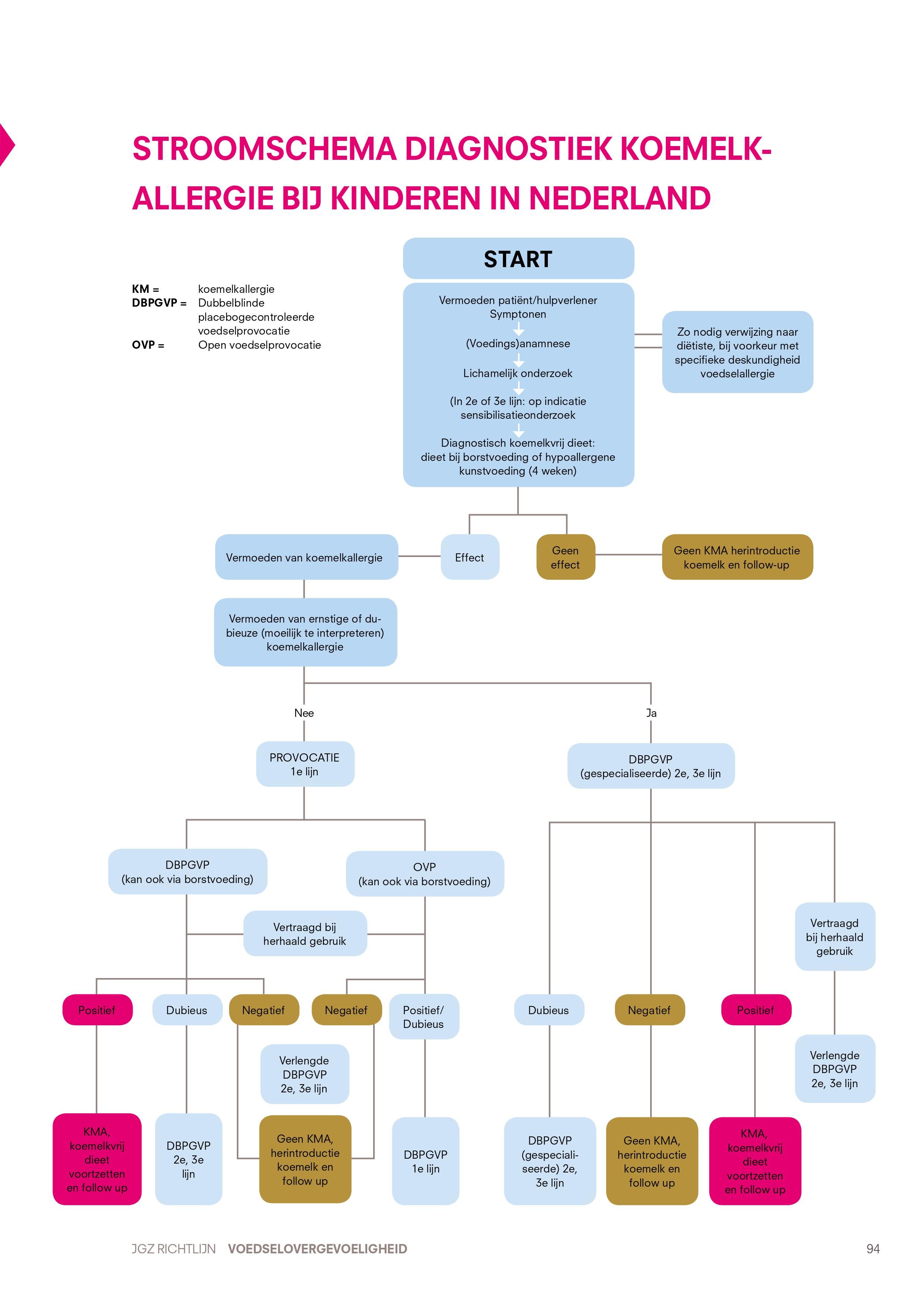
Open of dubbelblinde placebogecontroleerde koemelkprovocatietest?
Achtergrond
Voedselprovocaties worden uitgevoerd bij kinderen met een vermoeden van koemelkallergie om de diagnose koemelkallergie te bevestigen of uit te sluiten. Een voedselprovocatie moet worden voorafgegaan door een koemelkvrij dieet gedurende ten minste 4 weken met sterke afname van de symptomen. Tijdens een voedselprovocatietest krijgt het kind onder medisch toezicht koemelk in opklimmende doses toegediend. Het vermoeden van koemelkallergie komt tot stand op basis van (voedings)anamnese, lichamelijk onderzoek én een positief effect van een koemelkvrij dieet. Er zijn twee vormen van voedselprovocatietesten met koemelk.
• Open voedselprovocatietest (OVP). Hierbij krijgt het kind in oplopende doses onder medisch toezicht koemelk toegediend: op locatie, op locatie beginnend en thuis afgemaakt of thuis bij borstvoeding.
• Dubbelblinde placebogecontroleerde voedselprovocatietest (DBPGVP). Hierbij krijgt het kind op locatie in oplopende doses onder medisch toezicht in twee sessies testvoeding met of zonder koemelk toegediend, waarbij noch de betrokken behandelaars noch de ouders (en het kind) op de hoogte zijn wanneer de testvoeding koemelk bevat.
Wat is de diagnostische waarde van de DBPGVP ten opzichte van OVP?
Bij het beantwoorden van deze vraag is uitgegaan van de RAND-working-paper opgesteld voor de recent gepubliceerde Amerikaanse NIAID-richtlijn voor de diagnose en behandeling van voedselallergie, omdat de vraag in dit rapport beantwoord is met behulp van de GRADE-methode ([151]). Aanvullende informatie is verkregen uit de DRACMA en NIAID en een update van de literatuurzoekstrategie van de RAND ([19]; [42]).
Hoewel de DBPGVP door moet gaan voor de gouden standaard zijn er weinig studies die de diagnostische waarde van de OVP ten opzichte van de DBPGVP hebben onderzocht. De DBPGVP wordt niet op grote schaal toegepast door gebrek aan gespecialiseerd personeel, tijd en geld, het risico op anafylaxie en een gebrek aan overeenstemming over de criteria voor een positieve test. Toch is het van groot belang om de diagnose koemelkallergie goed te stellen om foutpositieve diagnoses te voorkomen en zo onnodige eliminatiediëten te voorkomen, evenals deficiënties in het dieet, zorgen en sociale isolatie. Niet-specifieke symptomen zoals huiduitslag kunnen ten onrechte worden toegeschreven aan voedselallergie. Het grootste probleem bij de diagnostiek van voedselallergie is dat er geen eenheid is in de literatuur over diagnostische criteria ([29]).
Samenvattend wordt gesteld dat, hoewel de DBPGVP de gouden standaard is, deze test op veel onderdelen nog niet gevalideerd en gestandaardiseerd is. Er zijn slechts weinig studies over de noodzaak en methodologie van DBPGVP’s. Valkuilen bij het uitvoeren van DBPGVP’s kunnen placeboreacties zijn, de samenstelling van de testvoeding en de vorm waarin het allergene voedingsmiddel is verwerkt in de testvoeding. De kwaliteit van de geïncludeerde studies is matig.
Overige overwegingen
Het grootste voordeel van de DBPGVP ten opzichte van de OVP is dat mogelijke bias (subjectieve, bevooroordeelde waarneming) bij patiënten én betrokken hulpverleners wordt gereduceerd ([19]). Hierdoor is de DBPGVP de meest betrouwbare test. Nadelen van de DBPGVP zijn de lange tijdsduur en hoge kosten ten opzichte van de makkelijker uitvoerbare OVP. Zie voor de gedetailleerde beschrijving van de DBPGVP de richtlijn ‘Diagnostiek van Koemelkallergie bij Kinderen in Nederland’ van de Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde ([166]).
In het rapport ‘Voedselallergie’ van de Gezondheidsraad en in het rapport ‘Diagnostiek van koemelkallergie in Nederland: Anders’ wordt aanbevolen om een makkelijk uitvoerbare DBPGVP te ontwikkelen voor de eerste lijn ([146]; [154]). In de knelpuntenanalyse voorafgaand aan het ontwikkelen van deze richtlijn kwam de behoefte naar voren van JGZ-professionals aan een objectieve test om koemelkallergie te diagnosticeren, zie 9.1 Knelpuntenanalyse.
Een OVP kan worden gebruikt voor het uitsluiten van de diagnose koemelkallergie en voor herevaluatie van de noodzaak van het koemelkvrije dieet na een eerdere positieve DBPGVP.
Voor het doen van sensibilisatieonderzoek kan specifiek IgE tegen koemelk worden bepaald of kan een huidpriktest met koemelk worden uitgevoerd. In de eerste lijn wordt een sIgE-bepaling voor koemelk of een ‘screeningtest voor voedselallergenen’ (een IgE-bepaling voor een mix van voedingsbestanddelen) afgeraden. Bij aantoonbaar sIgE voor koemelk is sensibilisatie aangetoond, maar is het nog niet bewezen dat er een verband bestaat met de symptomen. Anderzijds kan een kind een koemelkallergie hebben zonder aantoonbare sensibilisatie (Anonymous, 2000; [24]; [42]). Over het algemeen zijn sensitiviteit en specificiteit van sIgE en huidpriktest bij koemelkallergie laag (Anonymous, 2000; [24]). Hierdoor bestaat de kans dat bij kinderen met sensibilisatie voor koemelk de diagnose koemelkallergie onterecht alleen op basis van sensibilisatieonderzoek wordt gesteld.
Waar kunnen voedselprovocatietesten het beste worden uitgevoerd?
Er is geen systematische review bekend op basis waarvan deze vraag beantwoord kan worden. De aanbevelingen berusten op een aantal internationale en nationale publicaties en consensus binnen de werkgroep.
Veiligheid
Bij het uitvoeren van voedselprovocatieonderzoek staat veiligheid voorop. Dat betekent dat ernstige reacties moeten worden voorkomen en – als zij onverhoopt toch optreden – adequaat moeten kunnen worden opgevangen (Anonymous, 2000; [24]; [42]). Tot ernstige reacties worden luchtweg- en cardiovasculaire symptomen gerekend (Anonymous, 2000; [57]). Het is niet goed mogelijk om de ernst van een allergische reactie te voorspellen. Wel zijn er verschillende risicofactoren die de kans op een ernstige reactie kunnen vergroten (Anonymous, 2000; [24]; [64]; [89]; [90]).
- Ernstige (anafylactische) reactie.
- Instabiel astma of ernstig astma.
- Toename van de ernst van de reacties in de tijd.
- Eerdere reactie op een kleine hoeveelheid koemelk.
- Leeftijd ouder dan 5 jaar. Een dodelijke afloop bij voedselallergie is vooral beschreven bij kinderen ouder dan 5 jaar.
De genoemde risicofactoren zijn ontleend aan observationele studies naar (bijna) fatale reacties bij voedselallergie in het dagelijkse leven ([102]; [104]; [105]). Een paar studies hebben onderzoek gedaan naar de veiligheid van voedselprovocaties ([16]; [67]; [169]). Hieruit blijkt dat voedselprovocaties, mits door ervaren mensen verricht, veilig kunnen worden uitgevoerd. James et al. bestudeerden in 1994 in een derdelijnscentrum DBPGVP-testen bij 320 kinderen en volwassenen (leeftijd 0,5-30 jaar, mediane leeftijd 4,4 jaar) met constitutioneel eczeem ([67]). 59% van de 205 patiënten met een positieve test ontwikkelde luchtwegsymptomen. Slechts 7% had een daling van de longfunctie (FEV1) van meer dan 20%. De symptomen die Perry et al. vonden bij 584 kinderen die een DBPGVP hadden ondergaan in een tweede-/derdelijnscentrum waren alle behandelbaar met kortwerkende antihistaminica, adrenaline, beta-antagonisten of corticosteroïden ([102]). Er traden geen cardiovasculaire symptomen op en ziekenhuisopname was niet nodig.
In de literatuur wordt aangegeven dat voedselprovocaties onder medisch toezicht moeten plaatsvinden. Verlengde voedselprovocaties, waarbij een milde vertraagde reactie op herhaalde doses wordt verwacht, kunnen ook thuis worden uitgevoerd ([42]; [92]). De DRACMA geeft aan dat alleen bij afwezigheid van sensibilisatie een verlengde provocatie thuis kan plaatsvinden ([42]). Laagrisicoprovocaties kunnen ook in een praktijksetting van een arts worden uitgevoerd en worden in de Amerikaanse literatuur geduid als ‘office challenges’ ([42]; [92]). Dit laatste is ook afhankelijk van de ervaring van de superviserende arts en zijn/ haar staf. Hoogrisicoprovocaties moeten in het ziekenhuis plaatsvinden ([92]). Voor de Nederlandse situatie is de zogenaamde office challenge vergelijkbaar met een praktijksituatie in de JGZ- en de huisartsenpraktijk, met dit verschil dat in de VS meestal vrijgevestigde specialisten (kinderartsen of allergologen) de voedselprovocaties uitvoeren.
Situatie in Nederland
Uit de knelpuntanalyse van de JGZ komt naar voren dat het thuis uitvoeren van een OVP als knelpunt wordt ervaren omdat reacties niet geobjectiveerd kunnen worden. De NHG-Standaard Voedselovergevoeligheid uit 2010 geeft aan dat een OVP met koemelk in de huisartsenpraktijk uitgevoerd kan worden, behalve bij een doorgemaakte ernstige reactie, louter subjectieve reacties of ernstig therapieresistent constitutioneel eczeem ([159]; [161]).
De werkgroep is verdeeld over de vraag waar de OVP (als ‘second best’ test) moet worden uitgevoerd als een DBPGVP niet mogelijk is: geheel op locatie (JGZ) binnen een tijdsbestek van enkele uren of met de huidige methode waarbij de eerste dosis in de JGZ wordt verstrekt en de rest van de provocatie uitgesmeerd over een paar dagen in de thuissituatie wordt verricht. Hierbij gelden de volgende randvoorwaarden: de symptomen worden thuis geregistreerd, de provocatie wordt niet door de ouders zonder overleg met de arts afgebroken en de ouders komen terug voor objectivering van symptomen.
Nadelen van het uitvoeren van een OVP die thuis wordt afgemaakt zijn: kans op ernstige reacties thuis bij verkeerde indicatiestelling voor thuisprovocatie, geen observatiemogelijkheden waardoor de interpretatie van de symptomen bij de ouders wordt gelegd, het risico van het eigenhandig staken van de provocatie door de ouders en het risico van verwatering van randvoorwaarden voor het goed uitvoeren van de OVP thuis.
De werkgroep is van mening dat de locatie waar de provocatie kan worden uitgevoerd ten eerste wordt bepaald door het risico op (ernstige) reacties van het kind en de mogelijkheid om eventuele ernstige reacties adequaat te kunnen behandelen ([151]; [92]). Daarnaast spelen praktische aspecten een rol, zoals de mogelijkheid om testvoeding te bereiden, expertise van het personeel en de mogelijkheid de patiënt te observeren en adequaat te kunnen behandelen ([92]). Ook moeten er goede afspraken gemaakt worden tussen JGZ, huisarts en spoedeisende hulp waar de patiënt kan worden gezien indien er vertraagde reacties zijn.
Op grond van het bovenstaande kan voor de Nederlandse situatie worden geconcludeerd dat hoogrisico-DBPGVP’s en hoogrisico-OVP’s met koemelk voorbehouden zijn aan ervaren tweede- en derdelijnscentra. Laagrisicoprovocaties met koemelk kunnen in de eerste, tweede en derde lijn plaatsvinden. Laagrisico-DBPGVP’s moeten volledig op locatie worden uitgevoerd. Laagrisico-OVP’s (als ‘second best tests’) in de eerste lijn kunnen zowel volledig op locatie als ten dele thuis worden uitgevoerd.
Randvoorwaarden
Bij provocatie in de JGZ moet aan de volgende voorwaarden worden voldaan ([151]; [92]):
1. Ervaren personeel
Het kind moet adequaat kunnen worden behandeld bij het optreden van allergische reacties. Hiervoor is het nodig dat de JGZ-professionals geschoold worden in het verrichten van provocaties en het vroegtijdig herkennen van (ernstige) reacties en er in de JGZ antihistaminica en adrenaline(auto)injectoren beschikbaar komen. Goede monitoring en protocollaire afspraken omtrent het toedienen van medicatie (antihistaminica en/of adrenaline i.m.) zijn noodzakelijk. Overleg met de Inspectie voor de Gezondheidszorg is nodig. Bovendien is multidisciplinaire samenwerking tussen jeugdartsen, jeugdverpleegkundigen, verpleegkundig specialisten en diëtisten nodig.
2. Observatie tot 2 uur na de laatste dosis
In de JGZ kan aan deze voorwaarde in de huidige situatie niet of nauwelijks worden voldaan vanwege de beperkte openingstijden. De openingstijden zouden aangepast moeten worden. Voor jonge kinderen die tussendoor slapen kan de wachtruimte te vol en te druk zijn.
3. Adequate honorering van voedselprovocatietesten
Hiervoor zal overleg gevoerd moeten worden met de zorgverzekeraars. Enerzijds kost het uitvoeren van voedselprovocatietesten geld, anderzijds kan door het uitvoeren van provocatieonderzoek de instroom naar de tweede en derde lijn worden beperkt. Ook wordt met het terugdringen van foutpositieve diagnostiek van koemelkallergie onnodig gebruik van het duurdere eHF voorkomen.
4. Testvoeding
Voor het gemakkelijk en snel bereiden van de testvoeding op basis van intensief gehydrolyseerde voeding zullen naar verwachting speciale gestandaardiseerde en gevalideerde provocatiekits met alle gangbare intensief gehydrolyseerde kunstvoedingen binnenkort beschikbaar komen. Deze provocatiekits bestaan uit zakjes met poeder voor zowel de placeboprovocatie als de verumprovocatie die alleen hoeven worden aangelengd met water.
5. Nauwe samenwerking met de huisarts
De huisarts wordt geïnformeerd wanneer de koemelkprovocatie gaat plaatsvinden. Er zijn lokale afspraken nodig over wie het kind bij late reacties, met name buiten ‘kantooruren’, beoordeelt: jeugdarts, huisarts, kinderarts of arts van de spoedeisende hulp.