugdigen. Hiervoor dient men goed op de hoogte te zijn van normale variaties en alarmsignalen. Met de juiste uitleg en advisering kunnen onnodige zorgen en onnodig gebruik van de zorg worden voorkomen. Het belang van tijdig opsporen van aandoeningen aan de extremiteiten is voorkómen dat aandoeningen en klachten verergeren, omdat dit kan leiden tot een afwijkende of achterblijvende motoriek, tijdelijke of blijvende functiebeperking of standsafwijking, pijnklachten en onnodig zorggebruik.
* De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en zij werkt op expertniveau. Zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ-team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
1.1 Leeswijzer
De richtlijn start met een korte inhoudelijke inleiding met daarin informatie over het lichamelijk onderzoek, het beoordelen van het looppatroon en het neurologisch onderzoek.
In sectie 2.2 worden algemene aandoeningen aan de extremiteiten beschreven, met aanbevelingen voor het beleid door JGZ-professionals: tenenloop, toeing-in en hypermobiliteit.
In sectie 2.3 worden standsafwijkingen aan de extremiteiten beschreven, met aanbevelingen voor het beleid door JGZ-professionals: polydactylie, syndactylie, camptodactylie, triggervinger, O- en X-benen (genua vara en genua valga), beenlengteverschil, klompvoet (pes equinovarus), hakvoet (pes calcaneus), metatarsus adductus, metatarsus primus varus, krulteen en platvoeten.
In sectie 2.4 worden pijnklachten aan de extremiteiten beschreven, met aanbevelingen voor het beleid door JGZ-professionals: coxitis fugax, epifysiolysis capitis femoris, ziekte van Perthes, Osgood-Schlatter, ziekte van Sever en groeipijn.
* De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en zij werkt op expertniveau. Zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ-team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
1.2 Afbakening
De JGZ Richtlijn ‘Extremiteiten’ is ontwikkeld op basis van de knelpuntenanalyse, zoals deze is uitgevoerd door het CBO & de Argumentenfabriek [36]. Bij de knelpuntenanalyse waren diverse JGZ-professionals betrokken. De aldaar geformuleerde uitgangsvragen zijn beantwoord. De uitgangsvragen worden in de tekst per onderwerp beantwoord. Uit praktische overwegingen zijn de aanbevelingen per onderwerp niet gebaseerd op de uitgangsvragen, maar op de handelingsadviezen voor de JGZ-professional.
De uitgangsvragen die in deze richtlijn zijn beantwoord:
- Welke kennis over specifieke aandoeningen aan extremiteiten moeten JGZ-professionals hebben om afwijkingen aan extremiteiten te signaleren?
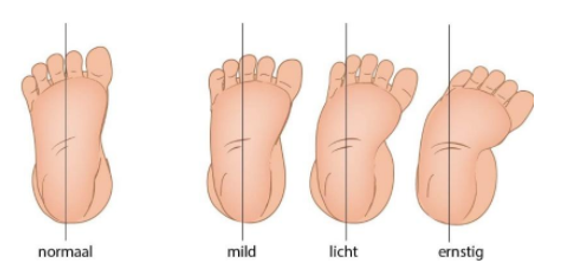
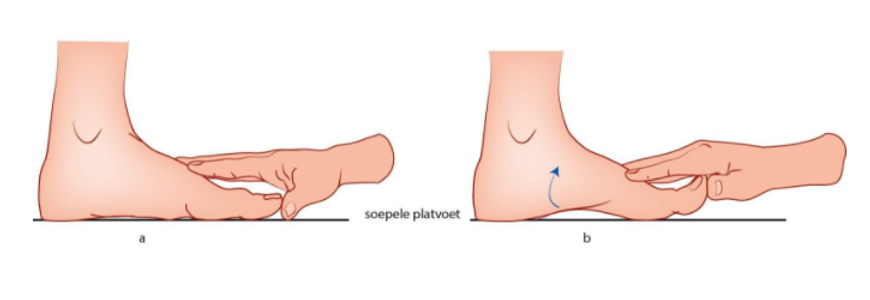
- Hoe kunnen JGZ-professionals de normale, leeftijdsgebonden variatie in extremiteiten, zoals bij O- en X-benen, platvoeten en groeipijn, onderscheiden van aandoeningen?
- Hoe moeten JGZ-professionals lichamelijk onderzoek uitvoeren om afwijkingen aan extremiteiten betrouwbaar te signaleren?
- Wat zijn alarmsignalen bij afwijkingen aan extremiteiten van kinderen die JGZ-professionals moeten kennen om tijdig door te verwijzen?
- Welke adviezen kunnen JGZ-professionals geven aan ouders en kinderen bij vragen en signalering van afwijkingen aan extremiteiten om klachten of problemen te voorkomen of te verhelpen?
- Welke verwijscriteria moeten JGZ-professionals gebruiken om kinderen met beperkingen door afwijkingen aan extremiteiten tijdig door te verwijzen naar de juiste zorgverlener?
De JGZ Richtlijn ‘Extremiteiten’ sluit aan bij richtlijnen van onder andere het Nederlands Huisartsen Genootschap (NHG) en de Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde (NVK). Dit zijn onder andere:
- Richtlijn Primaire Idiopathische Klompvoet, Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging, 2013
- Richtlijn Marfan Syndroom, Vereniging Klinische Genetica Nederland, 2013
- NHG-Standaard Niet-traumatische knieklachten, NHG, 2016
- JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling (naar verwachting gereed in 2019)
- JGZ Richtlijn Heupdysplasie (2018)
- JGZ Richtlijn Overgewicht (2012)
- JGZ Richtlijn Kindermishandeling (2016)
- JGZ Richtlijn Lengtegroei (2019)
1.3 Verklarende woordenlijst
| Abductie | Beweging of stand van het lichaam af |
| Adductie | Beweging of stand naar het lichaam toe |
| AJN | Jeugdartsen Nederland |
| Arthogryposis | Een aandoening met contracturen aan handen en voeten |
| CBO | Centraal Begeleidings Orgaan, kwaliteitsinstituut voor de Gezondheidszorg |
| Congenitaal | Aanwezig vanaf de geboorte |
| Deformatie | Vervorming door inwerking van een kracht |
| Distaal | Aan het uiteinde van een extremiteit |
| Dysplasie | Gestoorde ontwikkeling |
| EBRO | Evidence Based Richtlijn Ontwikkeling |
| Extensie | Strekking |
| Flexie | Buiging |
| Hypertrofie | Overmatige groei |
| JGZ | Jeugdgezondheidszorg |
| Lateraal | Naar opzij |
| Mediaal | Naar het midden |
| NVDA | Nederlandse Vereniging van Doktersassistenten |
| Progressief | Toenemend in ernst |
| Pronatie | Draaiende beweging van de voet of onderarm, waarbij de buitenrand van de hand/voet wordt opgetrokken. Bij pronatie wordt de handpalm naar onder gedraaid |
| Proximaal | Aan de kant van de romp |
| Supinatie | Draaiende beweging van de voet of onderarm, waarbij de binnenrand van de hand/voet wordt opgetrokken. Bij suprinatie wordt de handpalm naar boven gedraaid |
| Valgus | X-stand of naar binnen gebogen |
| Varus | O-stand of naar buiten gebogen |
| V&VN | Verpleegkundigen en Verzorgenden Nederland |
2 Kennismodule achtergrondinformatie
2.1 Inleiding in extremiteiten
Dit hoofdstuk bevat algemene kennis die nodig is als achtergrondinformatie voor de inhoudelijke thema’s. Voor een goede voorlichting, (vroeg)signalering, begeleiding en verwijzing voor aandoeningen aan de extremiteiten is enige achtergrondkennis van de gebruikte terminologie noodzakelijk. Diverse (orthopedische) termen worden in bijlage 1 uitgelegd. Voor uitgebreidere informatie wordt verwezen naar de handboeken (bijlage 2). Voor sommige onderwerpen wijken de adviezen af van de aanbevolen handboeken. Het advies aan de JGZ-professional is om dan de aanbevelingen uit deze richtlijn te volgen, omdat deze zo veel mogelijk is gebaseerd op (recent) wetenschappelijk bewijs. Daarnaast zijn de aanbevelingen opgesteld in samenwerking met vele betrokken partijen.
2.1.1 Onderzoeksmomenten
Deze richtlijn bevat slechts enkele aandoeningen die actief opgespoord dienen te worden door JGZ-professionals, in de meeste gevallen wordt gereageerd op vragen en zorgen van ouders. In de richtlijn worden daarom geen specifieke aanbevelingen gedaan voor onderzoeksmomenten.
2.1.2 Lichamelijk onderzoek
De uitvoering en beoordeling van het lichamelijk onderzoek worden door de jeugdarts* verricht. De jeugdarts verricht een compleet lichamelijk onderzoek, hierbij kunnen ook dysmorfe kenmerken en andere aanwijzingen voor syndromale aandoeningen aan de extremiteiten worden gesignaleerd. De jeugdarts combineert de bevindingen bij lichamelijk onderzoek en anamnese met de medische voorgeschiedenis van de jeugdige, en stelt een differentiaaldiagnose op.
De jeugdverpleegkundige observeert de jeugdige en bij twijfel over uitwendig zichtbare bijzonderheden overlegt zij met de jeugdarts.
Het onderzoek van de extremiteiten en/of gewrichten bestaat uit de volgende onderdelen:
- Inspectie. Hierbij wordt onder andere gelet op zwelling, afwijkende vorm, kleur of stand, littekens, spieratrofie.
- Palpatie. Hierbij wordt onder andere gelet op zwellingen, pijn of gevoeligheid, warmte.
- Beweging. Hierbij worden zowel actieve (waarbij de jeugdige de extremiteit zelf beweegt) als passieve (waarbij de onderzoeker de extremiteit beweegt) bewegingen onderzocht.
- Zo nodig specifieke testen per gewricht.
Daarnaast worden de volgende aspecten beoordeeld:
- Houding
- Looppatroon
- Motorische ontwikkeling
2.1.3 Looppatroon
Over het algemeen lopen kinderen los vanaf de leeftijd van 13-15 maanden (met een spreiding van ongeveer 10-18 maanden). Voordat een kind los kan lopen, moet het zijn evenwicht en houdingsmotoriek zodanig beheersen dat het een staande positie kan aanhouden terwijl de voeten zich alternerend verplaatsen.
Jonge kinderen zijn nog instabiel tijdens het lopen, en hebben daarom een breed gangspoor. Jonge kinderen lopen op platte voeten en met korte stapjes. De loopsnelheid is wisselend, stoppen is in het begin nog moeilijk.
In de loop van de tijd wordt het looppatroon meer stabiel (zowel in evenwicht als in loopsnelheid). Vanaf de leeftijd van ongeveer 4 jaar is het looppatroon vergelijkbaar met dat van een volwassene.
Voor een goede beoordeling van het looppatroon is de jeugdige ontkleed met alleen het ondergoed aan. Bij jonge kinderen (dreumes/jonge peuter) wordt het looppatroon bij voorkeur beoordeeld zonder luier aan. Vanaf de leeftijd van 2 jaar moet het lopen beoordeeld kunnen worden over een afstand van minimaal 5 meter [37]. Naast de observatie wordt ook de mening van de ouders over het looppatroon gevraagd. Bij observatie van het looppatroon wordt gelet op de volgende aspecten:
- De symmetrie van houding en beweging
- De soepelheid van bewegen
- De bewegingsrichting van de armen ten opzichte van de benen
- De breedte van het gangspoor
- Het contact van de voeten met de vloer
- De wendbaarheid/het vermijden van voorwerpen op de vloer
2.1.4 Oriënterend neurologisch onderzoek
Voor een beschrijving van het oriënterend neurologisch onderzoek zie JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling.
2.1.5 Betrokken (para)medici en hulpverleners
De volgende partijen kunnen betrokken zijn bij de signalering, verwijzing, diagnosticering en behandeling van kinderen met aandoeningen aan de extremiteiten:
Medische zorg:
- Het JGZ-team (jeugdarts, verpleegkundig specialist, jeugdverpleegkundige, doktersassistente): speelt een signalerende rol bij bijzonderheden aan de extremiteiten, normaliseert waar mogelijk de bevindingen en adviseert ouders/jeugdigen;
- De huisarts: bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is;
- De (kinder)orthopeed: bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is;
- De plastisch chirurg: bepaalt of (en welke) behandeling of aanvullend onderzoek nodig is;
- De kinderarts: is betrokken bij kinderen met een ontwikkelingsachterstand of een (verdenking op) een syndroom;
- De kinderneuroloog: behandelt kinderen met een (mogelijke) neurologische aandoening;
- De kinderrevalidatiearts: begeleidt jeugdigen met beperkingen in het functioneren ten gevolge van een aandoening of ongeluk
- De sportarts: behandelt (sport)blessures en kijkt daarbij naar belasting en belastbaarheid;
- De klinisch geneticus: onderzoekt of er (mogelijk) sprake is van een erfelijke of syndromale oorzaak, en geeft erfelijkheidsadvies.
Paramedische zorg:
- De kinderfysiotherapeut: heeft gespecialiseerde kennis en vaardigheden met betrekking tot de motorische ontwikkeling en specifieke bewegings- en houdingsaandoeningen op de kinderleeftijd, zoals bijvoorbeeld verkorte achillespezen of hypermobiliteit;
- De kinderoefentherapeut: De oefentherapeut behandelt aandoeningen op het gebied van houding en beweging, waarbij de kinderoefentherapeut gespecialiseerd is in de behandeling van kinderen met motorische problemen die een negatieve invloed hebben op het dagelijks functioneren;
- De (kinder)ergotherapeut: Adviseert en begeleidt bij barrières in dagelijkse activiteiten, denkt mee over de keuze en verdeling van activiteiten over de dag;
- De podotherapeut: behandelt een uitgebreid scala aan voet- en houdingsklachten, in de vorm van zooltjes/inlays.
De werkgroep adviseert verwijzing naar een therapeut (ongeacht de beroepsgroep) die een aanvullende specialisatie op het gebied van kinderen heeft gevolgd.
Er is niet altijd een duidelijk onderscheid te maken tussen de verwijsindicaties voor kinderfysiotherapeut en kinderoefentherapeut. Er is namelijk overlap in het aanbod en de behandelmogelijkheden van deze beroepsgroepen. Beide beroepsgroepen behandelen indien nodig ook aan huis. De JGZ-professional kan op basis van de lokale sociale kaart en in overleg met ouders een keuze maken naar welke beroepsgroep wordt verwezen.
De titels ‘fysiotherapeut’ en ‘oefentherapeut’ zijn beiden beschermde beroepstitels, dat betekent dat niet iedereen zich zomaar ‘fysiotherapeut’ en ‘oefentherapeut’ mag noemen. Beide opleidingen zijn een Hbo-opleiding, met een aanvullende specialisatie gericht op kinderen. Qua opleiding zijn er wel inhoudelijke verschillen tussen de beide beroepsgroepen.
Ten tijde van het schrijven van deze richtlijn (2019) geldt voor beide beroepsgroepen geldt dat de basisverzekering de eerste 9 behandelingen voor jeugdigen vergoed, op indicatie worden de volgende 9 behandelingen ook vergoed. Het Zorginstituut Nederland biedt actuele informatie over de inhoud van het basispakket van de zorgverzekering.
* Daar waar ‘jeugdarts’ staat, kan ook ‘verpleegkundig specialist’ worden gelezen. De verpleegkundig specialist preventieve zorg is een verpleegkundige met een BIG geregistreerde masteropleiding die werkzaamheden van het medisch domein combineert met die van het verpleegkundig domein binnen het eigen deskundigheidsgebied en zij werkt op expertniveau. Zij is binnen dit expertisegebied o.a. bevoegd om zelfstandig te werken, diagnoses te stellen en te verwijzen waar nodig is. De verpleegkundig specialist is lid van het JGZ-team, zij maakt net als de andere teamleden gebruik van de expertise van collega’s en speciaal van de jeugdarts als het gaat om complexe medische problematiek.
2.2 Algemene aandoeningen
2.2.1 Tenenlopen
Beschrijving aandoening
Tenenloop (of tenengang) komt relatief vaak voor bij kinderen die recent zijn gaan lopen, in de loop van enkele maanden verdwijnt dit looppatroon ook weer. Veel auteurs beschouwen het als een normale variatie in de motorische ontwikkeling tot de leeftijd van ongeveer twee jaar. Oudere kinderen lopen ook wel uit gewoonte op hun tenen, bijv. als ze enthousiast of opgewonden zijn.
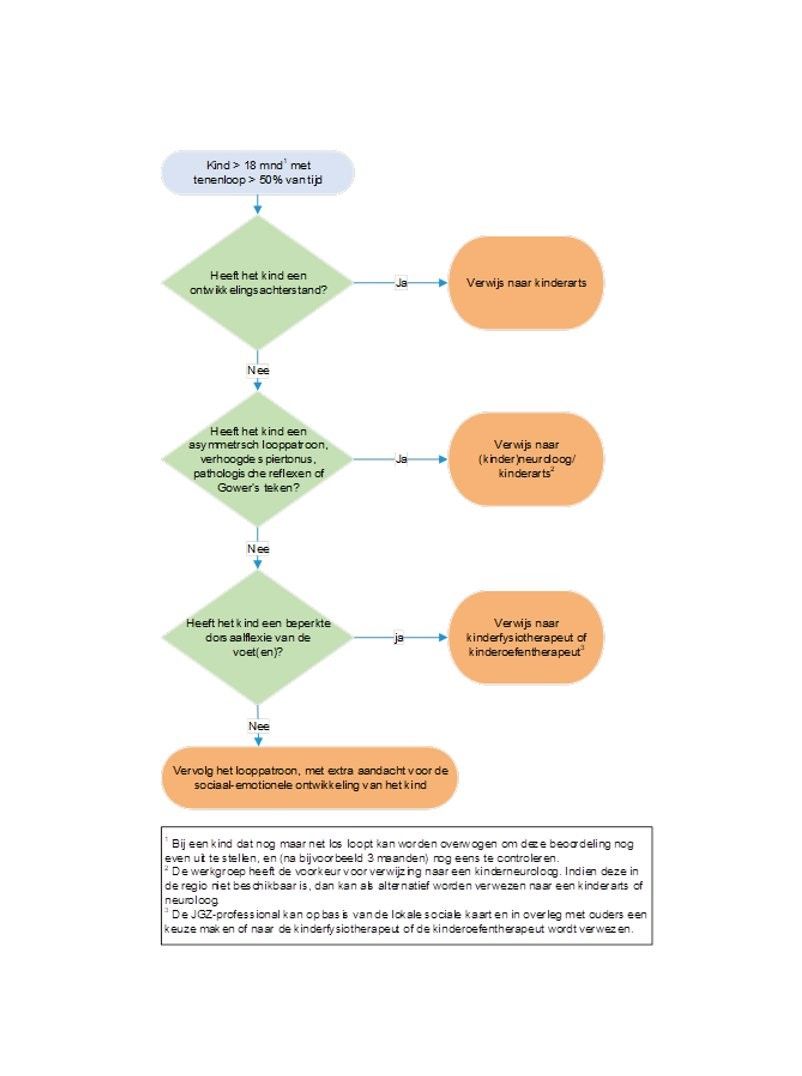
Afbeelding 1: stroomschema onderzoek en beleid bij kinderen met tenenloop.
Het onderwerp tenenloop is opgenomen in de richtlijn omdat het een onderwerp is waar JGZ-professionals vragen over krijgen. Bij kinderen t/m 3 jaar dient het looppatroon actief beoordeeld te worden. Het looppatroon wordt beoordeeld met behulp van het Van Wiechen onderzoek.
Zie Evidence 2.2.1.1 voor onderbouwing
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij kinderen met tenenloop worden de volgende zaken nagevraagd, o.a. om een onderliggende oorzaak uit te sluiten:
- Problemen tijdens zwangerschap en bevalling
- Medische voorgeschiedenis
- Familieanamnese
- Ontwikkeling (motoriek, communicatie, cognitief, sociaal-emotioneel)
- Leeftijd start lopen en tenenloop, inschatting hoeveel % van de tijd tenenloop, in staat om normaal te lopen?
- Tenenloop uni- of bilateraal?
- Klachten (zoals pijn of vaak vallen)
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Tijdens het lichamelijk onderzoek van kinderen met tenenloop worden de volgende zaken door de jeugdarts onderzocht:
- Looppatroon. Als er sprake is van een asymmetrisch looppatroon of het kind niet in staat is tot een normaal looppatroon kan dit wijzen op een onderliggende oorzaak.
- Spiertonus in de benen en kniepees-/voetzoolreflex. Als er sprake is van een verhoogde spiertonus of pathologische reflexen kan dit wijzen op een onderliggende neurologische oorzaak.
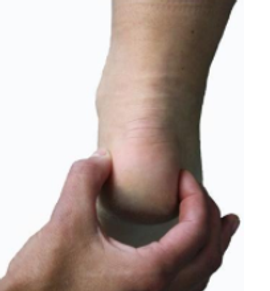
- Dorsaalflexie voet. Houd met één hand het onderbeen van de jeugdige vast, en met de andere hand wordt de voet voorzichtig naar dorsaal gebogen. Dit kan zowel met gebogen als met gestrekte knie worden getest. Indien de voet voorbij de neutrale stand gebogen kan worden is de achillespees voldoende lang.
- Opstaan vanuit zittende houding op de grond. Als het kind tijdens het opstaan met de handen op de bovenbenen steunt (Gower’s teken) kan dit wijzen op de aanwezigheid van spierdystrofie of een andere spierziekte als onderliggende oorzaak.
Alarmsignalen
Indien er sprake is van tenenloop in combinatie met bevindingen zoals een ontwikkelingsachterstand, asymmetrisch looppatroon, verhoogde spiertonus, pathologische reflexen of Gower’s teken dient de mogelijkheid van een onderliggende oorzaak te worden overwogen en dient te worden verwezen.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals
(adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden), zie ook boven het stroomschema in afbeelding 1.
- Bij kinderen t/m 3 jaar dient het looppatroon actief beoordeeld te worden. Het looppatroon wordt beoordeeld met behulp van het Van Wiechen onderzoek.
- Indien een kind na de leeftijd van 18 maanden >50% van de tijd op de tenen loopt, dient de jeugdarts na te gaan of er sprake is van alarmsignalen (een ontwikkelingsachterstand, asymmetrisch looppatroon, verhoogde spiertonus, pathologische reflexen of Gower’s teken) of een verminderde dorsaalflexie van de voet. Bij een kind dat nog maar net los loopt kan worden overwogen om deze beoordeling nog even uit te stellen, en (na bijvoorbeeld 3 maanden) nog eens te controleren.
- Indien er sprake is van tenenloop in combinatie met een ontwikkelingsachterstand dient te worden verwezen naar de kinderarts of Integrale Vroeghulp.
- Indien er sprake is van tenenloop in combinatie met een asymmetrisch looppatroon, verhoogde spiertonus, pathologische reflexen of Gower’s teken dient te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)neuroloog/kinderarts.*
- Indien er sprake is van tenenloop in combinatie met een verminderde dorsaalflexie van de voet dient te worden verwezen naar de kinderfysiotherapeut of kinderoefentherapeut. Bespreek met ouders dat zij bij onvoldoende verbetering terugkomen voor een hernieuwde beoordeling, en vraag dit in de verwijsbrief ook aan de kinderfysiotherapeut of kinderoefentherapeut. Bij onvoldoende verbetering dient te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed of naar de (kinder)neuroloog/kinderarts* (bij verdenking op neurologische problematiek).
- Indien er geen sprake is van tenenloop in combinatie met alarmsignalen of een verminderde dorsaalflexie van de voet, dan dient de JGZ het looppatroon te vervolgen (na 3-6 maanden, afhankelijk van de leeftijd van de jeugdige) en extra aandacht te hebben voor de sociaal-emotionele ontwikkeling van het kind (omdat tenenloop een signaal kan zijn van ontwikkelingsproblematiek of spanning).
Aanbevelingen
2.2.2 Toeing-in (met de voeten naar binnen lopen)
Het onderwerp toeing-in is opgenomen in de richtlijn omdat het een onderwerp is waar JGZ-professionals vragen over krijgen. JGZ-professionals kunnen dit looppatroon signaleren tijdens hun contactmomenten, maar hoeven het niet actief op te sporen.
Toeing-in (met de voeten naar binnen lopen of endorotatiegang) wil zeggen dat een kind met de voeten naar binnen gedraaid loopt. Toeing-in is geen diagnose, het is een fysiologisch verschijnsel of (afhankelijk van de ernst van het beeld) een klinisch symptoom van een anatomische variatie.
Toeing-in kan worden veroorzaakt door endorotatie op drie anatomische niveaus, te weten:
- Bovenbeen: Meestal is femorale anteversie (inwaartse draaiing van het dijbeen) de oorzaak van toeing-in. De stand van de heup ten opzichte van de knie wordt bepaald door de anteversiehoek van de femurhals met de femurschacht. Bij kinderen met (versterkte) femorale anteversie staan behalve de voeten ook de patellae (knieschijven) naar binnen. Bij het ouder worden zal de anteversiehoek kleiner worden en het probleem lost zich dan meestal spontaan op.
- Onderbeen: Minder vaak is tibiale endotorsie de oorzaak van toeing-in. Hierbij staat het onderbeen naar binnen gedraaid. Bij kinderen met (versterkte) tibiale endotorsie staan de patellae recht naar voren. Bij het ouder worden draait de tibia naar buiten en het probleem lost zich meestal spontaan op. Dat wil zeggen, in 90% van de gevallen is de tibiale endotorsie vanzelf verdwenen voordat het kind de leeftijd van 8 jaar bereikt [5].
- Voet: Soms zijn de voeten de oorzaak van toeing-in. Dan staan heup, knie en enkel in normale positie ten opzichte van elkaar, maar is de voorvoet naar binnen gericht. Dit wordt een metatarsus adductus genoemd. Ook een platvoet kan de naar binnen gerichte stand benadrukken.
Toeing-in levert meestal geen functionele problemen op, soms struikelen kinderen vaker dan leeftijdsgenoten. Soms is tijdens het rennen een uitwaartse draaiing van de onderbenen zichtbaar, dit kan opvallend zijn maar het levert geen functioneel probleem op. Uit de literatuur blijkt dat toeing-in geen gevolgen heeft voor de motorische ontwikkeling of slijtage van de gewrichten [40].
Vrijwel alle jonge kinderen lopen in meer of mindere mate met de voeten naar binnen. In de loop van de jaren neemt dit af, tot de leeftijd van 16 jaar (zo lang het kind groeit) is verbetering mogelijk. Ongeveer 30% van de kinderen tussen 2 en 7 jaar loopt met de voeten naar binnen. Bij volwassenen is dit nog 4% [41]. Er is vaak sprake van een positieve familieanamnese.
Actieve behandeling van toeing-in is in de meeste gevallen dan ook niet nodig. Uitleg aan ouders over het normale beloop is gewenst, om te voorkomen dat ouders zorgen blijven houden. Het verwisselen van de linker- en rechterschoen is geen juist advies, dit is oncomfortabel en heeft geen effect op de onderliggende oorzaak.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij kinderen met toeing-in wordt nagevraagd of er sprake is van klachten zoals vallen, struikelen, pijnklachten of problemen met de schoenen.
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij kinderen met toeing-in worden de volgende punten onderzocht:
- Tijdens het lopen wordt de mate van toeing-in beoordeeld. Dit kan worden vastgelegd door de hoek te schatten tussen de richting waarin het kind loopt en de stand van de voeten, waarbij een positieve hoek aangeeft dat de voeten naar buiten wijzen, en een negatieve hoek aangeeft dat de voeten naar binnen wijzen (de foot-progression angle). Een normale bevinding is een hoek tot ongeveer -10° [5]. Daarnaast wordt tijdens het beoordelen van het looppatroon gelet op de spierspanning en de coördinatie in de benen.
- In staande houding wordt de stand van de patellae en de stand van de voeten ten opzichte van de patellae beoordeeld. Als er sprake is van (versterkte) femorale anteversie dan zullen zowel de patellae als de tenen naar binnen wijzen. Als het kind de voeten recht naar voren zet dan zullen de patellae ook recht naar voren komen te staan. Als er sprake is van tibiale endotorsie dan staan de voeten naar binnen en de patellae recht naar voren.
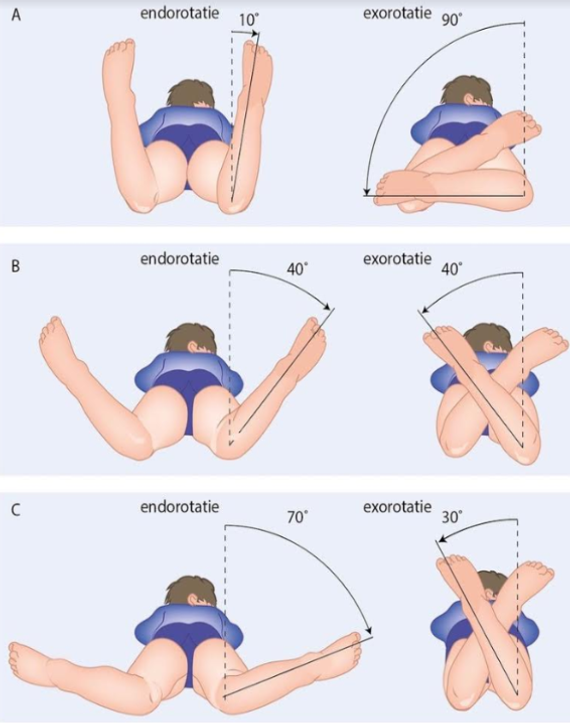
- Heuprotatie (i.v.m. femorale anteversie, afbeelding 2): Exorotatie en endorotatie van de heup worden beoordeeld terwijl het kind op de buik ligt met de knie in een hoek van 90°.
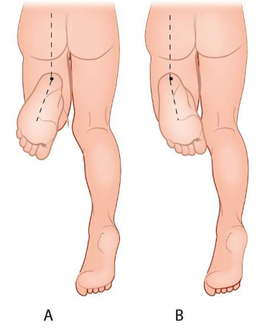
- Dij-voet hoek (i.v.m. tibiale endotorsie, afbeelding 3): de hoek tussen de voet en het femur
- wordt beoordeeld terwijl het kind op de buik ligt met de knie in een hoek van 90°.
De jeugdarts laat ouders meekijken tijdens het onderzoek en geeft uitleg over de bevindingen. Hiermee wordt voor ouders duidelijk wat de oorzaak is van het looppatroon.
FIGUUR
Afbeelding 2: Beoordelen heuprotatie (i.v.m. femorale anteversie): exorotatie en endorotatie van de heup worden beoordeeld terwijl het kind op de buik ligt met de knie in een hoek van 90°. Het naar buiten draaien van de onderbenen is endorotatie, het naar binnen draaien is exorotatie.
A: bij pasgeborenen is er sprake van versterkte exorotatie van de heupen van ongeveer 80° tot 90° en een verminderde endorotatie van 10° tot 20°.
B: vanaf de leeftijd van ongeveer 4 jaar zijn endo- en exorotatie meestal symmetrisch verdeeld.
C: soms treedt bij kinderen tussen de vier en zes jaar een versterkte femorale anteversie op. Er is dan sprake van een versterkte endorotatie en een verminderde exorotatie. Als de endorotatie van de heupen 70° of meer bedraagt, gaat het kind met de tenen naar binnen lopen.
FIGUUR
Afbeelding 3: Beoordelen dij-voet hoek (i.v.m. tibiale endotorsie). De hoek tussen de voet en het femur wordt beoordeeld terwijl het kind op de buik ligt met de knie in een hoek van 90°.
A: de voet is ten opzichte van het bovenbeen 20° buitenwaarts gericht (normale stand).
B: als er sprake is van een endotorsie van het linker onderbeen, zal de voet ten opzichte van het bovenbeen naar binnen zijn gericht.
Alarmsignalen
Indien er naast toeing-in sprake is van een opvallend lage en/of hoge spierspanning en/of verminderde coördinatie in de benen, dient te worden gedacht aan een neurologische oorzaak en is aanvullend onderzoek wenselijk.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Indien er geen alarmsignalen zijn (een opvallend lage en/of hoge spierspanning en/of verminderde coördinatie in de benen) en de bevindingen bij het lichamelijk onderzoek passen bij de leeftijd: geef de ouders uitleg over het natuurlijke beloop en benadruk dat toeing-in geen verhoogde kans geeft op een achterblijvende motorische ontwikkeling of slijtage van de gewrichten. Zowel de verhoogde femorale anteversie als tibiale endotorsie en metatarsus adductus van de voeten corrigeren meestal vanzelf tijdens de groei. Aan ouders wordt uitgelegd dat deze correctie langzaam gaat en dat het dus jaren kan duren (tot de leeftijd van 16 jaar, afhankelijk van de oorzaak) voordat de stand van de voeten merkbaar veranderd is.
- Indien er sprake is van een verergering in plaats van verbetering in de tijd dan dient het kind te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
- Indien er een verdenking is op een cerebrale parese in verband met een opvallend lage en/of hoge spierspanning en/of verminderde coördinatie in de benen dan dient het kind te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)neuroloog/kinderarts.*
* De werkgroep heeft de voorkeur voor verwijzing naar een kinderneuroloog. Indien deze in de regio niet beschikbaar is, dan kan als alternatief worden verwezen naar een kinderarts of neuroloog.
Overwegingen
De werkgroep is van mening dat toeing-in in de meeste gevallen geen actieve behandeling behoeft. De JGZ-professional speelt een belangrijke rol in het normaliseren: indien er geen alarmsignalen worden gevonden is een goede uitleg aan de ouders zeer belangrijk.
JGZ-professionals krijgen regelmatig vragen van ouders over de zithouding van kinderen, in het bijzonder over de W-zit (ook wel kikkerzit of TV-zit genoemd). Hierbij zitten kinderen met hun benen in de vorm van een ‘W’. De knieën zijn gebogen, de benen zijn van het lichaam afgedraaid. Er is de werkgroep geen bewijs bekend dat dit schadelijk zou zijn voor de ontwikkeling van het kind. Als jonge kinderen soms in de W-zit zitten, en daarnaast deze houding afwisselen met andere zithoudingen, is dat geen probleem. De JGZ-professional kan ouders dan geruststellen dat dit geen kwaad kan. Alleen als kinderen altijd in de W-zit zitten, is het raadzaam om ouders hierop te wijzen en tips te geven om kinderen op andere manieren te laten zitten. De JGZ-professional kan dan overwegen om de mobiliteit van de heupen en de spierspanning in de benen te controleren.
Aanbevelingen
2.2.3 Hypermobiliteit
Beschrijving aandoening
Hypermobiliteit kan worden gezien als een uiterste in de normaalverdeling van zeer stijve tot zeer soepele gewrichten.
Hoewel hypermobiliteit in principe fysiologisch is, kan hypermobiliteit aanleiding geven tot klachten en symptomen. Echter, niet alle jeugdigen met hypermobiliteit hebben een probleem, en niet alle jeugdigen met hypermobiliteit hebben behandeling nodig. In sommige situaties kan hypermobiliteit zelfs een voordeel zijn, bijvoorbeeld voor muzikanten en dansers.
Hypermobiliteit kan gepaard gaan met een diversiteit aan andere problemen, zoals [11]:
- Vermoeidheid
- Vertraagde motorische ontwikkeling (zie JGZ Richtlijn Motorische ontwikkeling (in ontwikkeling)): op latere leeftijd loslopen, verminderde coördinatie, ‘onhandigheid’ (struikelen, vallen, stoten).
- Gewrichtsklachten, vooral na langdurig staan en lopen, soms gepaard gaand met zwellingen rond de gewrichten.
- Groeipijn
- (Sub)luxatie gewrichten
- Rugklachten
- Platvoeten
- Zindelijkheidsproblematiek (chronische obstipatie, enuresis nocturna)
- Snel bloeduitstortingen (blauwe plekken) krijgen
Zie voor onderbouwing Evidence 2.2.3.1
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met het vermoeden van hypermobiliteit wordt nagevraagd of er sprake is van (pijn)klachten. Zo ja, vraag dan naar de aard, timing en locatie van de pijn, verergerende factoren, en eventuele beperkingen in sport of vrijetijdsbesteding.
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Er zijn verschillende methoden om hypermobiliteit vast te stellen. De meest gebruikte methode is de Beighton-score. Daarnaast wordt soms gebruik gemaakt van de Brighton-criteria of de Bulbena-score. De Brighton-criteria bevatten naast items over hypermobiliteit ook items over gewrichts- en andere klachten, en zijn meer gericht op het vaststellen van het hypermobiliteit syndroom. Geen van deze methoden is gevalideerd voor het vaststellen van hypermobiliteit bij jeugdigen. De Beighton-score is om praktische redenen, waaronder de duur van de test, goed bruikbaar binnen de JGZ.
De Beighton-score bestaat uit 5 items, waarop maximaal 9 punten kunnen worden gescoord (tabel 1). Bij een score ≥4 is er sprake van hypermobiliteit. In de literatuur worden verschillende afkappunten gehanteerd (bijvoorbeeld ook ≥5, ≥6), waaruit blijkt dat een absoluut afkappunt niet bekend is.
Tabel 1. Het bepalen van de Beighton-score. In de JGZ te gebruiken bij jeugdigen > 6 jaar met klachten van vermoeidheid in combinatie met rug- en/of gewrichtsklachten.
Er wordt gescoord met een 1, indien er sprake is van hypermobiliteit in dat gewricht. De score 0 wordt gegeven indien er geen sprake is van hypermobiliteit van het gewricht.
| Item | Links | Rechts |
|
Pink Kun je met je arm en hand plat op de tafel je pink zo ver mogelijk naar je toe bewegen? Positief als de pink >90° dorsaalflexie maakt |
1 | 1 |
|
Duim Kun je met een gestrekte arm je duim tegen je onderarm aandrukken? Positief als de duim de onderarm raakt |
1 | 1 |
|
Elleboog Hoe ver kun je met een uitgestrekte arm je elleboog overstrekken? Positief bij hyperextensie van de elleboog > 10° |
1 | 1 |
|
Knie Hoe ver kun je je knieën overstrekken terwijl je staat? Positief bij hyperextensie van de knie > 10° |
1 | 1 |
|
Wervelkolom Kun je met gestrekte knieën voorover buigen en met je handpalmen plat op de grond komen? Positief als de handpalmen plat op de grond komen met de knieën gestrekt |
1 | |
| Totaal | (max. 9) | |
Alarmsignalen
Indien er sprake is van hypermobiliteit in combinatie met bevindingen zoals pectus excavatum (trechterborst), arachnodactylie (lange dunne vingers), grote lengte, zeer rekbare huid, of blauwe sclerae dient de mogelijkheid van een syndroom, zoals het Ehlers-Danlos syndroom, het Marfan syndroom of osteogenesis imperfecta, te worden overwogen.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Bij jeugdigen > 6 jaar met klachten van vermoeidheid in combinatie met rug- en/of gewrichtsklachten bepaalt de jeugdarts of er sprake is van hypermobiliteit.
- Voor het onderzoek naar hypermobiliteit bepaalt de jeugdarts de Beighton-score (tabel 1).
- Indien er sprake is van hypermobiliteit in combinatie met bevindingen zoals pectus excavatum (trechterborst), arachnodactylie (lange dunne vingers), grote lengte of blauwe sclerae dan dient de jeugdige te worden verwezen naar de kinderarts.
- Indien er sprake is van hypermobiliteit in combinatie met klachten dan dient de jeugdige, afhankelijk van de klachten, te worden verwezen naar de huisarts, kinderfysiotherapeut of kinderoefentherapeut.** Indien er sprake is van vermoeidheid die participatie in het dagelijks leven belemmert is samenwerking met de ergotherapeut van meerwaarde.
- Bij schoolverzuim door hypermobiliteit is het een taak van de JGZ om samen met de ouders/jeugdige, school en behandelaar(s) te bepalen hoe het onderwijs optimaal gevolgd kan worden: wat heeft de jeugdige nodig om wel naar school te gaan? Voor de begeleiding bij schoolverzuim kan bijvoorbeeld gebruik gemaakt worden van de onderbouwde interventie M@zl.
- Bij jeugdigen met hypermobiliteit bespreekt de JGZ-professional zo nodig (als er vragen zijn over sportbeoefening) met ouders en/of jeugdige dat hypermobiliteit geen beperking in sportactiviteiten hoeft op te leveren. Als er sprake is van verergering van klachten als gevolg van sportactiviteiten of regelmatige blessures kan een verwijzing naar de kinderfysiotherapeut en/of kinderoefentherapeut** en/of sportarts worden overwogen.
- De JGZ-professional kan (naar aanleiding van vragen van ouders of leerkrachten) in contacten met school benoemen dat hypermobiliteit geen beperking in sportactiviteiten hoeft op te leveren. Indien school een verergering van de klachten als gevolg van sportactiviteiten bemerkt, dient school dit met de ouders te bespreken.
** De JGZ-professional kan op basis van de lokale sociale kaart en in overleg met ouders een keuze maken of naar de kinderfysiotherapeut of de kinderoefentherapeut wordt verwezen.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen jeugdigen met hypermobiliteit signaleren tijdens contactmomenten, maar hoeven niet alle jeugdigen te screenen op hypermobiliteit.
De JGZ-professional speelt een belangrijke rol in het normaliseren: alle jonge kinderen tot de leeftijd van 4-6 jaar hebben relatief soepele gewrichten. Daarom adviseert de werkgroep om de Beighton-score pas vanaf 6 jaar af te nemen. Tot de leeftijd van 4-6 jaar is het moeilijk te beoordelen of er sprake is van hypermobiliteit, alhoewel deze term wel regelmatig gebruikt wordt bij jonge kinderen. Belangrijke aandachtspunten voor de JGZ-professional bij het jonge kind zijn dysmorfie, andere aanwijzingen voor syndromen en de motorische ontwikkeling.
De JGZ-professional dient zich er van bewust te zijn dat hypermobiliteit aanleiding kan geven tot klachten en de jeugdarts dient zo nodig te onderzoeken of er sprake is van hypermobiliteit met behulp van de Beighton-score. De werkgroep vindt het belangrijk dat JGZ-professionals zich bewust zijn van het feit dat hypermobiliteit een normale variatie is, die niet altijd gepaard gaat met klachten en waarvoor behandeling meestal niet noodzakelijk is.
De werkgroep is van mening dat van de verschillende methoden om hypermobiliteit vast te stellen, de Beighton-score de beste methode is om in de JGZ te gebruiken. De redenen hiervoor zijn dat de test geen aanvullende hulpmiddelen vereist en relatief snel kan worden afgenomen. Daarnaast sluit de test aan bij de door overige beroepsgroepen gebruikte tests (zoals kinderfysiotherapeuten of kinderoefentherapeuten).
Bij de multidisciplinaire behandeling van kinderen met hypermobiliteit die gepaard gaat met klachten is mogelijk ook een rol weggelegd voor de podotherapeut. De podotherapeut kan gericht schoenadvies geven, een schoen/zoolaanpassing in de bestaande schoenen adviseren of podotherapeutische inlays aanmeten. De werkgroep is van mening dat verwijzing naar de podotherapeut geen eerste keus is voor de JGZ, maar dat deze keus wel gemaakt kan worden door de behandelend kinderfysiotherapeut, kinderoefentherapeut of specialist**.
** De JGZ-professional kan op basis van de lokale sociale kaart en in overleg met ouders een keuze maken of naar de kinderfysiotherapeut of de kinderoefentherapeut wordt verwezen.
Aanbevelingen
2.3 Standsafwijkingen
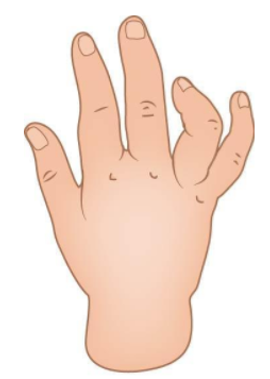
2.3.1 Polydactylie
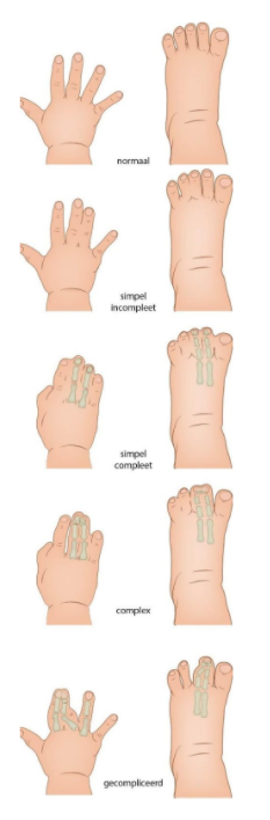
Beschrijving aandoening
Polydactylie is een aandoening waarbij er meer dan vijf vingers of tenen aanwezig zijn bij het kind (afbeelding 4). Deze aandoening is een relatief veel voorkomende aangeboren afwijking aan de hand en voet en het komt vaker voor bij meisjes dan bij jongens. Soms is er sprake van een erfelijke aandoening, en hebben meerdere mensen in de familie dezelfde aandoening. De prevalentie in Europa is ongeveer 0,9:1.000 geboortes [45], dit betekent dat er per jaar ongeveer 158 kinderen worden geboren met polydactylie. De incidentie van preaxiale polydactylie (duim) in Nederland is 60-80 per jaar [46]. Afro-Amerikanen hebben vaker dan andere etnische groepen een extra pink, terwijl Aziaten en Kaukasiërs vaker een extra duim hebben [43]. De aandoening varieert van een klein weke delen aanhangsel (dus zonder bot) aan één van de vingers/tenen of aan de duim tot een hand of voet met acht stralen.
Er zijn verschillende vormen van polydactylie:
- Preaxiaal: verdubbeling aan de radiale kant (duim/grote teen)
- Centraal of axiaal: verdubbeling bij de vingers/tenen 2-4
- Postaxiaal: verdubbeling aan de ulnaire kant (pink/kleine teen)
De meest voorkomende vorm van polydactylie is de postaxiale, minder voorkomend is de preaxiale en zeldzaam is de centraal/axiale vorm.
Bij de meeste kinderen is polydactylie geïsoleerd aanwezig, dus zonder andere afwijkingen. Ongeveer 15-20% van de kinderen die geboren worden met polydactylie hebben ook andere aangeboren afwijkingen, vaak als onderdeel van een erfelijk syndroom.
De behandeling van polydactylie is afhankelijk van de vorm. Zo wordt een extra pink op een steel van huid vaak al op zeer jonge leeftijd behandeld. Vaak vindt operatieve correctie, indien mogelijk, pas rond of na het eerste jaar plaats in verband met het risico dat een narcose op jonge leeftijd met zich meebrengt. Analyse vindt bij voorkeur eerder plaats in het kader van mogelijke syndromale aandoeningen.
Afbeelding 4: polydactylie.
Anamnese en lichamelijk onderzoek
De diagnose polydactylie kan soms tijdens de prenatale echo worden gesteld, maar wordt meestal bij de geboorte gesteld.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
Kinderen met een extra vinger of teen moeten worden verwezen naar de (kinder) plastisch chirurg of (kinder)orthopeed, waarbij de voorkeur uitgaat naar een ziekenhuis met een multidisciplinair behandelteam.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen kinderen met polydactylie tegenkomen tijdens hun contactmomenten, maar hoeven de aandoening niet actief op te sporen. De werkgroep vindt het belangrijk dat er aanvullend onderzoek plaatsvindt om eventuele andere aangeboren afwijkingen tijdig op te sporen.
Polydactylie wordt bij voorkeur behandeld door een multidisciplinair team met een (kinder) plastisch chirurg of (kinder)orthopeed. In een dergelijk team is vaak ook een kinderrevalidatiearts, klinisch geneticus, kinderfysiotherapeut en kinderergotherapeut beschikbaar.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.2 Syndactylie
Beschrijving aandoening
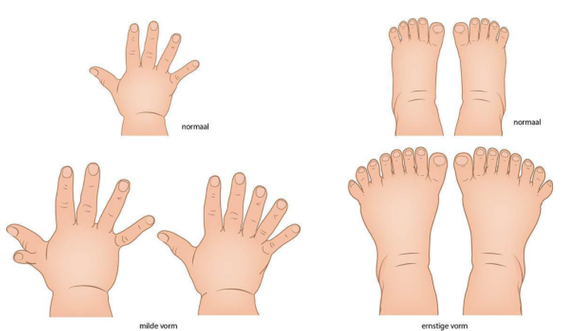
Bij syndactylie is er sprake van een vergroeiing van (meestal) twee vingers of tenen (afbeelding 5). Soms zijn alleen de weke delen vergroeid, soms ook de botten. Het is zichtbaar als een ontbrekende of onvolledig gevormde ruimte tussen twee vingers of tenen. Syndactylie is een van de meest voorkomende aangeboren afwijkingen aan de hand, en kan erfelijk zijn. De prevalentie in Europa is ongeveer 0,4:1.000 geboortes [45], dit betekent dat er per jaar ongeveer 70 kinderen worden geboren met syndactylie. Syndactylie kan onderdeel zijn van een syndroom, zoals het Apert-syndroom of Poland-syndroom. Het Apert-syndroom is een erfelijke aangeboren aandoening waarbij er (in wisselende mate) sprake is van craniosynostose (te vroeg sluiten van schedelnaden), slechthorendheid, verstandelijke beperking en afwijkingen aan de handen en de voeten. Het Poland-syndroom is een aangeboren aandoening waarbij er sprake is van een onderontwikkelde borstspier en afwijkingen aan de onderarmen en vingers.
Er kan onderscheid gemaakt worden in complete/incomplete en simpele/complexe syndactylie:
- Simpel incompleet: gedeeltelijk vergroeide vingers/tenen, de vergroeiing betreft alleen de huid en weke delen
- Simpel compleet: geheel vergroeide vingers/tenen, de vergroeiing betreft alleen de huid en weke delen
- Complex: ook de botten zijn vergroeid
- Gecompliceerd: met bijkomende andere afwijkingen aan de vingers.
Afbeelding 5: syndactylie.
FIGUUR
Syndactylie aan de handen kan, afhankelijk van de ernst van de vergroeiing, een functionele beperking of groeibeperking veroorzaken. Daarom is chirurgische correctie geïndiceerd. Syndactylie aan de voeten behoeft geen behandeling, omdat het geen klachten of beperkingen veroorzaakt.
Anamnese en lichamelijk onderzoek
De diagnose syndactylie wordt al bij de geboorte gesteld. Kinderen kunnen een functioneel probleem ervaren, maar geen pijn.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Kinderen met syndactylie aan de handen moeten worden verwezen naar de (kinder) plastisch chirurg of (kinder)orthopeed, waarbij de voorkeur uitgaat naar een ziekenhuis met een multidisciplinair behandelteam.
- Kinderen met syndactylie aan de voeten: geef uitleg aan ouders dat de aandoening geen functionele beperkingen oplevert, en dat behandeling niet nodig is. Alleen bij duidelijke klachten of bijkomende aanwijzingen voor een syndromale afwijking moet worden verwezen naar de (kinder) plastisch chirurg of (kinder)orthopeed.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen kinderen met syndactylie tegenkomen tijdens hun contactmomenten, maar hoeven de aandoening niet actief op te sporen. Syndactylie aan de handen wordt bij voorkeur behandeld door een multidisciplinair team met een (kinder) plastisch chirurg of (kinder)orthopeed. In een dergelijk team is vaak ook een kinderrevalidatiearts, klinisch geneticus, kinderfysiotherapeut en kinderergotherapeut beschikbaar.
Aanbevelingen
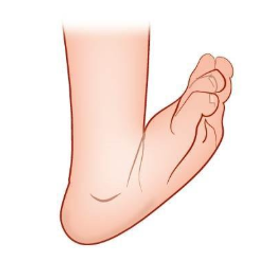
2.3.3 Camptodactylie
Beschrijving aandoening
Camptodactylie is een aangeboren anatomische afwijkende aanleg van de pezen van een vinger, waardoor de vinger in een gebogen stand staat (afbeelding 6). De kromstand treedt meestal op aan de pink, en meestal in het proximale interfalangeale gewricht (het eerste gewricht van de vinger). In de meerderheid van de gevallen (ongeveer twee-derde) zijn beide handen aangedaan. Als er sprake is van een enkelzijdige aandoening dan betreft het meestal de rechterhand.
De aandoening is vaak erfelijk en kan progressief zijn, en komt voor bij ongeveer 10:1.000 personen. Verergering treedt meestal op tijdens groeispurten. Het presenteert zich bij geboorte of pas op oudere leeftijd. Bij betrokkenheid van meerdere vingers moet gedacht worden aan een distale arthrogryposis (een aandoening met contracturen aan handen en voeten).
Over het algemeen ervaren jeugdigen met camptodactylie weinig functionele beperkingen. De stand van de vinger kan wel aanleiding zijn tot zorgen en vragen bij de ouders en/of de jeugdige. Als de ernst van de contractuur toeneemt ontstaan er klachten van ‘blijven haken’ met de vinger tijdens dagelijkse bezigheden.
De behandeling van camptodactylie is in principe conservatief met een spalk of splint. In ernstige gevallen (geen effect van conservatieve behandeling en een contractuur >60˚) kan een operatieve ingreep overwogen worden. De indicatie tot operatieve ingreep wordt beperkt gesteld omdat de resultaten van een operatieve ingreep vaak slechts beperkt zijn.
Afbeelding 6: Camptodactylie. Flexiecontractuur ter hoogte van het proximale interfalangeale gewricht van de vierde vinger.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met camptodactylie worden de volgende punten nagevraagd:
- Familieanamnese: komen er handafwijkingen in de familie voor?
- Medische voorgeschiedenis: is er sprake geweest van operaties of andere behandelingen? Is er sprake geweest van trauma’s (zoals fracturen, vingers tussen de deur)?
- Is er sprake van (pijn)klachten of beperkingen?
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij jeugdigen met camptodactylie worden de volgende punten onderzocht:
- Beweeglijkheid van de vingers, zowel actief als passief. Bij onderzoek staat het aangedane gewricht in flexie, het gewricht is zowel actief als passief niet beweeglijk richting extensie (verder buigen is wel mogelijk).
- Palpeer de flexorpees (in de handpalm, net proximaal van het MCP-gewricht) en let op een eventueel drukpijnlijke en met de beweging van de flexorpees meebewegende zwelling. Er wordt (in tegenstelling tot bij de triggervinger of een peesschede ganglion) geen verdikking gevonden van de flexorpees.
Alarmsignalen
Indien er sprake is van meerdere aangedane vingers of andere vingers dan de pink en ringvinger moet gedacht worden aan een distale arthrogryposis (een aandoening met contracturen aan handen en voeten).
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Op basis van bovenstaande informatie kan zo nodig uitleg worden gegeven over de aard en het verloop van de aandoening.
- Indien er sprake is van camptodactylie met milde tot ernstige functionele beperkingen wordt verwijzing naar de (kinder) plastisch chirurg of (kinder)orthopeed geadviseerd, waarbij de voorkeur uitgaat naar een ziekenhuis met een multidisciplinair behandelteam.
- Indien er sprake is van meerdere aangedane vingers of andere vingers dan de pink en ringvinger dan dient op korte termijn naar een ziekenhuis met een multidisciplinair behandelteam te worden verwezen.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen tijdens hun contactmomenten een jeugdige met camptodactylie signaleren. De werkgroep is van mening dat niet alle jeugdigen met camptodactylie hoeven te worden verwezen of behandeld. Het beleid is afhankelijk van de mate van functiebeperking.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.4 Triggervinger of -duim
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij een triggervinger of -duim is er sprake van een ‘hokken’ of ‘klikken’ bij het buigen van de vinger of duim. Uiteindelijk kan de vinger of duim in gebogen stand vast komen te staan.
De duim is bij kinderen (tot 10 keer) vaker aangedaan dan de andere vingers [13]. Een triggerduim wordt het meest gezien bij kinderen tussen 1 en 4 jaar, met een incidentie van ongeveer 1:1.000. De pathologie/etiologie van een triggerduim is niet duidelijk. Een triggervinger kan worden veroorzaakt door een anatomische afwijking of een onderliggende (metabole) aandoening.
Klachten die kinderen kunnen ervaren zijn een pijnlijk en vervelend gevoel van de vingers, pijn bij het buigen en ‘hokken’ bij strekken.
Een triggerduim wordt behandeld door middel van spalken gedurende de slaap (zowel overdag als ’s nachts). Indien er sprake is van een gefixeerde triggerduim (waarbij de duim in gebogen stand vast staat) dan is operatieve correctie noodzakelijk. De behandeling van een triggervinger is (mede) afhankelijk van een eventuele onderliggende aandoening.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij kinderen met een triggervinger of -duim worden de volgende punten nagevraagd:
- Lokalisatie van de klachten
- Klachten bij buigen en strekken van de vingers
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Tijdens het lichamelijk onderzoek van kinderen met een triggervinger of -duim worden de volgende zaken onderzocht:
- Palpeer de flexorpees (in de handpalm, net proximaal van het MCP-gewricht) en let op een eventueel drukpijnlijke en met de beweging van de buigpezen meebewegende zwelling.
- Onderzoek alle vingers (en duimen) op eventuele bewegingsbeperking.
Alarmsignalen
Geen.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
Kinderen met een triggerduim dienen te worden verwezen naar de (kinder) plastisch chirurg of (kinder)orthopeed, waarbij de voorkeur uitgaat naar een ziekenhuis met een multidisciplinair behandelteam.
Kinderen met een triggervinger dienen te worden verwezen naar een ziekenhuis met een multidisciplinair ‘handenteam’.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen tijdens hun contactmomenten een jeugdige met een triggervinger of -duim signaleren. Voor het onderzoek naar een eventueel onderliggend lijden en het bepalen van de behandeling gaat de voorkeur uit naar een multidisciplinair team.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.5 O-benen (genua vara) en X-benen (genua valga)
Beschrijving aandoening
De normale standsontwikkeling van de benen is als volgt (tabel 2 en afbeelding 7) [43]:
Bij alle kinderen staan de benen bij de geboorte in een O-stand (genua vara, d.w.z. de knieën staan uit elkaar als de enkels tegen elkaar worden gezet). De knieën staan in een neutrale positie als een kind begint te lopen (1-1,5 jaar). Rond het tweede jaar gaat de O-stand over in een X-stand (genua valga, d.w.z. de enkels staan uit elkaar als de knieën tegen elkaar staan). De X-stand neemt dan snel toe, met een maximum op de leeftijd van drie jaar. Vanaf het derde jaar neemt de X-stand weer geleidelijk af. Rond het zevende jaar wordt een vrijwel rechte beenstand bereikt.
Tabel 2. Normale standsontwikkeling van de benen
| 0 tot 2 jaar | O-benen (genua vara) |
| 2 tot 7 jaar | X-benen (genua valga) |
| 7 jaar en ouder | Bijna rechte beenstand (veelal lichte X-stand) |
De mate van O-stand als onderdeel van de normale ontwikkeling varieert enorm tussen kinderen. Dat geldt ook voor de mate van X-stand, zij het minder dan bij O. Als de O- of X-stand symmetrisch is en binnen de genoemde leeftijden valt, is het daarom onmogelijk aan te geven waar de grens ligt tussen een normale en een pathologische beenstand. Alleen als de O- of X-stand asymmetrisch is (d.w.z. het ene been heeft meer een O- of X-stand dan het andere) of als er sprake is van een O- of X-stand die buiten de genoemde leeftijden valt, dan moet pathologie overwogen worden [43]. Cijfers over de incidentie van een pathologische oorzaak voor O- of X-stand zijn in de literatuur niet bekend [38]. Het kan dan gaan om zeldzame skeletdysplasieën, nierziekten, of stofwisselingsstoornissen, maar ook om een maligniteit. Een asymmetrische beenstand kan ontstaan na een fractuur. Beeldvormend onderzoek geeft verdere aanwijzingen over pathologische oorzaken. O-benen kunnen ook veroorzaakt worden door rachitis (o.b.v. vitamine D-gebrek) of een zeldzame groeistoornis van het mediale deel van de proximale epifyse van de tibia (de ziekte van Blount) [38][43]. Deze groeistoornis kan zowel enkel- als dubbelzijdig een O-stand veroorzaken, en komt vooral voor in het Caribisch gebied, West-Afrika en Scandinavië [38]. De meest voorkomende oorzaak van rachitis is vitamine D-deficiëntie, dit komt vaak voor bij niet-westerse immigranten [47]. Rachitis komt in Nederland weinig voor en dan vooral bij kinderen met een donkere huidskleur [38]. Mogelijke symptomen van rachitis zijn spierzwakte, vertraagde groei en een verdikte pols.
X-benen worden vaker gezien bij kinderen met overgewicht.

Afbeelding 7: X- en O benen.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij kinderen met O- of X-benen worden de volgende punten nagevraagd:
- Klachten, functiebeperking
- Verloop van de ontwikkeling (zie ook JGZ-dossier)
- Relevante voorgeschiedenis (fracturen, ziekte, operaties; zie ook JGZ-dossier)
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
De benen dienen geheel ontbloot te zijn, de luier of onderbroek blijft aan. Dan vindt inspectie plaats, zowel staand als lopend. Er wordt gelet op asymmetrie, O- of X-stand en toeing-in. Als gevolg van een X-stand, staan bij kinderen ook vaak de voeten naar binnen gedraaid. Omgekeerd staan de voeten bij een normale O-stand veelal meer naar buiten. Wanneer een kind met X-benen hardloopt kan er een zwabberende gang zijn.
Als de jeugdarts de mate van O- of X-stand wil onderzoeken dan wordt dat als volgt gedaan: bij het kind in rugligging met gestrekte benen wordt gekeken naar de afstand tussen de mediale femurcondylen (=knieën; in geval van O-benen) of de mediale malleoli (=enkels; in geval van X-benen). Het inschatten of er sprake is van uitgesproken grote kniehoeken of een snelle toename van de kniehoeken is een klinische beoordeling en professionele inschatting van de jeugdarts. Hiervoor zijn geen normaal- of afkapwaarden te beschrijven.
Alarmsignalen
Indien er sprake is van een duidelijk verschil tussen het linkerbeen en rechterbeen (asymmetrische O- of X-stand) of een snel toenemende standsafwijking kan dit wijzen op de aanwezigheid van (onder andere) een infectie, maligniteit of de ziekte van Blount en dient te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- De jeugdarts geeft ouders uitleg over het normale verloop van de ontwikkeling van de stand van de benen, dat O- of X-benen meestal geen klachten geven en vrijwel nooit behandeling behoeven. Nachtelijke correctieapparaten, steunzolen en houdings- of oefentherapie hebben geen invloed op de beenstand [38], en worden derhalve afgeraden. In extreme gevallen kan de beenstand eventueel door de (kinder)orthopeed chirurgisch worden gecorrigeerd.
- Als de stand van de benen afwijkt van de normale ontwikkeling voor de leeftijd (tabel 2), controleert de jeugdarts de stand van de benen door deze na 9-18 maanden nog eens te onderzoeken.
- De jeugdarts verwijst naar de (kinder)orthopeed:
- Bij O-benen met uitgesproken grote kniehoeken vóór de leeftijd van twee jaar of O-benen na de leeftijd van twee jaar die bij controle na 6-9 maanden persisteren;
- Bij X-benen met uitgesproken grote kniehoeken vóór de leeftijd van zeven jaar of X-benen na de leeftijd van zeven jaar die bij controle na 9-12 maanden persisteren;
- Bij asymmetrische O- of X-stand;
- Bij snel toenemende O- of X-stand;
- Bij O- of X-stand met functionele beperkingen.
- De jeugdarts verwijst naar de kinderarts bij verdenking op rachitis.
- Indien er sprake is van O-benen in combinatie met overgewicht of obesitas, dan bespreekt de jeugdarts het hogere risico op progressie van de O-stand. Daarnaast wordt gehandeld volgens de JGZ-richtlijn Overgewicht.
- Het meten van de intermalleolaire afstand bij genua valga en de intercondylaire afstand bij genua vara en het gebruik van tabellen met ‘normaalwaarden’ wordt afgeraden voor de JGZ.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.6 Beenlengteverschil
Beschrijving aandoening
Een beenlengteverschil betekent dat de afstand tussen spina iliaca anterior superior en hiel links verschillend is ten opzichte van rechts. Er is sprake van een vertraging of een versnelling van de groei in één of beide benen. Een beenlengteverschil <2 cm komt bij ongeveer 50% van de volwassenen voor. Er kunnen verschillende oorzaken voor een beenlengteverschil zijn: aanlegstoornis, paralyse, infectie, trauma, tumor, heupdysplasie en congenitale vaatanomalieën. Van de aanwijsbare oorzaken komen traumata waarschijnlijk het meest frequent voor.
Een beenlengteverschil kan aanleiding geven tot een compensatoire scoliose (of houdingsscoliose).
Een beenlengteverschil geeft vaak pas klachten bij overbelasting [38]. Jeugdigen kunnen klachten aangeven zoals mank lopen of een spitsvoet. Daarnaast kan de jeugdige pijnklachten in been of rug ervaren.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met een beenlengteverschil worden de volgende punten nagevraagd:
- Klachten en duur van de klachten
- Opmerkingen van ouders over een beenlengteverschil
- Beenfracturen of osteomyelitis in het verleden
- Aangeboren (familiaire) heupafwijkingen
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Het onderzoek naar een beenlengteverschil wordt op indicatie verricht. Afhankelijk van de leeftijd van de jeugdige kiest de jeugdarts voor onderzoek in liggende of staande houding. Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij jeugdigen met een (mogelijk) beenlengteverschil worden de volgende punten onderzocht:
- Onderzoek in liggende houding: Bij het beoordelen van de beenlengte ligt het kind op de rug, geheel recht, het gezicht in de middenpositie. De benen zijn gestrekt en de voeten wijzen naar boven. Vervolgens wordt beoordeeld of de onderzijde van de hielen en de binnenzijde van de enkels gelijk liggen. Vervolgens worden de heupen en knieën in negentig graden flexie gebracht. In deze houding is een verschil in lengte van de bovenbenen het meest duidelijk. Een beenlengteverschil kan wijzen op aanwezigheid van een eenzijdig (sub)luxeerbare heup, zie de JGZ-richtlijn Heupdysplasie. Wanneer het kind op de buik wordt gelegd met de knieën in 90 graden zal een verschil in lengte van de onderbenen het meest duidelijk zichtbaar zijn.
- Onderzoek in staande houding: De jeugdige staat rechtop met de knieën maximaal gestrekt en de voeten naast elkaar. De onderzoeker staat achter de patiënt en plaatst beide duimen op de spinae iliacae posteriores (of anteriores) superiores. Vervolgens wordt beoordeeld of de duimen op gelijke hoogte liggen. Wanneer de beide duimen niet op gelijke hoogte staan is er waarschijnlijk sprake van een beenlengteverschil.
- In staande houding wordt het beenlengteverschil bepaald met behulp van de ‘plankjesmethode’. Hierbij wordt de ruimte onder het kortste been opgevuld met een plankje van 0,5, 1 of 2 cm dik totdat de duimen op de spinae iliacae posteriores superiores even hoog staan.
Voor de overige onderdelen van het onderzoek op indicatie naar heupdysplasie wordt verwezen naar de JGZ-richtlijn Heupdysplasie.
Alarmsignalen
Hoe jonger de leeftijd van het kind met een beenlengteverschil, hoe groter de kans dat het verschil toeneemt in de loop der jaren.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Vanaf de leeftijd van 2 jaar maakt het onderzoek van de beenlengte deel uit van het lichamelijk onderzoek naar heupdysplasie. Dit onderzoek wordt verricht als er vragen, zorgen, klachten of opvallende observaties zijn van ouders/kind en/of jeugdverpleegkundige en/of jeugdarts.
Bij kinderen jonger dan 10 jaar:
- Bij een beenlengteverschil < 1 cm dient het beenlengteverschil na 6-12 maanden te worden gecontroleerd (hoe jonger het kind, hoe korter de controletermijn).
- Bij een beenlengteverschil ≥ 1 cm dient te worden verwezen naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
Bij kinderen ouder dan 10 jaar:
- Bij een beenlengteverschil < 2 cm: verwijzing is niet nodig. Zo nodig kan na 6-12 maanden nogmaals het beenlengteverschil gemeten worden. Wanneer dit verschil constant blijft is het zeer onwaarschijnlijk dat er nog een toename in het beenlengteverschil zal zijn.
- Bij een beenlengteverschil ≥ 2 cm dient te worden verwezen naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.7 Klompvoet (pes equinovarus)
Beschrijving aandoening
De klompvoet (pes equinovarus of talipes equinovarus) wordt gedefinieerd als een congenitale afwijking van de voet met spitsstand, varus positie van de achtervoet en adductie en supinatie van de voorvoet (afbeelding 8). Een klompvoet is niet naar een neutrale positie te brengen. Een klompvoet is meestal kleiner met een hogere wreef dan een niet aangedane voet, en de desbetreffende kuit is meestal iets dunner.
De klompvoet is een aangeboren afwijking. Vaak is de oorzaak onbekend, maar genetische factoren en omgevingsfactoren tijdens de zwangerschap kunnen een rol spelen bij het ontwikkelen van een klompvoet. De incidentie van deze afwijking is in Europa ongeveer 1-1,5:1.000 geboorten, dit betekent dat er per jaar ongeveer 175-260 kinderen worden geboren met een klompvoet. Een klompvoet komt 3 keer zo vaak voor bij jongens als bij meisjes. In 50% van gevallen is de klompvoet bilateraal. De incidentie is mede afhankelijk van de etniciteit: de klompvoet is zeldzaam bij Aziaten en komt vaker voor bij Afrikanen, Aboriginals en Polynesiërs [20]. Wanneer ouders een kind met klompvoeten hebben, dan is de kans op een klompvoet 2-3% bij het tweede kind. Wanneer één van de twee ouders klompvoeten heeft, dan is de kans dat hun kind een klompvoet krijgt 10-25%.
De klompvoetbehandeling vindt in Nederland gecentraliseerd plaats in zogenaamde ‘klompvoetcentra’. Het is belangrijk om indien haalbaar zo snel mogelijk met de behandeling van de klompvoet te beginnen. Klompvoeten worden behandeld met gipsredressie volgens Ponseti. Er zijn meerdere gipsredressies nodig. Tevens wordt in de meeste gevallen een achillespees tenotomie verricht, hierbij wordt de achillespees onder lokale verdoving doorgesneden. Na de gipsredressie krijgt het kind een voetabductiebrace voor drie maanden (dag en nacht), daarna tot het vierde levensjaar alleen ’s nachts (14 uur per dag).
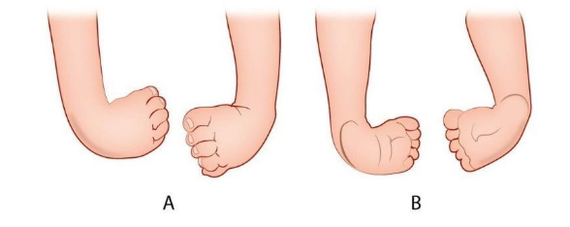
Afbeelding 8: Pes equinovarus (klompvoet) beiderzijds. A: van vooraf gezien; B: van achteraf gezien.
Anamnese
Een congenitale klompvoet wordt veelal prenataal ontdekt tijdens de 20-weken echo of bij de geboorte vastgesteld. Eventueel heeft er reeds een antenataal consult bij de kinderorthopedie plaatsgevonden. Relevant zijn de aanwezigheid van een klompvoet in de familie en bijzonderheden tijdens de zwangerschap zoals een stuitligging [49].
Lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij lichamelijk onderzoek staat de voorvoet in adductie en supinatie en de achtervoet in spits en varus. Deze standsafwijkingen zijn slechts gedeeltelijk te corrigeren, waarbij de mate van correctie bepaalt of het een soepele of stugge klompvoet is. Wanneer de klompvoet volledig te corrigeren is (met name de spits), dan is er sprake van een voorkeurspositie en niet van een echte klompvoet. Verder kan de voet iets kleiner zijn.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
Kinderen met een klompvoet worden op het moment van diagnose (of verdenking op de diagnose) verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed. Dit betekent dat de behandeling in veel gevallen al is gestart voor het eerste contact met de JGZ.
- Wijs ouders op de website van de patiëntenvereniging: www.klompvoet.nl.
- De jeugdverpleegkundige of jeugdarts brengt ouders op de hoogte van een (zo nodig) aangepaste werkwijze rondom vaccineren en het meten van lengte en gewicht: de plaats van vaccineren wordt in overleg met ouders bepaald. De JGZ verricht geen lengtemeting als een kind een (dubbelzijdige) behandeling ondergaat. Het kind kan eventueel gewogen worden met gips of voetabductiebrace.
- De jeugdarts en jeugdverpleegkundige zorgen dat de JGZ-assistente op de hoogte is van de (zo nodig) aangepaste werkwijze rondom vaccineren en het meten van lengte en gewicht.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen tijdens hun contactmomenten kinderen tegenkomen die worden behandeld voor klompvoeten. De werkgroep vindt het belangrijk dat er tijdens de contactmomenten rekening wordt gehouden met de behandeling en heeft er voor gekozen om hierbij zo veel mogelijk aan te sluiten bij de adviezen van de JGZ-richtlijn Heupdysplasie.
Meten en wegen
Bij een kind dat behandeld wordt voor klompvoeten wordt afgezien van het meten van de lengte. Het kind kan eventueel gewogen worden met gips. Het uitvoeren van de lengtemeting van een liggend kind is beschreven in het boekje ‘Groeidiagrammen 2010. Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen’ [50].
Vaccineren
De wijze van behandeling kan invloed hebben op de keuze waar te vaccineren. De eerste voorkeursplaats voor injecties bij zuigelingen in de leeftijd van 0 tot 12 maanden is het dijbeen (musculus vastus lateralis) [51]. Boven de leeftijd van 12 maanden is er geen voorkeur voor het dijbeen of de bovenarm. Bij kinderen die worden behandeld met gipsredressie, waarbij het gips niet kan worden afgenomen, is de bovenarm de aangewezen plek voor de vaccinatie. Bij de voet-abductiebrace gaat de voorkeur uit naar het bovenbeen als plek voor de vaccinatie, maar de plek (bovenbeen of bovenarm) waar de vaccinatie plaatsvindt wordt, na het geven van uitleg, in overleg met ouders bepaald.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.8 Hakvoet (pes calcaneus)
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij de hakvoet (pes calcaneus, hielvoet) staat de voorvoet neutraal (afbeelding 9). De achtervoet staat in extreme dorsaalflexie met lichte valguskanteling. De aandoening komt bij ongeveer 10:1.000 pasgeborenen voor. Dit betekent dat er per jaar ongeveer 1750 kinderen worden geboren met een hakvoet. Het komt vaker voor bij jongens dan bij meisjes (2:1) en in 50% van de gevallen is de hakvoet bilateraal.
Een hakvoet is meestal congenitaal en berust bijna altijd op een positioneringseffect gedurende de zwangerschap. In enkele gevallen is er een neurologische oorzaak (zoals een spina bifida), maar dan staat het neurologisch beeld duidelijk op de voorgrond.
In de eerste weken na de geboorte normaliseert de hakvoet spontaan doordat de plantairflexoren (de voetbuigers) sterker zijn dan de voetheffers. Gipsredressies zijn niet zinvol. Over de effectiviteit van massage is geen informatie gevonden. Op de leeftijd van de eerste contactmomenten met de JGZ (2 weken en/of 4 weken) zou er al een forse verbetering in de voetstand moeten zijn opgetreden.
Afbeelding 9: Pes calcaneus (hakvoet): de achtervoet staat in extreme dorsaalflexie met lichte valguskanteling.
Lichamelijk onderzoek
Tijdens het lichamelijk onderzoek valt op dat de voet in forse dorsaalflexie staat (omhoog gekanteld naar het onderbeen). Direct na de geboorte soms zelfs met de wreef tegen het scheenbeen aan. De voet kan voorzichtig in plantairflexie worden gebracht.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Als de jeugdverpleegkundige een hakvoet signaleert op de leeftijd van 2 weken dan vraagt zij bij de ouders na of de stand van de voet is verbeterd sinds de geboorte. Indien er sprake is van een forse verbetering van de voetstand in de eerste levensweken: geef uitleg aan ouders dat de voetstand vanzelf normaliseert en dat behandeling niet nodig is. Bij twijfel kan een extra controle bij de jeugdarts worden afgesproken.
- Bij geringe of matige spontane verbetering van de voetstand op de leeftijd van 2 tot 4 weken, of bij twijfel aan de diagnose: verwijzen naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen kinderen met een hakvoet tegenkomen tijdens hun contactmomenten, maar hoeven de aandoening niet actief op te sporen. Tijdens de eerste contactmomenten van de JGZ zou de stand van de voet al fors verbeterd moeten zijn. Als dat niet het geval is, is dit voldoende reden om te twijfelen aan de diagnose hakvoet.
De werkgroep is van mening dat het niet nodig is om ouders de voet thuis speciaal te laten masseren of oefenen. Ook verwijzing naar de kinderfysiotherapie of kinderoefentherapie is niet nodig vanwege het spontane herstel. Inbakeren hoeft niet te worden afgeraden, mits dit op een veilige wijze gebeurt waarbij de voeten voldoende bewegingsruimte hebben.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.9 Metatarsus adductus
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij een metatarsus adductus staat de voorvoet in adductiestand ten opzichte van de achtervoet, er is geen afwijking in de midden- en achtervoet (afbeelding 10). De voetzool is C- of boonvormig met een concave mediale en convexe laterale zijde. Het wordt waarschijnlijk veroorzaakt door de positie van de foetus in de baarmoeder. De aandoening kan zowel enkel- als dubbelzijdig voorkomen.
De aandoening komt bij ongeveer 1:1.000 pasgeborenen voor [10,30]. Dit betekent dat er per jaar ongeveer 175 kinderen worden geboren met metatarsus adductus. Bij een groot aantal kinderen zal de stand zich spontaan corrigeren: in 85-90% van de gevallen verdwijnt de metatarsus adductus spontaan in het eerste jaar [10]. Behandeling is vaak niet nodig. Indien er op de leeftijd van 6 maanden geen enkele spontane correctie op de leeftijd van 6 maanden is opgetreden dan is nader onderzoek wenselijk. Indien de aandoening aan het eind van het eerste levensjaar niet spontaan is gecorrigeerd, kan behandeling geïndiceerd zijn. Dit gebeurt dan meestal door middel van gipsredressie.
Er zijn verschillende manieren om metatarsus adductus in te delen. Klinisch kan metatarsus adductus ingedeeld worden in een milde (flexibele, passief corrigeerbare), matige (semi-flexibele, reduceerbare) en ernstige (rigide) vorm.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij kinderen met metatarsus adductus hoeven geen specifieke aanvullende vragen te worden gesteld naast de gebruikelijke vragen naar bijzonderheden rond zwangerschap en geboorte en de familieanamnese.
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij kinderen met metatarsus adductus worden de volgende punten onderzocht:
- Bij inspectie wordt gelet op de vorm van de voet: is deze (vanaf de voetzool bekeken) typisch C- of boonvormig? Is er sprake van een valgusstand van de achtervoet?
- Daarnaast wordt gelet op plooien in de voetzool: bij metatarsus adductus worden geen diepe huidplooien in de voetzool gezien. Indien een diepe huidplooi aanwezig is, is de diagnose metatarsus adductus onwaarschijnlijk en moet worden gedacht aan een metatarsus primus varus.
- Bij palpatie wordt gelet op de soepelheid van de voet. Is de voet makkelijk in de juiste stand te brengen? Door met de vinger langs de laterale voetrand te gaan, kan worden nagegaan of de voet actief in een normale stand kan worden gebracht. Indien actieve correctie niet mogelijk is, is de diagnose metatarsus adductus onwaarschijnlijk en moet differentiaal diagnostisch worden gedacht aan een metatarsus primus varus.
Alarmsignalen
Geen.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Als er sprake is van een milde metatarsus adductus, waarbij de voet makkelijk in de juiste stand te brengen is, dan geeft de JGZ-professional uitleg aan ouders over de bevindingen en het te verwachten natuurlijk beloop.
- Als er sprake is van een matige of ernstige metatarsus adductus, waarbij de voet niet (makkelijk) in de juiste stand te brengen is, dient op de leeftijd van 6-12 maanden te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
- Als er sprake is van diepe huidplooien in de voetzool en/of het ontbreken van actieve correctie en/of een valgusstand van de achtervoet en/of progressie, dient direct te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.10 Metatarsus primus varus
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij een metatarsus primus varus staat het os metatarsale I in adductiestand ten opzichte van de rest van de voet (afbeelding 11). De laterale zijde van de voet is recht, in tegenstelling tot de bevindingen bij metatarsus adductus. Er is vaak een opvallend grote ruimte tussen de grote en de tweede teen (sandal gap). Over het algemeen is metatarsus primus varus een meer rigide deformatie dan metatarsus adductus.
In de literatuur wordt vermeld dat metatarsus primus varus minder frequent voorkomt dan metatarsus adductus, maar prevalentiecijfers zijn niet gevonden. De aandoening komt veel voor bij kinderen met het syndroom van Down.
Als metatarsus primus varus niet wordt behandeld is er op latere leeftijd een grotere kans op het ontwikkelen van een hallux valgus. De grootte van deze kans wordt niet vermeld in de literatuur. Daarnaast kan het cosmetische klachten of problemen met het dragen van schoenen veroorzaken. De behandeling bestaat uit gipsredressie.
Afbeelding 11: Metatarsus primus varus.
Anamnese
Er zijn geen specifieke aandachtspunten in de anamnese bij kinderen met metatarsus primus varus.
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij kinderen met metatarsus primus varus worden de volgende punten onderzocht, dit kan (afhankelijk van de leeftijd) in zittende of staande houding:
- Bij inspectie wordt gelet op de vorm van de voet: is de laterale voetrand recht? Hoe is de ruimte tussen de grote en tweede teen? Daarnaast wordt gelet op plooien in de voetzool: bij metatarsus primus varus wordt vaak een diepe huidplooi in de voetzool gezien aan de mediale zijde van de voet.
Alarmsignalen
Geen.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Als er sprake is van een metatarsus primus varus (os metatarsale I staat in adductiestand, ongeacht of deze stand rigide of flexibel is) dient, ongeacht de leeftijd, te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.11 Krulteen (Curly toes)
Beschrijving aandoening
Een krulteen is een fysiologische variatie, die veroorzaakt wordt door enige spierdisbalans (afbeelding 12). Het is de meest voorkomende, meestal familiaire, afwijking van de kleine tenen en is meestal aanwezig bij de geboorte. Wanneer het kind begint te lopen kan de krulteen beter zichtbaar worden. De vierde en vijfde teen zijn de meest betrokken tenen. De aangedane teen ligt onder de mediaal naastliggende teen. Het komt tweezijdig symmetrisch voor en geeft over het algemeen geen klachten. De distale falanx is naar mediaal afgebogen en geëxoroteerd. Bij 25% van de kinderen verbetert deze standsafwijking spontaan. De krulteen levert meestal geen klachten op, daarom is behandeling vrijwel nooit geïndiceerd. Bij aanhoudende klachten kan een verwijzing naar een podotherapeut worden overwogen voor het aanmeten van een siliconen orthese of gericht schoenadvies. Tevens kan een operatieve correctie worden overwogen.
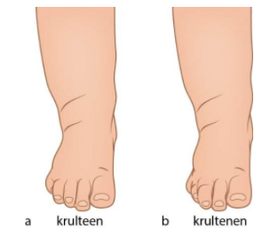
Afbeelding 12: krultenen van de vijfde teen (a) en de vierde en vijfde teen (b).
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met een krulteen worden de volgende punten nagevraagd:
- Zijn er klachten, zoals pijn, roodheid of blaarvorming?
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Tijdens het lichamelijk onderzoek valt de stand van de teen op. De stand is passief te corrigeren, maar na loslaten neemt deze de oorspronkelijke positie weer in.
Alarmsignalen
Geen.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- JGZ-professionals geven ouders uitleg over de aard van de standsafwijking, de kans op spontane verbetering, en de zeer kleine kans op klachten.
- Indien er sprake is van pijn, roodheid of blaarvorming kan de JGZ-professional ouders (algemeen) schoenadvies geven (bijlage 5.2 Algemene schoenadviezen).
- Bij aanhoudende klachten kan een verwijzing naar een podotherapeut worden overwogen.
Aanbevelingen
2.3.12 Platvoeten
Beschrijving aandoening
Alle kinderen worden geboren met platvoeten. De mediale voetboog (ook voetgewelf genoemd) ontwikkelt zich in de eerste 7-10 jaar [15][16]. De prevalentie van platvoeten neemt af met het toenemen van de leeftijd [17]. De gerapporteerde prevalenties zijn wisselend, dit wordt mede veroorzaakt door variatie in de gehanteerde definitie en onderzoeksmethode. In de leeftijdsgroep 3 tot 6 jaar worden prevalenties van 26% tot 54% gerapporteerd [17][18]. Er zijn geen studies gevonden waarin de relatie is onderzocht tussen platvoeten op jonge leeftijd en klachten op volwassen leeftijd.
Er is sprake van een platvoet (pes planus, pes planovalgus) als de mediale voetboog verminderd of niet aanwezig is. De hiel is hierbij vaak naar binnen gekanteld (valgusstand). Er zijn geen (inter)nationale officiële criteria vastgesteld voor het stellen van de diagnose. Platvoeten worden vaak ingedeeld in twee vormen: de soepele (of flexibele) platvoet, en de rigide (of starre) platvoet. De kans op een onderliggende oorzaak is het grootst bij een rigide platvoet. Vaak is er dan sprake van een tarsale coalitie, een vergroeiing tussen 2 botten in de midden- of achtervoet. Een tarsale coalitie kan klachten geven van pijn, stijfheid van de voet en recidiverende inversietrauma’s (verstuikingen) van de enkel. Een platvoet kan veroorzaakt worden of verergeren door een verkorte achillespees.
Stolzman verrichtte een systematische review van 13 studies naar de relatie tussen platvoeten en het hebben van overgewicht en obesitas [33]. Alle 13 studies toonden een toegenomen prevalentie van platvoeten bij jeugdigen met overgewicht/obesitas. Andere (niet-systematische) reviews vermeldden slap bindweefsel, hyperlaxiteit en een positieve familieanamnese als risicofactoren voor platvoeten.
Soms hebben jeugdigen met platvoeten last van vermoeide voeten en enkels, kramp en pijn onder of in de voet. Dit kan ook blijken doordat een kind niet graag loopt, getild wil worden of in de buggy wil, snel moe is of pijn in de benen aangeeft. In de literatuur wordt niet vermeld welk percentage kinderen met platvoeten last heeft van klachten. In een studie bij 218 jeugdigen van 11-15 jaar onderzocht Tudor de relatie tussen de hoogte van de mediale voetboog en de prestaties op 17 motorische tests [20]. Er werd geen relatie gevonden, jeugdigen met platvoeten presteerden niet anders dan jeugdigen zonder platvoeten.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met platvoeten wordt nagevraagd of er sprake is van (pijn)klachten. Zo ja, vraag dan naar de aard, timing en locatie van de pijn, verergerende factoren, en eventuele beperkingen in sport of vrijetijdsbesteding. Bij jonge kinderen kan gevraagd worden naar eventueel weigeren de voet of het been te belasten of mank lopen.
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij jeugdigen met platvoeten (alle leeftijden) worden de volgende punten onderzocht (zie ook het stroomschema in afbeelding 13):
- Is de platvoet soepel of rigide? Dit kan op 3 manieren worden onderzocht:
- De jeugdige kan gevraagd worden op de tenen te gaan staan. Bij een soepele platvoet wordt de mediale voetboog zichtbaar, bij een rigide platvoet is dit niet het geval.
- Bij jonge kinderen kan de voetboog worden beoordeeld als zij in ontspannen toestand op schoot zitten met afhangende voeten. Bij een soepele platvoet is de mediale voetboog zichtbaar in ontspannen onbelaste toestand, bij een rigide platvoet is dit niet het geval.
- De ‘Hubscher test’ (of ‘toe raising test’ of ’Jack-test’) (afbeelding 14): terwijl de jeugdige (met gestrekte knieën) op de voeten staat buigt de onderzoeker de grote teen omhoog (dorsaalflexie). Bij een soepele platvoet wordt de mediale voetboog zichtbaar, bij een rigide platvoet is dit niet het geval.
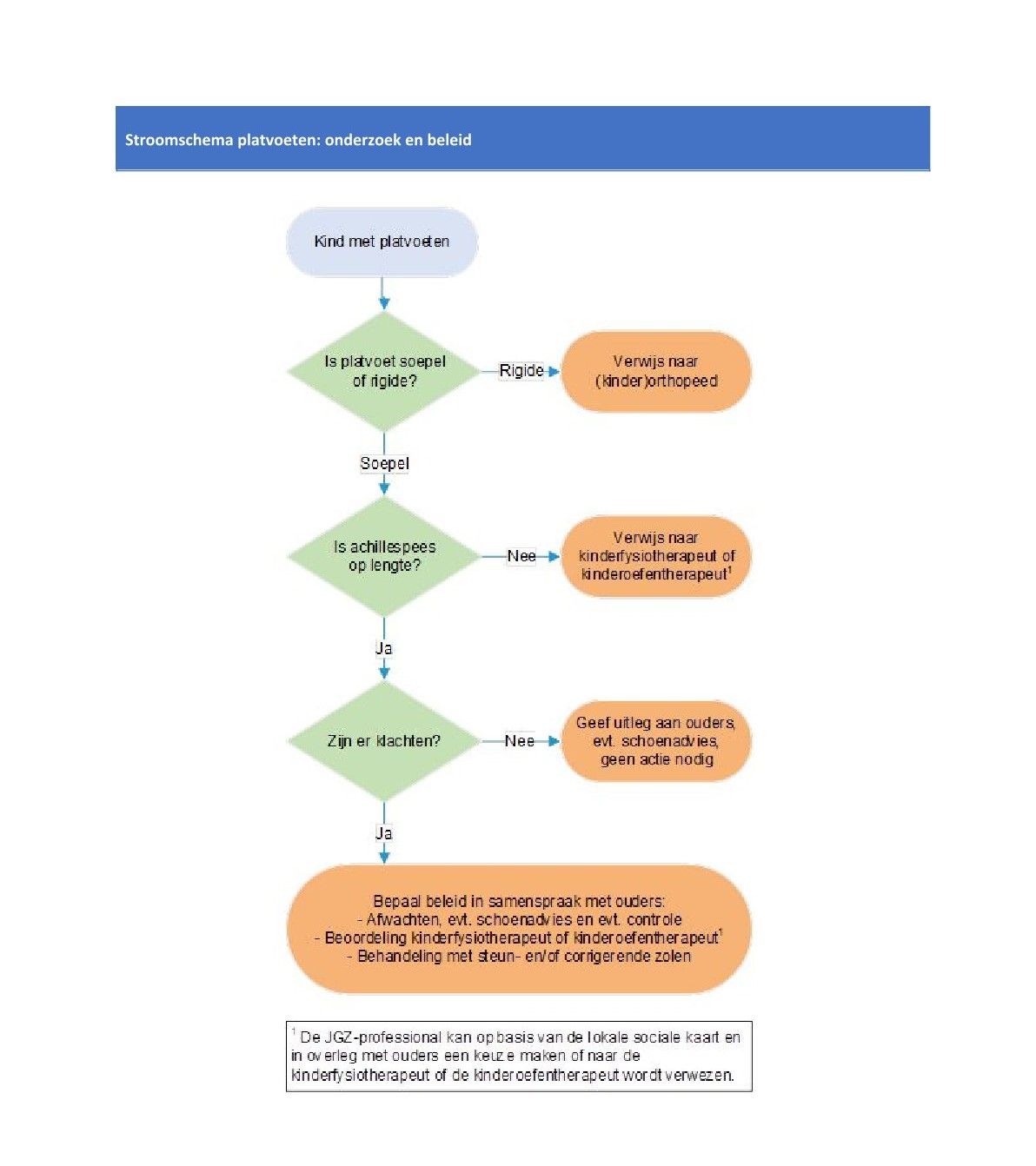
Afbeelding 13: Stroomschema lichamelijk onderzoek
Afbeelding 14: Hubscher test.
- Is de achillespees op lengte? Houd met één hand het onderbeen van de jeugdige vast, en met de andere hand wordt de voet voorzichtig naar dorsaal gebogen. Dit kan zowel met gebogen als met gestrekte knie worden getest. Indien de voet voorbij de neutrale stand gebogen kan worden is de achillespees voldoende lang. Bij een te korte achillespees staat de achtervoet vaak ook in valgusstand.
Alarmsignalen
Indien er sprake is van een rigide platvoet is de kans op een onderliggende oorzaak verhoogd. Er dient dan aanvullend onderzoek gedaan te worden.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
Er is in de literatuur veel discussie over de behandeling van jeugdigen met platvoeten. MacKenzie et al. onderzochten de kwaliteit van studies naar het effect van niet-chirurgische interventies voor platvoeten, en concludeerden dat deze vaak van lage en zeer variabele kwaliteit zijn [21].
In een prospectieve gerandomiseerde studie hebben Wenger et al. het effect van behandeling onderzocht bij jeugdigen van 1-6 jaar oud met soepele platvoeten [22]. Zij vergeleken het effect van orthopedische schoenen, een speciaal hielstuk (Helfet heel cup) of een op maat gemaakte plastic inlegzool met een controlegroep en vonden na ≥ 3 jaar geen verschil tussen de verschillende groepen in de stand van de voeten. Whitford et al. verrichtten een randomized clinical trial (RCT) en vergeleken het effect van (standaard en op maat gemaakte) steunzolen met een onbehandelde groep [23]. Zij includeerden 178 jeugdigen van 7-11 jaar met soepele platvoeten, en vonden geen significant effect van behandeling op de motoriek, conditie, pijnklachten en het zelfbeeld van de jeugdigen. Een Cochrane review naar niet-chirurgische interventies voor platvoeten vond slechts 3 studies van voldoende kwaliteit, en concludeerde dat steunzolen waarschijnlijk geen effect hebben in de behandeling van jeugdigen met asymptomatische platvoeten [24]. Deze conclusie is gebaseerd op de beschreven onderzoeken van Wenger et al. [22] en Whitford et al. [23].
Voor jeugdigen met platvoeten wordt het volgende beleid geadviseerd (zie ook het stroomschema in afbeelding 13 hierboven):
- Het beleid is voor jeugdigen van alle leeftijden hetzelfde, bij jongere kinderen (< 10 jaar) dient de JGZ-professional zich te realiseren dat de natuurlijke ontwikkeling nog niet is voltooid.
- Rigide platvoet: jeugdigen met (een) rigide platvoet(en) dienen te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed voor nader onderzoek, in verband met een verhoogde kans op een onderliggende oorzaak zoals een tarsale coalitie.
- Verkorte achillespees: jeugdigen met (een) verkorte achillespees(-pezen) dienen te worden verwezen naar de kinderfysiotherapeut of kinderoefentherapeut voor behandeling.
- Soepele platvoeten met klachten: bespreek met ouders dat er geen bewezen effectieve behandeling bestaat, en dat er meerdere vervolgstappen mogelijk zijn. In overleg met ouders wordt een keuze gemaakt.
- Een afwachtend beleid, na uitleg en schoenadvies (bijlage 3). Geef ouders uitleg over het natuurlijke beloop, dat soepele platvoeten een normale variatie zijn, geen nadelig effect op de lange termijn hebben en vaak vanzelf verbeteren. Desgewenst kan een controle na 6-12 maanden worden afgesproken.
- Een beoordeling door een kinderfysiotherapeut of kinderoefentherapeut11. Deze kan onderzoek doen naar de mogelijke oorzaak van de klachten, en zo nodig behandeling starten.
- Behandeling met steun- en/of corrigerende zolen kan worden overwogen. Bespreek met de ouders dat er geen bewijs is dat op maat gemaakte steun- en/of corrigerende zolen een meerwaarde hebben boven standaard steunzolen. Steun- en/of corrigerende zolen kunnen worden verkregen via een podotherapeut, dit wordt echter niet vanuit de basisverzekering vergoed. Vaak worden de kosten wel (geheel of deels) vergoed door de aanvullende verzekering, maar steun- en/of corrigerende zolen kunnen kosten voor de ouders met zich meebrengen. Indien na een proefperiode (bijvoorbeeld 3 maanden) geen verbetering van de klachten optreedt, kan het gebruik van steun- en/of corrigerende zolen worden gestopt.
- Soepele platvoeten zonder klachten: hiervoor is geen behandeling nodig. Geef de ouders uitleg over het natuurlijke beloop, dat soepele platvoeten een normale variatie zijn, geen nadelig effect op de lange termijn hebben en vaak vanzelf verbeteren. Geef de ouders advies over de schoenkeuze (bijlage 5.2 Algemene schoenadviezen), en leg uit dat steun- en/of corrigerende zolen of aangepaste schoenen geen aangetoond positief effect hebben op de ontwikkeling van de voet. Indien er sprake is van overgewicht kan de relatie tussen overgewicht en platvoeten met de ouders en jeugdige worden besproken, en wordt de JGZ-richtlijn ‘Overgewicht’ gevolgd.
Aanbevelingen
2.4 Pijnklachten Heupen
2.4.1 Coxitis fugax
Beschrijving aandoening
Coxitis fugax is een ontstekingsreactie aan het heupgewricht. De oorzaak van de aandoening is onbekend, maar vermoed wordt dat het een virale ontsteking betreft. De gebruikelijke duur is enkele dagen, maar soms duren de klachten langer. De aandoening komt voor bij kinderen tussen 2 en 12 jaar, met een licht hogere frequentie bij jongens. Zie ook tabel 3 voor de meest voorkomende redenen voor pijn in de heup en/of mank lopen per leeftijdscategorie.
De symptomen bestaan uit pijn in de heupregio, het bovenbeen of de knie, mank lopen of trekken met het been. Het is de meest voorkomende oorzaak van mank lopen bij kinderen onder de 10 jaar. Soms zijn de symptomen van coxitis fugax de eerste tekenen van de ziekte van Perthes. Differentiaal diagnostisch moet worden gedacht aan septische coxitis en osteomyelitis. Bij deze aandoeningen zijn de klachten en het ziek-zijn vaak ernstiger en is de koorts veelal hoger. Andere aandoeningen in de differentiaal diagnose zijn developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH, heupdysplasie), epifysiolysis capitis femoris (slipped capital femoral epiphysis; SCFE) of de ziekte van Perthes.
Tabel 3. Meest voorkomende redenen voor pijn in de heup en/of mank lopen per leeftijdscategorie.
| Leeftijd | Oorzaak |
| 0-2 jaar |
|
| 2-10 jaar |
|
| 10-15 jaar |
|
Anamnese
Er dient nagevraagd te worden hoelang de (pijn)klachten bestaan, waar de (pijn)klachten zitten en of het kind ook verkouden is geweest of koorts heeft (gehad).
Wanneer kinderen pijnklachten ervaren zal dit worden aangegeven in de knie, bovenbeen of lies. Meestal is de pijn niet heel hevig, kinderen kunnen zich wel vaak ziek voelen. Het begin van de klachten is vaak sluimerend. Soms gaat er een infectieuze periode aan vooraf, wat tot speculatie over het reactieve karakter heeft geleid. In sommige gevallen hebben kinderen een subfebriele temperatuur [49].
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Tijdens het lopen zal het kind mank lopen of het aangedane been ontzien. Bij lichamelijk onderzoek wordt de beweeglijkheid van het heupgewricht en de knie onderzocht. Er is vaak een lichte bewegingsbeperking van de heup, waarbij de endorotatie meestal beperkt en pijnlijk is.
Alarmsignalen
Bij hoge koorts of ernstig ziek zijn dient te worden gedacht aan septische coxitis en osteomyelitis. Wanneer het kind opnieuw mank gaat lopen of pijn heeft (bovenbeen, knie of lies) na dagen van rust dan moeten de ouders contact opnemen met de huisarts. Dit kan namelijk opnieuw een coxitis fugax zijn, maar het kan ook duiden op een beginsymptoom van de ziekte van Perthes.
Nachtelijke pijnklachten kunnen een aanwijzing zijn voor het bestaan van een maligniteit.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Alle mank lopende kinderen dienen binnen 24 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts voor aanvullend onderzoek.
- Coxitis fugax gaat na enkele dagen rust weer over. Het kind mag het been belasten aan de hand van de klachten. Indien de klachten (bij een initieel gediagnosticeerde coxitis fugax) langer dan 3 dagen aanhouden dan dient binnen 24 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts voor aanvullend (laboratorium of röntgen) onderzoek.
- Indien er sprake is van hoge koorts of ernstig ziek zijn dient de jeugdige met spoed (dezelfde dag) verwezen te worden naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals zullen niet vaak een jeugdige met coxitis fugax zien. Als er sprake is van pijnklachten of mank lopen zullen ouders meestal contact met de huisarts opnemen.
De werkgroep vindt het echter belangrijk dat JGZ-professionals op de hoogte zijn van het ziektebeeld. De diagnose coxitis fugax wordt gesteld na uitsluiting van andere diagnoses en aanvullend onderzoek is van belang. Daarom is de werkgroep van mening dat alle kinderen die mank lopen binnen 24 uur dienen te worden verwezen naar de huisarts.
Aanbevelingen
2.4.2 Epifysiolysis capitis femoris (Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis; SCFE)
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij deze zeldzame aandoening glijdt de heupkop af ter hoogte van de groeischijf. Epifysiolysis capitis femoris komt voornamelijk bij jongens voor, de geschatte prevalentie is bij jongens 0,5:1.000. Het komt het meest voor bij kinderen tussen 10 en 15 jaar. Bij meisjes treedt het vaak wat eerder op dan bij jongens, omdat de puberteit bij meisjes eerder begint. Zie ook tabel 3 voor de meest voorkomende redenen voor pijn in de heup en/of mank lopen per leeftijdscategorie. Kinderen met obesitas hebben een verhoogd risico op epifysiolysis capitis femoris. De klachten kunnen bilateraal voorkomen: de afwijking treedt in 20-25% van de gevallen ook aan de contralaterale zijde op. De differentiaaldiagnose bij een mank lopende tiener is een laat ontstane ziekte van Perthes. Differentiatie tussen deze twee aandoeningen kan door middel van een röntgenfoto.
Epifysiolysis capitis femoris is onder te verdelen in:
- Acute afglijding: de klachten zijn plotseling ontstaan en duren korter dan drie weken. Als klacht wordt pijn in de heup, dijbeen of knie aangegeven. Daarnaast kan een val of een struikeling worden aangegeven als moment waarop de klachten zijn begonnen.
- Chronische afglijding: de klachten duren langer dan drie weken en zijn geleidelijk ontstaan. Het kind loopt mank, maar kan het desbetreffende been wel belasten.
- Acute fase bij een chronische afglijding: een acute toename van klachten bij reeds bestaande geleidelijk ontstane klachten, die langer dan drie weken duren.
De meest voorkomende vorm is de chronische afglijding, namelijk in 85% van de gevallen. In 5% is er sprake van acuut afglijden en bij 10% gaat het om een acute fase bij een chronische afglijding. De behandeling van epifysiolysis capitis femoris is chirurgisch, waarbij de heupkop zo mogelijk wordt gereponeerd en gefixeerd.
De belangrijkste complicatie van epifysiolysis capitis femoris ontstaat als de doorbloeding van de heupkop wordt verstoord, waardoor het bot afsterft (avasculaire botnecrose of kopnecrose genoemd). Het risico op kopnecrose hangt samen met de mate van afglijden: bij acute afglijding is de kans ongeveer 15%. De belangrijkste complicatie van een onbehandelde epifysiolysis capitis femoris is coxartrose op jonge leeftijd.
Anamnese
Er dient nagevraagd te worden hoelang de (pijn)klachten bestaan, waar de (pijn)klachten zitten en of het kind ook koorts heeft (gehad). De klachten die kinderen ervaren hangen af van de snelheid van het afglijden en kunnen variëren van langzaam ontstaan van mank lopen en pijn in knie en heup, tot relatief acute, heftige pijn waarna soms het been (bijna) niet meer belastbaar is. Er zijn ook combinaties mogelijk: na een periode van mank lopen treedt plotseling een verergering op (acuut op chronisch). Alertheid is vereist bij het signaleren van dit beeld bij mank lopende kinderen, vooral op de tienerleeftijd.
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij lichamelijk onderzoek wordt het looppatroon onderzocht. De heup kan wisselend pijnlijk zijn, afhankelijk van de ernst. Bij het afglijden van de heupkop wordt de exorotatie in de heup groter dan de endorotatie. Bij een acute en volledige epifysiolyse is het been onbelastbaar. De symptomen zijn soms heel mild (vaak wordt pijn in de knie gevoeld) waardoor het stellen van de diagnose vaak moeilijk is.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- De jeugdarts dient alle mank lopende kinderen binnen 24 uur te verwijzen naar de huisarts voor aanvullend onderzoek.
- Indien er een verdenking is op epifysiolysis capitis femoris dient de jeugdige met spoed (dezelfde dag) te worden verwezen naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals zullen niet vaak een jeugdige met epifysiolysis capitis femoris zien. Als er sprake is van pijnklachten of mank lopen zullen ouders meestal contact met de huisarts opnemen.
De werkgroep vindt het echter belangrijk dat JGZ-professionals op de hoogte zijn van het ziektebeeld. Bij verdenking op epifysiolysis capitis femoris dient de jeugdige met spoed te worden verwezen naar een (kinder)orthopeed.
Bij de begeleiding van kinderen met epifysiolysis capitis femoris is mogelijk ook een rol weggelegd voor de ergotherapeut. Een ergotherapeut kan advies uitbrengen t.a.v. aangepast vervoermiddel en dagelijkse activiteiten. Ook kan een ergotherapeut de ouders informeren waar zij hulpmiddelen kunnen huren of lenen; hoe zij aanspraak kunnen maken op hun zorgverzekering of de gemeente. De werkgroep is van mening dat verwijzing naar de ergotherapeut geen eerste keus is voor de JGZ, maar dat deze keus wel gemaakt kan worden door de behandelend specialist.
Aanbevelingen
2.4.3 Ziekte van Perthes
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij de ziekte van Perthes is er sprake van vormveranderingen van de heup, die waarschijnlijk ontstaan door een tijdelijk verminderde doorbloeding in de heupkop waarbij de botcellen ter plaatse doodgaan. Het is een idiopathische avasculaire necrose van de heupkop. Jongens hebben vier tot vijf keer zoveel kans op deze aandoening ten opzichte van meisjes. De maximale incidentie ligt tussen het vijfde en achtste levensjaar. Eén op de 1.000 kinderen krijgt de ziekte van Perthes. In 10% van de gevallen is deze ziekte bilateraal. Zie ook tabel 3 voor de meest voorkomende redenen voor pijn in de heup en/of mank lopen per leeftijdscategorie.
In een periode van 4 tot 6 jaar doorloopt de ziekte vier fasen:
- Synovitisfase, duurt enkele weken en op de röntgenopname zijn geen afwijkingen zichtbaar. Pijnklachten staan op de voorgrond.
- Collapsfase, deze fase duurt 6 tot 12 maanden. De epifyse zakt in elkaar, waardoor er hoogteverlies ontstaat. Door het inzakken ontstaat er weefselverdichting waardoor de epifyse op de röntgenfoto een witter aspect krijgt. Pijnklachten staan op de voorgrond.
- Fragmentatiefase, deze fase duurt één tot twee jaar. Het necrotisch bot wordt geresorbeerd, dit is te zien op de röntgenfoto als een vlekkige de-ossificatie. Een eventuele deformatie van de femurkop treedt tijdens deze fase op. Functiebeperkingen staan op de voorgrond.
- Herstelfase. Deze fase kan zich over enkele jaren uitspreiden en duurt langer wanneer een kind ouder wordt. Functiebeperkingen staan op de voorgrond.
De ziekte van Perthes kan een vervroegde slijtage (artrose) van de heup geven. De prognose is gunstiger voor kinderen jonger dan 7 jaar, vanwege het grotere remodellerende vermogen van het bot op jongere leeftijd. Daarnaast is de prognose afhankelijk van de ernst van de aandoening.
De behandeling van de ziekte van Perthes is primair conservatief. Het doel is het ontlasten van het heupgewricht om de beweeglijkheid en de bolvorm van het gewricht te behouden en daarnaast de pijn te verlichten. Vaak wordt de jeugdige geadviseerd de heup te ontlasten door gebruik te maken van krukken. De totale duur van het ziekteproces neemt jaren in beslag, soms meer dan 6 jaar. Gedurende deze tijd staat het kind onder controle van de (kinder)orthopeed.
Over het algemeen mag de jeugdige belasten op geleide van de pijnklachten. Zo lang er sprake is van pijnklachten mag de jeugdige meestal niet sporten. Sporten waarbij de heup weinig wordt belast (zoals fietsen, wandelen en zwemmen) mogen vaak als eerste weer worden opgepakt.
Anamnese
De kinderen gaan, zonder een acuut moment, mank lopen. Kinderen ervaren pijn in de knie, het bovenbeen of in de lies/heup. De klachten bij de ziekte van Perthes duren weken- tot maandenlang en niet zoals bij coxitis fugax enkele dagen.
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Het kind loopt mank. Bij lichamelijk onderzoek is er vaak een pijnlijke beperking van de heupfunctie, vooral abductie en endorotatie zijn beperkt.
Alarmsignalen
Het klinische beeld van de ziekte van Perthes is identiek aan dat van coxitis fugax: pijn in de knie, het bovenbeen of de heup/lies, mank lopen of niet willen staan/lopen. De duur van de klachten is echter onderscheidend, bij klachten die >7-10 dagen bestaan wordt de diagnose ziekte van Perthes meer waarschijnlijk.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Alle mank lopende kinderen dienen binnen 24 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts voor aanvullend onderzoek.
- Bij verdenking op de ziekte van Perthes dient een kind op korte termijn te worden verwezen naar de (kinder)orthopeed.
- Bij kinderen die worden behandeld in verband met de ziekte van Perthes bepaalt de behandelaar de belastbaarheid. Dit betekent dat de JGZ-professional alleen in overleg met de behandelaar adviezen geeft over de belastbaarheid. De JGZ biedt het gezin desgewenst extra begeleiding, omdat de aandoening vaak een behoorlijke impact heeft op het dagelijks leven van een jeugdige en de overige gezinsleden.
- De JGZ-professional kan (mits er toestemming is van jeugdige/ouder(s) voor het delen van informatie) in contacten met school benoemen dat de behandelaar het beweegbeleid bepaalt. In het algemeen kan aan school worden aangegeven: meestal mag de jeugdige belasten op geleide van de pijnklachten. Zo lang er sprake is van pijnklachten mag de jeugdige meestal niet sporten.
Overwegingen
JGZ-professionals kunnen tijdens hun contactmomenten kinderen tegenkomen die worden behandeld voor de ziekte van Perthes. In de eerste fase, als er sprake is van pijnklachten of mank lopen, zullen ouders meestal contact met de huisarts opnemen.
De werkgroep vindt het belangrijk dat JGZ-professionals op de hoogte zijn van het ziektebeeld, en is van mening dat alle kinderen die mank lopen binnen 24 uur dienen te worden verwezen naar de huisarts.
Bij de begeleiding van kinderen met de ziekte van Perthes is mogelijk ook een rol weggelegd voor de ergotherapeut. Een ergotherapeut kan advies uitbrengen t.a.v. aangepast vervoermiddel en dagelijkse activiteiten. Ook kan een ergotherapeut de ouders informeren waar zij hulpmiddelen kunnen huren of lenen; hoe zij aanspraak kunnen maken op hun zorgverzekering of de gemeente. De werkgroep is van mening dat verwijzing naar de ergotherapeut geen eerste keus is voor de JGZ, maar dat deze keus wel gemaakt kan worden door de behandelend specialist.
Aanbevelingen
2.5 Pijnklachten – Knieën – Osgood Schlatter
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij de ziekte van Osgood-Schlatter (apofysitis tuberositas tibia) is de aanhechting van de kniepees op het scheenbeen geïrriteerd en ontstoken. Onder de knie is een bult te zien die pijn doet, vooral als er op wordt gedrukt [52]. Soms voelt de bult warm aan [25] De klachten ontstaan geleidelijk, er is geen acuut moment aan te wijzen. De pijnklachten zijn erger bij sporten (vooral als er veel gerend en gesprongen wordt) en bij hurken, langdurig zitten en traplopen [25]. Meestal betreffen de klachten één knie, maar in 30% van de gevallen zijn er beiderzijds klachten [38]. De ziekte ontstaat vooral bij jongens van 10 tot 15 jaar en bij meisjes van 8 tot 14 jaar die het afgelopen jaar veel gegroeid zijn en die actief een sport beoefenen [52][38][25]. Algemeen wordt aangenomen dat de klachten worden veroorzaakt door herhaalde tractie van de patellapees ter plaatse van het verbeningscentrum van de tuberositas tibiae [52]. De pijnklachten kunnen enkele maanden tot 2 jaar aanhouden maar gaan na de groeispurt vanzelf over. Wel kan na het verdwijnen van de pijnklachten een zwelling blijven bestaan. Dit berust vooral op een verdikking van de patellapees [52]. Het kind heeft hier meestal geen last van.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met Osgood-Schlatter worden de volgende punten nagevraagd:
- Ontstaan (acuut of geleidelijk) van de klachten en beloop van de klachten
- Aard en lokalisatie van de klachten
- Omstandigheden die de klachten verergeren
- Eerder trauma
- Soort en mate van sportbeoefening
- Beperkingen
- Groei in het afgelopen jaar
- Bijkomende klachten zoals slotklachten of kliksensaties
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
De knie wordt onderzocht. Er is een drukpijnlijke zwelling ter hoogte van de proximale tibiale tuberositas aan de kant van de patellapees aanhechting. Soms kan er een benige onregelmatigheid worden gepalpeerd [38]. Soms kunnen de pijnklachten uitgelokt worden door het actief tegen een weerstand in strekken van de knie [25].
Alarmsignalen
Zeldzame, ernstige oorzaken van knieklachten zijn maligne tumoren of een osteomyelitis. Verwijs de jeugdige bij alarmsignalen zoals koorts, zwelling, warmte, roodheid, gewichtsverlies, gewrichtspijn in rust, algehele malaise of vermoeidheid door naar de huisarts.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- De jeugdarts bepaalt of er sprake is van de ziekte van Osgood-Schlatter, en brengt zo nodig de huisarts op de hoogte.
- De jeugdarts legt de oorzaak en het te verwachten beloop van de klachten uit en adviseert één of twee maanden de (sport)activiteiten die de pijn uitlokken te verminderen [52]. Dit zal bij een aanzienlijk deel van de jeugdigen met pijnklachten door de ziekte van Osgood-Schlatter helpen [52]. Adviseer de (sport)activiteiten weer geleidelijk op te voeren als de klachten na een tot twee maanden zijn verminderd. Eventueel kan gezocht worden naar bewegingsalternatieven zoals fietsen en zwemmen.
- Bij heftige of aanhoudende pijnklachten kan verwezen worden naar de huisarts.
- Verwijzing naar een (kinder)orthopeed of sportarts wordt niet aanbevolen [52].
- Indien er sprake is van koorts, zwelling, warmte, roodheid, gewichtsverlies, gewrichtspijn in rust, algehele malaise of vermoeidheid dient binnen 24 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts.
- De JGZ-professional kan (mits er toestemming is van jeugdige/ouder(s) voor het delen van informatie) in contacten met school benoemen welk advies er is gegeven over (sport)activiteiten.
Aanbevelingen
2.6 Pijnklachten – Voeten – Ziekte van Sever
Beschrijving aandoening
De ziekte van Sever (ook wel apofysitis calcanei of ziekte van Sever Schinz) wordt veroorzaakt door een overbelasting van de apofyse van de calcaneus (achterzijde van de hiel). Kinderen met de ziekte van Sever ervaren pijn aan de achterzijde van de hiel, ter hoogte van de aanhechting van de achillespees. In 60% van de gevallen heeft het kind pijn aan beide voeten. Klachten ontstaan tijdens of kort na het sporten. Daarnaast kan een kind hielpijn ervaren tijdens het lopen of bij rust. Kinderen kunnen de hielpijn proberen te verminderen door op de tenen te gaan lopen. Deze aandoening komt vaker voor bij jongens dan bij meisjes, en wordt meestal gezien in de leeftijdsperiode van 7 – 15 jaar. Bij meisjes is het meestal eerder over (13-14 jaar), jongens blijven er iets langer last van houden (14-15 jaar). In Nederland is de incidentie in huisartspraktijken 3,7 per 1.000 patiënten [26].
Oorzaken van de ziekte van Sever zijn sporten, overgewicht, pes planovalgus en een kort gastrocnemius-soleus-complex. Daarnaast kunnen de klachten ontstaan tijdens de groeispurt. Over het algemeen ontstaan klachten bij sporten zoals basketbal, voetbal, hardlopen of andere rennende sporten/activiteiten.
De ziekte van Sever wordt meestal behandeld met een periode van rust (2-6 weken geen sport), rekoefeningen van de kuitspier, koelen na de sport en eventueel een schoenaanpassing [38]. Perhamre et al. vonden dat het gebruik van een heel cup (een op maat gemaakt plastic hielstuk) of een hielverhoging van 5 mm tijdens het sporten een vermindering van de klachten geeft [27]. In een vervolgonderzoek werd het effect van deze 2 behandelmethoden vergeleken, waarbij bleek dat de meeste deelnemers (77%) een voorkeur had voor de heel cup [28]. In een vergelijkend onderzoek naar drie behandelmethoden voor de ziekte van Sever vonden Wiegerinck et al. dat zowel afwachten, het dragen van een hakverhogende inlegzool, als kinderfysiotherapie, alledrie een significante afname van de pijn gaven bij kinderen met de ziekte van Sever [29].
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met de ziekte van Sever worden de volgende zaken nagevraagd [38]:
- Aard en beloop van de klachten
- Een- of tweezijdigheid van de klachten
- Veranderd looppatroon. Op de tenen lopen om de hiel te ontlasten.
- Eventueel trauma of bijzondere activiteit in de afgelopen week
- Verandering van hakhoogte van schoeisel
- (verandering) van sportactiviteiten
- Invloed van rust en activiteiten op de klachten
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij jeugdigen met de ziekte van Sever worden de volgende punten onderzocht:
- De squeeze-test: hierbij wordt aan weerszijden van het achterste deel van de hiel geknepen (afbeelding 15). Dit is pijnlijk bij kinderen met de ziekte van Sever.
- De dorsaalflexie van de enkel dient te worden onderzocht. Dorsaalflexie is pijnlijk maar niet beperkt.
- Jeugdigen met de ziekte van Sever hebben geen zwelling, roodheid of warmte van de hiel.
Afbeelding 15: Squeeze test (bron: Wiegerinck 2012 [53]).
Alarmsignalen
Koorts, nachtpijn, gewichtsverlies, algehele malaise of vermoeidheid zijn symptomen die niet passen bij de ziekte van Severs. Nachtpijn in combinatie met koorts en/of vermoeidheid, gewichtsverlies of malaise kan wijzen op een pathologisch proces, fractuur of een posterieure exostose van de calcaneus. De pijn dient snel te verminderen wanneer het sporten gestaakt wordt.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- De jeugdarts bepaalt of er sprake is van de ziekte van Sever, en brengt zo nodig de huisarts op de hoogte.
- De behandeling van de ziekte van Sever bestaat uit uitleg aan de ouders en jeugdige en een (tijdelijke) stop van de sport (3-6 weken). Hierna kunnen de activiteiten weer worden opgebouwd op geleide van de pijn (pijn is een teken om rust te houden). Binnen enkele maanden zouden de klachten moeten zijn afgenomen. Aanvullend kunnen rekoefeningen van de kuitspier, koelen na de sport en eventueel een schoenaanpassing (heel cup of heel raise) geadviseerd worden. Deze zijn onder andere online verkrijgbaar.
- Indien de klachten na 6 – 12 weken met de bijbehorende adviezen niet minder zijn, dient er verwezen te worden naar de huisarts of kinderfysiotherapeut.
- Indien er sprake is van koorts, nachtpijn, gewichtsverlies, algehele malaise of vermoeidheid dan dient de jeugdige binnen 24 uur te worden verwezen naar de huisarts.
- De JGZ-professional kan (mits er toestemming is van jeugdige/ouder(s) voor het delen van informatie) in contacten met school benoemen welk advies er is gegeven over (sport)activiteiten.
Aanbevelingen
2.7 Pijnklachten Overig – Groeipijn
Beschrijving aandoening
Bij groeipijn is er sprake van pijn in de benen, vaak gelokaliseerd in de onderbenen. De pijn wordt gewoonlijk in beide benen gevoeld, maar niet per se aan beide benen op hetzelfde moment. De pijn treedt meestal op aan het eind van de dag of het begin van de nacht, vaak na een dag met veel lichamelijke activiteit. Kinderen kunnen wakker worden van de pijnklachten. De frequentie van de pijnaanvallen is variabel, van bijna dagelijks tot eens per 3 maanden.
Groeipijn komt vooral voor bij kinderen van 4-12 jaar, geschat wordt dat ongeveer 10-20% van de kinderen wel eens groeipijn heeft gehad [32]. Groeipijn komt mogelijk iets vaker voor bij meisjes, en er is regelmatig sprake van een positieve familieanamnese voor groeipijn [33].
De term ‘groeipijn’ is misleidend, omdat groeipijn waarschijnlijk niet wordt veroorzaakt door het groeien van het kind. Groeipijn komt namelijk het meest voor op een leeftijd waarop de groei van een kind relatief langzaam verloopt, en komt weinig voor op leeftijden waarop snelle groei plaatsvindt. Daarnaast is de pijn vaak niet gelokaliseerd ter plaatse van de groeischijven. Over de oorzaak van groeipijn bestaat enige discussie in de literatuur. De volgende factoren spelen mogelijk een rol:
- Overbelasting. Groeipijn treedt vaker op na een dag met veel lichamelijke activiteit zoals intensief sporten of veel buitenspelen [33].
- Lagere pijndrempel. Kinderen met groeipijn hebben mogelijk een lagere pijndrempel. Zij hebben ook vaker last van buikpijn en hoofdpijn dan kinderen zonder groeipijn [33].
- Anatomische oorzaak. Kinderen met hypermobiliteit en/of platvoeten lijken vaker last te hebben van groeipijn [32].
Groeipijn is geen aandoening of ziekte, en gaat na een aantal maanden of jaren vanzelf weer over. Er is geen relatie aangetoond met medische problemen op de langere termijn.
Er is weinig bekend over de effectiviteit van diverse behandelingen van groeipijn, er is alleen beperkt bewijs voor de effectiviteit van rekoefeningen voor quadriceps, hamstrings en kuitmusculatuur [35] en massage van de pijnlijke plek.
Anamnese
In de anamnese bij jeugdigen met groeipijn worden de volgende punten nagevraagd:
- De momenten van optreden en de relatie met inspanning of een trauma
- De aard en de plaats van de pijn
- Bijkomende klachten zoals koorts, mank lopen, ochtendstijfheid
- Eventuele beperkingen in activiteiten overdag als gevolg van pijn of slaaptekort
- Wat is er gedaan om de pijn te verlichten en wat was het effect
(Aanvullend) lichamelijk onderzoek
Bij het lichamelijk onderzoek bij jeugdigen met groeipijn worden de volgende punten onderzocht:
- Hoe is het looppatroon?
- Is er sprake van roodheid, warmte, zwelling?
- Is er sprake van pijn ter plaatse van de heup, knie of enkel (bij palpatie of bij bewegen)?
- Hoe is de beweeglijkheid van heup, knie en enkel?
Alarmsignalen
Differentiaal diagnostisch moet worden gedacht aan bot- of gewrichtsontsteking, leukemie of bottumoren. Als er sprake is van aanhoudende unilaterale pijn, gewrichtsklachten, systemische verschijnselen (koorts, afvallen, malaise), pijnklachten gedurende de dag en/of mank lopen moet worden gedacht aan een andere oorzaak en dient verwezen te worden naar de huisarts.
Beleid door JGZ-professionals (adviezen, verwijscriteria, verwijsmogelijkheden)
- Als er sprake is van een anamnestisch passend klachtenpatroon (klachten beiderzijds, aan eind van de dag, vaak na veel lichamelijke activiteit) en er worden geen bijzonderheden gevonden bij het lichamelijk onderzoek dan mag ervan worden uitgegaan dat er sprake is van groeipijn.
- De JGZ-professional geeft de ouders uitleg over de klachten. Benoem hierbij dat de klachten vanzelf weer over gaan, en dat ouders bij aanhoudende zorgen opnieuw contact op mogen nemen.
- De JGZ-professional adviseert ouders over wat zij kunnen doen tijdens een pijnaanval: starten met rekoefeningen voor quadriceps, hamstrings en kuitmusculatuur of massage van de pijnlijke plek, bij ernstige pijnklachten kan paracetamol worden gegeven. Hoewel bewijs voor de effectiviteit ontbreekt, kan het aanbrengen van warmte door middel van een kruik o.i.d. mogelijk ook verlichting van de klachten geven. De jeugdige hoeft niet beperkt te worden in de dagelijkse activiteiten.
- Als er sprake is van aanhoudende unilaterale pijn, gewrichtsklachten, systemische verschijnselen (koorts, afvallen, malaise), pijnklachten gedurende de dag en/of mank lopen moet worden gedacht aan een andere oorzaak en dient binnen 24 uur verwezen te worden naar de huisarts.
Aanbevelingen
3 Totstandkoming richtlijn
3.1 Werkwijze
Een projectgroep van TNO (J. Deurloo, R. van Zoonen en C. Lanting) heeft de teksten voor de conceptrichtlijn geschreven. Voor de start van het project is een werkgroep samengesteld, deze werkgroep is bij alle fasen van de ontwikkeling van de richtlijn intensief betrokken geweest. De werkgroep is samengesteld uit experts op het gebied van aandoeningen aan de extremiteiten en/of JGZ. Zie voor de leden van de werkgroep paragraaf ‘c’. Met elk werkgroeplid zijn afspraken gemaakt en vastgelegd over taken en rollen in elke fase van het project. De tool ’organisatie en samenwerking bij multidisciplinaire richtlijnontwikkeling’ van het Haringproject [55] is hierbij als uitgangspunt genomen.
Tijdens de eerste werkgroepvergadering zijn de uitgangsvragen besproken en zo nodig nader gespecificeerd. Hierna is een systematisch literatuuronderzoek verricht op de uitgangsvragen. De leden van de projectgroep hebben de literatuur bestudeerd en samengevat. De teksten waren voor de deelnemers aan de werkgroep inzichtelijk en te bewerken op Google Drive. Deze teksten zijn tijdens vier werkgroepvergaderingen doorgenomen en aangepast, en er zijn aanbevelingen opgesteld.
Tevens is een klankbordgroep samengesteld. Zie voor de deelnemers aan de klankbordgroep paragraaf ‘d’. De klankbordgroep was verantwoordelijk voor het becommentariëren en aanvullen van conceptteksten vanuit ieders eigen ervaring en expertise. De klankbordgroep heeft schriftelijk gereageerd in oktober 2017. De reacties van de klankbordgroep zijn verwerkt door de projectgroep en besproken met de werkgroep.
Op basis van de inhoud van de richtlijn zijn een registratieprotocol en indicatoren opgesteld.
Het eerste concept van de richtlijn is op 13 november 2017 beoordeeld door de Richtlijn Advies- en Autorisatie Commissie (RAC). Hierna is gestart met een praktijktest gedurende 4 maanden bij 20 individuele deelnemers (van 8 JGZ-organisaties), om de werkbaarheid in de praktijk te onderzoeken. De conceptrichtlijn is in deze periode ook verspreid voor de landelijke commentaarronde.
Het registratieprotocol behorend bij deze richtlijn is beoordeeld door de redactieraad BDS van het NCJ.
Na het verwerken van de resultaten van de praktijktest en de landelijke commentaarronde is de richtlijn op 28 januari 2019 opnieuw beoordeeld door de RAC. Naar aanleiding van deze bespreking is de inhoud van de richtlijn opnieuw bijgesteld. Op 1 april 2019 heeft de RAC de richtlijn definitief geautoriseerd.
3.2 Leden van de werkgroep
| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| Carla Luimes – Remmerswaal | jeugdverpleegkundige | CJG Rijmond, in werkgroep namens V&VN |
| Hetty van Velzen | arts M&G | onafhankelijk voorzitter |
| Marjolein van Velsen | kinderfysiotherapeut | Fysiokids Linsingerland, in werkgroep namens NVFK |
| Michiel van de Sande | kinderorthopeed | LUMC, in werkgroep namens NOV en WKO |
| Petra Luttekes | ouder | Namens Ouders & Onderwijs |
| Rita Gelauf | jeugdarts KNMG, instituutopleider | TNO; onderwijsteam opleiding jeugdarts KNMG, in werkgroep namens AJN |
| Saskia van Vugt | huisarts | UMC Utrecht, in werkgroep namens NHG |
| Selma van der Harst | arts M&G | ActiZ, in werkgroep namens AJN |
| Tineke Piket | doktersassistente | CJG Rijnmond |
3.3 Klankbordgroep en meelezers
| Naam | Functie | Organisatie |
| A. Stroet-Duives | ergotherapeut | Ergotherapie Nederland |
| E. Schoots | sportarts | Vereniging voor Sportgeneeskunde (VSG) |
| E. Jongbloed | jeugdarts KNMG | |
| H. Stemerdink | kinderfysiotherapeut | Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kinderfysiotherapie (NVKF) |
| Kar li Chan | jeugdarts KNMG in opleiding | CJG Den Haag |
| M. van Denderen | jeugdarts KNMG | JGZ Kennemerland |
| M. Hepping | kinderrevalidatiearts | Nederlandse vereniging van Revalidatieartsen (VRA) |
| D. Lansink en L. Fuit | podotherapeuten | Nederlandse Vereniging van Podotherapeuten |
| Drs. D.R.J. Kempink | orthopaedisch chirurg | NOV/WKO |
| Dr. C.A. van Nieuwenhoven | plastisch chirurg | NVPC |
3.4 Cliëntparticipatie
De cliëntenparticipatie bij de ontwikkeling van de JGZ Richtlijn ‘Extremiteiten’ is vormgegeven door deelname van een ouder namens oudervereniging Ouders & Onderwijs aan alle werkgroepvergaderingen.
4 Verantwoording
4.1 Wetenschappelijke bewijsvoering
In samenspraak met de werkgroep is bepaald welke onderwerpen evidence based dan wel practice based beschreven zouden moeten worden. Belangrijke criteria voor de keuze voor een evidence based beschrijving waren: variatie in zorg en beschikbare kennis.
Voor de onderwerpen die evidence based beschreven zijn is gestart met een systematisch literatuuronderzoek (zie tabel 5). De zoektermen zijn in overleg met de werkgroepleden bepaald. Gevonden artikelen werden beoordeeld op relevantie. Relevante artikelen werden vervolgens gewaardeerd aan de hand van drie aspecten, namelijk methodologische kwaliteit, toepasbaarheid in de praktijk en toepasbaarheid binnen de Nederlandse gezondheidszorg. Voor het beoordelen van de methodologische kwaliteit werd gebruik gemaakt van de EBRO-systematiek (Evidence Based Richtlijn Ontwikkeling), ontwikkeld door het kwaliteitsinstituut voor de gezondheidszorg CBO.
De richtlijntekst is zoveel mogelijk gebaseerd op bewijs uit de literatuur, maar dat bleek vaak niet mogelijk, meestal omdat er geen literatuur voorhanden was van voldoende kwaliteit. Daar waar het niet mogelijk was om uit te gaan van eigen, door de projectgroep uitgevoerd, systematisch literatuuronderzoek werd gebruik gemaakt van richtlijnen, protocollen en verslagen van nationale en internationale gezondheidsorganisaties, beroepsorganisaties en wetenschappelijke verenigingen. Daarnaast werd gebruik gemaakt van zogenaamde ‘grijze literatuur’, zoals rapporten van overheden en kennisinstituten, doctoraalscripties, populairwetenschappelijk werk en handboeken. Pas als ook dat niet mogelijk was is gezocht naar consensus binnen de werkgroep van de richtlijn.
Voor de onderwerpen die practice based beschreven zijn is gebruik gemaakt van enkele nationale en internationale handboeken en richtlijnen, aangevuld met de expert opinion van de werkgroep leden.
Aanbevelingen in deze richtlijn zijn kortom daar waar mogelijk gebaseerd op wetenschappelijk bewijs, aangevuld met kennis, ervaring en mening van de werkgroep leden. Voor het formuleren van aanbevelingen zijn daarnaast andere aspecten meegewogen, zoals: voorkeuren van jongeren en ouders, kosten, beschikbaarheid, randvoorwaarden of organisatorische aspecten.
4.2 Zoekstrategie
Voor het zoeken van literatuur werden de databases Pubmed, Cochrane en PsycInfo geraadpleegd. Er is gezocht naar reviews in het Nederlands en Engels, alleen de jaren vanaf 2000 zijn geselecteerd. De in Pubmed gehanteerde zoekstrategieën en de bijbehorende resultaten worden hieronder weergegeven. Er is aanvullende gezocht in de velden titel/abstract omdat de meest recente records nog geen Mesh termen hebben.
Tabel 5. De gehanteerde zoekstrategieën en de bijbehorende resultaten.
| Onderwerp | Gehanteerde zoekstrategie | Aantal reviews |
| Algemene aandoeningen | Search: (((mass screening[Ti/Ab] OR diagnostic test[Ti/Ab] OR sensitivity[Ti/Ab] OR history[Ti/Ab] OR predictive value of test[Ti/Ab] OR diagnosis[Ti/Ab] OR prognostic value[Ti/Ab] OR “mass screening”[MeSH Terms] OR “diagnostic tests, routine”[MeSH Terms] OR “sensitivity and specificity”[MeSH Terms] OR “predictive value of tests”[MeSH Terms] OR “diagnosis”[MeSH Terms]) AND (joint instability[MeSH Terms]OR ehlers-danlos syndrome[MeSH Terms] OR hypermobility[Ti/Ab] OR generalized joint hypermobility[Ti/Ab]OR hypermobilities[Ti/Ab]OR joint hypermobility[Ti/Ab] OR generalised joint hypermobility[Ti/Ab]OR hypermobility syndrome[Ti/Ab]OR hypermobility joint syndrome[Ti/Ab]OR hypermobile[Ti/Ab]OR hyperlaxity OR hyperlax[Ti/Ab] OR joint laxity[Ti/Ab] OR ligamentous laxity[Ti/Ab] OR ligament laxity[Ti/Ab]OR ehlers-danlos syndrome[Ti/Ab] OR knee hypermobility[Ti/Ab] OR beighton score[Ti/Ab] OR beighton scale[Ti/Ab] OR toe walking [Ti/Ab] OR toe walk [Ti/Ab] OR toe walker [Ti/Ab] OR toewalkers [Ti/Ab] OR intoeing [Ti/Ab] OR in-toeing [Ti/Ab]) AND (child, preschool[MeSH Terms] OR adolescent[MeSH Terms] OR infant[MeSH Terms] OR infant, newborn[MeSH Terms] OR child*[Ti/Ab] OR infant[Ti/Ab] OR adolescent[Ti/Ab] OR newborn [Ti/Ab]))) | 207 |
| Standsafwijkingen | Search: (((mass screening[Ti/Ab] OR diagnostic test[Ti/Ab] OR sensitivity[Ti/Ab] OR history[Ti/Ab] OR predictive value of test[Ti/Ab] OR diagnosis[Ti/Ab] OR prognostic value[Ti/Ab] OR “mass screening”[MeSH Terms] OR “diagnostic tests, routine”[MeSH Terms] OR “sensitivity and specificity”[MeSH Terms] OR “predictive value of tests”[MeSH Terms] OR “diagnosis”[MeSH Terms]) AND (“metatarsus adductus”[Ti/Ab] OR “metatarsus varus”[Ti/Ab] OR “metatarsal deformity”[Ti/Ab] OR “Deformities Metatarsal”[Ti/Ab] OR “Deformity Metatarsal”[Ti/Ab] OR “Metatarsal Deformities”[Ti/Ab] OR “Metatarsal varus”[Ti/Ab] OR “hallux valgus”[Ti/Ab] OR “metatarsus varus”[Ti/Ab] OR “Curly toes”[Ti/Ab] OR “Hammer toe”[Ti/Ab] OR “hammer toe syndrome”[Ti/Ab] OR “claw toe”[Ti/Ab] OR “crossover toe”[Ti/Ab] OR “pes planus”[Ti/Ab] OR “pes planovalga”[Ti/Ab] OR flatfoot[MeSH Terms] OR flatfeet[Ti/Ab] OR “flat foot”[Ti/Ab] OR “flat feet”[Ti/Ab] OR “pes planovalgus”[Ti/Ab] OR “convex pes valgus”[Ti/Ab] OR “genu valga”[MeSH Terms] OR “genu valgum”[MeSH Terms]OR “genu valgum”[Ti/Ab] OR “genu valga”[Ti/Ab] OR “knock knee”[Ti/Ab] OR “knock knees”[Ti/Ab] OR “bow-legs [Ti/Ab]OR bowlegs”[Ti/Ab] OR “bowed legs”[Ti/Ab] OR camptodactyly[Ti/Ab] OR “trigger finger”[MeSH Terms] OR “stenosing tenovagnitis”[MeSH Terms] OR “trigger thumb”[MeSH Terms] OR “trigger finger”[Ti/Ab] OR “trigger thumb”[Ti/Ab] OR “snapping finger”[Ti/Ab] OR “trigger digit”[Ti/Ab] OR “leg length discrepancies”[Ti/Ab] OR “leg length inqualities” OR “limb length discrepancies”[Ti/Ab] OR “limb length discrepancy”[Ti/Ab] OR “leg length inequality”[MeSH Terms] OR “leg length discrepancy”[MeSH Terms]) AND (child, preschool[MeSH Terms] OR adolescent[MeSH Terms] OR infant[MeSH Terms] OR infant, newborn[MeSH Terms] OR child*[Ti/Ab] OR infant[Ti/Ab] OR adolescent[Ti/Ab] OR newborn [Ti/Ab]))) | 123 |
| Pijnklachten | Search: (((mass screening[Ti/Ab] OR diagnostic test[Ti/Ab] OR sensitivity[Ti/Ab] OR history[Ti/Ab] OR predictive value of test[Ti/Ab] OR diagnosis[Ti/Ab] OR prognostic value[Ti/Ab] OR “mass screening”[MeSH Terms]) OR “diagnostic tests, routine”[MeSH Terms] OR “sensitivity and specificity”[MeSH Terms] OR “predictive value of tests”[MeSH Terms] OR “diagnosis”[MeSH Terms] AND (camptodactyly[Ti/Ab] OR “Osgood-Schlatter disease”[Ti/Ab] OR “Osgood Schlatter disease”[Ti/Ab] OR “tibial tubercle apophysitis”[Ti/Ab] OR “Osgood-schlateer”[Ti/Ab] OR [Ti/Ab] OR “Texting thumb”[Ti/Ab] OR “app thumb”[Ti/Ab] OR “calcaneal apophysitis”[Ti/Ab] OR “heel pain”[Ti/Ab] OR “severs disease”[Ti/Ab] OR text [Ti/Ab] OR texter[Ti/Ab] OR texters[Ti/Ab] OR texting[Ti/Ab] OR mobile [Ti/Ab] OR phone [Ti/Ab] OR gaming [Ti/Ab] OR smartphone[Ti/Ab] OR phones[Ti/Ab] OR touchscreen [Ti/Ab] OR overuse [Ti/Ab] OR sms [Ti/Ab] OR typing[Ti/Ab] OR thumb[Ti/Ab] or Thumbs[Ti/Ab] OR finger[Ti/Ab] or fingers[Ti/Ab] OR camptodactyly[Ti/Ab] OR “Osgood-Schlatter disease”[Ti/Ab] OR “Osgood Schlatter disease”[Ti/Ab] OR “tibial tubercle apophysitis”[Ti/Ab] OR “Osgood-schlateer”[Ti/Ab] OR [Ti/Ab] OR “Texting thumb”[Ti/Ab] OR “app thumb”[Ti/Ab] OR “calcaneal apophysitis”[Ti/Ab] OR “heel pain”[Ti/Ab] OR “severs disease”[Ti/Ab]) AND (child, preschool[MeSH Terms] OR adolescent[MeSH Terms] OR infant[MeSH Terms] OR infant, newborn[MeSH Terms] OR child*[Ti/Ab] OR infant[Ti/Ab] OR adolescent[Ti/Ab] OR newborn [Ti/Ab]))) | 58 |
Bij alle onderwerpen is er een aanvullende search gedaan met de zoektermen:
ethnic groups[MeSH Terms] OR cultural diversity[MeSH Terms] OR emigrants[MeSH Terms] AND immigrants[MeSH Terms] OR “ethnic groups”[Ti/Ab] OR “cultural diversity”[Ti/Ab] OR emigrant[Ti/Ab] OR immigrant[Ti/Ab] OR diversity[Ti/Ab] OR “ethnic difference”[Ti/Ab]
Daar zijn geen extra referenties uitgekomen.
4.3 Overwegingen
De overwegingen van de werkgroep zijn per onderwerp opgenomen in de voorgaande thema’s.
4.4 Kennislacunes
De werkgroep is tot de conclusie gekomen dat op de volgende onderwerpen sprake is van kennislacunes:
- Diverse uitgangsvragen zijn practice based beantwoord, omdat wetenschappelijke kennis en onderbouwing op diverse onderwerpen ontbreekt.
- Er is onvoldoende literatuur en kennis om aanbevelingen te doen over de overbelaste duim (als gevolg van SMS, WhatsApp of andere media).
4.5 Knelpuntanalyse
Als pdf op te vragen bij NCJ
4.6 Belangenverstrengeling
Alle deelnemers aan de projectgroep en werkgroep hebben een belangenverklaring ingevuld. Er zijn geen mogelijke belangenverstrengelingen gemeld.
5 Bijlagen
5.1 Bijlage – Handboeken en websites
Handboeken
Bruikbaar voor dagelijkse praktijk:
- Eekhof JAH, Knuistingh Neven A, Opstelten W. Kleine kwalen bij kinderen. Elsevier Gezondheidszorg, Maarsen, 2009.
- Visser, J. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. Telenga drukwerk service, Groningen, 2012.
- Sluijs JA, Sakkers RJB, Bronswijk JAHM. Praktische Kindergeneeskunde: Kinderorthopedie. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten, 2009.
Indien verdieping gewenst is:
- Hefti F. Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 2007. ISBN-13: 978-3-540-69963-7.
- Neligan PC. Plastic Surgery, volume 6: Hand and upper extremity. Elsevier, 2017. ISBN-13: 978-0323356305.
Websites
- www.nvfk.kngf.nl: de website van de Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kinderfysiotherapie
- www.dekinderfysiotherapeut.com: de website van de Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kinderfysiotherapie
- www.vvocm.nl: de website van de beroepsvereniging voor oefentherapeuten Cesar en Mensendieck
- www.kinderoefentherapie.nl: de website van het platform kinderoefentherapie, een specialisatie binnen de oefentherapie Cesar en Mensendieck
- www.sportzorg.nl: de voorlichtingswebsite van alle sportartsen in Nederland
- www.ergotherapie.nl: de website van de beroepsvereniging voor ergotherapeuten
- www.podomedics.nl: de website van samenwerkende podotherapeuten
- www.thuisarts.nl: website met informatie over gezondheid en ziekten. Huisartsen gebruiken Thuisarts.nl als ondersteuning bij hun voorlichting aan patiënten voor, tijdens en na het consult.
- Vereniging kinderorthopedie: website met informatie over diverse kinderorthopedische onderwerpen
- www.kinderneurologie.eu: website met informatie over verschillende neurologische ziektebeelden die kunnen optreden bij kinderen.
5.2 Bijlage – Algemene schoenadviezen
Bron: www.groeigids.nl (tekst aangepast)
- Als kinderen leren lopen volstaan blote voeten (binnenshuis) of leren slofjes.
- De lengte én de breedte van de schoen zijn belangrijk.
- De voet moet genoeg ruimte hebben in de schoen, zodat de tenen goed kunnen bewegen.
- Koop schoenen met een stevige hiel.
- Die hiel moet goed aansluiten om de voet. Anders glijdt het kind uit de schoen bij het lopen of op de tenen staan.
- De zool moet soepel zijn. Als je de zool buigt met de tenen naar boven, moet de schoen dubbel te buigen zijn (de achterkant van de schoen moet de voorkant kunnen raken).
- De zool moet stroef zijn. Dan glijdt het kind niet uit bij het lopen of rennen.
- Koop voor een kind met zweetvoeten leren schoenen en katoenen sokken.
- Koopt u sandalen voor de zomer? Zorg dan dat die goed passen om te voorkomen dat er snel steentjes in komen.
Referenties
[1] Pin T, Eldridge B, Galea MP. A review of the effects of sleep position, play position, and equipment use on motor development in infants. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):858-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979866[1] Pin T, Eldridge B, Galea MP. A review of the effects of sleep position, play position, and equipment use on motor development in infants. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2007;49(11):858-67
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17979866[2] Engström P, Tedroff K. The prevalence and course of idiopathic toe-walking in 5-year-old children. Pediatrics 2012;130(2):279-84
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-0225 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22826572[2] Engström P, Tedroff K. The prevalence and course of idiopathic toe-walking in 5-year-old children. Pediatrics 2012;130(2):279-84
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-0225 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22826572[3] Engström P, Van't Hooft I, Tedroff K. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and problems among children with idiopathic toe-walking. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):848-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31826bec08 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147630[3] Engström P, Van't Hooft I, Tedroff K. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and problems among children with idiopathic toe-walking. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):848-52
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31826bec08 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147630[4] Oetgen ME, Peden S. Idiopathic toe walking. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2012;20(5):292-300
http://dx.doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-20-05-292 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22553101[4] Oetgen ME, Peden S. Idiopathic toe walking. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2012;20(5):292-300
http://dx.doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-20-05-292 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22553101[5] Sass P, Hassan G. Lower extremity abnormalities in children. American family physician 2003;68(3):461-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12924829[5] Sass P, Hassan G. Lower extremity abnormalities in children. American family physician 2003;68(3):461-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12924829[6] McCluskey G, O'Kane E, Hann D, Weekes J, Rooney M. Hypermobility and musculoskeletal pain in children: a systematic review. Scandinavian journal of rheumatology 2012;41(5):329-38
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/03009742.2012.676064 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22639794[6] McCluskey G, O'Kane E, Hann D, Weekes J, Rooney M. Hypermobility and musculoskeletal pain in children: a systematic review. Scandinavian journal of rheumatology 2012;41(5):329-38
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/03009742.2012.676064 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22639794[7] Rikken-Bultman DG, Wellink L, van Dongen PW. Hypermobility in two Dutch school populations. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology 1997;73(2):189-92
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9228503[7] Rikken-Bultman DG, Wellink L, van Dongen PW. Hypermobility in two Dutch school populations. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology 1997;73(2):189-92
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9228503[8] van der Giessen LJ, Liekens D, Rutgers KJ, Hartman A, Mulder PG, Oranje AP. Validation of beighton score and prevalence of connective tissue signs in 773 Dutch children. The Journal of rheumatology 2001;28(12):2726-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11764224[8] van der Giessen LJ, Liekens D, Rutgers KJ, Hartman A, Mulder PG, Oranje AP. Validation of beighton score and prevalence of connective tissue signs in 773 Dutch children. The Journal of rheumatology 2001;28(12):2726-30
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11764224[9] Cheng JC, Chan PS, Hui PW. Joint laxity in children. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1991;11(6):752-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1960200[9] Cheng JC, Chan PS, Hui PW. Joint laxity in children. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1991;11(6):752-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1960200[10] Remvig L, Jensen DV, Ward RC. Epidemiology of general joint hypermobility and basis for the proposed criteria for benign joint hypermobility syndrome: review of the literature. The Journal of rheumatology 2007;34(4):804-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17407233[10] Remvig L, Jensen DV, Ward RC. Epidemiology of general joint hypermobility and basis for the proposed criteria for benign joint hypermobility syndrome: review of the literature. The Journal of rheumatology 2007;34(4):804-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17407233[11] Murray KJ. Hypermobility disorders in children and adolescents. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology 2006;20(2):329-51
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16546060[11] Murray KJ. Hypermobility disorders in children and adolescents. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology 2006;20(2):329-51
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16546060[12] Armon K. Musculoskeletal pain and hypermobility in children and young people: is it benign joint hypermobility syndrome? Archives of disease in childhood 2015;100(1):2-3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-306556 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25336435[12] Armon K. Musculoskeletal pain and hypermobility in children and young people: is it benign joint hypermobility syndrome? Archives of disease in childhood 2015;100(1):2-3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-306556 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25336435[13] Bauer AS, Bae DS. Pediatric Trigger Digits. The Journal of hand surgery 2015;40(11):2304-9; quiz 2309
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.04.041 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26440744[13] Bauer AS, Bae DS. Pediatric Trigger Digits. The Journal of hand surgery 2015;40(11):2304-9; quiz 2309
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.04.041 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26440744[14] Lincoln TL, Suen PW. Common rotational variations in children. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2003;11(5):312-20
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14565753[14] Lincoln TL, Suen PW. Common rotational variations in children. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2003;11(5):312-20
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14565753[15] Nurzynska D, Di Meglio F, Castaldo C, Latino F, Romano V, Miraglia R, Guerra G, Brunese L, Montagnani S. Flatfoot in children: anatomy of decision making. Italian journal of anatomy and embryology = Archivio italiano di anatomia ed embriologia 2012;117(2):98-106
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23420997[15] Nurzynska D, Di Meglio F, Castaldo C, Latino F, Romano V, Miraglia R, Guerra G, Brunese L, Montagnani S. Flatfoot in children: anatomy of decision making. Italian journal of anatomy and embryology = Archivio italiano di anatomia ed embriologia 2012;117(2):98-106
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23420997[16] Carr JB, Yang S, Lather LA. Pediatric Pes Planus: A State-of-the-Art Review. Pediatrics 2016;137(3):e20151230
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-1230 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26908688[16] Carr JB, Yang S, Lather LA. Pediatric Pes Planus: A State-of-the-Art Review. Pediatrics 2016;137(3):e20151230
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-1230 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26908688[17] Stolzman S, Irby MB, Callahan AB, Skelton JA. Pes planus and paediatric obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Clinical obesity 2015;5(2):52-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cob.12091 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25808780[17] Stolzman S, Irby MB, Callahan AB, Skelton JA. Pes planus and paediatric obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Clinical obesity 2015;5(2):52-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cob.12091 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25808780[18] Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M. The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1987;69(3):426-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3818704[18] Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M. The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1987;69(3):426-8
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3818704[19] Pfeiffer M, Kotz R, Ledl T, Hauser G, Sluga M. Prevalence of flat foot in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics 2006;118(2):634-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16882817[19] Pfeiffer M, Kotz R, Ledl T, Hauser G, Sluga M. Prevalence of flat foot in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics 2006;118(2):634-9
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16882817[20] Tudor A, Ruzic L, Sestan B, Sirola L, Prpic T. Flat-footedness is not a disadvantage for athletic performance in children aged 11 to 15 years. Pediatrics 2009;123(3):e386-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2262 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19254974[20] Tudor A, Ruzic L, Sestan B, Sirola L, Prpic T. Flat-footedness is not a disadvantage for athletic performance in children aged 11 to 15 years. Pediatrics 2009;123(3):e386-92
http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2262 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19254974[21] Jane MacKenzie A, Rome K, Evans AM. The efficacy of nonsurgical interventions for pediatric flexible flat foot: a critical review. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):830-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182648c95 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147627[21] Jane MacKenzie A, Rome K, Evans AM. The efficacy of nonsurgical interventions for pediatric flexible flat foot: a critical review. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2012;32(8):830-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182648c95 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23147627[22] Wenger DR, Mauldin D, Speck G, Morgan D, Lieber RL. Corrective shoes and inserts as treatment for flexible flatfoot in infants and children. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1989;71(6):800-10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2663868[22] Wenger DR, Mauldin D, Speck G, Morgan D, Lieber RL. Corrective shoes and inserts as treatment for flexible flatfoot in infants and children. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 1989;71(6):800-10
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2663868[23] Whitford D, Esterman A. A randomized controlled trial of two types of in-shoe orthoses in children with flexible excess pronation of the feet. Foot & ankle international 2007;28(6):715-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17592702[23] Whitford D, Esterman A. A randomized controlled trial of two types of in-shoe orthoses in children with flexible excess pronation of the feet. Foot & ankle international 2007;28(6):715-23
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17592702[24] Rome K, Ashford RL, Evans A. Non-surgical interventions for paediatric pes planus. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2010
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006311.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20614443[24] Rome K, Ashford RL, Evans A. Non-surgical interventions for paediatric pes planus. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2010
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006311.pub2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20614443[25] Calmbach WL, Hutchens M. Evaluation of patients presenting with knee pain: Part II. Differential diagnosis. American family physician 2003;68(5):917-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13678140[25] Calmbach WL, Hutchens M. Evaluation of patients presenting with knee pain: Part II. Differential diagnosis. American family physician 2003;68(5):917-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13678140[26] Wiegerinck JI, Yntema C, Brouwer HJ, Struijs PAA. Incidence of calcaneal apophysitis in the general population. European journal of pediatrics 2014;173(5):677-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2219-9 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24297670[26] Wiegerinck JI, Yntema C, Brouwer HJ, Struijs PAA. Incidence of calcaneal apophysitis in the general population. European journal of pediatrics 2014;173(5):677-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2219-9 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24297670[27] Perhamre S, Janson S, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury: treatment with insoles provides effective pain relief. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):819-23
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01051.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20492591[27] Perhamre S, Janson S, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury: treatment with insoles provides effective pain relief. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):819-23
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01051.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20492591[28] Perhamre S, Lundin F, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury; treat it with a heel cup: a randomized, crossover study with two insole alternatives. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):e42-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01140.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20673253[28] Perhamre S, Lundin F, Norlin R, Klässbo M. Sever's injury; treat it with a heel cup: a randomized, crossover study with two insole alternatives. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2011;21(6):e42-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01140.x https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20673253[29] Wiegerinck JI, Zwiers R, Sierevelt IN, van Weert HCPM, van Dijk CN, Struijs PAA. Treatment of Calcaneal Apophysitis: Wait and See Versus Orthotic Device Versus Physical Therapy: A Pragmatic Therapeutic Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2016;36(2):152-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000417 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25985369[29] Wiegerinck JI, Zwiers R, Sierevelt IN, van Weert HCPM, van Dijk CN, Struijs PAA. Treatment of Calcaneal Apophysitis: Wait and See Versus Orthotic Device Versus Physical Therapy: A Pragmatic Therapeutic Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2016;36(2):152-7
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000417 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25985369[30] Cassas KJ, Cassettari-Wayhs A. Childhood and adolescent sports-related overuse injuries. American family physician 2006;73(6):1014-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16570735[30] Cassas KJ, Cassettari-Wayhs A. Childhood and adolescent sports-related overuse injuries. American family physician 2006;73(6):1014-22
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16570735[31] Chiodo WA, Cook KD. Pediatric heel pain. Clinics in podiatric medicine and surgery 2010;27(3):355-67
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2010.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20691369[31] Chiodo WA, Cook KD. Pediatric heel pain. Clinics in podiatric medicine and surgery 2010;27(3):355-67
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2010.03.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20691369[32] Mohanta MP. Growing pains: practitioners' dilemma. Indian pediatrics 2014;51(5):379-83
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24953579[32] Mohanta MP. Growing pains: practitioners' dilemma. Indian pediatrics 2014;51(5):379-83
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24953579[33] Lowe RM, Hashkes PJ. Growing pains: a noninflammatory pain syndrome of early childhood. Nature clinical practice. Rheumatology 2008;4(10):542-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0903 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18762787[33] Lowe RM, Hashkes PJ. Growing pains: a noninflammatory pain syndrome of early childhood. Nature clinical practice. Rheumatology 2008;4(10):542-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0903 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18762787[34] Pavone V, Lionetti E, Gargano V, Evola FR, Costarella L, Sessa G. Growing pains: a study of 30 cases and a review of the literature. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2011;31(5):606-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318220ba5e https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21654473[34] Pavone V, Lionetti E, Gargano V, Evola FR, Costarella L, Sessa G. Growing pains: a study of 30 cases and a review of the literature. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2011;31(5):606-9
http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318220ba5e https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21654473[35] Baxter MP, Dulberg C. "Growing pains" in childhood--a proposal for treatment. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1988;8(4):402-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3292578[35] Baxter MP, Dulberg C. "Growing pains" in childhood--a proposal for treatment. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 1988;8(4):402-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3292578[36] Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg CBO & Argumentenfabriek 2015
[36] Knelpuntenanalyses jeugdgezondheidszorg CBO & Argumentenfabriek 2015
[37] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de JGZ. Koninklijke van Gorcum BV 2005;ISBN-13: 9789023241911():
[37] Laurent de Angulo MS, Brouwers-de Jong EA, Bijlsma-Schlösser JFM, Bulk-Bunschoten AMW, Pauwels JH, Steinbuch-Linstra I. Ontwikkelingsonderzoek in de JGZ. Koninklijke van Gorcum BV 2005;ISBN-13: 9789023241911():
[38] Eekhof JAH, Knuistingh Neven A, Opstelten W. Kleine kwalen bij kinderen. Elsevier Gezondheidszorg 2009
[38] Eekhof JAH, Knuistingh Neven A, Opstelten W. Kleine kwalen bij kinderen. Elsevier Gezondheidszorg 2009
[39] Le Cras S, Bouck J, Brausch S, Taylor-Haas A. Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center: Evidence-based clinical care guideline for Management of Idiopathic Toe Walking 2011;Guideline 040():1
http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/service/j/anderson-center/evidence-based-care/occupational-therapy-physical-therapy/[39] Le Cras S, Bouck J, Brausch S, Taylor-Haas A. Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center: Evidence-based clinical care guideline for Management of Idiopathic Toe Walking 2011;Guideline 040():1
http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/service/j/anderson-center/evidence-based-care/occupational-therapy-physical-therapy/[40] Staheli LT.. Fundamentals of pediatric orthopedics Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 2014;ISBN-13: 978-0781774970():
[40] Staheli LT.. Fundamentals of pediatric orthopedics Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 2014;ISBN-13: 978-0781774970():
[41] Thackeray C, Beeson P. In-toeing gait in children. A review of the literature. The foot 1996;6():1
[41] Thackeray C, Beeson P. In-toeing gait in children. A review of the literature. The foot 1996;6():1
[42] Visser J. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. Groningen Telengg drukwerk service 2012
[42] Visser J. Pluis of niet pluis. Een leidraad voor de eerstelijns gezondheidszorg. Groningen Telengg drukwerk service 2012
[43] Hefti F. Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York 2007; ISBN-13: 978-3-540-69963-7():
[43] Hefti F. Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York 2007; ISBN-13: 978-3-540-69963-7():
[44] Neligan PC. Plastic Surgery, volume 6: Hand and upper extremity. Elsevier 2017;6(ISBN-13: 978-0323356305.):
[44] Neligan PC. Plastic Surgery, volume 6: Hand and upper extremity. Elsevier 2017;6(ISBN-13: 978-0323356305.):
[45] EUROCAT Website Database
http://www.eurocat-network.eu/ACCESSPREVALENCEDATA/PrevalenceTables%20(data%20uploaded%2008/02/2017)[45] EUROCAT Website Database
http://www.eurocat-network.eu/ACCESSPREVALENCEDATA/PrevalenceTables%20(data%20uploaded%2008/02/2017)[46] Dijkman RR. Radial polydactyly: double or nothing? Proefschrift, Rotterdam 2016
http://www.publicatie-online.nl/uploaded/flipbook/13797-r-dijkman/index.html#8[46] Dijkman RR. Radial polydactyly: double or nothing? Proefschrift, Rotterdam 2016
http://www.publicatie-online.nl/uploaded/flipbook/13797-r-dijkman/index.html#8[47] Meer IM. Vitamine D tekort in een multi-etnische populatie; determinanten, prevalentie en consequenties. Samenvatting proefschrift. Epidemiologisch bulletin 2010;45():3
[47] Meer IM. Vitamine D tekort in een multi-etnische populatie; determinanten, prevalentie en consequenties. Samenvatting proefschrift. Epidemiologisch bulletin 2010;45():3
[48] Richtlijn Primaire Idiopathische Klompvoet Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging 2013
[48] Richtlijn Primaire Idiopathische Klompvoet Nederlandse Orthopaedische Vereniging 2013
[49] Sluijs JA, Sakkers RJB, Bronswijk JAHM. Praktische Kindergeneeskunde: Kinderorthopedie. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten 2009
[49] Sluijs JA, Sakkers RJB, Bronswijk JAHM. Praktische Kindergeneeskunde: Kinderorthopedie. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten 2009
[50] Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen. TNO: Groeidiagrammen. 2010
[50] Handleiding bij het meten en wegen van kinderen en het invullen van groeidiagrammen. TNO: Groeidiagrammen. 2010
[51] RIVM: Richtlijn Uitvoering RVP 2017
http://rivm.nl/[51] RIVM: Richtlijn Uitvoering RVP 2017
http://rivm.nl/[52] NHG-Standaard Niet-traumatische knieklachten 2016
[52] NHG-Standaard Niet-traumatische knieklachten 2016
[53] Wiegerinck JI, Struijs PA, Oudhof B, van Weert HCPM. Hielpijn bij kinderen. Huisarts en Wetenschap 2012;55(6):260
[53] Wiegerinck JI, Struijs PA, Oudhof B, van Weert HCPM. Hielpijn bij kinderen. Huisarts en Wetenschap 2012;55(6):260
[54] Stakenborg J, Hobma S. Kinderen met hielpijn Huisarts en Wetenschap 2015;58(5):274
[54] Stakenborg J, Hobma S. Kinderen met hielpijn Huisarts en Wetenschap 2015;58(5):274
[55] Hilbink M, Ouwens M, Kool T. De HARING-tools. Dertien instrumenten voor ondersteuning bij het opstellen, herzien, implementeren en evalueren van richtlijnen. Scientific Institute for Quality of Healthcare (IQ healthcare), Nijmegen 2013
[55] Hilbink M, Ouwens M, Kool T. De HARING-tools. Dertien instrumenten voor ondersteuning bij het opstellen, herzien, implementeren en evalueren van richtlijnen. Scientific Institute for Quality of Healthcare (IQ healthcare), Nijmegen 2013
Heb je suggesties voor verbetering van deze JGZ-richtlijn?
Geef jouw feedbackLET OP: print de JGZ-richtlijn in liggende afdrukstand!
Grote tabellen zijn niet volledig zichtbaar als de JGZ-richtlijn in staande afdrukstand geprint wordt. Om kleuren in de printversie goed door te laten komen, moet bij de printerinstellingen Achtergrondillustraties aangezet worden.
Disclaimer printversie JGZ-richtlijnen
De printversie van de JGZ-richtlijn bevat de algemene tekst inclusief de aanbevelingen. De wetenschappelijke onderbouwing is terug te vinden op de website, bij de aanbevelingen onder de link “Evidence”.